Human Antimicrobial Protein Hcap18/ll
Human cathelicidin antimicrobial protein, hCAP18, and its C-terminal peptide LL-37 is a multifunctional protein. In addition to being important in antimicrobial defense, it induces chemotaxis, stimulates an giogenesis and promotes tissue repair. We previously showed that human breast cancer cells express high amounts of hCAP18, and hypothesised that hCAP18/LL-37 may be involved in tumor progression.
Prognostic Impact Of Tumor
It has been previously reported that tumor-specific expression of the rate-limiting enzyme, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutharyl-coenzyme A reductase , in the mevalonate pathway is associated with more favorable tumor parameters in breast cancer. In the present study, it is examined the prognostic value of HMG–CoAR expression in a large cohort of primary breast cancer patients with long-term follow up.
General Breast Cancer Terms
Here are some of the key words used to describe breast cancer.
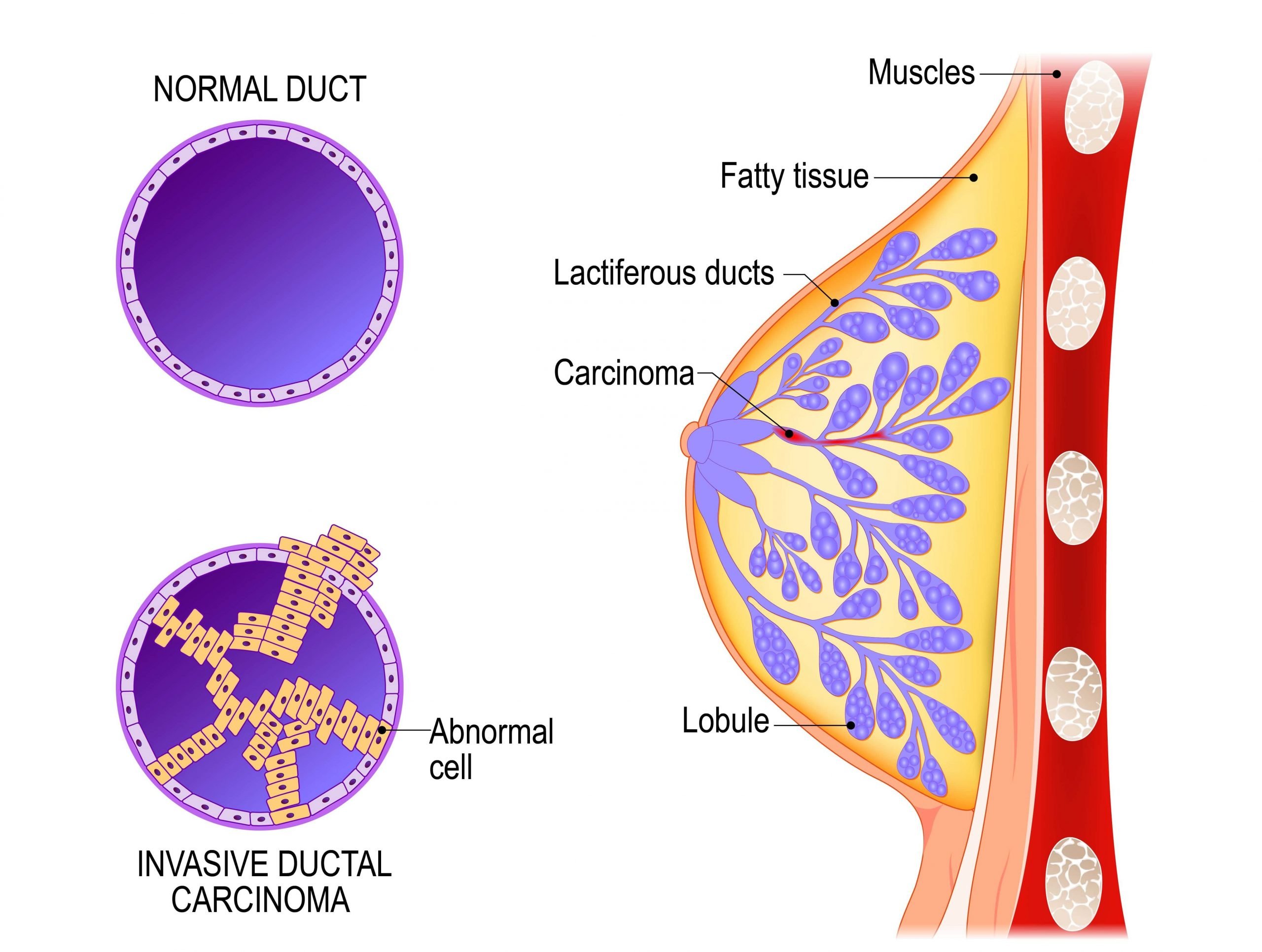
Carcinoma
This term describes a cancer that begins in the lining layer of organs such as the breast. Nearly all breast cancers are carcinomas .
