About External Beam Radiation Therapy
With external beam radiation therapy, a treatment machine will aim a beam of radiation directly to the tumor from outside your body. The radiation will pass through your body and destroy the cancer cells in its path. You wont see or feel it.
You may be having external beam radiation therapy to 1 or more of the following areas:
- Your breast
- The lymph nodes near your collarbone
- The lymph nodes under your arm
- The lymph nodes near your sternum
Your radiation oncologist and nurse will talk with you about your treatment plan.
What Is The Prognosis After Recurrence
Many patients with a recurrence of breast cancer can be successfully treated, often with methods other than radiation if radiation was used in the initial treatment. For patients treated initially for invasive breast cancer, five percent to 10 percent will be found to have distant metastases;at the time of discovery of the breast recurrence. The same proportion will have recurrences that are too extensive to be operated on. While in these cases the patient’s disease can often be managed over a period of years, the goals of treatment change from obtaining a cure to preventing further progression or managing symptoms. Five-year cure rates for patients with relapse after breast conservation therapy are approximately 60 percent to 75 percent if the relapse is confined to the breast and a mastectomy is then performed.
For patients treated initially for DCIS, about one-half of recurrences are invasive and one-half noninvasive DCIS. Long-term control rates following recurrence after initial breast conservation therapy have been high, often over 90 percent.
If Youre Getting Radiation Therapy To The Chest
Radiation treatment to the chest may cause side effects such as:
- Sore throat
Radiation can also cause other problems in the heart or lungs.
Heart complications
Getting radiation to the middle portion of the chest can raise your risk of heart disease. This risk increases with higher radiation doses and larger treatment areas in this part of your body. Radiation can also cause hardening of the arteries , heart valve damage, or irregular heartbeats.
Radiation pneumonitis
Radiation pneumonitis is inflammation of the lungs that can be caused by radiation treatment to the chest . It may occur about 3 to 6 months after getting radiation therapy. Its more likely if you have other lung diseases, like emphysema . Common symptoms of radiation pneumonitis include:
- Shortness of breath that usually gets worse with exercise
- Chest pain, which is often worse when taking in a deep breath
- Cough
- Weakness
Sometimes there are no symptoms, and radiation pneumonitis is found on a chest x-ray.
Symptoms often go away on their own, but if treatment is needed, it is based on trying to decrease the inflammation. Steroids, like prednisone, are usually used. With treatment, most people recover without any lasting effects. But if it persists, it can lead to pulmonary fibrosis . When this happens, the lungs can no longer fully inflate and take in air.
Be sure you understand what to look for, and tell your cancer care team if you notice any of these side effects.
Read Also: How Many People Die From Breast Cancer
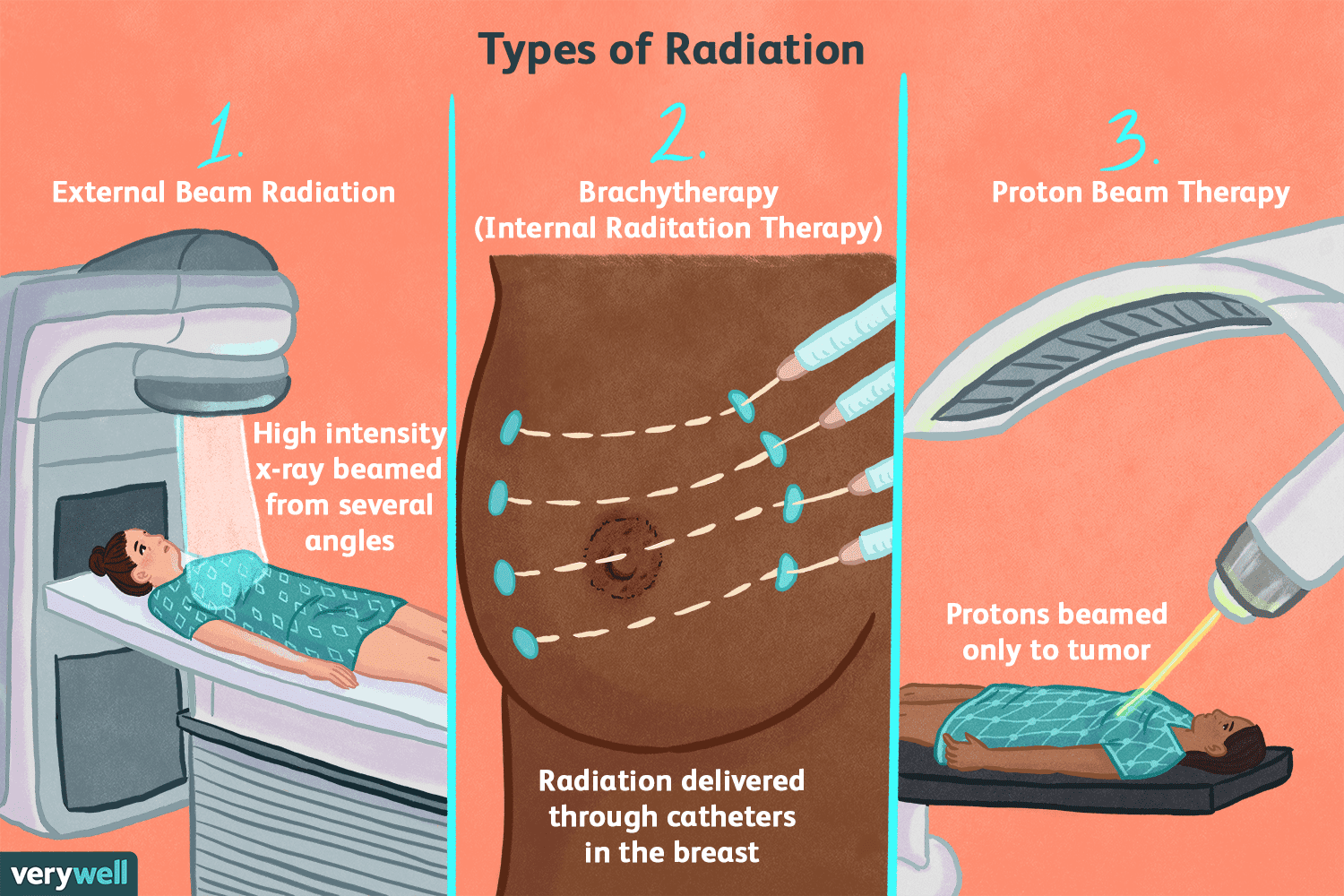
Types Of Radiation Therapy
- External beam radiation is most commonly used to treat breast cancer. A machine outside your body aims a beam of radiation on the area affected by the disease.
