Genetic Testing For Hereditary Breast And Ovarian Cancer
Genetic testing is available for hereditary breast and ovarian cancer. Most breast and ovarian cancer is not caused by inherited mutations, so genetic testing will not help most women with a family health history of breast and ovarian cancer. Genetic testing will not identify the cause for some hereditary breast and ovarian cancers, because the genes affected in these cancers are not yet known.
Genetic counseling before genetic testing for hereditary breast and ovarian cancer is important to determine whether you and your family are likely enough to have a mutation that it is worth getting tested. Usually, genetic testing is recommended if you have:
- A strong family health history of breast and ovarian cancer
- A moderate family health history of breast and ovarian cancer and are of Ashkenazi Jewish or Eastern European ancestry
- A personal history of breast cancer and meet certain criteria
- A personal history of ovarian, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal cancer
- A known BRCA1, BRCA2, or other inherited mutation in your family
The BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes
Genetic counseling after genetic testing is important to help you understand your test results and decide the next steps for you and your family:
Genetic Counseling And Testing For Breast Cancer Risk
Some people inherit changes in certain genes that increase their risk of breast cancer . Genetic testing can look for mutations in some of these genes. While it can be helpful in some cases, not everyone needs to be tested, and each person should carefully consider the pros and cons of testing. Its very important to understand what genetic testing can and cant tell you before these tests are done.
Tests To Stage Breast Cancer
After youre diagnosed with breast cancer, the next step is identifying your stage. Knowing the stage is how your doctor determines the best course of treatment. Staging depends on the size and location of the tumor and whether it has spread outside your breast to nearby lymph nodes and other organs. The speed of growth and the likelihood that the growth will spread is another component of staging.
Cancer cells that spread to lymph nodes can travel to different parts of your body. During the staging process, your doctor may order a complete blood panel including, liver function and kidney function tests, and a mammogram of your other breast to check for signs of a tumor. A doctor may also test for breast cancer tumor markers, CA 27-29 and CA 15-3.
Your doctor may also use any of the following tests to determine the extent of your cancer and assist with diagnosis :
Don’t Miss: How Curable Is Breast Cancer
How To Get Brca Genetic Testing
Genetic counseling is recommended for those who are interested in being tested for breast cancer gene mutations. You can talk to a doctor about getting a referral to a genetic counselor, who can help determine whether genetic testing would make sense based on family history and risk factors. Since many genetic tests only look for one specific gene mutation, the counselor can often help determine which mutations to test for.
The genetic test itself simply involves taking a small sample of blood or saliva, which is sent to a lab for analysis. Results can take several weeks or months.
Genetic testing results are not always clear-cut:
- A test result can be positive, meaning that the patient does carry the gene mutation.
- A negative test result indicates that they do not have that particular known gene mutation. It does not, however, rule out the possibility of having mutations in other genes. It also does not rule out the possibility of developing breast cancer. Most breast cancer cases are not hereditary, so everyone should still have an early detection plan.
- Genetic test results can also be uncertain or ambiguous. An ambiguous test result means that a mutation has been found on the gene, but it is not yet known whether that particular mutation has any effect on the chances of developing breast cancer.
- Someone is either negative or positive. Over time, a person cannot go from being negative to being positive or vice versa for the specific gene mutations they were tested for.
Screening In The Age Of Covid19

BreastScreen Australia has implemented COVIDSafe measures.
There are also a few things you can do to help keep yourself and others safe, such as:
- practicing physical distancing
- attending your appointment alone where possible
- arriving no more than five minutes early
- practicing good hygiene, including hand washing
- keeping a distance of 1.5 metres from others where possible
- staying at home if unwell and rescheduling your appointment.
Currently capacity varies from state to state, so contact your local BreastScreen Australia service on 13 20 50 for more information.
Recommended Reading: Stage 3 Invasive Breast Cancer
Positron Emission Tomography Scan
For a PET scan, a slightly radioactive form of sugar is injected into the blood and collects mainly in cancer cells.
PET/CT scan: Often a PET scan is combined with a CT scan using a special machine that can do both at the same time. This lets the doctor compare areas of higher radioactivity on the PET scan with a more detailed picture on the CT scan.