Adenocarcinoma
An adenocarcinoma is a type of carcinoma that starts in glandular tissue . The ducts and lobules of the breast are glandular tissue , so cancers starting in these areas are sometimes called adenocarcinomas.
Carcinoma in situ
This is an early stage of cancer, when it is confined to the layer of cells where it began. In breast cancer, in situ means that the abnormal cells remain confined to ducts . These cells have not grown into deeper tissues in the breast or spread to other organs in the body. Ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast is sometimes referred to as non-invasive or pre-invasive breast cancer because it might develop into an invasive breast cancer if left untreated.
When cancer cells are confined to the lobules it is called lobular carcinoma in situ . This is not actually a true pre-invasive cancer because it does not turn into an invasive cancer if left untreated. It is linked to an increased risk of invasive cancer in both breasts. LCIS is rarely, if ever seen in men.
Invasive carcinoma
An invasive cancer is one that has already grown beyond the layer of cells where it started . Most breast cancers are invasive carcinomas, either invasive ductal carcinoma or invasive lobular carcinoma.
Sarcoma
Read Also: How To Treat Stage 0 Breast Cancer
Types Based On Where Cancer Starts Or Spreads
One of the ways doctors describe breast cancer is based on where in your body it starts or spreads.
Carcinoma and Adenocarcinoma. Carcinomas start in the tissues that line your breasts and other organs. Most breast cancers are carcinomas.
Breast cancers are often a type of carcinoma called an adenocarcinoma. These cancers start in the cells lining the milk ducts or the glands that produce milk .
Ductal Carcinoma. Ductal carcinoma is cancer of the cells that line the milk ducts in your breast.
Ductal carcinoma in situ is the earliest form of ductal carcinoma. “In situ” means it’s only in the milk ducts, and isn’t likely to spread to other parts of your body. About 1 in 5 people who are newly diagnosed with breast cancer have DCIS. This type is very curable.
Invasive ductal carcinoma is the most common type of breast cancer, affecting about 80% of people who are diagnosed. “Invasive” means the cancer is able to spread outside of the milk duct where it started.
There are several subtypes of invasive ductal carcinoma:
You might also hear about lobular carcinoma in situ . But LCIS isn’t really cancer, and won’t spread outside of the lobule. Doctors usually find it when they do a breast biopsy.
Phyllodes Tumor of the Breast. These rare tumors grow in the breast’s connective tissue. They’re more common in women who have an inherited condition called Li-Fraumeni syndrome. Only 1 in 4 phyllodes tumors are cancer. The rest are noncancerous .
Medullary Carcinoma Of The Breast

Medullary carcinoma of the breast is another rare subtype of invasive ductal carcinoma . It accounts for around less than 5 percent of all breast cancer cases.
The tumor is typically a soft, fleshy mass rather than a lump in the breast tissue. The mass most often develops in the middle of the breast and is most often found in women with the BRCA1 mutation.
