How Is Breast Cancer Stage Determined
The breast cancer staging process helps doctors determine how much cancer there is and where its located. The higher the breast cancer stage number, the more advanced the disease.
Breast cancer staging is so important because it provides cancer care teams which include breast surgeons, oncologists, pathologists, radiologists and many others an agreed upon way to talk about the disease. This makes it easier for them to understand diagnoses and collaborate on treatment plans.
Infiltrating/invasive Lobular Breast Carcinoma
Infiltrating lobular carcinoma usually appears as a subtle thickening in the upper-outer breast quadrant.
As the name suggests, these tumours originate mostly in the breast lobules rather than the lining of the breast ducts.
Invasive lobular cancer is a less common type of breast cancer than invasive ductal cancer. This cancer accounts for about 10% of all invasive breast cancer cases.
Prognosis for infiltrating and invasive lobular breast carcinomas will naturally be influenced by tumor size, grade, stage and hormone receptor status..
However, lobular breast cancers, when positive for estrogen and progesterone receptors, tend to respond very well to hormone therapy.
The overall breast cancer survival rates for infiltrating lobular carcinoma, when matched by stage, are a little higher than for ductal carcinoma for the first 5 years.
Survival rates range from about 77% to 93%, but on average, the 5-year survival rate was estimated at about 90%.
90%2010
What Is The Significance Of The Reported Size Of The Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
If the entire tumor or area of DCIS is removed , the pathologist will say how big the DCIS is by measuring how long it is across , either by looking at it under the microscope or by gross examination of the tissue taken out at surgery. Another way to measure DCIS is to note the number of microscopic slides that contain DCIS. For example, the report may say that DCIS was found in 3 slides.
On needle biopsy, measurements of the area of DCIS are not often reported because this type of biopsy only samples a part of the tumor. Later, when the entire area of DCIS is removed , an accurate measurement can be done.
The larger the area of DCIS, the more likely it is to come back after surgery. Doctors use information about the size of the DCIS when recommending further treatments.
Also Check: How Do You Check For Male Breast Cancer
Is Inoperable Breast Cancer Still Treatable
Although stage 3C breast cancer is defined as either operable or inoperable, an inoperable diagnosis doesnt necessarily mean that it cant be treated.
The term inoperable may mean that all the cancer in the breast and surrounding tissue cant be removed through simple surgery. When breast cancer is removed, a rim of healthy tissue around the tumor, called a margin, is also removed.
For breast cancer to be successfully removed, there needs to be healthy tissue in all margins of the breast, from your clavicle down to a few inches below the breast mound.
It is possible for inoperable breast cancer to become operable following a treatment to shrink the cancer.
What Is The Prognosis For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Based on individual markers and prognostic factors, including the staging of your tumor, your physician will work to give you a prognosis. At Johns Hopkins Medicine, our team of breast cancer specialists is dedicated to developing cutting-edge techniques for surgery, breast reconstruction, chemotherapy, biologic targeted therapy, radiation therapy and other hormonal therapies. Our research allows us to make great strides forward for patients with breast cancer.