Who Needs Hormone Receptor Testing
Hormone receptor testing is generally recommended for all breast cancers, including DCIS. If your doctor orders this test, you may be asked to discontinue taking any prescribed hormones for a period of time before the breast tissue sample is obtained. Usually, the sample comes from a biopsy, but the test may also be performed on tissue removed during a lumpectomy or mastectomy. It is standard of care however to obtain these types of pathology results on biopsy tissue.
You May Like: What Is Stage Three Cancer
How To Check For Breast Cancer
Doru Paul, MD, is triple board-certified in medical oncology, hematology, and internal medicine. He is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Weill Cornell Medical College and attending physician in the Department of Hematology and Oncology at the New York Presbyterian Weill Cornell Medical Center.
It’s important that every woman knows how to do a breast self-examination , as it can help in early detection of breast cancer, such as lumps, nipple changes, and more.
Being familiar with what is normal for you will make it easier to recognize any new developments. Furthermore, knowing what’s not normal for anyone can help prompt you to bring such issues to your doctor’s attention, should you notice them during your BSE.
This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing.
Screening Tests Can Have Harms
Not all breast cancers will cause death or illness in a woman’s lifetime, so they may not need to be found or treated.
Decisions about screening tests can be difficult. Not all screening tests are helpful and most have harms. Before having any screening test, you may want to discuss the test with your doctor. It is important to know the harms of the test and whether it has been proven to reduce the risk of dying fromcancer.
Recommended Reading: Cancer Stages 3
Your Genes Can Say A Lot About Your Riskbut They Dont Tell The Whole Story
While these gene mutations clearly play a critical role in breast cancer risk, its also important to know that only 5-10 percent of breast cancer cases are related to genetic history. Not having BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene mutations doesnt mean youre not at risk for breast cancer, and you still should talk with your health care professional about the right breast cancer screening for you.
Want to learn more about BRCA1 and BRCA2? Read this fact sheet from the National Cancer Institute. You can talk with your health care professional about whether this test makes sense for you.
For more information about breast cancer prevention and early detection, visit preventcancer.org/breast.
Molecular Breast Imaging Gives An Inside Look At Cancer Cell Activity
Researchers are also exploring the possibility of using molecular breast imaging to detect breast cancer. It may be used together with a mammogram or ultrasound for women who have dense breast tissue or are at higher risk of developing breast cancer.
This form of imaging works by injecting small amounts of radioactive material into the arm. Then, small cameras record the tracer for about 40 minutes to create images of each breast. Cancer cells absorb the tracer faster than regular cells, so areas that show the most tracer will appear highlighted in the image. This technology may help doctors get a better look at breast tissue to determine whether a biopsy is needed, which can help you avoid unneeded procedures.
Molecular breast imaging is a new technology and is not yet widely available. You can learn more from Mayo Clinic.
Read Also: How Do You Get Rid Of Breast Cancer
Why It Is Done
A BRCA gene test is done to find out if you have BRCA gene changes that increase your risk of breast and ovarian cancer.
The results of a BRCA gene test can help you find out how high your cancer risk is. If it is high, you might decide to take steps to lower your risk. There are several things you might do, such as:
- Have checkups and tests more often.
- Have surgery to remove your breasts.
- Have surgery to remove your ovaries.
- Take medicines that may help prevent breast cancer.
If you have a family member who has breast or ovarian cancer, you may want to ask that family member to have a gene test first. If your relative’s test finds a changed BRCA gene, you and other family members can then be tested for that specific gene change. But if your family member’s test is negative, it is not likely that you carry the gene change.