- Brachytherapy delivers radiation to the cancer through something implanted in your body.
- Proton therapy sends highly targeted radiation just to your breast tissue and not into your heart or lungs.
How Can I Make A Decision Between Mastectomy And Breast Conservation Therapy
Breast conservation therapy is often used for patients with early-stage invasive breast cancers . It is also used for patients with DCIS . Some of the reasons to not have breast conservation therapy include: personal preference; increased risk of complications from radiation therapy in individuals with certain rare medical conditions such as certain autoimmune disorders; surgery that would require removing a large amount of diseased breast tissue that would lead to a poor cosmetic result; and tumors that are more likely than average to have a relapse in the breast with breast conservation therapy.
Most patients may choose a treatment based on other factors, such as convenience or personal preference . Most women prefer to keep their breast if this is possible to do safely, but there is no right answer that is best for everyone. This decision is one that is ideally made in partnership between a patient and her physician. In some cases a pre-surgical consultation with a radiation oncologist may be helpful in answering questions about breast-conserving therapy.
Nearly all physicians will recommend patients be treated with mastectomy instead of breast conservation therapy when the risk of recurrence in the breast is more than 20 percent. This is the case if the tumor is large or multifocal . This situation occurs for only a small number of women, however.
Recommended Reading: How Do Doctors Treat Breast Cancer
What Are The Different Kinds Of Radiation Therapy
Most radiation therapy is administered by a radiation oncologist at a radiation center and usually begins three to four weeks after surgery. The radiation is used to destroy undetectable cancer cells and reduce the risk of cancer recurring in the affected breast.
There are two main kinds of radiation therapy that may be considered,;and some people have both.
- External Beam Breast Cancer Radiation;
- Internal Breast Cancer Radiation;
Keep in mind that the course of treatment you decide is something you should discuss with your radiation oncologist in order to ensure that it is as effective as possible.
How Will I Feel During Implant Therapy
Youre not likely to have a lot of pain or feel sick while implants are being put in. The drugs used while theyre being placed might make you feel drowsy, weak, or sick to your stomach, but these side effects dont last long. If your implant is held in place by an applicator, you may have some discomfort in that area. If you have the kind of implant where you need to be in bed for a few days, you may have aches and pains from being inactive. Ask for medicine to help you relax or to relieve pain if needed. Be sure to tell your cancer care team if you have ;burning, sweating, or other symptoms.
Don’t Miss: Where To Buy Breast Cancer Merchandise
When Is Radiation Therapy Recommended
Radiation therapy is recommended:
- after breast-conserving surgery
- after a mastectomy if pathology results suggest the risk of recurrence is high or if the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes you may have radiation to the chest wall and lymph nodes above the collarbone
- if the sentinel node is affected you may have radiation to the armpit instead of axillary dissection.
