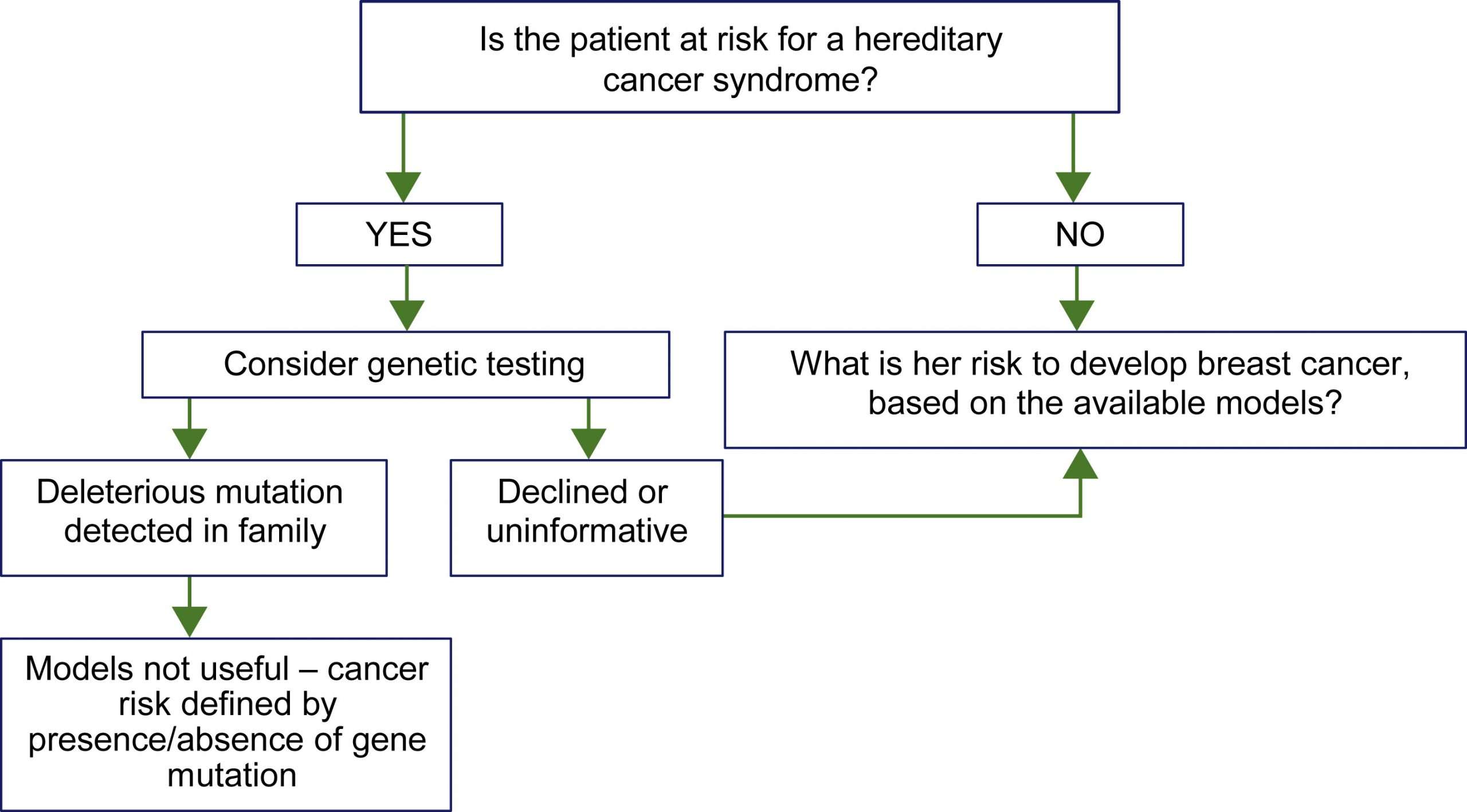
Clinical Considerations And Recommendations
How should individual breast cancer risk be assessed?