Questions To Ask The Doctor
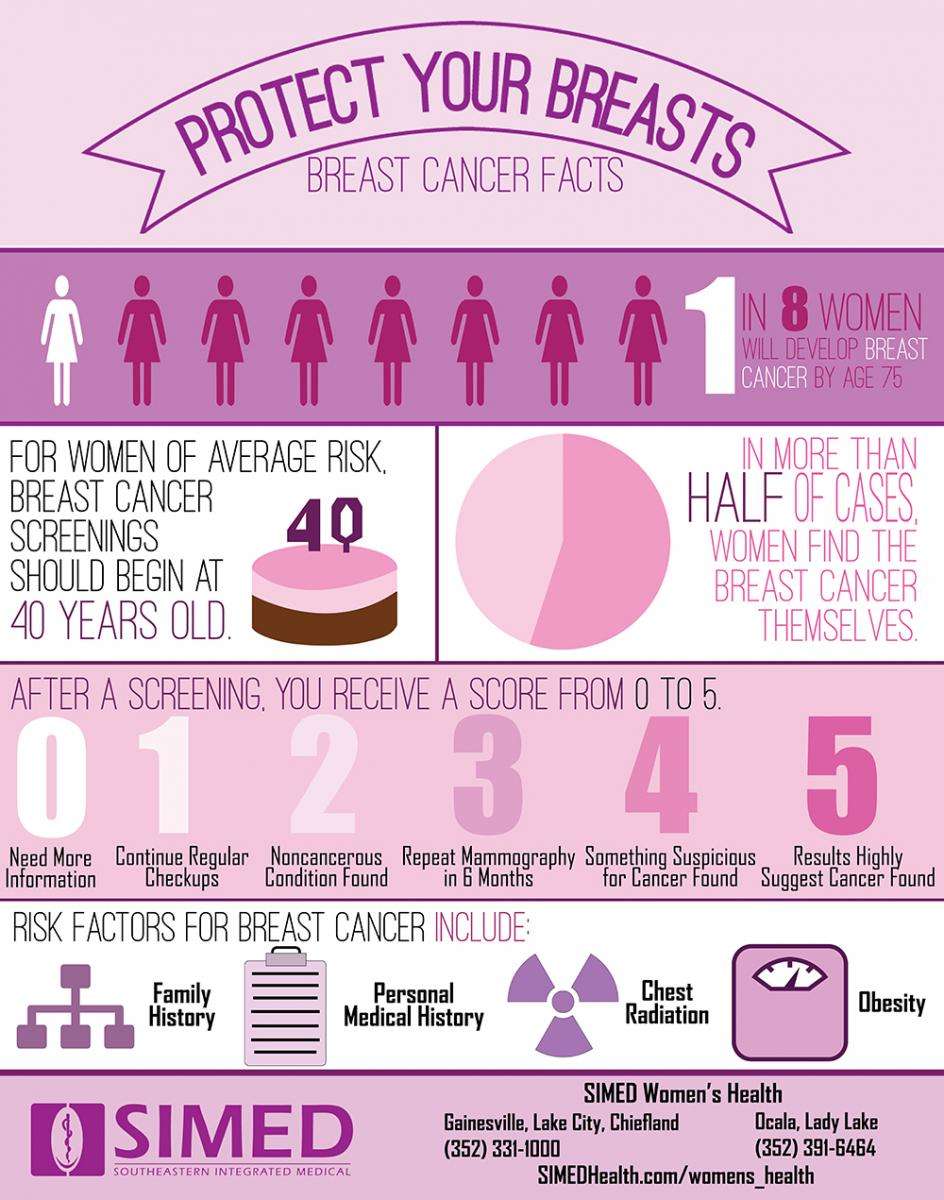
- Do you know the stage of the cancer?
- If not, how and when will you find out the stage of the cancer?
- Would you explain to me what the stage means in my case?
- Based on the stage of the cancer, how long do you think Ill live?
- Do you know if my cancer has any of these proteins: estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, or the HER2 protein?
- What does it mean if my cancer has any of these proteins?
- What will happen next?
There are many ways to treat breast cancer.
Surgery and radiation are used to treat cancer in a specific part of the body . They do not affect the rest of the body.
Chemotherapy, hormone treatment, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy drugs go through the whole body. They can reach cancer cells almost anywhere in the body.
