Data Collection And Image Interpretation
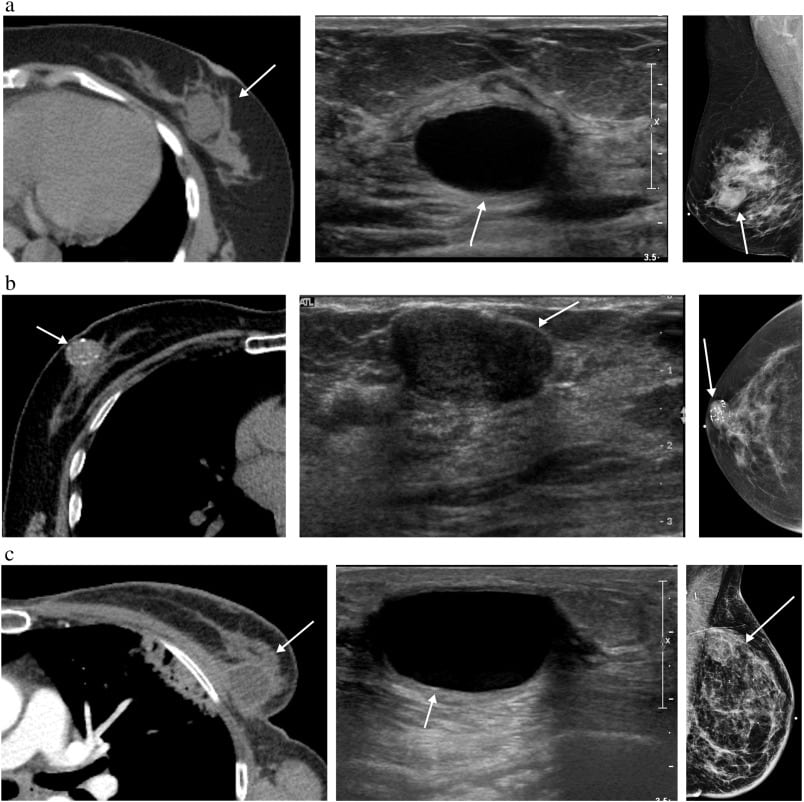
Imaging features for these 43 eligible patients were recorded according to the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System lexicon by the single reader blinded to clinical and pathology outcomes.15 This included the specific MRI finding type abutting the pectoralis muscle: a mass, a spicule of a mass , or non-mass enhancement. The presence of associated mass effect from the tumor on the pectoralis muscle was also assessed. For each eligible patient, clinical history and surgical pathology details were also recorded, including whether the posterior margins were clear, close or positive for tumor involvement, as well as whether tumor invasion of the pectoralis muscle was seen on surgical pathology. If posterior margins were clear and no skeletal muscle was present on surgical pathology, the case was recorded as having no muscle invasion. The number of months of clinical follow-up for each patient and the clinical status of the patient at follow-up, including whether recurrence or the development of metastasis occurred during follow-up, was also recorded.
Can You Pull A Muscle Under Your Left Breast
The terms pulled muscle and muscle strain refer to an injury that involves an overstretched or torn muscle. A person with a muscle strain in the chest may experience sudden, sharp pain in this area. Although uncomfortable, a strained chest muscle is usually a minor injury that tends to heal within days or weeks.
Can A Tumor Grow Overnight
They emerge at night, while we sleep unaware, growing and spreading out as quickly as they can. And they are deadly. In a surprise finding that was recently published in Nature Communications, Weizmann Institute of Science researchers showed that nighttime is the right time for cancer to grow and spread in the body.
Also Check: Clinical Trial For Breast Cancer
A Unique Case Of Muscle
Academic Editor: Received
Abstract
Breast cancer rarely metastasizes to the muscles, and it is even more unusual for this phenomenon to result in airway compromise. We present a unique case of an 84-year-old female who presented with neck swelling and upper airway obstruction due to metastatic breast cancer invading the sternocleidomastoid muscles. After establishing the diagnosis and discussing possible treatment options, the patient elected for antiestrogen therapy, palliative tracheostomy, radiation therapy, and hospice services.