Although these cancer cells often have an aggressive appearance, they dont grow quickly and usually dont spread to the lymph nodes. This makes it easier to treat than some other types of breast cancer.
- the patients preference
Possible treatment options for breast cancer include:
You May Like: How Effective Is Chemotherapy For Breast Cancer
What Are The Stages Of Breast Cancer
There are two different staging systems for breast cancer. One is called anatomic staging while the other is prognostic staging. The anatomic staging is defined by the areas of the body where the breast cancer is found and helps to define appropriate treatment. The prognostic staging helps medical professionals communicate how likely a patient is to be cured of the cancer assuming that all appropriate treatment is given.
The anatomic staging system is as follows:
Stage 0 breast disease is when the disease is localized to the milk ducts .
Stage I breast cancer is smaller than 2 cm across and hasn’t spread anywhere including no involvement in the lymph nodes.
Stage II breast cancer is one of the following:
- The tumor is less than 2 cm across but has spread to the underarm lymph nodes .
- The tumor is between 2 and 5 cm .
- The tumor is larger than 5 cm and has not spread to the lymph nodes under the arm .
Stage III breast cancer is also called “locally advanced breast cancer.” The tumor is any size with cancerous lymph nodes that adhere to one another or to surrounding tissue . Stage IIIB breast cancer is a tumor of any size that has spread to the skin, chest wall, or internal mammary lymph nodes .
Stage IV breast cancer is defined as a tumor, regardless of size, that has spread to areas away from the breast, such as bones, lungs, liver or brain.
Treatments For Breast Cancer
If you have breast cancer, your healthcare team will create a treatment plan just for you. It will be based on your health and specific information about the cancer. When deciding which treatments to offer for ductal carcinoma and lobular carcinoma, your healthcare team will consider:
- the stage
- if you have reached menopause
- the hormone receptor status of the cancer
- the HER2 status of the cancer
- the risk that the cancer will come back, or recur
- your overall health
Also Check: What Is The Name Of The Breast Cancer Gene
What Is Metaplastic Carcinoma
Also known as metaplastic breast cancer, metaplastic carcinoma is a rare type of invasive breast cancer with a unique characteristic: It contains a mix of two or more types of breast cancer cells, usually carcinoma combined with sarcoma. Metaplastic means that one form is turning into another. Various leading-edge techniques are used to analyze the exact genetics and biology of these confused cancers to find out if the tumor is more similar to carcinoma or sarcoma, since these two types of cancer have very different treatments.
What Is The Prognosis Of Patients With Inflammatory Breast Cancer
The prognosis, or likely outcome, for a patient diagnosed with cancer is often viewed as the chance that the cancer will be treated successfully and that the patient will recover completely. Many factors can influence a cancer patients prognosis, including the type and location of the cancer, the stage of the disease, the patients age and overall general health, and the extent to which the patients disease responds to treatment.
Because inflammatory breast cancer usually develops quickly and spreads aggressively to other parts of the body, women diagnosed with this disease, in general, do not survive as long as women diagnosed with other types of breast cancer.
It is important to keep in mind, however, that survival statistics are based on large numbers of patients and that an individual womans prognosis could be better or worse, depending on her tumor characteristics and medical history. Women who have inflammatory breast cancer are encouraged to talk with their doctor about their prognosis, given their particular situation.
Ongoing research, especially at the molecular level, will increase our understanding of how inflammatory breast cancer begins and progresses. This knowledge should enable the development of new treatments and more accurate prognoses for women diagnosed with this disease. It is important, therefore, that women who are diagnosed with inflammatory breast cancer talk with their doctor about the option of participating in a clinical trial.
You May Like: When Can You Get Breast Cancer Age
Symptoms Of Breast Cancer
Breast cancer can have several symptoms, but the first noticeable symptom is usually a lump or area of thickened breast tissue.
Most breast lumps are not cancerous, but it’s always best to have them checked by a doctor.
