Surgery Can Reveal Additional Cancer
There is a small possibility that invasive cancer will be found during the final pathology examination after surgical removal of DCIS. When that happens, Sun says, the diagnosis would be upgraded and additional surgery and other treatments may be needed. We take each situation individually and the most optimal treatment will be tailored. This is important because each tumor and each patient is different.
She notes that at Johns Hopkins Medicine, the pathologists with whom she works are especially skilled in identifying any invasive cancer that might be present. Having DCIS treated at a comprehensive breast center ensures you are in the best possible hands, Sun says.
What Is The Prognosis For Patients Who Have Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
Because DCIS is contained within a specific area of the breast and has not spread, the disease can be controlled and cured with appropriate treatment. After treatment, the outcome for the patient with DCIS is usually excellent.
However, those patients who have had DCIS, even if treated successfully, are at a greater risk than people who have never had breast cancer to have the cancer return or for another type of breast cancer to develop.
How Fast Can Breast Cancer Spread
Metastasis occurs when breast cancer cells begin to grow in another body part.
It is hard to say exactly how quickly breast cancer can grow, including the timeframe, as the disease affects each person differently.
Cancer occurs due to mutations in human cells. Mutations do not follow normal, predictable patterns of cell division, so it is difficult to predict the progression.
Tumors appear when damaged cells replicate over and over to form a clump of abnormal cells. Breast cancer cells can break off and move through the lymph or blood vessels to other areas of the body.
If breast cancer cells begin to grow in another body part, this is called metastasis. Breast cancer is most likely to metastasize to the lymph nodes, lungs, and bones.
Regardless of the location of the new tumor, doctors still consider it to be breast cancer.
Breast cancer growth and its chances of spreading depend on the following:
Recommended Reading: Breast Cancer Stage 4 Treatment
Is Surgery Always Necessary For Dcis
We almost always recommend surgery. Even though DCIS is noninvasive and not life-threatening, it has the potential to turn into something more serious. When we do surgery for DCIS, 20% of the time we find an invasive cancer in the tissue that we did not know about from the needle biopsy. For this reason, the only time we dont do surgery for DCIS is when we think the risks of the surgery dont outweigh the benefits. For example, some patients might not be able to tolerate the procedure because of their age or other health problems.
It’s Confusing Even For Doctors
A recent study in the Annals of Internal Medicine found that pathologists disagree with one another about 8% of the time when diagnosing breast biopsy samples, and that cases of DCIS were the most difficult to reach a conclusion about. About 19% of DCIS cases were overinterpreted in the study, meaning they were mistakenly categorized at a higher grade or as invasive cancer, and about 12% were underinterpreted, or mistakenly categorized at lower grades.
The authors write that non-invasive breast lesions represent a “gray zone” in medicine, where there’s not always a right or wrong diagnosis. They say that revised guidelines are needed to make sure DCIS patients get a consistent diagnosis they can trust.
You May Like: What Is The Prognosis For Stage 4 Breast Cancer
What Type Of Follow
Each patient is different, and the doctor will work with each individual on a follow-up plan after surgery and radiation therapy. Typically, a patient can expect to see the doctor for a physical exam every six to 12 months for five years after treatment, then annually after that. An annual mammogram will also be recommended.
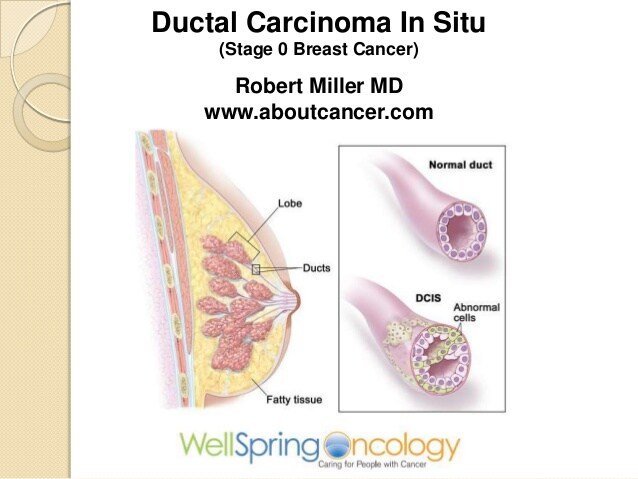
Dcis Is A Noninvasive Precancer Which Is Not Life Threatening
DCIS appears as microcalcifications on a mammogram. When these microcalcifications are seen, it is recommended that a woman have a core biopsy or a wire localization biopsy. This will determine whether you actually have DCIS. If you do, the next step should always be to have another mammogram to see if the biopsy has gotten rid of all the microcalcifications, as no matter how thorough your surgeon has been, there still may be a few remaining. If the diagnosis is DCIS, make sure your pathology report includes information about the grade, presence of necrosis, margin, and estrogen receptor. This information is needed to determine how to treat the DCIS.