1. Introduction
2. Case Report
An 84-year-old African-American female with no known history of malignancy initially presented at a local Emergency Department with complaint of dyspnea for several months. Patient was diagnosed with asthma and given an albuterol inhaler. Five months later, she presented to our ED with progressive neck swelling and dysphagia. Urgent evaluation with Otolaryngology was arranged as she was noted to have difficulty controlling her secretions. During ENT evaluation, she acutely developed respiratory failure requiring emergent fiber-optic nasotracheal intubation and transfer to the medical intensive care unit .
3. Discussion
4. Conclusion
Conflicts of Interest
Can Breast Lobules Be Felt
Adenosis of the breast is a non-cancerous condition in which the lobules increase in size and number. This can cause the breasts to be painful, and lumps may be felt in the breasts. Adenosis can be seen on mammogram, and these may require a sample of the tissue to be biopsied to make sure it isnt breast cancer.
You May Like: What To Wear For Radiation Breast Cancer
What Is The Chest Cavity
The chest cavity is a space that is enclosed by the spine, ribs and sternum and is separated from the abdomen below by the diaphragm. The chest cavity contains the heart, the thoracic aorta, lungs, and esophagus among other important organs. The wall of the chest cavity is made up of the rib cage and diaphragm. The chest wall is firm enough to protect the organs in the chest cavity but flexible enough to move outward and inward with respiration . As is the case with any other structure in your body, the chest wall can develop tumors.
What Is Stage Ii Breast Cancer
Stage II describes cancer that is in a limited region of the breast but has grown larger. It reflects how many lymph nodes may contain cancer cells. This stage is divided into two subcategories.
Stage IIA is based on one of the following:
- Either there is no tumor in the breast or there is a breast tumor up to 20 millimeters , plus cancer has spread to the lymph nodes under the arm.
- A tumor of 20 to 50 millimeters is present in the breast, but cancer has not spread to the lymph nodes.
Stage IIB is based on one of these criteria:
- A tumor of 20 to 50 millimeters is present in the breast, along with cancer that has spread to between one and three nearby lymph nodes.
- A tumor in the breast is larger than 50 millimeters, but cancer has not spread to any lymph nodes.
Also Check: What Does Triple Negative Breast Cancer Look Like
Preoperative Pectoralis Muscle Index Predicts Distant Metastasis
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Harbin Medical University Cancer Hospital, Harbin Medical University, Harbin, China
- 2School of Computer Science and Technology, Harbin University of Science and Technology, Harbin, China
Background: Breast cancer is one of the most commonly diagnosed cancers, and the fourth leading cause of cancer deaths in females worldwide. Sarcopenia is related to adverse clinical outcomes in patients with malignancies. Muscle index is a key parameter in evaluating sarcopenia. However, there is no data investigating the association between muscle index and distant metastasis in breast cancer. The aim of this study was to explore whether muscle index can effectively predict distant metastasis and death outcomes in breast cancer patients.
Study Design: The clinical data of 493 breast cancer patients at the Harbin Medical University Cancer Hospital between January 2014 and December 2015 were retrospectively analyzed. Quantitative measurements of pectoralis muscle area and skeletal muscle area were performed at the level of the fourth thoracic vertebra and the eleventh thoracic vertebra of the chest computed tomography image, respectively. The pectoralis muscle index and skeletal muscle index were assessed by the normalized muscle area . Survival analysis was performed using the log-rank test and Cox proportional hazards regression analysis.
Low PMI/T4 is associated with worse DMFS and OS in breast cancer patients. Future prospective studies are needed.
Where Do Malignant Tumors Originate
The most common malignant chest wall tumors are sarcomas. Primary tumors originate in the bone or muscle of the chest wall. Less than half of malignant chest wall tumors are primary. Secondary tumors originate elsewhere in the body and spread to the chest wall. Almost all secondary tumors are malignant.
