Symptoms Of Metastatic Breast Cancer
The symptoms of metastatic breast cancer may be different than those of early-stage breast cancer, but not always. Sometimes, there are no symptoms at all.
You should always speak with your doctor if you experience any new signs or symptoms, but here are some of the most common signs that breast cancer has spread:
- Bone pain or bone fractures due to tumor cells spreading to the bones or spinal cord
- Headaches or dizziness when cancer has spread to the brain
- Shortness of breath or chest pain, caused by lung cancer
- Jaundice or stomach swelling
The symptoms of breast cancer metastasis may also vary depending on where in the body the cancer has spread. For example:
- If the breast or chest wall is affected, symptoms may include pain, nipple discharge, or a lump or thickening in the breast or underarm.
- If the cancer has spread to bones, symptoms may include pain, fractures or decreased alertness due to high calcium levels.
- If the cancer has spread to the lungs, symptoms may include shortness of breath, difficulty breathing, coughing, chest pain or fatigue.
- If the cancer has spread to the liver, symptoms may include nausea, fatigue, swelling of the feet and hands or yellowing skin.
- If cancer has spread to the central nervous system, which includes the brain or spinal cord, symptoms may include pain, memory loss, headache, blurred or double vision, difficulty with and/or movement or seizures.
How Quickly Breast Cancer Develops
You may have heard remarks that cancer has been present for five years before it is diagnosed, and this may sometimes be true.
The actual time it takes for breast cancer to grow from a single cancer cell to a cancerous tumor is unknown, as estimates based on doubling time assume that this is constant throughout the duration of tumor growth.
If doubling time were constant, cancer with a doubling time of 200 days would take 20 years to develop into a detectable tumor, and a doubling time of 100 days would take 10 years to be evident on exam.
In contrast, a breast tumor with a doubling time of 20 days would take only 2 years to develop.
Since the majority of studies have found the average doubling time to be between 50 days and 200 days, it’s likely that most breast cancers that are diagnosed began at least 5 years earlier .
Bone Weakening And Fracture
Secondary breast cancer in the bone may mean that the affected bones are weakened, which can increase the risk of fracture. This is called a pathological fracture, which means the break in the bone is due to disease and not caused by an accident.
If a bone has fractured you may need surgery to try to repair the fracture. You may also be given drug treatment to stop this happening in the future.
Also Check: What Blood Test Can Detect Breast Cancer
What Are Dense Breasts
Breasts contain glandular, connective and fatty tissue. Breast density is a term used to describe the different proportions of these tissue types as detected by a mammogram. Dense breasts have relatively high amounts of connective and/or glandular tissue and low amounts of fatty tissue. Only a mammogram can show if a woman has dense breasts. Breast density is not related to how the breasts look, feel, their size or firmness.
On a mammogram, connective or fibrous tissue appears white while fatty tissue appears dark. Because breast cancers also appear white, this may make it more difficult for specialists to identify cancer in women with dense breasts. However, even with dense breasts, a screening mammogram is still the most effective method to detect breast cancer early for women over age 50.
Dense breasts also tend to be more common in younger women or women with a lower body mass index. In addition, breast density tends to decrease as women become older.
Treatment Of Local Recurrence After Previous Mastectomy
Most commonly the lesion is removed surgically and followed by radiation to the chest wall if the woman has not previously had radiation Treatment of local recurrence after mastectomy can involve a variety of different approaches, including surgery to remove the recurrence if it is confined to a limited area. Other options for treatment include radiation, chemotherapy, and endocrine therapy, or a combination of these.
Despite aggressive local treatment, many women with an isolated local recurrence following mastectomy eventually develop distant metastases. This is not because the local recurrence spreads, but rather because it is a sign that things have changed and dormant cells in other organs may also be waking up.
