Cost And Health Insurance
MRIs tend to be pricey and insurance coverage can vary. A 2018 research study found that the average cost of a breast MRI was $1,197.
If you have insurance, check to ensure that the facility is an in-network provider. Out-of-network providers almost always cost more.
Be aware that you may need to get prior authorization from your insurer before undergoing a breast MRI. Your healthcare provider’s office can usually help you with this. If you skip this step, your insurer could very well deny the claim.
If you are paying out of pocket, shop around for the best price. You can also ask the facility if they offer a monthly payment plan or a discount for upfront payment.
Breast Cancer Diagnosis By Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Since breast cancer can strike women without warning signs and symptoms, all women should be aware of screening and early detection of breast cancer. A number of clinical researches has indicated thatearly detection of breast cancer by using standard imaging approach digital mammogram and breast ultrasound is essentially important as it is strongly associated with an increased number of available treatment options, increased survival with improved quality of life. Besides digital mammogram and breast ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging or shortly called MRI greatly helps to detect breast abnormalities. MRI uses radio waves and strong magnets to make detailed pictures of the inside of the breast, allowing doctors to visualize a variety of tumors in the breast, if there any. Although there is no definitive method of preventing breast cancer, early detection provides the best possible chance of effective treatment, especially if the earliest stage of breast cancer is found.
Limitations Of Using Breast Mri For Cancer Screening
A breast MRI is a highly effective test. However, an MRI is not a replacement for mammography because it may sometimes fail to find cancer that a mammogram detects. A breast MRI may also lead to a “false-positive” result. This means that the test finds a mass or other change that seems to show cancer but it is not cancer. If this happens, your doctor may recommend a targeted ultrasound. If the area is still not seen with the ultrasound, he or she may recommend an MRI biopsy.
Recommended Reading: Carcinoma Left Breast
Mri Diagnoses More Lesions But Does It Detect Significant Disease
One of the problems with MRI breast cancer screening use, is that suspicious or unusual findings are seen at a much higher rate than with mammography. Often MRI will detect additional foci of contrast enhancement other than the main lesion in question. In fact this occurs about 30% of the time. As a result of these new findings, the treatment plan is altered in about 11% of patients.
There is no question that in some cases, MRI is able to detect a potential breast cancer threat very early and the interventions are warranted. But in many instances MRI detects secondary lesions which turn out in the end to be completely benign. There is a real danger that MRI screening leads to a more aggressive treatment than was really necessary.
There really is no consensus on what would constitute a significant disease discovered through MRI. Often, MRI detects subclinical diseases that would never have been clinically relevant. Also, MRI quite often detects breast cancer that is currently being treated adequately with systemic breast cancer therapies or radiation therapy.
What Can I Expect After A Breast Mri
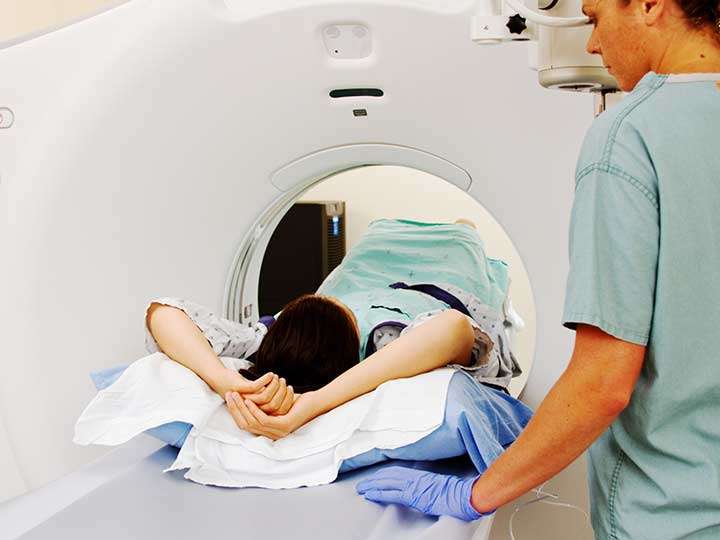
A breast MRI is usually an outpatient procedure. You can go home and resume your normal activities right away unless your doctor tells you otherwise.