Recommended Reading: What Age Do Women Get Breast Cancer
Primary Leiomyosarcoma Of The Breast: A Case Report
Department of Surgery, Baskent University Medical Faculty, Ankara, Turkey.
1Department of Pathology, Baskent University Medical Faculty, Ankara, Turkey.
Correspondence: Zülfikar Karabulut. Department of Surgery, Baskent University Medical Faculty, Ankara, Turkey. Tel: +90-312-327-27-27, Fax: +90-312-327-12-76,
Is Pectoralis Minor Superficial Or Deep
The pectoralis minor muscle is a small triangular shaped muscle that lies deep to pectoralis major muscle and passes as three muscular slips from the thoracic wall to the coracoid process of the scapula. Pectoralis minor draws the scapula forward and downward, and raises the ribs in forced inspiration.
Read Also: Can You Get Breast Cancer At 16
Patient Selection For Mri Evaluation Of The Ipsilateral Breast
Determining which patients are most likely to benefit from preoperative breast MRI has been the focus of a number of studies. Several studies have suggested that breast MRI may be most useful in women with mammographically dense breasts . This is intuitive, given the known decrease in mammographic sensitivity related to breast density suggesting a higher likelihood of occult disease in these patients . However, there may still be benefit for MRI in patients with nondense breasts because additional studies have found an equal number of occult malignancies in patients with newly diagnosed breast cancer with nondense breasts. Therefore preoperative MRI should not be reserved only for those patients with high mammographic density.
Mri Evaluation Of The Patient With Breast Cancer

In the absence of distant metastatic disease, breast cancer staging is based on the extent of local-regional disease in the breast and axilla. The American Joint Committee on Cancer TNM system is used to provide breast cancer patients and their clinicians criteria for determining prognosis and treatment options. The TNM system categorizes extent of disease using anatomic data from the primary tumor , regional lymph nodes , and distant metastases . Clinical staging is performed initially, then replaced by pathologic staging following complete resection of the primary tumor and lymph node sampling. The use of neoadjuvant treatments requires accurate preoperative clinical staging. Additionally, although not always altering the TNM stage, the extent of in-breast disease is critical to surgical planning.
You May Like: Does Breast Cancer Hurt Before Diagnosis
Can A Mammary Fibromatose Be Confused With Breast Carcinoma
Chest wall and mammary fibromatoses, o wing to their suspicious appearance on imaging and presentation as palpable breast masses, may be easily confused for breast carcinoma before a histologic diagnosis has been established . Characteristics of fibromatosis on various imaging modalitiesincluding mammography, ultrasound, and MRIhave been previously reported with significant variability. MRI, however, is particularly useful in evaluation of tumor extent and preoperative planning . This case represents a rare presentation of fibromatosis originating in the pectoralis muscle presenting as a palpable breast mass with clinical and imaging findings suspicious for breast carcinoma.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Technique
All 28 breast MRIs were performed at 1.5 Tesla using a dedicated bilateral breast coil . All studies met criteria for breast MRI accreditation set forth by the American College of Radiology. Water and fat axial images were acquired from a T2-weighted fast spin-echo acquisition using a modified 3-point Dixon method for fat suppression, field of view 28-40 cm, slice thickness 4.0 mm with 1.0 mm spacing, TR/TE 4505 ms/102 ms, echo-train length 14, matrix 320 × 224, NEX 2.0, and bandwidth 50.0 kHz. Axial, fat-suppressed pre-gadolinium and post-gadolinium 3D spoiled gradient-recalled images were acquired at 11.5 min, 23 min, and about 78 min after intravenous injection of gadolinium-based contrast agent using field of view 2840 cm, slice thickness 1.82.0 mm, in-plane resolution 1.0 mm, TR/TE 5.2 ms/2.5 ms, flip angle 10°, bandwidth 62.50 kHz, and phase direction LR. Between 3 and 7 min after contrast injection, a higher-resolution axial 3D SPGR image was acquired with field of view 28-40 cm, slice thickness 1.21.4 mm, in-plane resolution 1.0 mm, TR/TE 5.2 ms/2.5 ms, bandwidth 62.50 kHz, and phase direction AP.
