Is Tumour Dormancy The Sole Explanation For Recurrence
In pondering the mechanisms of metastatic relapse among breast cancer patients, one obvious question is whether early recurrence is simply the consequence of direct metastatic outgrowth, whereas late relapses reflect a period of tumour dormancy. To address this query, it is imperative to consider how long it takes for a single cancer cell to grow into a clinically detectable metastasis. Pioneering measurements of breast tumour volume doubling time carried out by radiographic analysis on more than 800 women concluded that it takes ~12 years on average for a single cell with a 10-µm diameter to reach a clinically detectable mass of 1cm,, and that metastases can have a TVDT up to twofold higher than their matched primary tumours. However, these initial analyses focused on a small number of samples, without taking into account the vast heterogeneity among breast tumours or the effect that adjuvant therapies might have on their growth rate, as the subjects in this study were untreated.
Fig. 3: The puzzling timing of metastatic relapse in breast cancer patients.
What Is Secondary Breast Cancer
Secondary breast cancer is when cancer cells from a cancer that started in the breast spread to other parts of the body. The cancer that started in the breast is called primary breast cancer.Secondary breast cancer is also called advanced breast cancer or metastatic breast cancer. The most common places for breast cancer to spread to are the:
Rarely, breast cancer may spread to other parts of the body, such as the bone marrow, ovaries or lining of the tummy which is called the peritoneum.
Breast cancer can spread to different parts of the body. This does not mean it will go to all these places.
Related Stories & Media
Conventional Stages Of Breast Cancer Progression: 0 Through Iv
As mentioned, there are five basic stages of breast cancer with a couple of sub-categories.
Stage 0
This is a bit of an unclear term which specialists use to describe the development of abnormal cells that are not yet invasive breast cancer. Indeed physicians consider Ductal Carcinoma in situ, or DCIS, stage 0 breast cancer.
Here the malignant cancer cells are present in the lining of the breast d uct but have not yet invaded the surrounding breast tissue or spread beyond the duct. Almost 100% of DCIS is curable, but it obviously, does need treatment.
Early-stage breast cancer Stage 1
Stage 1 breast cancer is an early stage breast cancer. There is a considerable difference in medical opinion as to what exactly constitutes early stag e breast cancer. Also, how aggressive the treatment for Stage I breast cancer is another area of debate.
The standard definition of a stage 1 breast tumor is that a certain amount of breast cancer cells invade tissues and structures beyond the duct lining. However, no cancer cells have spread beyond the breast.
Furthermore, the tumor size is less than 2 cm in diameter. If physicians can detect and treat breast cancer before it grows beyond 2cm, the prognosis is very very good.
The average age of diagnosis of a stage 1 breast tumor is about 52 years old. In over 90% of cases, treatment tends to involve breast conservation surgery, followed by radiation therapy.
Chance of stage 1 cancer recurrence or spreading.
Recommended Reading: What Is Stage 3 Cancer Mean
Tumour Dormancy And Reawakening
Tumour dormancy is generally defined as a prolonged state of asymptomatic micrometastatic disease. In cancer of the breast or prostate, cancer cells can remain dormant for years and even decades before recurring as metastatic disease. During this latent period, patients are considered to be disease-free due to the lack of any symptoms of illness and because they have no detectable neoplasms by clinical imaging. Often described as one of the most wicked cancer cell misbehaviours, tumour dormancy shares many features in common with chronic diseases. Yet, its nature appears to be reversible, as myriad mechanisms have been shown to induce a switch to reawaken indolent DTCs . Furthermore, tumour dormancy is not exclusively a phenomenon of end-stage tumorigenesis, as it can apply to the presence of occult neoplasms until clinical diagnosis , and/or to MRD left behind after treatment . Attention, however, must be paid to the molecular underpinnings of these two scenarios as mechanistic differences between primary and metastatic dormancy might exist.
What To Expect When Taking Keytruda
Keytruda is given as a 30-minute infusion, every 3 or 6 weeks, depending on the dose given at each infusion. The Keytruda infusion is given before the chemotherapy infusion. If you are receiving Keytruda for metastatic or unresectable locally advanced triple-negative breast cancer, you may continue treatment with Keytruda and chemotherapy for up to 2 years, unless the cancer grows or you develop unacceptable side effects.