You will usually start radiation therapy within eight weeks of surgery. If youre having chemotherapy after surgery, radiation therapy will begin about three to four weeks after chemotherapy has finished. In some circumstances, radiotherapy may be offered after neoadjuvant chemotherapy and before surgery.
How Long The Treatment Takes
Radiation therapy for early-stage breast cancer can be given in two different schedules.
- Standard radiation therapy. This is usually given 5 days a week. Treatment takes 5 to 6 weeks.
- Hypofractionated radiation therapy. This is given in slightly higher doses. It’s done 5 days a week. Treatment takes about 3 to 4 weeks.
The doctor will look at the stage of the tumor and other things. This is to help decide which course may be right for you. Ask your doctor to go over both of these options with you.
Recommended Reading: Does Breast Cancer Kill You
What Happens To Permanent Implants
The radioactive materials stop giving off radiation over time. It may take weeks or months. Talk to your cancer care team about how long it will take in your case. Once the radiation is gone, the implant are no longer active. They usually stay in place and cause no harm, so theres no need to take them out.
Is Radiation Therapy Safe
Some patients are concerned about the safety of radiation therapy. Radiation has been used successfully to treat patients for more than 100 years. In that time, many advances have been made to ensure that radiation therapy is safe and effective.
Before you begin receiving radiation therapy, your radiation oncology team will carefully tailor your plan to make sure that you receive safe and accurate treatment. Treatment will be carefully planned to focus on the cancer while avoiding healthy organs in the area. Throughout your treatment, members of your team check and re-check your plan. Special computers are also used to monitor and double-check the treatment machines to make sure that the proper treatment is given. If you undergo external beam radiation therapy, you will not be radioactive after treatment ends because the radiation does not stay in your body. However, if you undergo brachytherapy, tiny radioactive sources will be implanted inside your body, in the tumor or in the tissue surrounding the tumor, either temporarily or permanently. Your radiation oncologist will explain any special precautions that you or your family and friends may need to take.
Read Also: Can Breast Cancer Hurt Your Shoulder
What Happens During Radiation Therapy Treatment
What happens during your radiation therapy treatment depends on the kind of radiation therapy you receive.
External-beam radiation therapy
External-beam radiation therapy delivers radiation from a machine outside the body. It is the most common radiation therapy treatment for cancer.
Each session is quick, lasting about 15 minutes. Radiation does not hurt, sting, or burn when it enters the body. You will hear clicking or buzzing throughout the treatment and there may be a smell from the machine. Typically, people have treatment sessions 5 times per week, Monday through Friday. This schedule usually continues for 3 to 9 weeks, depending on your personal treatment plan.
This type of radiation therapy targets only the tumor. But it will affect some healthy tissue surrounding the tumor. While most people feel no pain when each treatment is being delivered, effects of treatment slowly build up over time and may include discomfort, skin changes, or other side effects, depending on where in the body treatment is being delivered. The 2-day break in treatment each week allows your body some time to repair this damage. Some of the effects may not go away until the treatment period is completed. Let the health care professionals if you are experiencing side effects. Read more about the side effects of radiation therapy.
Internal radiation therapy
-
The permanent implant loses it radioactivity
-
The temporary implant is removed
Weekly reports
Personal care
What Are Clinical Trials
Cancer specialists regularly conduct studies to test new treatments. These studies are called clinical trials. Clinical trials are available through cancer doctors everywhere- not just in major cities or in large hospitals.
Some clinical studies try to determine if a therapeutic approach is safe and potentially effective. Many large clinical trials compare the more commonly used treatment with a treatment that cancer experts think might be better. Patients who participate in clinical trials help doctors and future cancer patients find out whether a promising treatment is safe and effective. All patients who participate in clinical trials are carefully monitored to make sure they are getting quality care. It is important to remember that clinical trials are completely voluntary. Patients can leave a trial at any time. Clinical trials testing new treatments are carried out in phases:
Only you can make the decision about whether or not to participate in a clinical trial. Before making your decision, it is important to learn as much as possible about your cancer and the clinical trials that may be available to you. Your radiation oncologist can answer many of your questions if you are considering taking part in a trial or contact the National Cancer Institute at 1-800-4-CANCER or www.cancer.gov.
You May Like: How To Find Out You Have Breast Cancer
External Radiation Therapy Side Effects
One of the main side effects of external radiation therapy is skin changes in the treated area.
The reaction is much like a sunburn, with redness and possible itching, burning, soreness, peeling, blisters, or darkening of the skin. These skin changes happen gradually over the course of treatment and may happen only in certain areas.
Places where skin touches skin, such as the armpit and the area under the breasts, and places where you may have had a lot of sun exposure, such as the upper chest, are more likely to be affected. Some people have a change in skin color that lasts for years after treatment.