Health care providers periodically should assess breast cancer risk by reviewing the patients history. Breast cancer risk assessment is based on a combination of the various factors that can affect risk Box 1610111213. Initial assessment should elicit information about reproductive risk factors, results of prior biopsies, ionizing radiation exposure, and family history of cancer. Health care providers should identify cases of breast, ovarian, colon, prostate, pancreatic, and other types of germline mutation-associated cancer in first-degree, second-degree, and possibly third-degree relatives as well as the age of diagnosis. Women with a potentially increased risk of breast cancer based on initial history should have further risk assessment. Assessments can be conducted with one of the validated assessment tools available online, such as the Gail, BRCAPRO, Breast and Ovarian Analysis of Disease Incidence and Carrier Estimation Algorithm, International Breast Cancer Intervention Studies , or the Claus model 34.
Is screening breast self-examination recommended in women at average risk of breast cancer, and what should women do if they notice a change in one of their breasts?
Should practitioners perform routine screening clinical breast examinations in average-risk women?
When should screening mammography begin in average-risk women?
How frequently should screening mammography be performed in average-risk women?
The Importance Of Using Breast Cancer Risk Assessment Tools
One of the most prominent health risks today is breast cancer, specifically for women. The development and use of these tools are a great stride toward helping predict the likelihood of developing cancer throughout a womans lifetime. Both tools are insightful with their details but used together they can help provide more insight into risk factors and help the individual understand the importance of regular screenings. Using these models to predict risk, combined with close supervision of an OBGYN or specialist, cancer can be detected earlier, which gives the woman a better chance of fighting it successfully.
References
What Can I Do
Be proactive. Increasing your awareness and knowledge may help reduce your risk of developing breast cancer. Take action on your lifestyle risk factors. Know your body, watch for changes, and contact your health care provider with any questions or concerns about breast health and breast cancer prevention, early detection and screening.
Don’t Miss: What Is Estrogen Positive Breast Cancer
Risks For Breast Cancer
A risk factor is something that increases the risk of developing cancer. It could be a behaviour, substance or condition. Most cancers are the result of many risk factors. But sometimes breast cancer develops in women who dont have any of the risk factors described below.
Most breast cancers occur in women. The main reason women develop breast cancer is because their breast cells are exposed to the female hormones estrogen and progesterone. These hormones, especially estrogen, are linked with breast cancer and encourage the growth of some breast cancers.
Breast cancer is more common in high-income, developed countries such as Canada, the United States and some European countries. The risk of developing breast cancer increases with age. Breast cancer mostly occurs in women between 50 and 69 years of age.
What Is A Risk Assessment

The Breast Cancer Risk Assessment will help you understand your individual risk for developing breast cancer. It analyzes your unique risk factors using breast cancer risk models. These models look at factors such as family history of cancer, age of your first period, height and weight, lifestyle influences, and medical history to predict your risk of breast cancer.
At the time of your screening mammogram, the mammographer will ask you a series of questions to complete the risk model.
Read Also: Is Painful Lump In Breast Cancer
Patient Is At Higher Risk For Eobc
- Recommend an annual or semiannual mammogram and MRI. If the patient is under 30, start with an ultrasound. For patients with a history of thoracic radiation, start mammograms and MRIs 10 years after radiation.
- Refer to a genetic counselor for follow-up. Patients with known genetic risk factors may benefit from referral to a genetic counselor for additional follow-up.
What Does It Mean To Be At A High Risk For Breast Cancer
Being at a high risk for breast cancer means that you have an increased likelihood of developing breast cancer over the course of your lifetime. If you are classified as having a high risk for breast cancer, it doesnt mean that youll absolutely develop breast cancer sometime in the future. It means that youre at a high risk for the condition compared to the general population.
Don’t Miss: How To Pay For Breast Cancer Treatment
What Is The Tyrer
This risk assessment tool is designed to provide women with figures related to their chances of developing breast cancer within the next ten years and throughout their lifetime. It figures the likelihood of having some specific gene mutations known for causing cancer development. Its important to note that this risk assessment tool cant predict if the patient develops cancer, only the potential chance by giving a percentage figure based on personal details including family history and lifestyle. The figures given at the test completion are the percentages of risk of development over a lifetime and within the next 10 years.
