What Will The Her2/neu Results Tell Me
There are four tests for HER2, and results of these may appear on your pathology report, which may take several weeks to come back.
The first one is the IHC test, which is short for ImmunoHistoChemistry. It looks at whether there is excess HER2 protein in the cancerous cells. A result of 0 or 1+ indicates there is no excess, 2+ is borderline, and 3+ means the cells test positive for HER2 protein overexpression.
The remaining three tests all examine if the cells contain too many copies of the HER2 gene. These tests include:
- The FISH test
- The SPoT-Light HER2 CISH test
- The Inform HER2 Dual ISH test
There are only two possible results for these three tests: positive, meaning HER2 gene amplification, or negative, indicating the number of HER2 genes is not excessive.
In the pathology report, breast cancers with HER2 protein overexpression and HER2 gene amplification are called HER2-positive. This type of cancer often grows faster, spreads to other areas more readily, and has a higher likelihood of recurring versus HER2-negative breast cancer.
Can Exercise Help Reduce My Risk Of Developing Breast Cancer
Exercise is a big part of a healthy lifestyle. It can also be a useful way to reduce your risk of developing breast cancer in your postmenopausal years. Women often gain weight and body fat during menopause. People with higher amounts of body fat can be at a higher risk of breast cancer. However, by reducing your body fat through exercise, you may be able to lower your risk of developing breast cancer.
The general recommendation for regular exercise is about 150 minutes each week. This would mean that you work out for about 30 minutes, five days each week. However, doubling the amount of weekly exercise to 300 minutes can greatly benefit postmenopausal women. The longer duration of exercise allows for you to burn more fat and improve your heart and lung function.
The type of exercise you do can vary the main goal is get your heart rate up as you exercise. Its recommended that your heart rate is raised about 65 to 75% of your maximum heart rate during exercise. You can figure out your maximum heart rate by subtracting your current age from 220. If you are 65, for example, your maximum heart rate is 155.
Aerobic exercise is a great way to improve your heart and lung function, as well as burn fat. Some aerobic exercises you can try include:
- Walking.
- Dancing.
- Hiking.
Remember, there are many benefits to working more exercise into your weekly routine. Some benefits of aerobic exercise can include:
Common Tests After Breast Cancer Diagnosis
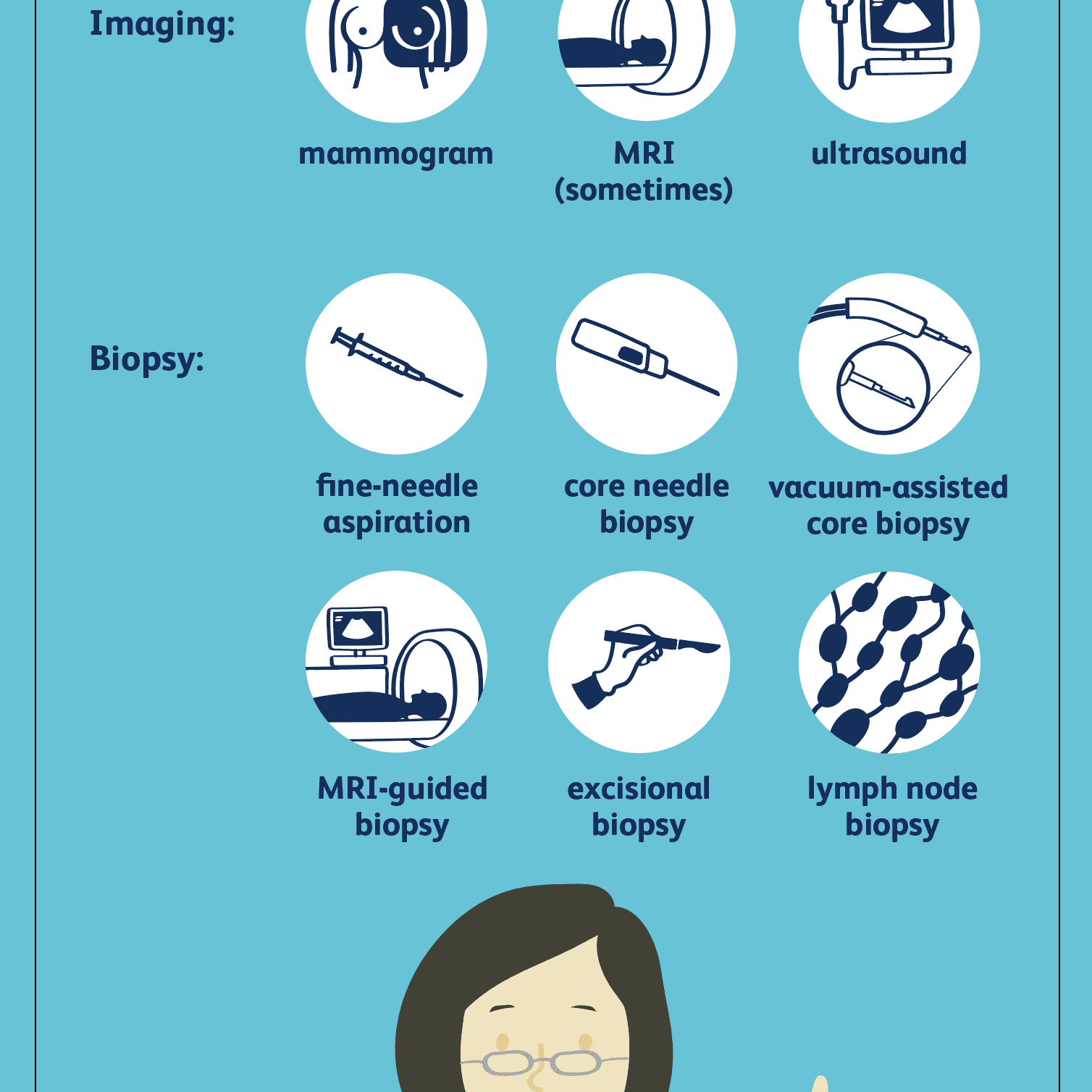
Once you have received a breast cancer diagnosis, you will likely undergo additional testing. This may include an MRI, mammogram or ultrasound of the other breast. Sentinel lymph node biopsy is also common. This relatively new technique allows a surgeon to sample your lymph nodes and determine whether breast cancer may have traveled there. In the procedure, blue dye is injected into the breast. After giving it time to travel to the lymph nodes, the surgeon removes only the lymph nodes in which the blue dye is found. These nodes will be sent to a pathologist for testing to see if cancer is present.
In addition, CT or CAT scans, PET scans and/or bone scans may be ordered to see if the cancer has spread to another part of the body. The most typical scans are:
