Lifetime Risk Of Breast Cancer Worldwide
Women who live in developed countries tend to have a higher lifetime risk of breast cancer than women who live in developing countries .
Although we dont know all the reasons for these differences, lifestyle and reproductive factors likely play a large role .
Low screening rates and incomplete reporting can make rates of breast cancer in developing countries look lower than they truly are and may also explain some of these differences.
What Is Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is an uncontrolled growth of breast cells. To better understand breast cancer, it helps to understand how any cancer can develop.
Cancer occurs as a result of mutations, or abnormal changes, in the genes responsible for regulating the growth of cells and keeping them healthy. The genes are in each cells nucleus, which acts as the control room of each cell. Normally, the cells in our bodies replace themselves through an orderly process of cell growth: healthy new cells take over as old ones die out. But over time, mutations can turn on certain genes and turn off others in a cell. That changed cell gains the ability to keep dividing without control or order, producing more cells just like it and forming a tumor.
A tumor can be benign or malignant . Benign tumors are not considered cancerous: their cells are close to normal in appearance, they grow slowly, and they do not invade nearby tissues or spread to other parts of the body. Malignant tumors are cancerous. Left unchecked, malignant cells eventually can spread beyond the original tumor to other parts of the body.
Over time, cancer cells can invade nearby healthy breast tissue and make their way into the underarm lymph nodes, small organs that filter out foreign substances in the body. If cancer cells get into the lymph nodes, they then have a pathway into other parts of the body. The breast cancers stage refers to how far the cancer cells have spread beyond the original tumor .
How Common Is Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is the most common cancer in women in the United States, except for skin cancers. It is about 30% of all new female cancers each year.
The American Cancer Society’s estimates for breast cancer in the United States for 2021 are:
- About 281,550 new cases of invasive breast cancer will be diagnosed in women.
- About 49,290 new cases of ductal carcinoma in situ will be diagnosed.
- About 43,600 women will die from breast cancer.
Breast cancer mainly occurs in middle-aged and older women. The median age at the time of breast cancer diagnosis is 62. This means half of the women who developed breast cancer are 62 years of age or younger when they are diagnosed. A very small number of women diagnosed with breast cancer are younger than 45.
Also Check: Type 4 Breast Cancer
In 3 Breast Cancers Are In Women Over 70
New national Be Clear on Cancer campaign targets older women to increase early diagnoses of breast cancer.
- From:
- 3 February 2014 See all updates
One in 3 women diagnosed with breast cancer in England each year are aged 70 or over. This age group also accounts for more than half of all breast cancer deaths annually, latest figures show. This age group also accounts for more than half of all breast cancer deaths annually, latest figures show.
This comes as Public Health England launches a new national Be Clear on Cancer campaign to remind older women dont assume youre past it, and to visit their doctor if they spot any changes in their breasts.
Surprisingly, two thirds of women aged 70 and over wrongly think women of all ages are equally likely to get breast cancer, when in fact a womans risk of breast cancer increases with age.
Around 13,500 women aged 70 and over are diagnosed with breast cancer in England each year, yet survival rates are lower in this age group compared to younger women. Lack of awareness of symptoms other than a lump, such as changes in the shape or size of the breast, is believed to be one of the reasons for this, which the campaign aims to change.