The average percentage for risk is currently less than a 15% score for the Tyrer-Cuzik model. Intermediate risk is between 15% and 19%. Anyone who is classified over 20% is considered to be at high risk of developing breast cancer. There is an online version of this risk assessment tool that provides this information conveniently.
How To Interpret Your Estimated Breast Cancer Risk
The Breast Cancer Risk Assessment Tool was designed to be used by health care providers. So, if you use the tool on your own, it may be hard to understand the results and use the information to make decisions about your care.
If you have questions about your breast cancer risk based on the results of this tool, talk with your health care provider.
Read Also: What To Do When You Have Breast Cancer
Preventive Steps You Can Take
If youre at a high risk of breast cancer, there are preventive steps that you can take. Talk to your doctor about which ones may be appropriate for your individual situation:
- Medications: There are medications, such as tamoxifen and raloxifene, that can help to lower your risk of developing breast cancer.
- Surgery: A prophylactic mastectomy is surgery to remove one or both breasts in order to reduce the chances of breast cancer.
- Lifestyle changes: Various lifestyle changes may also help to lessen your breast cancer risk. These include:
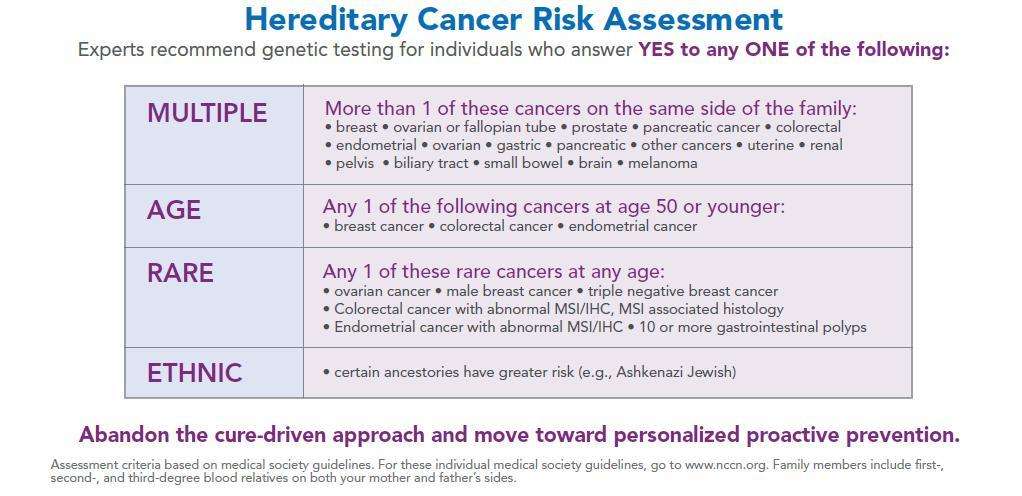
What Factors Put You At High Risk For Breast Cancer
Doctors consider several factors to determine if youre at a high risk of breast cancer. All of these factors, except for pregnancy history and radiation exposure, are things you cannot change:
- Family history: If youve had one or more close relatives, such as parents, siblings, or children with breast cancer, your risk increases.
- Genetics: Having inherited gene mutations that are associated with family cancer syndromes, particularly those in BRCA1 or BRCA2, significantly boost your risk of developing breast cancer.
- Age: The risk of breast cancer goes up as you get older.
- Personal history: A personal history of certain breast conditions raises your breast cancer risk. These include:
Remember that theres no standardized way to determine breast cancer risk. While breast cancer risk assessment tools are important in helping to estimate risk, they typically dont take all of the factors above into account.
Read Also: Can You Die From Stage 1 Breast Cancer
What Is The Gail Model
This model differs from the Tyrer-Cuzick breast cancer risk assessment tool in that it provides the outlook for developing invasive breast cancer over a specified time frame. This model was named for Dr. Mitchell Gail, the NCI Division of Breast Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics senior investigator.