You May Like: Will My Breast Cancer Come Back
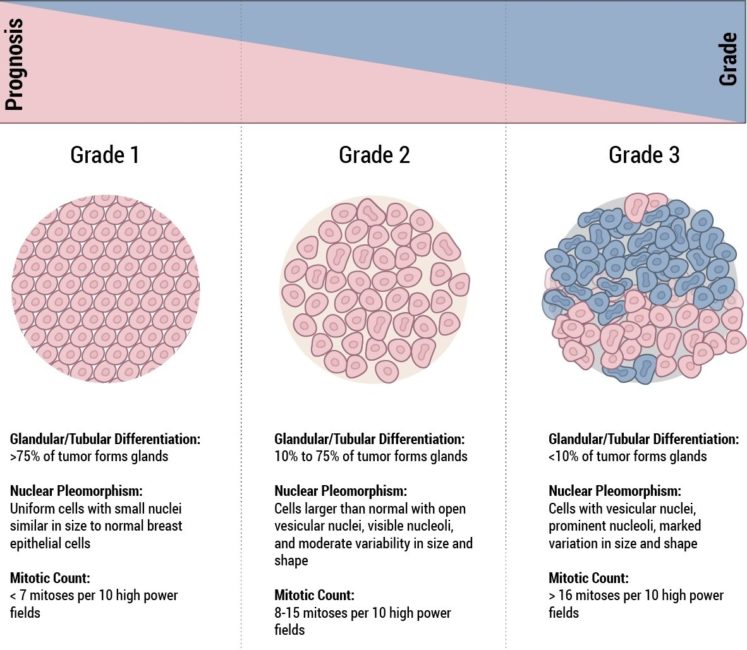
Grading Breast Cancer Cells
Three cancer cell features are studied and each is assigned a score. The scores are then added to get a number between 3 and 9 that;is used to get a grade of 1, 2, or 3, which is noted on your pathology report. Sometimes the terms well differentiated, moderately differentiated, and poorly differentiated are used to describe the grade instead of numbers:
- Grade 1;or well differentiated . The cells are slower-growing, and look more like normal breast tissue.
- Grade 2 or moderately differentiated . The cells are growing at a speed of and look like cells somewhere between grades 1 and 3.
- Grade 3;or poorly differentiated;. The cancer cells look very different from normal cells and will probably grow and spread faster.
Our information about pathology reports can help you understand details about your breast cancer.; ;
Stage 1 Breast Cancer
What is Stage 1 breast cancer?
Stage 1 breast cancers are still relatively small, and theyve either not yet spread to the lymph nodes or theres only been a tiny bit of spread in the sentinel lymph node which is where the cancer is most likely to spread first. There are two types of Stage 1 breast cancer:
- Stage 1A Stage 1A breast cancer means the tumor is no larger than 2 centimeters, and the cancer has not spread outside the breast or to lymph nodes.
- Stage 1B Stage 1B breast cancer means there are small groups of cancer cells in the lymph nodes. There may or may not be a tumor smaller than 2 centimeters in the breast.
What are the treatment options for Stage 1 breast cancer?
- Surgery Like with Stage 0, a lumpectomy and mastectomy are both options at this stage:
- Lumpectomy This kind of breast conservation surgery is a viable option when the cancerous cells are confined to one area of the breast.
- Mastectomy A mastectomy may be recommended if cancer is found throughout the breast.
Stage 1 breast cancer treatment timeline
You May Like: What Does Breast Cancer Cause
Tnm System For Breast Cancer
Doctors also group cancers by the letters T, N, or M. Each of those letters tells you something about your cancer.
âTâ stands for tumor, or the lump of cancer found in the breast itself. The higher the number assigned after it, the bigger or wider the mass.
âNâ stands for nodes, as in lymph nodes. These small filters are found throughout the body, and they’re especially dense in and around the breast. They’re meant to catch cancer cells before they travel to other parts of the body. Here, too, a number tells you whether the cancer has spread to lymph nodes near the breast and, if so, how many.
âMâ stands for metastasis. The cancer has spread beyond the breast and lymph nodes.
What Does It Mean If My Report On Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Mentions Estrogen Receptor Or Progesterone Receptor
ER and PR are special tests that the pathologist does that are important in predicting response of the DCIS to hormone therapy . Testing for ER is done for most cases of DCIS, but testing for PR is not typically needed. Results for ER and PR are reported separately and can be reported in different ways:
- Negative, weakly positive, positive
- Percent positive with something saying whether the staining is weak, moderate, or strong
Ask your doctor how these results will affect your treatment.
Don’t Miss: Is Stage 2 Breast Cancer Bad
Stage 4 Breast Cancer
What is Stage 4 breast cancer?
In Stage 4, the breast cancer has metastasized, which means the disease has spread to distant parts of your body. When breast cancer spreads, it can often invade the lungs, liver and bones, sometimes making its way to the brain or other organs.
What are the treatment options for Stage 4 breast cancer?