Bone Scans
These scans reveal if cancer has spread to the bones. They look at the bones for hot spots that may reveal cancer. To conduct a bone scan, your healthcare provider injects dye, then waits a few hours for it to move through the bloodstream so it can be visible in the scan.
Chest X-Ray
A chest x-ray may reveal if breast cancer has spread to the lungs.
CT/CAT Scan
Liver Scan
A liver scan involves having a contrast dye injected into the vein. The dye will collect in areas where there is activity that could indicate cancer growth.
MRI
PET Scan
PET CT Scan
A combination of the PET and CT Scans, performed at the same time, can present a more detailed image of the presence or extent of cancer in the body.
Also Check: How Fast Does Triple Negative Cancer Grow
If The Biopsy Is Positive: More Testing
If the pathology report reveals cancer, the doctors will first want to determine what stage your breast cancer is and what grade the tumor is.
The type of tests a woman will undergo next depends on what the cancerous cells look like. Those tests include blood tests, additional biopsies, a bone scan, a chest X-ray, breast ultrasound, or other specialized imaging or chemical testing.
One common imaging test is computerized tomography, or a CT scan, that takes cross-sectional X-rays of the body. Another common imaging is positron emission tomography, or PET scans, that look at cell activity. A PET scan involves injecting a person with a tiny amount of sugar substance and radioactive material so cameras can observe highlighted areas in the breast on a computer screen.
How Much Do Tamoxifen And Raloxifene Lower The Risk Of Breast Cancer
Multiple studies have shown that both tamoxifen and raloxifene can reduce the risk of developing estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer in healthy postmenopausal women who are at high risk of developing the disease. Tamoxifen lowered the risk by 50 percent. Raloxifene lowered the risk by 38 percent. Overall, the combined results of these studies showed that taking tamoxifen or raloxifene daily for five years reduced the risk of developing breast cancer by at least one-third. In one trial directly comparing tamoxifen with raloxifene, raloxifene was found to be slightly less effective than tamoxifen for preventing breast cancer.
Both tamoxifen and raloxifene have been approved for use to reduce the risk of developing breast cancer in women at high risk of the disease. Tamoxifen is approved for use in both premenopausal women and postmenopausal women . Raloxifene is approved for use only in postmenopausal women.
Less common but more serious side effects of tamoxifen and raloxifene include blood clots to the lungs or legs. Other serious side effects of tamoxifen are an increased risk for cataracts and endometrial cancers. Other common, less serious shared side effects of tamoxifen and raloxifene include hot flashes, night sweats, and vaginal dryness.
Also Check: Malignant Neoplasm Of Breast Definition
The Patient Undergoes A Breast Biopsy
Different methods may be used to get a sample of breast tissue to submit to the pathologists for evaluation. These methods include skin punch biopsy, fine needle aspiration , core needle biopsy, and excisional biopsy. The decision of which method to use is influenced by the characteristics of the mass as well as the patient’s breast tissue.