This model takes into consideration various pieces of information about the individual, including basic life statistics, ancestry, cancer in the family, and more. This model has tested different ethnic groups and provides higher accuracy for white women than black or Pacific Islander women. This model measures BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations. However, despite the baritone for accuracy among different ethnic groups, this model is thought to be highly accurate in contrast to other models with a tendency to underestimate breast cancer risk.
Q3 What Does It Mean To Have Dense Breast Tissue And Why Does It Matter For My Tyrer
Breast cancer research and advances in risk assessment have shown that having dense breasts is a contributing factor in determining a womans risk of breast cancer. Dense breast tissue refers to the appearance of breast tissue on a mammogram and the makeup of supportive and fatty tissue in the breast. The more fatty tissue, the less dense the breast is. Dense breast are common and can be caused by simply being younger, having a lower body mass index, or taking hormone therapy for menopause researchers are still studying why some women have dense breast and other do not. Non-dense tissue appears dark and transparent, whereas dense breast tissue appears as solid white area on a mammogram the solid white area can make it hard for radiologists to accurately analyze the image with a mammogram, so your provider may recommend supplemental imaging, like a breast ultrasound or other recommendations, to ensure no cancers are missed. Having dense breast alone is not cause for concern, and you should speak with your doctor about your breast density and how it affects your risk status.
Also Check: What Are The Early Signs And Symptoms Of Breast Cancer
The Risk Assessment Appointment
Try to find out as much about your family history as you can from other relatives before your appointment.
You may be asked to complete a questionnaire about your family history before being offered an appointment or you may be asked for this information at your appointment.
The nurse or genetic specialist looking at your family history will understand if you cannot find all the relevant information.
Breast Cancer Risk Assessment & Care Plan
At The Breast Center, every patient completes a personal and family history to determine if she could be at higher risk than average for developing breast cancer.
Most cancers happen by chance and are not passed down in families. However, families with more than one breast cancer or breast cancer at a young age may be at higher risk. Some families with high risk for breast cancer also have an increased risk of developing ovarian and other cancers. The good news is that there may be options for reducing the risk of breast and ovarian cancer.
If your history indicates that you may be at risk, the radiologist and/or technologist may recommend that you schedule a Risk Assessment Consultation with a specially trained nurse.
Watch this video from Dr. Danna Grear to learn more:
Recommended Reading: Where Do You Get Breast Cancer Lumps
Personal History Of Thoracic Radiation
Ionizing radiation is a recognized risk factor for development of BC this has been observed in the past in people exposed to atomic explosions such as Hiroshima or Nagasaki as well as in patients exposed to radiation treatments for diseases such as Hodgkin disease., Risk is inversely associated with age at radiation exposure and increased in women exposed to radiation before age 20 years compared with patients without a history of exposure. Personal risk in these patients has been shown to be as high as 56.7-fold greater than in the general population.,
Mantle radiation therapy is a form of extended field radiation and refers to radiation therapy that is administered to the mantle field that encompasses lymph nodes in the neck, chest, mediastinum, and axillary regions with the breast receiving about 3% to 15% of the administered dose.
Most studies demonstrate increased BC risk 10 to 15 years following radiation treatment with development of secondary BC being rare within 10 years of treatment., Current guidelines recommend that patients who underwent thoracic radiation treatment between the ages of 10 and 30 begin annual screening MRI in addition to mammogram beginning 8 to 10 years after undergoing radiation treatment.,,
Differences In The Models
In instances of predicting risk in women who have a higher familial cancer history, the Tyrer-Cuzick is likely the most appropriate choice. This is because the Gail model has a tendency to underestimate risk of developing breast cancer in women with familial history of cancer. The findings of both models show a significant risk increase for individuals who are obese in any age group. For example, the risk rises from 0.8% for the 35-39 age group to 1.5% for 65-69 years. However, the Tyrer-Cuzick model presented the highest degree of accuracy for potentially developing breast cancer.