You should also see a GP if you notice any of these symptoms:
- a change in the size or shape of one or both breasts
- discharge from either of your nipples, which may be streaked with blood
- a lump or swelling in either of your armpits
- dimpling on the skin of your breasts
- a rash on or around your nipple
- a change in the appearance of your nipple, such as becoming sunken into your breast
Breast pain is not usually a symptom of breast cancer.
Find out more about the symptoms of breast cancer.
Breast Cancer Symptoms You Can See
LUBBOCK, Texas – We all know October is supposed to be a scary month. Its more scary for the one in 8 women in this country who will be diagnosed with breast cancer this year. October is Breast Cancer Awareness Month.
While we tend to think of it as a womans problem, more than 2,600 men will face the same diagnosis this year.
In all, more than 40,000 people die from breast cancer annually.
Dr. Catherine Jones, an Oncologist and Texas Tech Physician, says mammograms are a good screening tool, but its up to all of us to know our bodies and recognize when something looks or feels different.
She says, If they do develop symptoms, commonly, theyll have changes in the skin of the breast, maybe dimpling of the skin, retraction. They can have changes in the nipple with retraction or dimpling of the nipple, a palpable lump in the breast. So, people can sometimes feel a mass or have a lump in their armpit, and see changes in the appearance of the skin can look red, hot, swollen. The breast can feel heavy and rarely, but not impossibly, women can complain of pain in the breast.
Dr. Jones says only 5 percent of breast cancers are inherited.
But in that case, she says men should know that if the BRCCA gene has been detected in women in the family, it means the men in that family are also at risk for certain cancers.
Most Read
Recommended Reading: How I Found Out I Had Breast Cancer
Types Of Breast Cancer In Men
Breast cancer can be separated into several types based on the way the cancer cells look under the microscope. In some cases a single breast tumor can be a combination of these types or be a mixture of invasive and in situ cancer. And in some rarer types of breast cancer, the cancer cells may not form a tumor at all.
Breast cancer can also be classified based on proteins on or in the cancer cells, into groups like hormone receptor-positive and triple-negative.
Ductal carcinoma in situ
Ductal carcinoma in situ is considered non-invasive or pre-invasive breast cancer. In DCIS , cells that lined the ducts have changed to look like cancer cells. The difference between DCIS and invasive cancer is that the cells have not spread through the walls of the ducts into the surrounding tissue of the breast . DCIS is considered a pre-cancer because some cases can go on to become invasive cancers. Right now, though, there is no good way to know for certain which cases will go on to become invasive cancers and which ones wont. DCIS accounts for about 1 in 10 cases of breast cancer in men. It is almost always curable with surgery.
Infiltrating ductal carcinoma
Infiltrating lobular carcinoma
This type of breast cancer starts in the breast lobules and grows into the fatty tissue of the breast. ILC is very rare in men, accounting for only about 2% of male breast cancers. This is because men do not usually have much lobular tissue.
Paget disease of the nipple
Inflammatory breast cancer
What Happens After The Local Breast Cancer Treatment
Following local breast cancer treatment, the treatment team will determine the likelihood that the cancer will recur outside the breast. This team usually includes a medical oncologist, a specialist trained in using medicines to treat breast cancer. The medical oncologist, who works with the surgeon, may advise the use of the drugs like tamoxifen or anastrozole or possibly chemotherapy. These treatments are used in addition to, but not in place of, local breast cancer treatment with surgery and/or radiation therapy.
After treatment for breast cancer, it is especially important for a woman to continue to do a monthly breast examination. Regular examinations will help you detect local recurrences. Early signs of recurrence can be noted in the incision area itself, the opposite breast, the axilla , or supraclavicular region .
Maintaining your follow-up schedule with your physician is also necessary so problems can be detected when treatment can be most effective. Your health care provider will also be able to answer any questions you may have about breast self-examination after the following procedures.