- Systemic therapies A combination of systemic therapies are often recommended at specific times during the treatment of Stages 1-3. But in stage four, these therapies are the primary treatment and include:
- Hormone therapy This type of therapy can help slow or stop the growth of cancerous cells.
- Chemotherapy This therapy can destroy cancerous cells throughout your body.
- Targeted drug therapies Like chemotherapy, these targeted drugs help reach cancer in distant areas of the body. But depending on your type of cancer, HER2 status and hormone receptor status, different targeted drugs can work alongside chemotherapy or even better than chemotherapy.
- Immunotherapy This therapy helps raise your bodys natural immune response to fight of the cancer.
How Quickly Do Breast Cancer Tumors Grow From Stage To Stage
Cancer cells divide and multiply quickly in such a way that as a tumor gets bigger, it divides and grows even faster. The average doubling time for breast cancer tumors is between 50 and 200 days. Breast cancer tumor growth rate is impacted by hormonal factors, such as hormone receptor status and HER2 status.
Recommended Reading: Does Red Wine Cause Breast Cancer
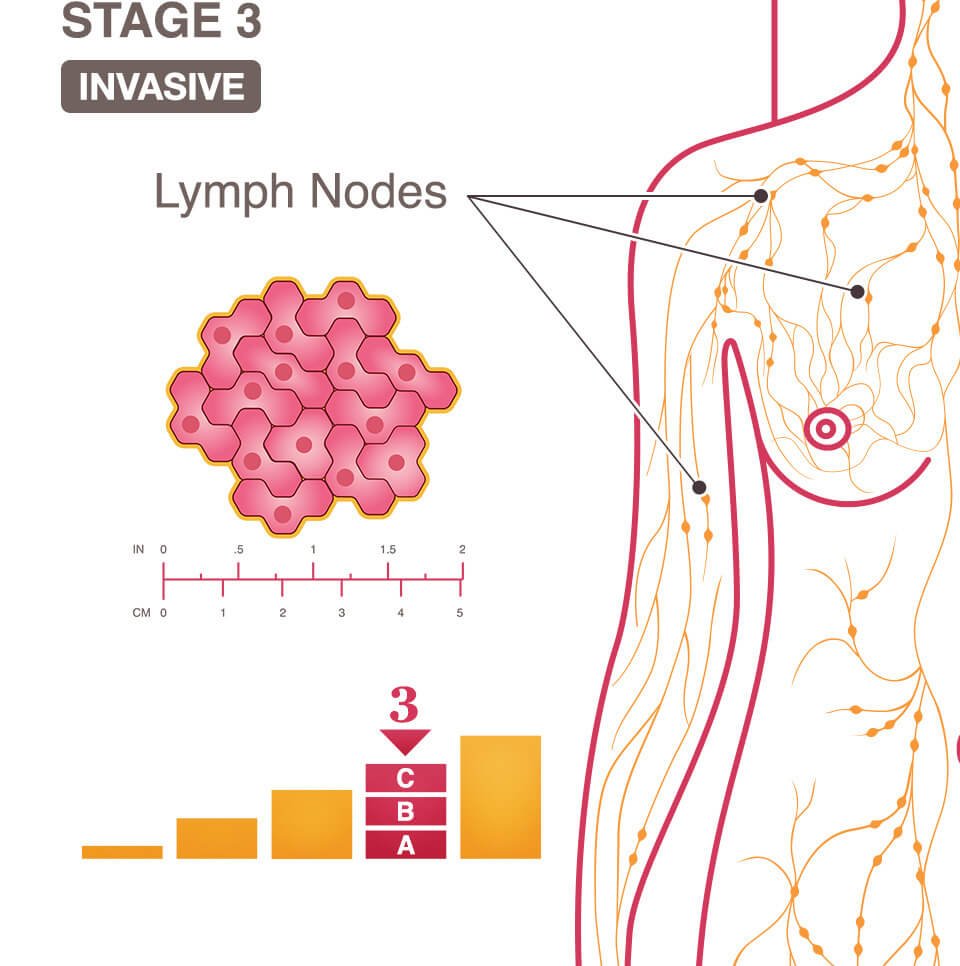
What Is The Life Expectancy For Stage 3 Breast Cancer
The life expectancy for people with breast cancer is improving, according to the American Cancer Society. It points out that current survival rates are based on people who were diagnosed and treated at least 5 years ago and treatments have advanced over that time.