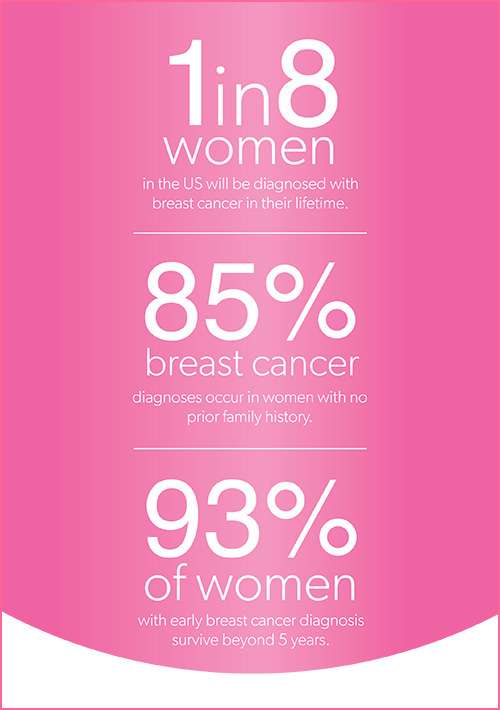
The earlier breast cancer is diagnosed, the higher the chance of survival more than 90% of all women diagnosed with the earliest stage survive for at least 5 years. This figure is around 15% for women diagnosed at a late stage.
Further Tests After Diagnosis
If the biopsy results show there are breast cancer cells, you will need further tests.
You may have the following tests to check your general health:
- Blood test
You have a blood test to check your general health and how well your kidneys and liver are working
- Chest x-ray
You will have a chest x-ray to check your lungs and heart.
You may have tests to find out more about the size of the cancer, or if it has spread anywhere else in the body :
- MRI scan
An MRI scan uses magnetism to build up detailed pictures of your body. It may be done to find out the size of the cancer and help decide on the operation you have.
- CT scan
A CT scan takes a series of x-rays, which build up a three-dimensional picture of the inside of the body.
- Bone scan
A bone scan shows up abnormal areas of bone. You have a small amount of a radioactive substance injected into a vein and wait for 2 to 3 hours to have the scan.
See also
Also Check: Treatment For Stage 4 Breast Cancer
How Can I Protect Myself From Breast Cancer
Follow these three steps for early detection:
- Get a mammogram. The American Cancer Society recommends having a baseline mammogram at age 35, and a screening mammogram every year after age 40. Mammograms are an important part of your health history. Recently, the US Preventive Services Task Force came out with new recommendations regarding when and how often one should have mammograms. These include starting at age 50 and having them every two years. We do not agree with this, but we are in agreement with the American Cancer Society and have not changed our guidelines, which recommend yearly mammograms starting at age 40.
- Examine your breasts each month after age 20. You will become familiar with the contours and feel of your breasts and will be more alert to changes.
- Have your breast examined by a healthcare provider at least once every three years after age 20, and every year after age 40. Clinical breast exams can detect lumps that may not be detected by mammogram.
Types Of Breast Cancer
There are several different types of breast cancer, which develop in different parts of the breast.
Breast cancer is often divided into either:
- non-invasive breast cancer found in the ducts of the breast which has not spread into the breast tissue surrounding the ducts. Non-invasive breast cancer is usually found during a mammogram and rarely shows as a breast lump.
- invasive breast cancer where the cancer cells have spread through the lining of the ducts into the surrounding breast tissue. This is the most common type of breast cancer.
Other, less common types of breast cancer include:
- invasive lobular breast cancer
- inflammatory breast cancer
It’s possible for breast cancer to spread to other parts of the body, usually through the blood or the axillary lymph nodes. These are small lymphatic glands that filter bacteria and cells from the mammary gland.
If this happens, it’s known as secondary, or metastatic, breast cancer.
Read Also: Lymph Node Positive Breast Cancer
Can Cancer Form In Other Parts Of The Breast
Cancers can also form in other parts of the breast, but these types of cancer are less common. These can include:
- Angiosarcomas. This type of cancer begins in the cells that make up the lining of blood or lymph vessels. These cancers can start in breast tissue or breast skin. They are rare.
- Inflammatory breast cancer. This type of cancer is rare and different from other types of breast cancer. It is caused by obstructive cancer cells in the skins lymph vessels.
- Paget disease of the breast, also known as Paget disease of the nipple. This cancer affects the skin of the nipple and areola .
- Phyllodes tumors. These are rare, and most of these masses are not cancer. However, some are cancerous. These tumors begin in the breasts connective tissue, which is called the stroma.