Read Also: Adjuvant Therapy Breast Cancer
More Intensive Treatment Of Dcis Reduces The Risk Of Invasive Breast Cancer
- By Kathryn Rexrode, MD, MPH, Contributor
Breast cancer screening with mammography or other tools has increased the rates of diagnosis of very early breast cancers knowns as DCIS . As opposed to invasive breast cancers, DCIS cancers are confined to the local area and have not spread to deeper tissues or elsewhere in the body. With increased rates of diagnosis, there has been considerable controversy about the true risks of DCIS and the best treatments, with some suggesting that women are being overtreated for a condition that does not substantially increase the long-term risk of death, and others advocating more intensive preventive treatment among women with DCIS.
Dcis And Invasive Breast Cancer
If DCIS is not treated, over time it may spread into the breast tissue surrounding the ducts. It then becomes an invasive breast cancer.
Not every untreated DCIS will develop into an invasive breast cancer. But breast specialists usually advise treating DCIS. This is because it is not possible to tell for certain which individual cases of DCIS will become an invasive cancer.
Having DCIS means you have a slightly higher risk of getting cancer elsewhere in the same breast or in your other breast.
See also
You May Like: What Is Stage 3a Breast Cancer
Some People With Dcis Get Radiation
Next, doctors and patients should decide together whether further treatment is needed to reduce the risk of another DCIS or an invasive cancer. This can be determined through genomic testing, or by looking at factors like the patient’s age, family history, and tumor size and grade.
“Several years ago, radiation would have been given to everyone who had DCIS, period,” says Dr. Meyers. “But now, it’s a little more tailored to the type of DCIS and the type of patient, and there’s been a downward trend of getting less radiation or avoiding it completely, if possible.”
Radiation does come with side effectsand it has not been shown to extend survival in patients with DCIS it’s only been shown to reduce the risk of another cancer occurring. So patients should weigh the pros and cons carefully, says Dr. Meyers, and make the best individual decision for them.
What Is The Treatment For Dcis
Lumpectomy with radiation. The standard treatment is breast-preserving surgery with radiation therapy, which results in successful outcomes for most patients. Cancers can be larger than expected, so about 20% of the time, patients need a re-excision lumpectomy another surgery to remove all of the cancer. Typically, the remaining breast will then have radiation therapy to reduce the risk of local recurrence. Lumpectomy plus radiation is a good alternative to mastectomy for treatment of DCIS.
Mastectomy. Some patients have ductal carcinoma in situ in more than one quadrant of the same breast . Sometimes, the DCIS is very large relative to the patients breast size. In these situations, a mastectomy is required to address malignant cells that are more widespread. Radiation therapy is not needed for DCIS treated with mastectomy.
Chemotherapy. Chemotherapy is not needed for DCIS since the disease is noninvasive.
Hormonal therapy. Hormonal therapy may be appropriate for those whose ductal carcinoma in situ is hormone receptor positive.
Also Check: Bad Breast Cancer
After Surgery What Other Treatments Might Be Needed
For those who have a mastectomy for DCIS, there is usually no need for additional treatment because the risk of the cancer coming back is very low. After a lumpectomy, there is still a risk that the DCIS may come back or become invasive cancer. To reduce this risk, the two main treatments are radiation therapy and, if the DCIS cells have the estrogen receptor, hormone therapy. These hormone-blocking drugs include tamoxifen, which blocks the estrogen receptor, and aromatase inhibitors, which block estrogen production.
Probably the hardest decision faced by people with DCIS is whether to have one of these additional treatments after a lumpectomy. A lot of factors must be considered, including the size and grade of the DCIS, how close the DCIS cells were to the final margin, and the age of the person at diagnosis. Younger patients tend to have a higher risk of recurrence compared to older individuals. And then as a doctor, I need to consider how each of my patients thinks about risk. For example, a 10% risk of recurrence in the next ten years can mean completely different things to two different people. Some patients want to do everything to lower their risk, while others are happy to just have it watched closely.
How Is It Diagnosed
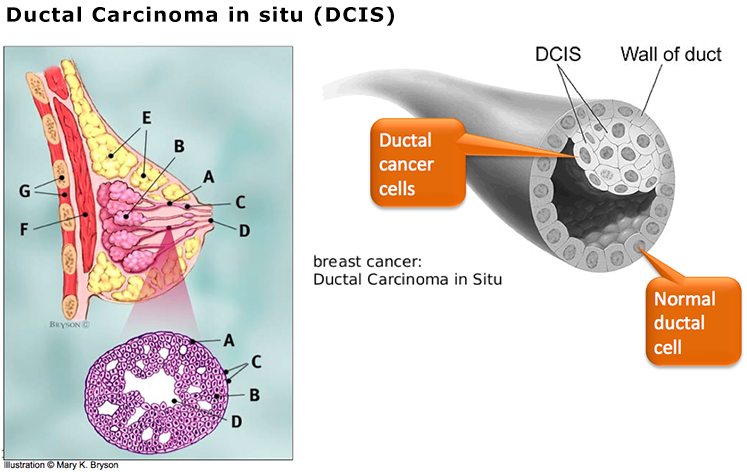
Most of the time, DCIS is diagnosed through a routine breast cancer screening.