You May Like: Is Grade 3 Breast Cancer Serious
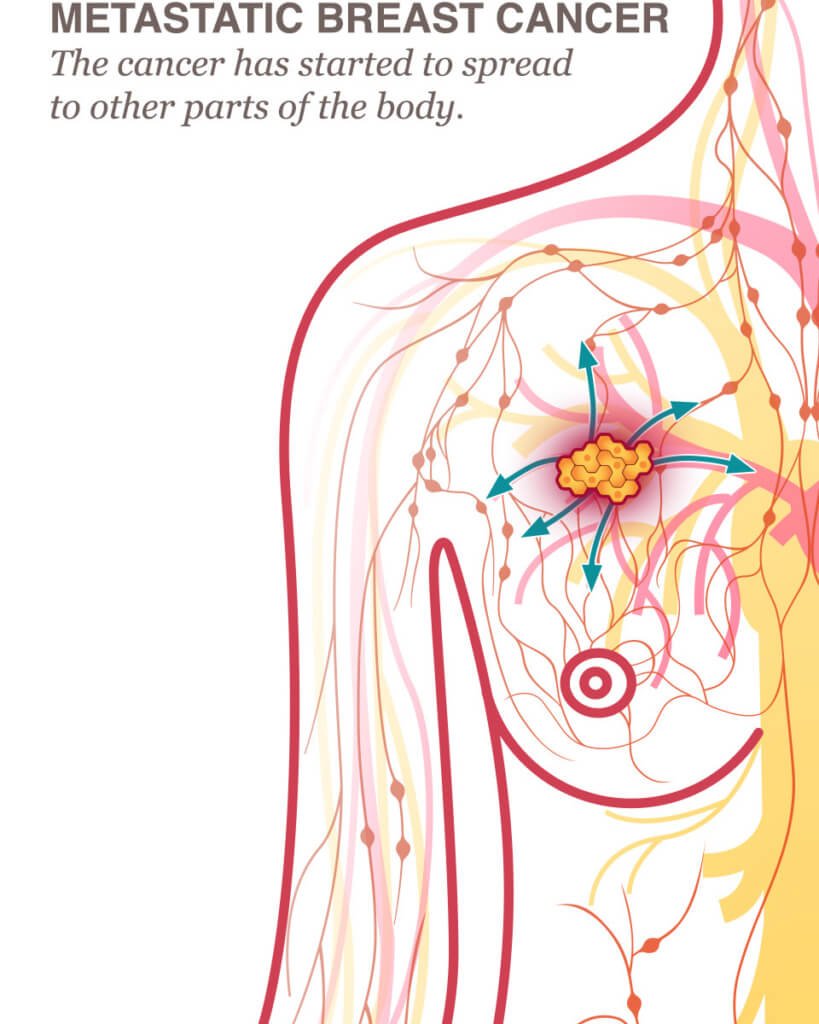
Most Common Places It Spreads
It’s still breast cancer, even if it’s in another organ. For example, if breast cancer spreads to your lungs, that doesn’t mean you have lung cancer. Although it can spread to any part of your body, there are certain places it’s most likely to go to, including the lymph nodes, bones, liver, lungs, and brain.
Can Green Tea Help Prevent Or Treat Breast Cancer
Amongst all the talk about the benefits of drinking green tea in recent years are several claims that a chemical found in green teaepigallocatechin-3-gallate may be a powerful weapon against breast cancer.
The low rate of breast cancer in regions where people drink large amounts of green tea is what made researchers start examining the relationship.
Before you put faith in your teacup, its important to dig into the sciencewhats known and what needs more examination.
Antioxidants and Free Radicals
Green teas cancer-fighting reputation comes from its polyphenols, which are chemicals that have antioxidant properties. Antioxidants protect the cells in your body from free radicals, highly reactive molecules that speed the damage caused by chemicals in the environment or aging, and that can lead to the development of cancer .
Free radicals can damage tissues in many ways, one of which is by directly damaging DNA. Since damage to DNA is what leads to the development of cancer, researchers have given a lot of attention to nutrients that can neutralize free radicals before they do their damage.
EGCG is one of the antioxidants found almost exclusively in green tea.