Women who are pregnant or planning to get pregnant should not be given Keytruda. Keytruda can cause embryo death and birth defects. Its important that you dont get pregnant while youre getting Keytruda you must use effective birth control.
Recommended Reading: Progesterone Negative Breast Cancer
A Disease No One Gets
Sadly, people donât âgetâ mets. In fact, a recent survey sponsored by Pfizer Oncology shows just how misunderstood it is. Sixty percent of the 2,000 people surveyed knew little to nothing about MBC while 72 percent believed advanced breast cancer was curable as long as it was diagnosed early. Even more disheartening, a full 50 percent thought breast cancer progressed because patients either didnât take the right treatment or the right preventive measures.
âTheyâve built an industry built on four words â early detection equals cure â and that doesnât even begin to define breast cancer,â said Schoger, who helped foundBreast Cancer Social Media, a virtual community for breast cancer patients, caregivers, surgeons, oncologists and others. âWomen are blamed for the fate of bad biology.â
The MBC Alliance, a consortium of 29 cancer organizations including the biggest names in breast cancer , addressed this lack of understanding and support as well as what many patient advocates term the underfunding of MBC research in a recently published landmark report.
Types Of Recurring Breast Cancer
Breast cancer may recur locally, regionally, or distantly:
Local recurring breast cancer occurs when a new tumor develops in the breast that was originally affected. If the breast has been removed, the tumor may grow in the chest wall or nearby skin.
Regional recurring breast cancer happens in the same region as the original cancer. In the case of breast cancer, this may be the lymph nodes above the collarbone or in the armpit.
Distant recurring breast cancer happens when cancer cells travel to a different part of the body. This new location is far away from the original cancer. When cancer recurs distantly, its considered metastatic cancer.
Not everyone with metastatic breast cancer experiences symptoms. When symptoms do occur, they can vary. Symptoms depend on the location of the metastasis and its severity.
Don’t Miss: Can Weight Gain Be A Symptom Of Breast Cancer
Can You Tell When Exactly My Breast Cancer Started
Often times, one of the most frequently asked questions I get when someone is diagnosed with breast cancer is when did it begin? says Roesch. And the general rule is that we really cant tell for sure when the cancer popped up. We can look at the subtype of breast cancer to perhaps get a better understanding if it was weeks vs. months for example, but theres no way to tell for sure.
When Metastatic Cancer Can No Longer Be Controlled
If you have been told your cancer can no longer be controlled, you and your loved ones may want to discuss end-of-life care. Whether or not you choose to continue treatment to shrink the cancer or control its growth, you can always receive palliative care to control the symptoms of cancer and the side effects of treatment. Information on coping with and planning for end-of-life care is available in the Advanced Cancer section of this site.
You May Like: Life Expectancy Of Metastatic Breast Cancer
Lessons From Hormonal Therapy And Anti
A schematic shows key pathways of breast tumorigenesis and their targeted agents.
Notes: Small molecules are highlighted in light shade antagonist antibodies are highlighted in dark shade *indicates multitargeted inhibitors.
Abbreviations: RTK, receptor tyrosine kinase AI, aromatase inhibitor SERM, selective estrogen receptor modulator.
Additional Tools For Diagnosing Advanced Breast Cancer
The additional tools below are often used specifically for diagnosing advanced cancer:
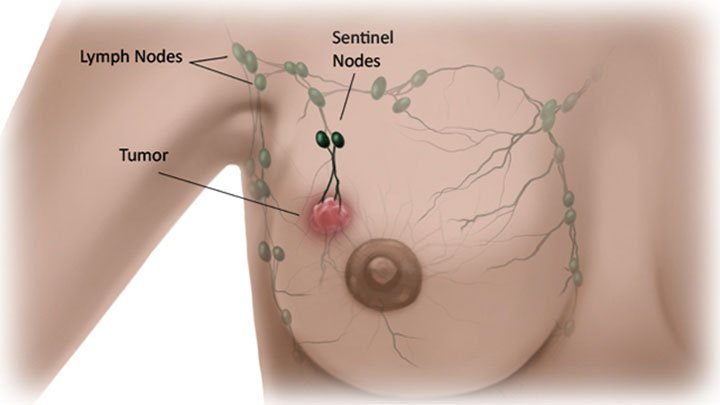
Sentinel lymph node biopsy: This procedure removes sentinel lymph node cells during surgery for examination. When breast cancer spreads, it often heads first to the lymph nodes.