Does A Benign Breast Condition Mean That I Have A Higher Risk Of Getting Breast Cancer
Benign breast conditions rarely increase your risk of breast cancer. Some women have biopsies that show a condition called hyperplasia . This condition increases your risk only slightly.
When the biopsy shows hyperplasia and abnormal cells, which is a condition called atypical hyperplasia, your risk of breast cancer increases somewhat more. Atypical hyperplasia occurs in about 5% of benign breast biopsies.
You May Like: How Long Is Breast Cancer Treatment
Biomarker Testing Is Performed On Cancers
One important aspect of the role of pathologists in the evaluation of breast cancer is biomarker testing, specifically the accurate assessment of:
- the estrogen receptor
- the progesterone receptor
- the HER-2 status of a patient’s breast cancer
Biomarkers can be prognostic, predictive, or both. Prognostic biomarkers are independent measures of prognosis such that the presence or absence of the biomarker is associated with a patient’s overall clinical outcome . Predictive biomarkers, in contrast, predict whether or not a patient will respond to a given therapy.
Stage Of Breast Cancer
When breast cancer is diagnosed, your doctors will give it a stage. The stage describes the size of the cancer and how far it has spread, and is used to predict the outlook.
Ductal carcinoma in situ is sometimes described as stage 0. Other stages of breast cancer describe invasive breast cancer and include:
- stage 1 the tumour measures less than 2cm and the lymph nodes in the armpit are not affected. There are no signs that the cancer has spread elsewhere in the body
- stage 2 the tumour measures 2 to 5cm, the lymph nodes in the armpit are affected, or both. There are no signs that the cancer has spread elsewhere in the body
- stage 3 the tumour measures 2 to 5cm and may be attached to structures in the breast, such as skin or surrounding tissues, and the lymph nodes in the armpit are affected. There are no signs that the cancer has spread elsewhere in the body
- stage 4 the tumour is of any size and the cancer has spread to other parts of the body
This is a simplified guide. Each stage is divided into further categories: A, B and C. If you’re not sure what stage you have, talk to your doctor.
Read Also: Symptoms Of Stage 2 Breast Cancer
How Is Breast Cancer Diagnosed
Magnetic resonance imaging may be used to diagnose breast cancer.
Doctors often use additional tests to find or diagnose breast cancer. They may refer women to a breast specialist or a surgeon. This does not mean that she has cancer or that she needs surgery. These doctors are experts in diagnosing breast problems.
- Breast ultrasound. A machine that uses sound waves to make pictures, called sonograms, of areas inside the breast.
- Diagnostic mammogram. If you have a problem in your breast, such as lumps, or if an area of the breast looks abnormal on a screening mammogram, doctors may have you get a diagnostic mammogram. This is a more detailed X-ray of the breast.
- Breast magnetic resonance imaging . A kind of body scan that uses a magnet linked to a computer. The MRI scan will make detailed pictures of areas inside the breast.
- Biopsy. This is a test that removes tissue or fluid from the breast to be looked at under a microscope and do more testing. There are different kinds of biopsies .
What If You Have Early
If you have early-stage breast cancer but no symptoms to suggest the cancer has spread, you should not get an imaging test to look for cancer in other places in your body. The chance that your cancer has spread is very small. Studies show that breast cancer spreads to the liver and bones in fewer than 6 out of 100 people. And this is usually in patients with stage III breast cancer.
Also Check: What Is Stage 3a Breast Cancer
Definitive Breast Cancer Diagnosis
Even if imaging tests show an abnormality or are suspicious for breast cancer, definitive diagnosis requires obtaining a tissue sample for analysis. The technique of obtaining a sample is called a biopsy. A biopsy may be taken of a small area of the abnormality , or the entire abnormal area may be removed at the time of biopsy . Biopsy allows the pathologist to determine if cancer is present and, if so, what type of cancer. Biopsy also provides a tissue sample for further tests that are done to help determine the best type of treatment.
How Is Breast Cancer Treated

If the tests find cancer, you and your doctor will develop a treatment plan to eradicate the breast cancer, to reduce the chance of cancer returning in the breast, as well as to reduce the chance of the cancer traveling to a location outside of the breast. Treatment generally follows within a few weeks after the diagnosis.
The type of treatment recommended will depend on the size and location of the tumor in the breast, the results of lab tests done on the cancer cells, and the stage, or extent, of the disease. Your doctor will usually consider your age and general health as well as your feelings about the treatment options.
Breast cancer treatments are local or systemic. Local treatments are used to remove, destroy, or control the cancer cells in a specific area, such as the breast. Surgery and radiation treatment are local treatments. Systemic treatments are used to destroy or control cancer cells all over the body. Chemotherapy and hormone therapy are systemic treatments. A patient may have just one form of treatment or a combination, depending on her individual diagnosis.