You May Like: How Rare Is Breast Cancer In Males
Metastatic Breast Cancer Treatment
When cancer has spread to other parts of the body, oncologists usually recommend systemic treatment, which can destroy abnormal cells in multiple locations. Depending on the specifics of a patients diagnosis, surgery may or may not be recommended.
Moffitt Cancer Center provides a complete range of breast cancer treatments through the Don & Erika Wallace Comprehensive Breast Program. This includes chemotherapy, radiation therapy and surgery, as well as immunotherapy, hormone therapy and supportive care. Patients with metastatic breast cancer may also consider enrolling in a clinical trial at Moffitt to expand their options even further.
If youd like to request an appointment, call or submit a new patient registration form online. Referrals are welcome, but never required.
- BROWSE
If Breast Cancer Spreads
Cancer cells can spread from the breast to other parts of the body. This spread is called metastasis.
Understanding how a type of cancer usually grows and spreads helps your healthcare team plan your treatment and future care.
If breast cancer spreads, it usually spreads to regional lymph nodes. These are lymph nodes on the same side of the body as the tumour in the following areas:
- under the arm
Breast cancer can also spread to:
- muscles on the chest
- the skin on the breast
- American Cancer Society. Breast Cancer. 2015: .
- Foxson SB, Lattimer JG & Felder B. Breast cancer. Yarbro, CH, Wujcki D, & Holmes Gobel B. . Cancer Nursing: Principles and Practice. 7th ed. Sudbury, MA: Jones and Bartlett 2011: 48: pp. 1091-1145.
- Morrow M, Burstein HJ, and Harris JR. Malignant tumors of the breast. DeVita VT Jr, Lawrence TS, & Rosenberg SA. Cancer: Principles and Practice of Oncology. 10th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins 2015: 79: 1117-1156.
Read Also: Can I Get Breast Cancer At 15
Diagnosing Metastatic Breast Cancer
Getting a clear picture of where breast cancer has spread is essential for creating a personalized treatment plan. Your care team will likely use a combination of the following tests and tools to diagnose both localized and advanced breast cancer:
Ultrasound exam: With this imaging technique, sound waves create a picture of internal areas of the body.
Magnetic resonance imaging : This procedure produces detailed images using magnetic fields and radio waves.
Blood chemistry studies: A blood sample is taken to measure the amounts of certain substances that are released by your organs and tissues. A higher or lower amount of a particular substance may be a sign of disease.
Biopsy: A biopsy is the removal of cells or tissues so a pathologist may view them through a microscope. Your original breast cancer diagnosis was likely confirmed with a biopsy.
What Is Stage Iv Breast Cancer
Stage IV is the most advanced stage of breast cancer. It has spread to nearby lymph nodes and to distant parts of the body beyond the breast. This means it possibly involves your organs such as the lungs, liver, or brain or your bones.
Breast cancer may be stage IV when it is first diagnosed, or it can be a recurrence of a previous breast cancer that has spread.
Also Check: What Is Her2 Neu Breast Cancer
How Is A Local Recurrence After Lumpectomy Diagnosed
After a diagnosis of early stage breast cancer, any remaining breast tissue should be evaluated annually with scans .
Most local recurrences within the breast after lumpectomy are detected on routine annual breast imaging, which usually takes the form of mammography and ultrasound, and on occasions MRI.
If you have a local recurrence or new primary breast cancer, you may find symptoms similar to an initial breast cancer. This includes:
- A new lump in the breast, armpit area or around the collarbone
- A change in breast size or shape
- Changes to the nipple, such as sores or crusting, an ulcer or inverted nipple
- Clear or bloody nipple discharge
- Changes to the skin including redness, puckering or dimpling
- Breast tenderness or pain
Once a local recurrence has been diagnosed, we do tests to see whether there are signs of cancer elsewhere in the body. These may include a chest X-ray, CT scan, bone scan or PET scan, and blood tests , then we have to figure out how best to treat the tumour in the breast. Usually in these cases we do a mastectomy, as the prior less drastic surgery and radiation didnt take care of it.