Chest X-ray: This detailed image of the chest may help doctors see whether cancer has spread to the bones.
Computed tomography scan: Also known as a CAT scan, this procedure takes detailed pictures of internal areas of the body using a computer linked to an X-ray machine. A dye may be used to help the organs show up more clearly in the images.
Bone scan: This procedure looks for bone metastasis, or cancer cells that have spread to the bone. A small amount of radioactive material is injected into the blood, then detected with a scanner.
Positron emission tomography scan: A PET scan is a detailed imaging tool that uses a radioactive drug, known as a tracer, to search for cancer cells within your body.
Read Also: 3rd Stage Breast Cancer
Myth #: People With Metastatic Breast Cancer Look Sick And Lose Their Hair
You dont look sick. You look so well. Why do you still have your hair? Are you sure you have cancer? These are comments that people with MBC report hearing. But there are many treatment options besides chemotherapy, and people often appear well while taking them.
As NancyHB comments: Id much rather be a poster child for how sometimes we can live with, rather than die from, MBC at least for a while. Instead, I find myself defending against people who are increasingly becoming impatient with my lack of cancer-patient appearance. Im grateful for this time of feeling good, and theyre harshing my buzz.
Some people with MBC report that they actually look better than they feel while in treatment. So they sometimes have to let family and friends know that even though they appear fine, they dont feel well.
Shetland Pony notes: If she looks good, she is good. Nope. Many of us suffer from the invisible disability of fatigue. I would venture to say every available treatment causes us some level of fatigue. We struggle to keep up. It may look like we are doing the bare minimum when we are really giving it our all.
JoE777 of Texas adds: The new normals advertised about therapies on TV are deceiving about the side effects. They talk about side effects while women are skipping through life. not looking to show the harsh side effects but think there is something wrong with me that my life is not like that.
How Does Cancer Spread Or Metastasize
The spread of cancer usually happens through one or more of the following steps:
- Cancer cells invade nearby healthy cells. When the healthy cell is taken over, it too can replicate more abnormal cells.
- Cancer cells penetrate into the circulatory or lymph system. Cancer cells travel through the walls of nearby lymph vessels or blood vessels.
- Migration through circulation. Cancer cells are carried by the lymph system and the bloodstream to other parts of the body.
- Cancer cells lodge in capillaries. Cancer cells stop moving as they are lodged in capillaries at a distant location and divide and migrate into the surrounding tissue.
- New small tumors grow. Cancer cells form small tumors at the new location
Also Check: What To Expect During Chemotherapy For Breast Cancer
What Is The Survival Rate For Triple Negative Breast Cancer
Survival rates are a way to discuss the prognosis and outlook of a cancer diagnosis. The number most frequently mentioned is 5-year survival. Many patients live much longer, and some die earlier from causes other than breast cancer. With a constant change and improvement in therapies, these numbers also change. Current 5-year survival statistics are based on patients who were diagnosed at least 5 years ago and may have received different therapies than are available today.
Below are the statistics from the National Cancer Institutes SEER database for survival of all patients with breast cancer, by tumor stage:
| Stage |
|---|
Also Check: Can Asbestos Cause Breast Cancer
What Are Breast Lobes And Breast Ducts
Each female breast contains 15-20 sections called lobes. Each lobe is made up of many smaller sacs called lobules . It is these lobules that produce milk in breastfeeding women. The lobes and lobules are connected to the nipple by tubes called ducts, which carry milk to the nipple. Milk flows through the nipple to the outside during breastfeeding.