Your life expectancy with stage 3 breast cancer depends on several factors, such as:
- your age
- the size of the tumors
You should talk with your doctor about how these factors may apply to you.
What Are The Risk Factors For Breast Cancer
Like many conditions, risk factors for breast cancer fall into the categories of things you can control and things that you cannot control. Risk factors affect your chances of getting a disease, but having a risk factor does not mean that you are guaranteed to get a certain disease.
Controllable risk factors for breast cancer
- Alcohol consumption. The risk of breast cancer increases with the amount of alcohol consumed. For instance, women who consume two or three alcoholic beverages daily have an approximately 20% higher risk of getting breast cancer than women who do not drink at all.
- Body weight. Being obese is a risk factor for breast cancer. It is important to eat a healthy diet and exercise regularly.
- Breast implants. Having silicone breast implants and resulting scar tissue make it harder to distinguish problems on regular mammograms. It is best to have a few more images to improve the examination. There is also a rare cancer called anaplastic large cell lymphoma that is associated with the implants.
- Choosing not to breastfeed. Not breastfeeding can raise the risk.
- Using hormone-based prescriptions. This includes using hormone replacement therapy during menopause for more than five years and taking certain types of birth control pills.
Non-controllable risk factors for breast cancer
Don’t Miss: How Treatable Is Breast Cancer
What Are The Signs Of Invasive Breast Cancer
Breast cancer may have no signs or symptoms, especially during the early stages. As the cancer grows, you may notice one or more of the following:
- A lump or thickening in or near the breast or in the underarm that continues after your monthly menstrual cycle
- A mass or lump, which may feel as small as a pea
- A change in the size, shape, or contour of the breast
- A blood-stained or clear fluid from the nipple
- A change in the feel or appearance of the skin on the breast or nipple — dimpled, puckered, scaly, or inflamed
- Redness of the skin on the breast or nipple
- A change in shape or position of the nipple
- An area that is distinctly different from any other area on either breast
- A marble-like hardened area under the skin
You may notice changes when you do a monthly breast self-exam. By doing a regular self-check of your breast, you can become familiar with the normal changes in your breasts.
Treatment Options For Stage 3 Cancer
In general, regimens for stage 3 cancers typically start with either surgery or treatment to shrink the tumor before surgery, such as chemotherapy, radiation, or a combination of both.
Stage 3 breast cancer;treatment: The first step is typically either chemotherapy or surgery.
Called neoadjuvant chemotherapy, because its given before other treatment, this may help shrink a tumor enough that breast-conserving surgery is possible. If it doesnt shrink enough, the patient may need a mastectomy; instead. HER2-positive cancers may also be treated with targeted drugs before surgery.
After surgery, depending on the type of breast cancer, your treatment may continue with radiation. Chemotherapy and/or targeted drugs may be part of your treatment plan after surgery as well.
Stage 3 lung cancer;treatment: This is highly dependent on how large the tumor is and which lymph nodes are affected. Generally, treatment begins with chemotherapy and/or radiation. You may have chemotherapy and radiation at the same time, or you may have them one after another. Surgery may follow this treatment if your care team thinks the remaining cancer may be successfully removed. After surgery, additional chemotherapy and/or radiation may be part of your treatment plan.
If chemotherapy, radiation or surgery arent appropriate options, immunotherapy;drugs may be.
Recommended Reading: Where To Buy Breast Cancer Merchandise
Inoperable Breast Cancer Is Often Still Treatable
Stage 3C breast cancer is divided into operable and inoperable stage 3C breast cancer. However, the term inoperable is not the same as untreatable.