The results of your breast MRI will determine your next steps. Benign results mean there is no cancer and no further treatment may be necessary. If the results indicate a problem, you may need more imaging exams, additional diagnostic tests , or treatment.
Recommended Reading: Breast Cancer Life Expectancy Without Treatment
What Is A Breast Mri
Magnetic resonance imaging is a noninvasive test doctors use to diagnose medical conditions.
MRI uses a powerful magnetic field, radiofrequency pulses, and a computer to produce detailed pictures of internal body structures. MRI does not use radiation .
Detailed MR images allow doctors to examine the body and detect disease.
MRI of the breast offers valuable information about many breast conditions that cannot be obtained by other imaging modalities, such as mammography or ultrasound.
Breast Mri Vs Mammography
Compared to mammography, screening with breast MRI has some drawbacks :
- Breast MRI is more invasive than mammography because a contrast agent is given by vein before the procedure. In rare cases, people can have a reaction to gadolinium.
- Gadolinium may build up in the brain over time in people who get MRIs on a regular basis, such as women at high risk of breast cancer who get regular breast MRI screening. Whether or not this build up has health risks is under study.
- Breast MRI has more false positive results than mammography. A false positive result shows a possible breast cancer, even though breast cancer isnt present. The suspicious area must be checked with follow-up tests, and sometimes a biopsy, to be sure theres no breast cancer.
- Some MRI centers dont have the special magnets needed to do an MRI of the breast or dont have radiologists specially-trained to read breast MRIs.
- Breast MRI is expensive and isnt always covered by insurance.
Also Check: Does Cancer Hurt In Breast
Who Should Have Screening With Mri
If you are aged under 50 and you are at high risk of breast cancer, it may be recommended that you consider having breast MRI in addition to a mammogram and ultrasound. If you have been assessed as being at high risk of breast cancer, you would probably:
- have a very strong family history of breast and/or ovarian cancer or cancer of the fallopian tubes, and have been assessed as potentially high risk through a familial cancer clinic or
- have had a genetic test showing that you carry a BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene mutation.
You can find out more about your risk of breast cancer by reading the Family history of breast cancer fact sheet.
The cost of breast MRI may be covered by Medicare for women at potentially high risk of breast cancer. There are very strict rules about who can qualify for a Medicare rebate, and you should discuss these with your doctor. To be eligible for a Medicare rebate, you must be under the age of 50, assessed as being in Category 3 for risk of breast cancer rather than a general practitioner, and have the scan on a particular type of MRI equipment.
When Should A Breast Mri Vs Mammogram Be Perform
It is recommended that women at high risk for developing breast cancer consult their doctor about having an MRI test done in conjunction with a mammogram. Several factors may place a patient in the high-risk category:
- BRCA1 and BRCA2 or other genetic mutations
- A first-degree relative who has an inheritable breast cancer mutation
- Breast cancer risk of 20 to 25 percent, based on National Cancer Institute assessment tools
- Received radiation therapy to the breast between the ages of 10 and 30
Additionally, women who have conditions known to predispose them to breast cancer, such as atypical ductal hyperplasia, may need an MRI. Breast MRIs may also be appropriate for women who have had a mastectomy on one side or have dense breast tissue.
Read Also: Recurrent Breast Cancer Symptoms
How Does The Procedure Work
Unlike x-ray and computed tomography exams, MRI does not use radiation. Instead, radio waves re-align hydrogen atoms that naturally exist within the body. This does not cause any chemical changes in the tissues. As the hydrogen atoms return to their usual alignment, they emit different amounts of energy depending on the type of tissue they are in. The scanner captures this energy and creates a picture using this information.