Physical Activity And Weight
Regular physical activity at all ages reduces the risk of breast cancer. Being physically active for more than 30 minutes a day could reduce breast cancer risk by 20%.
Not being active enough may increase the risk of breast cancer. This risk increases with increased sedentary time, particularly with watching television.
Maintaining a healthy weight throughout life could reduce the risk of postmenopausal breast cancer by 50%. Postmenopausal women who are overweight or obese and achieve a healthy weight may decrease their risk of breast cancer by 50%.
Also Check: Breast Cancer Stage 3 Symptoms
How Is Breast Cancer Diagnosed
During your regular physical examination, your doctor will take a thorough personal and family medical history. He or she will also perform and/or order one or more of the following:
- Breast examination: During the breast exam, the doctor will carefully feel the lump and the tissue around it. Breast cancer usually feels different than benign lumps.
- Digital mammography: An X-ray test of the breast can give important information about a breast lump. This is an X-ray image of the breast and is digitally recorded into a computer rather than on a film. This is generally the standard of care .
- Ultrasonography: This test uses sound waves to detect the character of a breast lump whether it is a fluid-filled cyst or a solid mass . This may be performed along with the mammogram.
Based on the results of these tests, your doctor may or may not request a biopsy to get a sample of the breast mass cells or tissue. Biopsies are performed using surgery or needles.
After the sample is removed, it is sent to a lab for testing. A pathologist a doctor who specializes in diagnosing abnormal tissue changes views the sample under a microscope and looks for abnormal cell shapes or growth patterns. When cancer is present, the pathologist can tell what kind of cancer it is and whether it has spread beyond the ducts or lobules .
Global Breast Cancer Statistics
- Breast cancer is the most common cancer worldwide.
- In 2020, there were 2.3 million women diagnosed with breast cancer and 685,000 deaths globally with breast cancer surpassing lung cancer as the most commonly diagnosed cancer.
- As of the end of 2020, there were 7.8 million women alive who were diagnosed with breast cancer over the past five years.
Read Also: Stage 4 Breast Cancer Life Expectancy Without Treatment
Symptoms Of Breast Cancer
Breast cancer can have several symptoms, but the first noticeable symptom is usually a lump or area of thickened breast tissue.
Most breast lumps are not cancerous, but it’s always best to have them checked by a doctor.
You should also see a GP if you notice any of these symptoms:
- a change in the size or shape of one or both breasts
- discharge from either of your nipples, which may be streaked with blood
- a lump or swelling in either of your armpits
- dimpling on the skin of your breasts
- a rash on or around your nipple
- a change in the appearance of your nipple, such as becoming sunken into your breast
Breast pain is not usually a symptom of breast cancer.
Find out more about the symptoms of breast cancer.
Breast Carcinoma In Situ Incidence By Age

Breast carcinoma in situ incidence is related to age, with the highest incidence rates being in the 65 to 69 age group. In the UK in 2016-2018, on average each year around a tenth of new cases were in people aged 75 and over. This is a lower proportion of cases in older age groups compared with most cancers.
Age-specific incidence rates in females, rise steeply from around age 35-39, then decrease steeply from age 65-69 and decrease steadily from age 75-79. In males rates increase from age 35-39. The highest rates are in in the 65 to 69 age group for females and the 80 to 84 age group for males.
Incidence rates are significantly higher in females than males in a number of age groups. The gap is widest at age 45 to 49, when the age-specific incidence rate is 888 times higher in females than males.
Breast carcinoma in situ , Average Number of New Cases per Year and Age-Specific Incidence Rates per 100,000 Population, UK, 2016-2018
For breast carcinoma in situ, most cases are identified through the breast screening programme. Incidence peaks first when routine screening starts at age 50, with a brief drop shortly after which reflects the diagnosis of prevalent cases at first-time screening. Incidence then falls rapidly when routine screening ends at age 70.