Also Check: What To Expect From Radiation For Breast Cancer
How Do Tamoxifen Raloxifene Anastrozole And Exemestane Reduce The Risk Of Breast Cancer
If you are at increased risk for developing breast cancer, four medications tamoxifen , raloxifene , anastrozole , and exemestane may help reduce your risk of developing this disease. These medications act only to reduce the risk of a specific type of breast cancer called estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. This type of breast cancer accounts for about two-thirds of all breast cancers.
Tamoxifen and raloxifene are in a class of drugs called selective estrogen receptor modulators . These drugs work by blocking the effects of estrogen in breast tissue by attaching to estrogen receptors in breast cells. Because SERMs bind to receptors, estrogen is blocked from binding. Estrogen is the fuel that makes most breast cancer cells grow. Blocking estrogen prevents estrogen from triggering the development of estrogen-receptor-positive breast cancer.
Anastrozole and exemestane are in a class of drugs called aromatase inhibitors . These drugs work by blocking the production of estrogen. Aromatase inhibitors do this by blocking the activity of an enzyme called aromatase, which is needed to make estrogen.
Types Of Invasive Breast Cancer
Figure 4.6 lists the types of invasive breast cancer.
- Invasive ductal carcinoma is the most common type of breast cancer . It may also be called infiltrating ductal carcinoma, invasive carcinoma of no special type or invasive carcinoma not otherwise specified.
- Invasive lobular carcinoma is the next most common type .
| Types of invasive breast cancer | Proportion of all invasive breast cancers | Tumor characteristics |
|---|---|---|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Adapted from select sources . |
Recommended Reading: What Are Some Signs And Symptoms Of Breast Cancer
Treatment For Intraductal Papilloma
Your doctor will probably recommend surgery to remove the papilloma and the duct in which it is formed. While the papilloma isn’t cancerous, there is a risk that the cells in it could change and become malignant over time. Removing the papilloma eliminates the possibility that it could turn into cancer later.â
The surgery to remove a duct and papilloma is similar to the lumpectomy procedure for removing a tumor. You will probably need general anesthesia for the operation. Once you are asleep, your doctor will make a small cut in your breast and use surgical tools to remove the duct. They will then close the incision using surgical glue or stitches.â
After surgery, you may have pain for several days. Your doctor will give you instructions to care for the wound. You might need to take antibiotics to prevent infection after the operation.
After surgery, your doctor may do more testing on the duct and papilloma to completely rule out cancer. There are rare cases that those tests may reveal cancer even if your doctor did not suspect it. If that happens, your doctor will work with you to develop a breast cancer treatment plan.â
If you have unexplained nipple discharge or have a lump in your breast, talk to your doctor. You should have tests to check for intraductal papilloma and rule out breast cancer.
What Is Breast Cancer
Breast cancer starts in the cells of the breast. A cancerous tumour is a group of cancer cells that can grow into and destroy nearby tissue. It can also spread to other parts of the body.
Cells in the breast sometimes change and no longer grow or behave normally. These changes may lead to non-cancerous breast conditions such as atypical hyperplasia and cysts. They can also lead to non-cancerous tumours such as intraductal papillomas.
But in some cases, changes to breast cells can cause breast cancer. Most often, breast cancer starts in cells that line the ducts, which are the tubes that carry milk from the glands to the nipple. This type of breast cancer is called ductal carcinoma. Cancer can also start in the cells of the lobules, which are the groups of glands that make milk. This type of cancer is called lobular carcinoma. Both ductal carcinoma and lobular carcinoma can be in situ, which means that the cancer is still where it started and has not grown into surrounding tissues. They can also be invasive, which means they have grown into surrounding tissues.
Less common types of breast cancer can also develop. These include inflammatory breast cancer, Paget disease of the breast and triple negative breast cancer. Rare types of breast cancer include non-Hodgkin lymphoma and soft tissue sarcoma.
You May Like: Does Breast Cancer Occur In Males