Advanced Or Metastatic Breast Cancer: Stage Iv
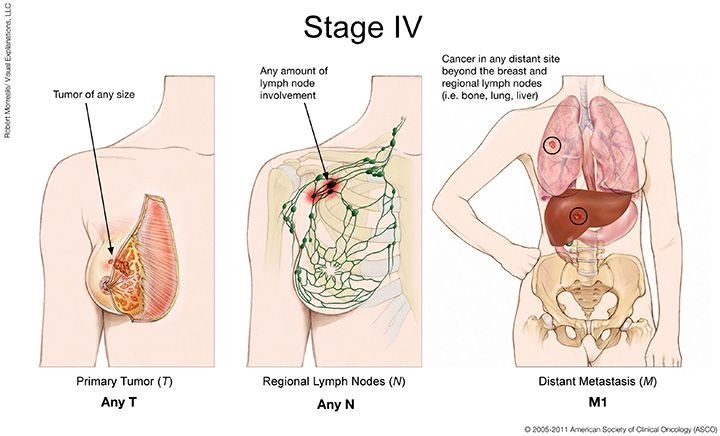
Stage IV breast cancers indicate the presence of distant metastasis to other parts of the body, such as the liver or bones.
About 5% of women, in 2017 have a stage IV breast cancer at the time of initial diagnosis.
The long term survival rate for stage IV breast cancer tends to be low, but is improving all the time. In 2012 the National Cancer Institute statistics show the 5-year survival rate for Stage IV breast cancer to be around 22%.
However, a more recent study shows that 37% of women survive for 3 years after a Stage IV breast cancer diagnosis.
Also, it is important to remember that each case is individual and there is no telling exact survival rates for any of the stages of breast cancer.
Don’t Miss: Do People Survive Stage 4 Breast Cancer
Treatment Options For Stage Iv Breast Cancer
For women with stage IV breast cancer, systemic therapies are the main treatments. These may include:
- Some combination of these
Surgery and/or radiation therapy may be useful in certain situations .
Treatment can often shrink tumors , improve symptoms, and help women live longer. These cancers are considered incurable.
Progression While Being Treated With Hormone Therapy
For hormone receptor-positive cancers that were being treated with hormone therapy, switching to another type of hormone therapy sometimes helps. For example, if either letrozole or anastrozole were given, using exemestane, possibly with everolimus , may be an option. Another option might be using fulvestrant or an aromatase inhibitor , along with a CDK inhibitor. If the cancer has a PIK3CA mutation and has grown while on an aromatase inhibitor, fulvestrant with alpelisib might be considered. If the cancer is no longer responding to any hormone drugs, chemotherapy is usually the next step.
You May Like: Is There An Alternative To Chemo For Breast Cancer
About Those Lymph Nodes
A surgeon will usually take a lymph node biopsy to determine if the breast cancer has spread to the axillary lymph nodes. This is not always necessary, however. A lymph node biopsy is not usually necessary for DCIS. However, for invasive breast cancer, yes, they do need to check the lymph nodes.
Sometimes, doctors will perform a sentinel node biopsy, rather than a full lymph node excisional biopsy if the concerns about cancer spread are minimal. Cancer cells tend to appear first in the sentinel node before spreading to the other nodes, or other areas of the body.
Breast Cancer Progression Tends To Be Consistent And Predictable
There are many ways that breast cancer can develop but most of the time it starts in the breast ducts.
While cancer is still confined to the breast ducts, specialists refer to it as ductal carcinoma in situ, or DCIS. The good news is that if breast screening detects cancer at this in-situ stage, the chance of survival is close to 100%.
As cancer moves into the breast duct wall and finally begins to affect the surrounding breast tissue, specialists call it infiltrative or invasive breast cancer.
If treatment does not occur, breast cancer will usually spread to other areas of the body . Very often the first area that cancer usually spreads to is the lymph nodes in the underarm area .
Once cancer enters the lymphatic system, it can and usually does spread to other areas of the body. Sometimes this is called distant metastasis.