All DWI images were acquired using a spin-echo echo-planar-imaging pulse sequence with b values 0, 800 s/mm2, TR/TE 4000 ms/minimum, slice thickness 5 mm, slice spacing 1 mm, and acquisition matrix 128 × 128 in the axial or sagittal planes.
Read Also: Breast Cancer Stage 3 Symptoms
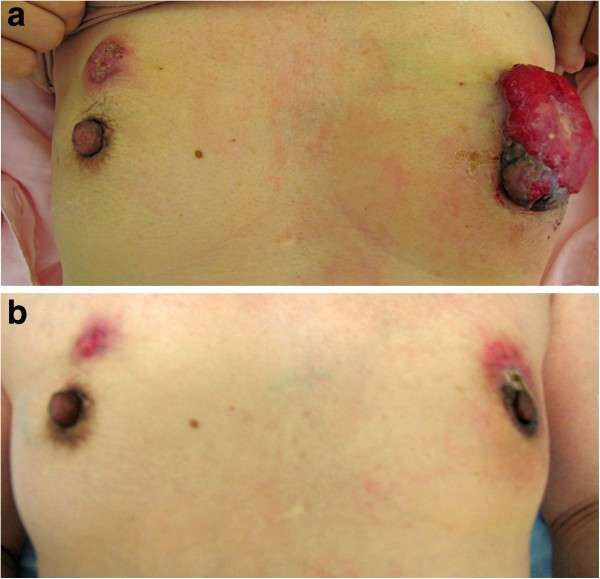
Can Breast Cancer Be In Pectoral Muscle
In the treatment of breast cancer, defects in the pectoralis major and minor muscle can have a significant impact on surgery and radiation therapy. An extremely rare case is reported, along with consideration of the implications with respect to before and after surgery for breast cancer on the affected side.
How Long Does It Take To Recover From Breast Cancer
The overall 10-year survival rate for breast cancer with a chest wall recurrence is around 50 percent, but that may now be changing with the introduction of better treatment options. The amount of time elapsed between the initial breast cancer and the locoregional recurrence plays an important role in survival.
Read Also: Metastatic Breast Cancer Access To Care Act
What Is Stage Iii Breast Cancer
In stage III breast cancer, the cancer has spread further into the breast or the tumor is a larger size than earlier stages. It is divided into three subcategories.
Stage IIIA is based on one of the following:
- With or without a tumor in the breast, cancer is found in four to nine nearby lymph nodes.
- A breast tumor is larger than 50 millimeters, and the cancer has spread to between one and three nearby lymph nodes.
In stage IIIB, a tumor has spread to the chest wall behind the breast. In addition, these factors contribute to assigning this stage:
- Cancer may also have spread to the skin, causing swelling or inflammation.
- It may have broken through the skin, causing an ulcerated area or wound.
- It may have spread to as many as nine underarm lymph nodes or to nodes near the breastbone.
In stage IIIC, there may be a tumor of any size in the breast, or no tumor present at all. But either way, the cancer has spread to one of the following places:
- ten or more underarm lymph nodes
- lymph nodes near the collarbone
- some underarm lymph nodes and lymph nodes near the breastbone
What Gets Stored In A Cookie
This site stores nothing other than an automatically generated session ID in the cookie no other information is captured.
In general, only the information that you provide, or the choices you make while visiting a web site, can be stored in a cookie. For example, the site cannot determine your email name unless you choose to type it. Allowing a website to create a cookie does not give that or any other site access to the rest of your computer, and only the site that created the cookie can read it.
Recommended Reading: Can Depression Cause Breast Cancer
Can Breast Cancer Cells Change After Mastectomy
But in a recurrence, the receptor status of the cancer cells can change, especially if it has been more than a year or two since your mastectomy. In other words, if you originally had a breast cancer tumor that was estrogen receptor-positive, your tumor cells may have changed and become estrogen receptor-negative.
