Colon And Rectal Cancer And Polyps
For people at average risk for colorectal cancer, the American Cancer Society recommends starting regular screening at age 45. This can be done either with a sensitive test that looks for signs of cancer in a persons stool , or with an exam that looks at the colon and rectum . Talk to your health care provider about which tests might be good options for you, and to your insurance provider about your coverage. No matter which test you choose, the most important thing is to get screened.
If youre in good health, you should continue regular screening through age 75.
For people ages 76 through 85, talk with your health care provider about whether continuing to get screened is right for you. When deciding, take into account your own preferences, overall health, and past screening history.
People over 85 should no longer get colorectal cancer screening.
If you choose to be screened with a test other than colonoscopy, any abnormal test result needs to be followed up with a colonoscopy.
How Common Is It
Breast cancer isnt common in women under 40.
A womans risk of breast cancer throughout her 30s is just 1 in 227, or about 0.4 percent. By age 40 to 50, the risk is roughly 1 in 68, or about 1.5 percent. From age 60 to 70, the chance increases to 1 in 28, or 3.6 percent.
Out of all types of cancer, though, breast cancer is the most common among U.S. women. A womans risk of developing breast cancer during her lifetime is about 12 percent.
Can Women In Their 30s Develop Breast Cancer
Most cases of breast cancer are diagnosed in older women. The median age for breast cancer diagnosis between 2010 and 2014 was 62 years. While uncommon, it is possible for young women to develop breast cancer.
Fewer than 5% of the total breast cancer cases in the U.S. are diagnosed in women under the age of 40.
According to Breast Cancer Facts and Figures 2017-2018 from the American Cancer Society, a 20-year-old woman has a 0.1% 10-year probability of developing invasive breast cancer. A 30-year-old woman has a 0.5% risk of developing invasive breast cancer in the next 10 years.
These figures represent absolute risk rather than personal risk of developing breast cancer.
Many other factors contribute to your personal risk for breast cancer including weight, lifestyle choices, and having dense breasts. Some women are born with BRCA1 or BRCA 2 gene mutations. Women with a BRCA1 gene mutation are at a 72% risk of developing breast cancer by the age of 80. Women with a BRCA2 mutation have a 69% risk for breast cancer.
Also Check: Progression Of Metastatic Breast Cancer
Living With Breast Cancer
Being diagnosed with breast cancer can affect daily life in many ways, depending on what stage it’s at and the treatment you will have.
How people cope with the diagnosis and treatment varies from person to person. There are several forms of support available, if you need it.
Forms of support may include:
- family and friends, who can be a powerful support system
- communicating with other people in the same situation
- finding out as much as possible about your condition
- not trying to do too much or overexerting yourself
- making time for yourself
Find out more about living with breast cancer.
If You Are Age 55 Or Over:
Mammograms are recommended every other year. You can choose to continue to have them every year.
Clinical breast exams and self-exams are not recommended. But you should be familiar with your breasts and tell a health care provider right away if you notice any changes in how your breasts look or feel.
Recommended Reading: How To Tell If Cancer Has Metastasized
Take Control Of Your Health And Help Reduce Your Cancer Risk
- Stay away from all forms of tobacco.
- Get to and stay at a healthy weight.
- Get moving with regular physical activity.
- Eat healthy with plenty of fruits and vegetables.
- It’s best not to drink alcohol. If you do drink, have no more than 1 drink per day for women or 2 per day for men
- Protect your skin.
- Know yourself, your family history, and your risks.
- Get regular check-ups and cancer screening tests.
How Quickly Breast Cancer Spreads
Since the spread of breast cancer to other parts of the body is responsible for over 90 percent of deaths related to breast cancer, the question of how rapidly breast cancer spreads is very important.
Breast cancer usually spreads first to lymph nodes under the arm . Even with the involvement of lymph nodes, breast cancer is considered an early stage and is potentially curable with treatment.
When a cancer spreads to regions such as the bones, brain, lungs, or liver, however, it is considered stage IV, or metastatic breast cancer, and is no longer curable.
Most breast cancers have the potential to spread. Carcinoma in situ or stage 0 breast cancer has not yet spread beyond something known as the basement membrane. These tumors are considered non-invasive and are theoretically 100 percent curable with surgery.
All other stages of breast cancer are considered invasive and have the potential to spread. Spread to lymph nodes, even when early stage, is very important, as these tumors have essentially declared their intent to spread beyond the breasts.
Recommended Reading: Is Stage 3 Breast Cancer Curable
Risk Factors You Can Change
- Not being physically active. Women who are not physically active have a higher risk of getting breast cancer.
- Being overweight or obese after menopause. Older women who are overweight or obese have a higher risk of getting breast cancer than those at a normal weight.
- Taking hormones. Some forms of hormone replacement therapy taken during menopause can raise risk for breast cancer when taken for more than five years. Certain oral contraceptives also have been found to raise breast cancer risk.
- Reproductive history. Having the first pregnancy after age 30, not breastfeeding, and never having a full-term pregnancy can raise breast cancer risk.
- Drinking alcohol. Studies show that a womans risk for breast cancer increases with the more alcohol she drinks.
Research suggests that other factors such as smoking, being exposed to chemicals that can cause cancer, and changes in other hormones due to night shift working also may increase breast cancer risk.
Factors Associated With More Rapid Spread
Some types of breast cancer, as well as molecular subtypes, are more likely to spread and spread earlier than other types. Ductal carcinoma is more likely to spread than lobular carcinoma, among tumors that are the same size and stage.