If your physician uses the word inoperable, it may simply mean that a simple;surgery;at this time would not be enough to get rid of all the breast cancer that is within the breast and the tissue around the breast. There must be healthy tissue at all of the margins of the breast when it is removed. Keep in mind that the breast tissue goes beyond the breast mound it goes up to the clavicle and down to a few inches below the breast mound. There must also be tissue to close the chest wound after the surgery is performed.
Another treatment method may be used first to shrink the breast cancer as much as possible before surgery is considered.;
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Stages
Invasive ductal carcinoma stages provide physicians with a uniform way to describe how far a patients cancer may have spread beyond its original location in a milk duct. This information can be helpful when evaluating treatment options, but it is not a prognostic indicator in and of itself. Many factors can influence a patients outcome, so the best source of information for understanding a breast cancer prognosis is always a physician who is familiar with the patients case.
In general, breast cancer stages are established based on three key variables: the size of a tumor, the extent of lymph node involvement and whether the cancer has spread to other areas of the body. This information may be obtained through a combination of clinical examinations, imaging studies, blood tests, lymph node removal and tissue samples . If, based on the initial test results, a physician believes that the cancer may have spread to other parts of the body, further testing may be ordered, such as a bone scan, positron emission tomography scan or liver function test.
Invasive ductal carcinoma is usually described through a numeric scale ranging from 1 to 4 . Specifically, the invasive ductal carcinoma stages are:
If youd like to learn more about invasive ductal carcinoma stages and treatment options, call or complete a new patient registration form online.
- BROWSE
You May Like: How Do I Self Check For Breast Cancer
Additional Grading Criteria: A Composite Total Of Tubular Nuclear And Mitotic Index Assesments
As a grade of low, intermediate or high is obtained through a composite sum by assigning a score based on the nuclear assessment, a mitotic index assessment, and a tubular assessment.
The nuclear assessment is based on the nuclear size within the invasive cells. They are described from small to medium to large in size, as well as by their uniformity in size and shape.
The tubular assessment refers to an approximate, quantitative account of the amount of cell groupings which remain in their normal tubular shape. The smaller the percentage of tubular structures in comparison to other shapes, the higher the score. Other structures to appear may include solid trabecula, vacuolated single cells, alveolar nests, and solid sheets of cells.
The mitotic index refers to evident patterns of cell division.Mitosis is a process by which a cell separates into two genetically identical daughter cells. . So, the mitotic index is assessment of the abundance of these pairs of daughter cells, measured in the count per square millimeter. Mitoses are only counted in the invasive area of the lesion .
| Histologic Grade | |
| 11-19 = 2 | >20 = 3. |
Want To Learn More About Your Breast Cancer Treatment Options Were Here For You
Whether you just received your diagnosis or youre looking for new treatment options, were here to help.
If youve just been diagnosed with breast cancer, your next stop will be to meet with a nurse navigator or breast surgeon, depending on your initial diagnosis, and start building your treatment plan. We offer cancer care clinic locations across the Twin Cities and western Wisconsin, so get started by selecting a location to make an appointment at.
Also Check: How To Tell If Breast Cancer Has Metastasized
Breast Cancer Survival Rates Are Affected By Tumor Grade
Breast cancer grade refers to the size and shape of the malignant breast cancer cells. If the breast cancer cells look very different than normal breast tissue cells, and somewhat random in appearance, they are called poorly differentiated and described as high grade.
There are three main breast cancer grades and these are as follows:-
- Grade 1: The cancer cells are well differentiated and look the most like normal cells. These type of cancers tend to be slow-growing.
- Grade 2: These cancer cells are moderately differentiated. This means that the cells look less like normal cells and tend to grow faster.
- Grade 3: Poorly differentiated cells do not appear like normal cells at all and tend to be very fast growing. Hence, the affect on prognosis.
Microscopic Images of Ductal cell carcinoma in Situ Grades 1, 2 and 3
Higher grade breast cancers tend to have a poorer prognosis.
You will be able to find the Grade of your tumor on your pathology report.