Not all breast cancers spread first to the axillary lymph nodes and then to the rest of the body. If the breast tumor occurs near the nipple, cancer may spread first to the internal mammary nodes beneath the sternum. And in some cases, the breast cancer can spread via the bloodstream without involving the lymphatic system.
You May Like: Can Birth Control Cause Breast Cancer
Symptoms Of Breast Cancer
Although a lump in the breast is a common symptom of breast cancer, not all breast cancers have obvious symptoms. For example, some lumps may be too small to be felt, but can be detected with a screening mammogram or other tests. There are also some benign conditions that can cause lumps in the breast, such as cysts and fibroadenomas .
Most breast changes are not caused by cancer. However, it is important to see your doctor if you notice any new lumps or other unusual breast changes as soon as possible. Early detection gives the best chance of survival if you are diagnosed with breast cancer.
Stem Cell Or Bone Marrow Transplant
A stem cell transplant, sometimes called bone marrow transplant, replaces damaged blood-forming cells with healthy ones. The procedure takes place following large-dose chemotherapy or radiation therapy to kill cancer cells and to stop your stem cells from producing cancerous cells.
Stem cell transplants can be used for several types of cancer, including multiple myeloma and some kinds of leukemia.
Read Also: Can You Have Breast Cancer At 21
Symptoms If Cancer Has Spread To The Lymph Nodes
Lymph nodes are part of a system of tubes and glands in the body that filters body fluids and fights infection.
The most common symptom if cancer has spread to the lymph nodes is that they feel hard or swollen. You might have any of the following symptoms if your cancer has spread to the lymph nodes:
- a lump or swelling under your armpit
- swelling in your arm or hand
- a lump or swelling in your breast bone or collar bone area
One of the first places breast cancer can spread to is the lymph nodes under the arm on the same side as the breast cancer. This is not a secondary cancer.
Where Does Breast Cancer Spread To First
Like all forms of cancer, breast cancer can potentially spread beyond the breast tissue where it initially developed to other areas of the body. In order for breast cancer metastasis to occur, cancerous cells must break away from the original tumor and attach themselves to the outer wall of a lymph vessel or a blood vessel. Then, the cancer must penetrate the vessel wall so that it can flow with the blood or lymphatic fluid to reach a lymph node or organ.
Don’t Miss: When You Have Breast Cancer Does It Hurt
What Are The Symptoms Of Metastatic Breast Cancer
Possible symptoms of metastatic breast cancer are listed below. Every womans experience of metastatic breast cancer is different. Symptoms depend on what part of the body is affected. They may develop over weeks or months.Its unlikely that a woman will have all of the symptoms listed below. Some symptoms may not be due to metastatic breast cancer at all.
Conventional Stages Of Breast Cancer Progression: 0 Through Iv
As mentioned, there are five basic stages of breast cancer with a couple of sub-categories.
Stage 0
This is a bit of an unclear term which specialists use to describe the development of abnormal cells that are not yet invasive breast cancer. Indeed physicians consider Ductal Carcinoma in situ, or DCIS, stage 0 breast cancer.
Here the malignant cancer cells are present in the lining of the breast d uct but have not yet invaded the surrounding breast tissue or spread beyond the duct. Almost 100% of DCIS is curable, but it obviously, does need treatment.
Early-stage breast cancer Stage 1
Stage 1 breast cancer is an early stage breast cancer. There is a considerable difference in medical opinion as to what exactly constitutes early stag e breast cancer. Also, how aggressive the treatment for Stage I breast cancer is another area of debate.
The standard definition of a stage 1 breast tumor is that a certain amount of breast cancer cells invade tissues and structures beyond the duct lining. However, no cancer cells have spread beyond the breast.
Furthermore, the tumor size is less than 2 cm in diameter. If physicians can detect and treat breast cancer before it grows beyond 2cm, the prognosis is very very good.
The average age of diagnosis of a stage 1 breast tumor is about 52 years old. In over 90% of cases, treatment tends to involve breast conservation surgery, followed by radiation therapy.
Chance of stage 1 cancer recurrence or spreading.
Recommended Reading: What Is Secondary Breast Cancer