Some people may have telangiectasias develop months to years after radiation to the breast. A telangiectasia is a small patch of tiny blood vessels on the skin of the treated area that looks like a tangle of thin red lines. Telangiectasias are not a sign of cancer recurrence, but they can sometimes cause bothersome symptoms such as itching or pain. If you develop telangiectasia after radiation therapy and wish to treat it, you can talk to a dermatologist about laser therapy or other treatments.
You may be more likely to have significant skin side effects if you have fair skin, larger breasts, certain health conditions that affect skin healing , or had mastectomy or chemotherapy before radiation.
Other common side effects of external radiation therapy are:
- swelling in the breast
Other, less common side effects that external radiation may cause are:
How Do I Prepare For My Treatments
Before your first radiation treatment, you will have a simulation appointment. This appointment will last approximately one to two hours. During this appointment, the doctor will identify the exact fields on your body to treat with radiation. This involves lying on a table while the radiation therapist marks the field with small dots made with permanent ink. Each dot is similar to a very small tattoo. You will not receive any radiation treatment during this appointment.
Recommended Reading: How To Screen For Breast Cancer
Brachytherapy Delivered Via Implantable Device
The doctor places a device inside the breast at the time of the surgery or shortly thereafter which carries targeted radiation to the tissue where the cancer originally grew . This type of radiation may take only one treatment delivered in the operating room or may take 5-7 days given on an outpatient basis in the radiation therapy department.In nearly all cases, the appropriate method is determined by the radiation oncologist based on the location and size of the tumor.
How Does Radiation Therapy Work
Radiation therapy uses special high-energy X-rays or particles to damage a cancer cells DNA. When a cancer cells DNA is damaged, it cant divide successfully and it dies.
Radiation therapy damages both healthy cells and cancer cells in the treatment area. Still, radiation affects cancer cells more than normal cells. Cancer cells grow and divide faster than healthy cells and also are less organized. Because of this, it’s harder for cancer cells to repair the damage done by radiation. So cancer cells are more easily destroyed by radiation, while healthy cells are better able to repair themselves and survive the treatment.
The treatment area may include the breast area, the lymph nodes, or another part of the body if the cancer has spread.
Radiation treatments are carefully planned to make sure you receive the greatest benefits and the fewest side effects possible.
- Brachytherapy/Internal Radiation
- Internal radiation, called brachytherapy by doctors, uses a radioactive substance sealed in seeds or tiny tubes that are placed inside your body directly into the cancer or the place where the cancer was. Read about brachytherapy.
Another type of radiation therapy, called intraoperative radiation therapy, is a type of partial-breast radiation. With intraoperative radiation therapy, the entire course of radiation is delivered at one time during breast cancer surgery. Read more about intraoperative radiation therapy.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Fish Test For Breast Cancer
External Beam Breast Cancer Radiation
External beam radiation is the most common kind of radiation treatment for breast cancer. Its a painless treatment, like getting an X-ray. A doctor will place a machine on the outside of your body and aim the radiation beams at the area of the cancer. Your doctor will figure out where to aim the rays and how much radiation to use before each treatment. They will mark the area with temporary or permanent ink.
Each treatment only lasts a few minutes. The session setup will take longer. External radiation treatment happens five days a week for about five to seven weeks. Its the longest type of radiation treatment available.
Short-term side effects of external radiation include:
- fatigue
- swelling and pain in the arm or chest
- weakened and fractured ribs
- future cancer in the inner lining of your blood vessels
External radiation does not leave radiation in your body. You will not be radioactive during or after treatment.
Radiation Therapy Timing And Breast Reconstruction
The timing of radiation treatment in your overall breast cancer treatment plan depends on your individual situation and the characteristics of the breast cancer.
In many cases, radiation therapy is given after surgery. If chemotherapy is planned after surgery, radiation usually follows chemotherapy.
If youre having mastectomy and have decided to have breast reconstruction, its important to know that radiation can cause a reconstructed breast to lose volume and change color, texture, and appearance.
In particular, radiation therapy is known to cause complications with implant reconstruction. Research also suggests that a reconstructed breast may interfere with radiation therapy reaching the area affected by cancer, though this can vary on a case-by-case basis.
For these reasons, some surgeons advise waiting until after radiation and other treatments, such as chemotherapy, are completed before breast reconstruction surgery is done.
Other surgeons may recommend a more staged approach, which places a tissue expander after mastectomy to preserve the shape of the breast during radiation treatments. Once radiation is completed and the tissues have recovered, the expander that was used to maintain the shape of the breast is removed and replaced with tissue from another part of the body or a breast implant.
Also Check: What Chemo Drugs Are Used For Triple Negative Breast Cancer