Don’t Miss: Treatment For Malignant Neoplasm Of Breast
Trends In Breast Cancer Deaths
Breast cancer is the second leading cause of cancer death in women. The chance that a woman will die from breast cancer is about 1 in 39 .
Since 2007, breast cancer death rates have been steady in women younger than 50, but have continued to decrease in older women. From 2013 to 2018, the death rate went down by 1% per year.
These decreases are believed to be the result of finding breast cancer earlier through screening and increased awareness, as well as better treatments.
Latest Breast Cancer Data
Breast cancer is the most commonly occurring cancer in women and the most common cancer overall. There were more than 2.26 million new cases of breast cancer in women in 2020.
The 10 countries with the highest rates of breast cancer in women and the highest number of deaths from breast cancer in women in 2020 are shown in the tables below.
ASR = age-standardised rates. These are a summary measure of the rate of disease that a population would have if it had a standard age structure. Standardisation is necessary when comparing populations that differ with respect to age because age has a powerful influence on the risk of dying from cancer.
You May Like: Signs Of Stage 3 Breast Cancer
Fact : There Is A Breast Cancer Susceptibility Window Before The First Full Term Pregnancy
Breast cancer surgeon, Angela Lanfranchi, MD, in collaboration with the Breast Cancer Prevention Institute, has contributed to a much greater understanding of normal breast development, as well as the pathophysiological mechanisms that lead to breast cancer.
A distinctive feature of the female breast is that this organ is not fully developed at birth. There is, of course, breast enlargement in girls at puberty, and this tissue is primarily stromal, or support tissue. However, between puberty and the FFTP, there is a susceptibility windowa time when the breast is most susceptible to forming cancer . This susceptibility occurs because the breast is composed primarily of Type 1 and Type 2 lobules.
Under the microscope, Type 1 and Type 2 lobules appear as twigs of a tree. Type 3 and Type 4 appear more like a cluster of grapes. Type 1 lobules account for 85 percent of all breast cancers, and Type 2 account for 12 percent of these cancers. Type 1 and Type 2 lobules have a higher density of hormone receptors, making them more susceptible to hormone stimulation that can result in cancer mutations.
Statistics At A Glance: The Burden Of Cancer In The United States
Statistics at a Glance: The Burden of Cancer Worldwide
- Cancer is among the leading causes of death worldwide. In 2018, there were 18.1 million new cases and 9.5 million cancer-related deaths worldwide.
- Generally, cancer rates are highest in countries whose populations have the highest life expectancy, education level, and standard of living. But for some cancer types, such as cervical cancer, the reverse is true, and the incidence rate is highest in countries in which the population ranks low on these measures.
Source: International Agency for Research on Cancer
Recommended Reading: How Long Does Chemo Last For Breast Cancer
Incidence Rates And The Number Of New Cases
To know whether or not breast cancer rates are changing over time, you have to compare rates, rather than the number of new cases.
For example, lets compare the number of new cases of breast cancer in U.S. in 2009 to the number of new cases in 2016. In 2009, there were an estimated 192,370 new cases of breast cancer in U.S. women . In 2016, there were an estimated 246,660 new cases .
Although more breast cancer cases occurred in 2016 than in 2009, this doesnt mean the rate of breast cancer increased over this time period.
We expect the number of cases to increase over time because the population of the U.S. increases over time . The more people there are, the more cancers there will be.
Our population is also living longer . Since age increases the risk of breast cancer, we expect to have more breast cancers over time.
To know if breast cancer rates are changing over time, we look at incidence rates, rather than the number of new cases. The incidence rate shows the number of breast cancer cases in a set population size. Its usually written as the number of cases in a population of 100,000 people.
The breast cancer incidence rate among women in 2009 was 131 and the estimated breast cancer incidence rate in 2016 was also 131 . This means there were 131 breast cancer cases per 100,000 women in the U.S. population in both time periods.
So, although the number of breast cancer cases increased over time, breast cancer rates were fairly stable.