In most MRI units, the magnetic field is produced by passing an electric current through wire coils. Other coils are inside the machine and, in some cases, are placed around the part of the body being imaged. These coils send and receive radio waves, producing signals that are detected by the machine. The electric current does not come into contact with the patient.
A computer processes the signals and creates a series of images, each of which shows a thin slice of the body. The radiologist can study these images from different angles.
MRI is often able to tell the difference between diseased tissue and normal tissue better than x-ray, CT, and ultrasound.
Literature Search Strategy And Selection Criteria
Using a software based on statistical text mining and machine learning methods , we identified 33 relevant articles in PubMed on staging of advanced breast cancer, metastatic breast cancer, bone disease and distant metastases between 2009 and 2019. We identified papers in English language, both original studies and review articles. Additionally, we searched the references listed for additional relevant papers, using a total of 40 scientific papers.
Read Also: Estrogen Positive Progesterone Negative Breast Cancer
Whats It Like To Get A Breast Mri
MRI scans are usually done in an outpatient setting in a hospital or clinic. You’ll first have an IV line placed a vein in your arm so that contrast material can be injected during the test.
Youll lie face down on a narrow, flat table with your arms above your head. Your breasts will hang down into an opening in the table so they can be scanned without being compressed. The technologist may use pillows to make you comfortable and help keep you from moving. The table then slides into a long, narrow tube.
The test is painless, but you have to lie still inside the narrow tube. You may be asked to hold your breath or keep very still during certain parts of the test. The machine may make loud thumping, clicking, and whirring noises, much like the sound of a washing machine, as the magnet switches on and off. Some facilities give you earplugs or headphones to help block noise out during testing.
When breast MRI is done to look for breast cancer, a contrast material called gadolinium is injected into a vein in the arm during the exam, which helps show any abnormal areas of breast tissue. Let the technologist know if you have any allergies or have had problems before with any contrast or dye used in imaging tests.
Its important to stay very still while the test is being done, which helps ensure the images will be of good quality.
For a newer MRI technique, known as abbreviated breast MRI, fewer images are taken, so the scan takes less time .
Breast Mri And Breast Cancer Screening For Women At Higher Risk

Compared to mammography alone, mammography plus breast MRI can increase detection of breast cancer in some women at higher than average risk of breast cancer .
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network recommends yearly screening with mammography plus breast MRI for some women at higher risk of breast cancer, including those with :
Both the NCCN and the American Cancer Society recommend women at higher risk of breast cancer begin screening at an earlier age than women at average risk . Figure 3.5 and Figure 3.6 outline their guidelines.
Talk with your health care provider about breast cancer screening. Together, you can make a screening plan thats right for you.
| For a summary of research studies on breast cancer screening with breast MRI plus mammography and mammography alone for women at higher than average risk of breast cancer, visit the Breast Cancer Research Studies section. |
Read Also: Stage Iv Breast Cancer Symptoms
The Role Of Breast Magnetic Resonance Imaging In Preoperative Evaluation
The use of breast MRI in the preoperative setting for women with a recent breast cancer diagnosis is controversial, with wide variations in practice. Preoperative MRI is likely to detect multifocal and multicentric lesions and evaluate the contralateral breast, especially in lobular cancers and in dense breast. A systematic review that included 3 RCT’s and 16 comparative studies were included in the meta-analysis was performed to identify studies reporting quantitative data on pre-operative MRI and surgical outcomes. This review concluded that pre-operative MRI is associated with increased odds of receiving ipsilateral mastectomy and contralateral prophylactic mastectomy as surgical treatment in newly diagnosed breast cancers .
MRI is also said to define the size and extent of the tumour better for planning surgery. While this is expected to reduce re-excision rates along with a decrease in the local recurrence rates and overall survival rates, this has actually not borne out in reality. It however leads to increase in additional biopsies, patient anxiety, cost, delay the onset of treatment and possibly increase in mastectomy rates.