Also Check: Breast Cancer In The Duct Glands
What Tests Are Used To Diagnose Breast Cancer
A breast cancer diagnosis usually begins with an imaging examination. You doctor may order a diagnostic mammogram, ultrasound or MRI. If your imaging results are abnormal, your doctor may then order a biopsy of the breast to obtain a small sample of tissue that will provide a definitive diagnosis. Should you be diagnosed with breast cancer, your doctor may order additional tests. These results can help identify cancer treatment options that will be most effective for you.
What Happens After The Local Breast Cancer Treatment
Following local breast cancer treatment, the treatment team will determine the likelihood that the cancer will recur outside the breast. This team usually includes a medical oncologist, a specialist trained in using medicines to treat breast cancer. The medical oncologist, who works with the surgeon, may advise the use of the drugs like tamoxifen or anastrozole or possibly chemotherapy. These treatments are used in addition to, but not in place of, local breast cancer treatment with surgery and/or radiation therapy.
After treatment for breast cancer, it is especially important for a woman to continue to do a monthly breast examination. Regular examinations will help you detect local recurrences. Early signs of recurrence can be noted in the incision area itself, the opposite breast, the axilla , or supraclavicular region .
Maintaining your follow-up schedule with your physician is also necessary so problems can be detected when treatment can be most effective. Your health care provider will also be able to answer any questions you may have about breast self-examination after the following procedures.
Also Check: Grade 1 Breast Cancer Treatment
Stages Of Breast Cancer
Banner MD Anderson knows each person is unique, and so is their breast cancer. While breast cancer staging helps doctors and patients understand the diseases progression, individual treatment options and results vary. Doctors use the results of your diagnostic tests to determine breast cancer stage, treatment options and prognosis.
- Stage 0: Cancer is contained within the breast milk ducts
- Stage I : Cancer is small and has started to spread to other breast tissue
- Stage II : Cancer has grown and/or spread to nearby tissue and/or up to three lymph nodes
- Stage III : Cancer has grown and/or spread to nearby tissue, chest wall, and/or four to nine lymph nodes
- Stage IV : Cancer has spread far away from the breast and lymph nodes to other parts of the body like the bones, lungs, liver and brain
Lobular Carcinoma In Situ
Lobular carcinoma in situ arises from the terminal duct apparatus and shows a rather diffuse distribution throughout the breast, which explains its presentation as a nonpalpable mass in most cases . Over the past 25 years, the incidence of LCIS has doubled, currently standing at 2.8 per 100,000 women. The peak incidence is in women aged 40-50 years.
Read Also: How Long Does Breast Cancer Take To Kill
Diagnosis Of Breast Cancer
Diagnosis is the process of finding out the cause of a health problem. Diagnosing breast cancer usually begins when you find a lump in your breast or a screening mammography suggests a problem with the breast. Your doctor will ask you about any symptoms you have and do a physical exam. Based on this information, your doctor may refer you to a specialist or order tests to check for breast cancer or other health problems.
The process of diagnosis may seem long and frustrating. Its normal to worry, but try to remember that other health conditions can cause similar symptoms as breast cancer. Its important for the healthcare team to rule out other reasons for a health problem before making a diagnosis of breast cancer.
The following tests are usually used to rule out or diagnose breast cancer. Many of the same tests used to diagnose cancer are used to find out the stage . Your doctor may also order other tests to check your general health and to help plan your treatment.
Mammogram And Breast Ultrasound
If you have symptoms and have been referred to a specialist breast unit by a GP, you’ll probably be invited to have a mammogram, which is an X-ray of your breasts. You may also need an ultrasound scan.
If cancer was detected through the NHS Breast Screening Programme, you may need another mammogram or ultrasound scan.
Your doctor may suggest that you only have a breast ultrasound scan if you’re under the age of 35. This is because younger women have denser breasts, which means a mammogram is not as effective as ultrasound in detecting cancer.
Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to produce an image of the inside of your breasts, showing any lumps or abnormalities.
Your breast specialist may also suggest a breast ultrasound if they need to know whether a lump in your breast is solid or contains liquid.
Find out more about breast screening.
You May Like: Stage Three Cancer
Breast Cancer Lab Tests Identify Risk Diagnose And Guide Treatment
A variety of breast cancer tests can help determine a persons genetic risk for the disease as well as diagnose breast cancer in the early stages. Lab tests for breast cancer may also be used to:
- Analyze characteristics of the breast cancer to determine appropriate treatment options
- Determine whether breast cancer has metastasized
- Monitor the effectiveness of breast cancer treatments and identify any recurrence of breast cancer
Lab tests for breast cancer include blood testing and biopsy.