Do Breast Cancer Lumps Feel Hard Or Soft
Those symptoms arent associated with cancer. There are often differences in the way benign and cancerous breast lumps feel. Benign lumps are softer, squishy, and tend to move around. In most cases, cancerous lumps are hard and stay put when you feel them. The nipples and skin may look different around them.
Recommended Reading: Can Getting Hit In The Breast Cause Cancer
How To Treat A Malignant Chest Wall Tumor
The treatment of a malignant chest wall tumor may involve chemotherapy, radiation, or surgery, or a combination of all three. A portion of the rib cage must frequently be removed to eradicate a chest wall tumor very effective reconstruction of the chest wall using adjacent muscle, mesh or mesh with plastic material is available. The amount of chest wall that must be removed, the proposed method of reconstruction, and associated risks and benefits of the operation are reviewed by the surgeon with the patient prior to scheduling the procedure.
Multifocal And Multicentric Disease
Several studies have shown that diffusion-weighted imaging and spectroscopy have shown promise in increasing the PPV of MRI. Further studies on these techniques are warranted.
False negatives, in which additional tumor is present but not detected, are also known to occur with MRI. Background diffuse parenchymal enhancement of normal tissue obscuring lesion enhancement is a common reason for false-negative imaging. Moderate and marked background enhancement can reduce the sensitivity for multifocal and multicentric lesions that are small and lack distinguishing morphologic features. Even extensive nonmasslike enhancement, which occurs with DCIS, is difficult to detect in the presence of moderate/marked background enhancement. Background parenchymal enhancement is hormonally mediated and does not correlate with mammographic density. Scheduling the patientâs MRI study during the first half of her menstrual cycle and discontinuing exogenous hormone therapy for several months before the study decrease the risk of excessive background enhancement. However, this is often not possible in patients with newly diagnosed malignancy, who need to avoid treatment delays.
You May Like: How Can You Tell If You Got Breast Cancer
What Is Chest Wall Recurrence
Coping. A chest wall recurrence is breast cancer that returns after a mastectomy. A chest wall recurrence may involve skin, muscle, and fascia beneath the site of the original breast tumor, as well as lymph nodes. When cancer recurs in the chest wall, it may be classed as a locoregional recurrence or it may be linked to distant metastasis.
Drug Treatment Before Surgery
You might have chemotherapy as a first treatment to shrink the cancer down.
You might have hormone therapy first if your cancer cells have hormone receptors. But you usually only have this if chemotherapy isnt suitable.
If your cancer cells have particular proteins called HER2 receptors you might also have a targeted cancer drug called trastuzumab .
These treatments might shrink the tumour enough to allow your surgeon to remove just the area of cancer. This is called breast conserving surgery or a wide local excision.
If the cancer doesnt shrink enough, you need to have the whole breast removed . You may be able to have a new breast made . Do speak to your surgeon about this.
Before your surgery the lymph nodes in the armpit are checked for cancer cells.
You usually have radiotherapy to the breast after surgery.
You May Like: How To Help Breast Cancer Awareness
Tnm Classification For Breast Cancer
The American Joint Committee on Cancer provides two principal groups for breast cancer staging: anatomic, which is based on extent of cancer as defined by tumor size , lymph node status , and distant metastasis and prognostic, which includes anatomic TNM plus tumor grade and the status of the biomarkers human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 , estrogen receptor , and progesterone receptor . The prognostic stage group is preferred for patient care and is to be used for reporting of all cancer patients in the United States.
In turn, prognostic stages are divided into clinical and pathological groups. Pathological stage applies to patients who have undergone surgery as the initial treatment for breast cancer. It includes all information used for clinical staging plus findings at surgery and pathological findings from surgical resection. Pathological prognostic stage does not apply to patients who received neoadjuvant therapy . See the tables below.
Table. TNM Classification for Breast Cancer