Also Check: Breast Cancer Gene Name
Myth #: The Mental And Emotional Experience Of People With Mbc Is The Same As That Of Earlier
People with MBC report hearing comments such as, At least you have a good type of cancer, Arent you glad so much research on breast cancer has been done?, Fortunately you have so many options. These might comfort people with early-stage breast cancer, who can look forward to one day finishing treatment and moving on but people with MBC dont have that luxury. They know they will be in treatment for the rest of their lives. They also know that their life is likely to be shorter than theyd planned.
Mentally and emotionally, people with MBC have a completely different experience. For them, the whole ringing the bell idea does not work, says Dr. Gupta. I have patients who are coming in once a week and have to plan their lives around their treatment. The whole pink brigade idea is very upsetting to them.
Fortunately, more and more people with MBC are speaking up and calling attention to how their experience differs from that of people with earlier-stage breast cancer. People with MBC live with cancer always in the background of their lives, but with new and emerging therapies, many are living longer and maintaining their quality of life.
Clearly, the experience of metastatic breast cancer is quite different from early-stage breast cancer. But there are so many patients who understand just what youre going through. Read more about Living with Metastatic Breast Cancer and join our discussion forum for people with stage IV/metastatic disease.
References
How Is A Local Recurrence After Lumpectomy Diagnosed
After a diagnosis of early stage breast cancer, any remaining breast tissue should be evaluated annually with scans .
Most local recurrences within the breast after lumpectomy are detected on routine annual breast imaging, which usually takes the form of mammography and ultrasound, and on occasions MRI.
If you have a local recurrence or new primary breast cancer, you may find symptoms similar to an initial breast cancer. This includes:
- A new lump in the breast, armpit area or around the collarbone
- A change in breast size or shape
- Changes to the nipple, such as sores or crusting, an ulcer or inverted nipple
- Clear or bloody nipple discharge
- Changes to the skin including redness, puckering or dimpling
- Breast tenderness or pain
Once a local recurrence has been diagnosed, we do tests to see whether there are signs of cancer elsewhere in the body. These may include a chest X-ray, CT scan, bone scan or PET scan, and blood tests , then we have to figure out how best to treat the tumour in the breast. Usually in these cases we do a mastectomy, as the prior less drastic surgery and radiation didnt take care of it.
You May Like: Anne Hathaway Breast Implants
Symptoms If Cancer Has Spread To The Bones
You may have any of these symptoms if your cancer has spread to the bones:
- an ache or pain in the affected bone
- breaks in the bones because they are weaker
- breathlessness, looking pale, bruising and bleeding due to low levels of blood cells – blood cells are made in the bone marrow and can be crowded out by the cancer cells
Sometimes when bones are damaged by advanced cancer, the bones release calcium into the blood. This is called hypercalcaemia and can cause various symptoms such as:
- tiredness
How Do Breast Cancers Spread
Cancer cells break away from the primary tumor, entering the bloodstream or the lymphatic system. As large vessels narrow, cancer cells stop traveling and lodge themselves in a new area. Then they begin dividing and moving into surrounding tissue. The cancer cells take over the new area, crowding out healthy cells and forming a new tumor. Cancer cells are insidious because the new tumor can set up its own network of blood vessels to obtain nutrients for growth and further spread.
You May Like: Stage 3 A Cancer
Metastatic Patterns Of Breast Cancer
It is well known from clinical observations that different tumor types display distinct organ tropisms in metastatic patterns. Breast cancer displays distinct tropisms depending on the subtypes. Bone, lung, liver, and brain are the common target organs for breast cancer metastasis, in addition to distant lymph nodes. ER+ tumors have the best prognosis with a low incidence rate within the first five years. But this rate gradually increases as the time extends beyond five years . Bone is the predominant metastatic site, whereas brain is much less affected. In contrast, TN breast tumors display the worst prognosis, with a spiking incidence rate within the first one to two years and virtually all metastases occurring within the first five years., Visceral organs, including brain and lung, are more frequently affected in TN tumors. HER2+ tumors are also considered an aggressive disease. With the invention of anti-HER2 therapy, the prognosis has been much improved and patient lifespan is significantly prolonged. The therapy is quite effective in controlling extracranial lesions but leave brain metastasis a remaining challenge.