If your doctor thinks you might have DCIS, youll probably need further tests to confirm the diagnosis. These tests may include:
- a diagnostic mammogram
- an MRI
- a biopsy
The report that comes back from the pathologists in the lab may contain some unfamiliar terms, like the ones described below:
A biopsy will also be able to determine the hormone receptor status of the DCIS cells. Many times, DCIS will have receptors that respond to the hormones estrogen or progesterone.
If these hormone receptors are present, it can help your doctor decide whether to offer you anti-estrogen medication to reduce the risk of recurrence.
You May Like: Can You Get Rid Of Breast Cancer
Removal Of Part Of The Breast
Many women have surgery to remove the area of DCIS and a border of healthy tissue around it. This is called breast conserving surgery, or a wide local excision or sometimes a lumpectomy.
After this surgery, you might have radiotherapy to the rest of the breast tissue if the DCIS cells look very abnormal . The radiotherapy treatment aims to kill off any abnormal cells that might still be in the breast tissue. Your doctor or breast care nurse will discuss with you the possible benefits and risks of radiotherapy.
Cautious Observation Followed By Swift Action
So whats the best way to handle DCIS? Know exactly what youre dealing with, and go from there.
I had one 37-year old patient who came to me for a pre-surgery screening. She had DCIS, and her physician recommended cutting it out. I wanted to know if she was at risk. But her pathologist didnt even know! The truth is, we dont do a very good job of screening DCIS cells, in most cases.
On the other hand, I had a different patient who presented with some worrying blood markers. I told her to get checked out, but she put it off. A year later, she had full-blown cancer.
So what should you do if you have a DCIS?
First, get as many preliminary tests done as possible. There are blood markers that can indicate pathology, if not point directly to cancer. Read in context with a DCIS, good doctors can draw reasonable conclusions of danger.
Second, get more than one opinion. Leaving a high-risk DCIS in place isnt the solution. But neither is treating a benign growth. More and more women are getting biopsies and insisting on an individualized study. They arent immediately leaping to surgery.
Thats the right thing to do. In most cases, vigilance is required first. After that, you can leap to surgery if necessary.
And third, take a good long breath. Remember, even with those women who had the most virulent cells and did nothing, over 90% survived. In all other cases, an even higher percentage made it out fine.
Automatically reaching for the scalpel can do more harm than good.
You May Like: Does Getting Hit In The Breast Cause Cancer
What Are The Symptoms Of Dcis
DCIS usually has no symptoms. Most cases of DCIS are found during routine breast screening or if a mammogram is done for some other reason.
Occasionally DCIS is found when someone has a breast change such as a lump or discharge from the nipple. However, if someone with DCIS has a breast change its more likely they will also have an invasive breast cancer.
Some people with DCIS also have a type of rash involving the nipple known as Pagets disease of the nipple, although this is rare.
About Those Lymph Nodes
A surgeon will usually take a lymph node biopsy to determine if the breast cancer has spread to the axillary lymph nodes. This is not always necessary, however. A lymph node biopsy is not usually necessary for DCIS. However, for invasive breast cancer, yes, they do need to check the lymph nodes.
Sometimes, doctors will perform a sentinel node biopsy, rather than a full lymph node excisional biopsy if the concerns about cancer spread are minimal. Cancer cells tend to appear first in the sentinel node before spreading to the other nodes, or other areas of the body.
Read Also: Is Breast Cancer Curable In The 3 Stage
Hormone Therapy After Surgery
If the DCIS is hormone receptor-positive , treatment with tamoxifen or an aromatase inhibitor for 5 years after surgery can lower the risk of another DCIS or invasive cancer developing in either breast. If you have hormone receptor-positive DCIS, discuss the reasons for and against hormone therapy with your doctors.
Whats The Most Effective Treatment For Dcis
Surgery is typically the first treatment for DCIS, and it is very effective. There are two types of surgery used for DCIS. The less-invasive option is a lumpectomy, in which a surgeon removes the area of DCIS as well as a little bit of the normal tissue around it, also referred to as a margin. The other option is a mastectomy, which involves removing the entire breast.
Most people with DCIS undergo a lumpectomy, possibly followed by additional treatments. In some cases, a mastectomy is recommended, especially if the DCIS covers a large area or appears in multiple spots throughout the breast. With either of these surgeries, the survival rate is excellent. Our job is to figure out which type of surgery is best for each patient.