Pre-operative MRI is probably not warranted routinely in patients who can be adequately analyzed by mammography and ultrasound examination. It certainly may be valuable in women with dense breasts and in patients with lobular cancer.
Is The Breast Mri Test Safe
A breast MRI is safe. The test poses no risk to the average patient if appropriate safety guidelines are followed.
People who have had heart surgery and people with the following medical devices can be safely examined with MRI:
- Surgical clips or sutures
-
A tissue expander with magnetic port after mastectomy
In addition, tell your doctor if you:
- Are pregnant
- Weigh more than 300 pounds
- Are not able to lie on your back for 30 to 60 minutes
- Have claustrophobia
Don’t Miss: Estrogen Receptor Negative Breast Cancer
Breast Mri Study Findings
Among the findings:
- Breast MRI was associated with a 22-day delay in the start of treatment. “We don’t know why,” Bleicher says. It could be because of the scheduling of the MRI itself, or perhaps MRI prompts other biopsies.” Three weeks should not change a patient’s survival chances, he says, but waiting can clearly add to a patient’s anxiety.
- Those who got the breast MRI were nearly twice as likely to have a mastectomy as breast-conserving surgery, even after controlling for size and stage of the tumor. One reason, he says, may be that the MRI, being highly sensitive, picked up something that looked like cancer but turned out not to be — a false positive.
- Those who got the breast MRI were slightly more likely to have what surgeons call positive margins, although this finding could have been a chance finding. The goal is negative margins. “The goal is to excise out the tumor so there is a margin of normal tissue around it, reassuring us the cancer has been completely removed,” he says.
- Younger women were more likely than older women to have MRIs, but the use of the MRI did not correlate with other factors such as family history of breast or ovarian cancer.
When Is Breast Mri Used
Breast MRI might be used in different situations.
To screen for breast cancer: For certain women at high risk for breast cancer, a screening breast MRI is recommended along with a yearly mammogram. MRI is not recommended as a screening test by itself, because it can miss some cancers that a mammogram would find.
Although MRI can find some cancers not seen on a mammogram, its also more likely to find things that turn out not to be cancer . This can result in some women getting tests and/or biopsies that end up not being needed. This is why MRI is not recommended as a screening test for women at average risk of breast cancer.
To look at the breasts if someone has symptoms that might be from breast cancer: Breast MRI might sometimes be done if breast cancer is suspected . Other imaging tests such as mammograms and breast ultrasound are usually done first, but MRI might be done if the results of these tests arent clear.
To help determine the extent of breast cancer: If breast cancer has already been diagnosed, breast MRI is sometimes done to help determine the exact size and location of the cancer, to look for other tumors in the breast, and to check for tumors in the other breast. Breast MRI isnt always helpful in this setting, so not every woman who has been diagnosed with breast cancer needs this test.
Read Also: How Often Is Chemo Given For Breast Cancer
How Often Should Your Schedule Breast Cancer Screenings
The American College of Radiologists recommends women take a breast cancer risk assessment when they reach 30 years old. This can help determine the need for additional screenings.
Women with an average risk of developing breast cancer should start routine mammogram screenings every year starting at age 40, but those with a higher risk should start sooner.
Women at high risk for developing breast cancer should have an annual breast MRI along with their mammogram. This especially applies to younger women who have a high risk of developing breast cancer. An example of this is a woman in her teens or 20s who finds out she has a family member with a BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation.
According to the American Cancer Society, women who are considered high risk should have annual breast MRIs in addition to mammograms. These include women who have:
- A BRCA1 or BRCA2 genetic mutation or have a first-degree relative with a BRCA1 or BRCA2 genetic mutation
- Received chest radiation therapy between the ages of 10 and 30 years old
- Li-Fraumeni syndrome, Cowden syndrome, or Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome or have a first-degree relative with Li-Fraumeni syndrome, Cowden syndrome, or Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome
However, not all women need annual breast MRIs. Thats because breast MRIs can sometimes find abnormalities that are not cancerthese are called false positives.