You May Like: How I Knew I Had Inflammatory Breast Cancer
Reproductive History Estrogen Is The Main Hormone Associated With Breast Cancer Estrogen Affects The Growth Of Breast Cells Experts Believe That It Plays An Important Role In The Growth Of Breast Cancer Cells As Well The Type Of Exposure And How Long Cells Are Exposed To Estrogen Affects The Chances That Breast Cancer Will Develop
Early menarche
The start of menstruation is called menarche. Early menarche is when menstruation starts at an early age . Starting your period early means that your cells are exposed to estrogen and other hormones for a greater amount of time. This increases the risk of breast cancer.
Late menopause
Menopause occurs as the ovaries stop making hormones and the level of hormones in the body drops. This causes a woman to stop menstruating. If you enter menopause at a later age , it means that your cells are exposed to estrogen and other hormones for a greater amount of time. This increases the risk for breast cancer. Likewise, menopause at a younger age decreases the length of time breast tissue is exposed to estrogen and other hormones. Early menopause is linked with a lower risk of breast cancer.
Late pregnancy or no pregnancies
Pregnancy interrupts the exposure of breast cells to circulating estrogen. It also lowers the total number of menstrual cycles a woman has in her lifetime.
Women who have their first full-term pregnancy after the age of 30 have a slightly higher risk of breast cancer than women who have at least one full-term pregnancy at an earlier age. Becoming pregnant at an early age reduces breast cancer risk.
The more children a woman has, the greater the protection against breast cancer. Not becoming pregnant at all increases the risk for breast cancer.
General Considerations For Screening
The goal of screening for cancer is to detect preclinical disease in healthy, asymptomatic patients to prevent adverse outcomes, improve survival, and avoid the need for more intensive treatments. Screening tests have both benefits and adverse consequences .
Breast self-examination, breast self-awareness, clinical breast examination, and mammography all have been used alone or in combination to screen for breast cancer. In general, more intensive screening detects more disease. Screening intensity can be increased by combining multiple screening methods, extending screening over a wider age range, or repeating the screening test more frequently. However, more frequent use of the same screening test typically is associated with diminishing returns and an increased rate of screening-related harms. Determining the appropriate combination of screening methods, the age to start screening, the age to stop screening, and how frequently to repeat the screening tests require finding the appropriate balance of benefits and harms. Determining this balance can be difficult because some issues, particularly the importance of harms, are subjective and valued differently from patient to patient. This balance can depend on other factors, particularly the characteristics of the screening tests in different populations and at different ages.
Also Check: Can You See Breast Cancer
Likely To Be At Increased Risk
compared with the general population for breast and ovarian cancer.
You did not know if you are of Ashkenazi Jewish ancestry. Talk to your family if you think you are of Ashkenazi Jewish ancestry. People of Ashkenazi Jewish ancestry have a 1 in 40 chance of carrying a BRCA mutation.
You have and 5 instances of breast cancer on your mother’s side.
We know this isnt the result you were hoping for, but knowledge of your family history and cancer risk is powerful. Youre in control of your healthcare.
Waiting For An Assessment
Being referred to a family history clinic for assessment can be a worrying time.
Its natural to feel anxious when youre waiting for a risk assessment.
Youll probably have your own way of managing your anxiety during this time of uncertainty, such as keeping busy or talking to family and friends.
If you would like to talk to someone about any concerns, you can call our free Helpline on 0808 800 6000.
Also Check: What Is The Worst Stage Of Breast Cancer
Talking With Your Health Care Provider About Your Risk Of Breast Cancer
If you have questions about your risk of breast cancer, talk with your doctor, nurse or other health care provider.
Your family health history plays a role in your breast cancer risk. Before you meet with your health care provider, its helpful to collect information about your family health history.
Information on any cancers diagnosed in both the women and the men in your family will be helpful in assessing your breast cancer risk.
If you are considering genetic testing to learn if a family history of cancer is due to an inherited gene mutation related to cancer risk, talk with your health care provider or a genetic counselor. They can help you decide if genetic testing is right for you and your family.
Learn more about family history of breast cancer and breast cancer risk.
|
My Family Health History Tool |
| My Family Health History tool is a web-based tool that makes it easy for you to record and organize your family health history. It helps you gather information that will be useful as you talk with your family members, doctor or genetic counselor. |