Doctors often use more than one treatment for breast cancer. The treatment plan thats best for you will depend on:
- The cancer’s stage and grade
- If the cancer has specific proteins, like the HER2 protein or hormone receptors
- The chance that a type of treatment will cure the cancer or help in some way
- Your age
- Other health problems you have
- Your feelings about the treatment and the side effects that come with it
Don’t Miss: What Does Invasive Breast Cancer Mean
Testing For Brca And Other Gene Mutations
Some expert groups have developed guidelines for which women should consider genetic counseling and possibly testing for BRCA and other gene mutations. These guidelines can be complex, and not all doctors agree with them, but in general they include two main groups of people:
Women who have already been diagnosed with breast cancer: Most doctors agree that not all women with breast cancer need genetic counseling and testing. But counseling and testing is more likely to be helpful if:
- You were diagnosed with breast cancer at a younger age
- You have triple-negative breast cancer
- You have been diagnosed with a second breast cancer
- You are of Ashkenazi Jewish descent
- You have a family history of breast cancer , ovarian cancer, pancreatic cancer, or prostate cancer
Other groups of people: Genetic counseling and testing might also be recommended for other people who are at higher risk for inherited gene mutations, including:
- People with a known family history of a BRCA gene mutation
- Women diagnosed with ovarian cancer or pancreatic cancer, or men diagnosed with breast cancer, pancreatic cancer, or high-grade or metastatic prostate cancer
- People with a family history of breast cancer at a younger age, more than one family member with breast cancer, or breast cancer in a male family member
- People with a close family member with a history of ovarian cancer, pancreatic cancer, or metastatic prostate cancer
When To Get Screened
Breast cancer was expected to be the most common cancer diagnosed in Ontario women in 2018. Screening mammography can find breast cancers when they are small, less likely to have spread and more likely to be treated successfully. Your age and family medical history help determine when you should get screened:
- If you are age 50 to 74, the Ontario Breast Screening Program recommends that most women in your age group be screened every 2 years with mammography. Find your nearest OBSP site by calling 1-800-668-9304 or visiting Ontario Breast Screening Program locations.
- If you are age 30 to 69 and meet any of the following requirements, talk to your doctor about referral to the High Risk Ontario Breast Screening Program:
- You are known to have a gene mutation that increases your risk for breast cancer
- You are a first-degree relative of someone who has a gene mutation that increases their risk for breast cancer
- You have a personal or family history of breast or ovarian cancer
- You have had radiation therapy to the chest to treat another cancer or condition before age 30 and at least 8 years ago
For every 200 women screened in the Ontario Breast Screening Program, about 18 are referred for further tests and 1 will have breast cancer.
Also Check: What Does Her2 Negative Mean In Breast Cancer
What To Do If You Find A Lump
Dont panic if you think you feel a lump in your breast. Most women have some lumps or lumpy areas in their breasts all the time, and most breast lumps turn out to be benign . There are a number of possible causes of non-cancerous breast lumps, including normal hormonal changes, a benign breast condition, or an injury.
Dont hesitate to call your doctor if youve noticed a lump or other breast change that is new and worrisome. This is especially true for changes that last more than one full menstrual cycle or seem to get bigger or more prominent in some way. If you menstruate, you may want to wait until after your period to see if the lump or other breast change disappears on its own before calling your doctor. The best healthcare provider to call would be one who knows you and has done a breast exam on you before for example, your gynecologist, primary care doctor, or a nurse practitioner who works with your gynecologist or primary care doctor.
Make sure you get answers. Its important that your doctor gives you an explanation of the cause of the lump or other breast change and, if necessary, a plan for monitoring it or treating it. If youre not comfortable with the advice of the first doctor you see, dont hesitate to get a second opinion.
Where To Get Screened
Women ages 50 to 74 can call the nearest Ontario Breast Screening Program location to make an appointment .
Women in the North West and Hamilton Niagara Haldimand Brant regions may be eligible for screening in one of our mobile screening coaches.
If you think you may be at high risk for breast cancer, talk to your doctor about a referral to the High Risk Ontario Breast Screening Program based on family or medical history.
You May Like: 3a Breast Cancer
What To Expect During A Tumor Marker Test
Blood will be drawn from a vein in your arm. The entire process only takes a few minutes. Heres what you can expect:
What Happens During The Appointment
A breast screening appointment usually takes about 30 minutes. When you arrive, you will meet the receptionist or the person doing the mammogram . They will check your name, date of birth and address. The mammogram is done by female staff.
They will ask you questions about your health and whether you have had any breast problems. The mammographer will explain how the mammogram images are taken and can answer any questions you have. If you are happy with this, you will then have your mammogram.
The staff are trained to reassure and support you. If you feel it would help, you may be able to bring someone with you. Contact the screening unit before your appointment to arrange this. Men are not usually allowed in the screening area, but can wait in the waiting room.
Also Check: Hr Positive Breast Cancer Treatment