Read Also: How Likely Am I To Get Breast Cancer
Can Dcis Be Left Untreated
Because theres no way of knowing when or if DCIS will become invasive, treatment is usually recommended. It is possible that this may lead to unnecessary or overtreatment for some people.
The aim of treatment is to remove all the DCIS from within the breast to reduce the chance of it becoming an invasive cancer.
Research is ongoing to identify which cases of DCIS will go on to become invasive and which might be safe to leave untreated. If you are diagnosed with low-grade DCIS, you may be invited to join a clinical trial.
A Test Can Help You Determine Your Risk
Sometimes doctors will recommend a genomic test, called the Oncotype DX test, to help determine a DCIS patient’s risk of getting another cancer in the future. A sample from the DCIS biopsy or lumpectomy is sent to a lab, where pathologists study the activity of 12 different cancer-related genes.
“You get back what’s called a DCIS score, from zero to 100, that tells you the likelihood of a DCIS recurrence or of an invasive cancer in the next 10 years,” says Dr. White. “I want to help patients keep their breasts, so if they have a high risk of recurrence we want to recommend radiation so they can prevent that invasive cancer in the future.”
Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center has also developed a free online assessment tool to helps DCIS patients estimate their risk of another cancer, based on age, family history, and details about their specific tumor. “We want to help patients understand their individual risks, so they can make an informed decision about how much treatment they’re going to have,” says Dr. White.
Don’t Miss: Stage 2 Aggressive Breast Cancer
Difficult Decisions For Patients
Toro de Stefani is one of 60,000 U.S. women diagnosed with DCIS each year. Each must decide on a treatment option.
Current guidelines that recommend lumpectomy and radiation are causing concerns that the condition may be overtreated, since most cases never become invasive.
This gives medical professionals enormous uncertainty about how to advise women on an individual basis, says Thompson, professor of Surgery at MD Anderson. And therefore, historically the treatments have ranged from active surveillance on one end of the pectrum all the way to mastectomies on the other.
Thompson says DCIS diagnoses have increased as breast imaging has become more accurate and frequent. The National Institutes of Health estimates that by 2020, more than 1 million women in the U.S. will be living with a DCIS diagnosis, compared to 500,000 in 2005.
Before mammograms became common, many women had the condition for years without being aware of it, because it grows so slowly and causes no symptoms.
Perhaps, surprisingly, given that breast screening has been around for three or four decades, were only now really coming to grips with the fact that we often diagnose some conditions like DCIS as breast cancer even though theyre not conventional, invasive breast cancers, Thompson says.
Hes participating in three DCIS research studies that he hopes will make treatment decisions easier.
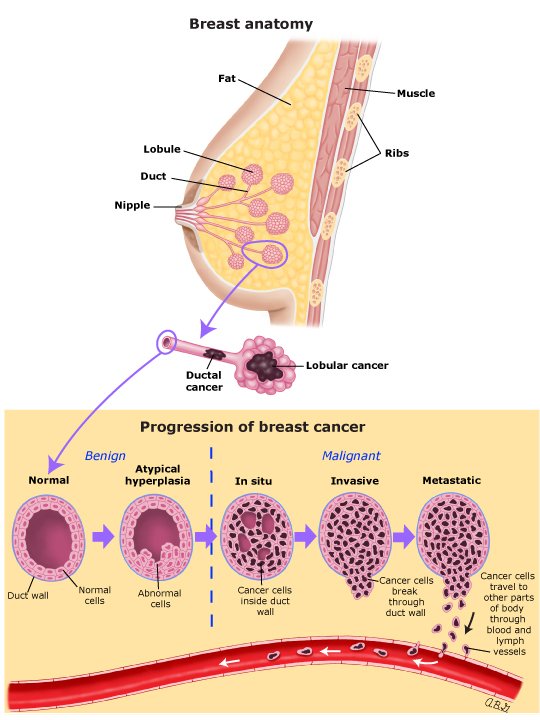
The Stages Of Breast Cancer
NOTE: Although a lot of this information is still valid, The American Joint Committee on Cancer has recently updated their classifications for staging breast tumors.
We will be updating all our articles on staging in the near future. In the meantime, please click HERE for a brief summary of the major changes in January 2018.
If a breast biopsy confirms that breast cancer is indeed the diagnosis, the staging process begins.
The stages of breast cancer are really the extent of breast cancer. So, in order to choose and begin the best treatment, it is necessary to stage breast cancer. The staging process shows the progression of breast cancer.
Breast cancer progresses in relatively predictable and consistent ways, so it is possible to categorize breast cancer in terms of stages.
There are basically five stages of breast cancer, with some subcategories .
You May Like: What Is Estrogen Positive Breast Cancer