While many breast cancers do not spread to lymph nodes until the tumor is at least 2 cm to 3 cm in diameter, some types may spread very early, even when a tumor is less than 1 cm in size.
You May Like: Will My Breast Cancer Come Back
What Are The Signs Of Breast Cancer
A woman who has breast cancer may have no problems, or she may find a painless lump in her breast. If women examine their breasts monthly, they can help find lumps or other changes that a doctor should examine.
Most breast lumps are not cancer, but all lumps should be checked out by a doctor to be sure. Breast lumps that are not cancer may be scar tissue or cysts or they can be due to normal breast changes associated with hormone changes or aging.
Girls who are beginning puberty might notice a lump underneath the nipple when their breasts start developing. Usually, this is a normal. You can ask a parent or your doctor about it to be sure.
P
Can A 12 Year Old Girl Get Breast Cancer
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Don’t Miss: Symptoms Of Breast Cancer Mayo Clinic
Noticing Changes To Your Breasts
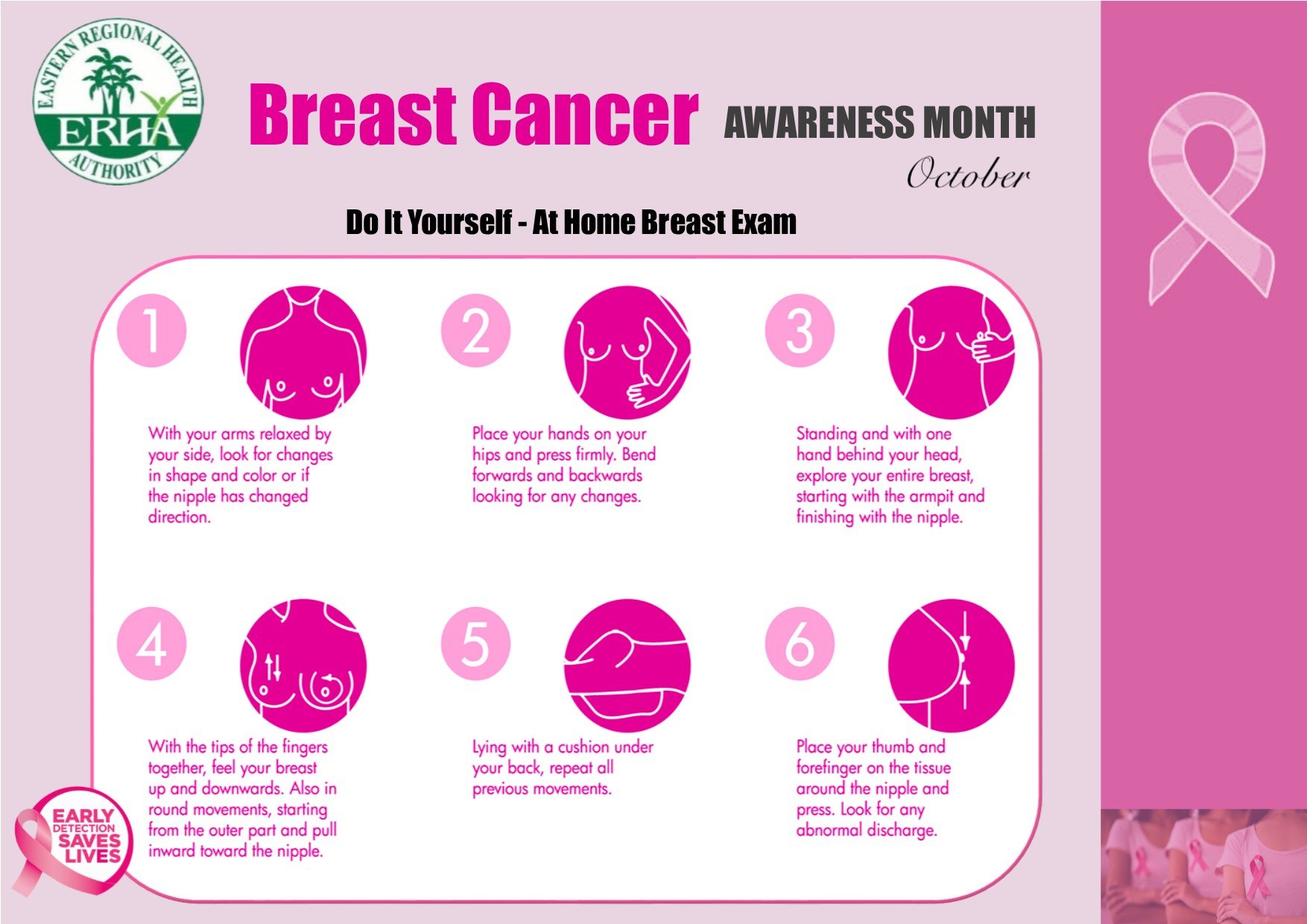
The ACS no longer recommends regular breast self-exams, since theres no evidence that they help reduce breast cancer deaths.
However, knowing how your breasts normally look and feel can help you identify any changes early on. Take notice of the following:
- lumps
- skin dimpling
- sores
Once youve established a baseline for how your breasts look and feel, itll be easier to identify any changes in the future.
If you do notice any changes, or if anything causes you worry, let your doctor know. They can determine if theres cause for concern.
Its common to see asymmetry in breast size, which can be normal.
A note on breast exams
The American Cancer Society no longer recommends regular clinical breast exams or breast self-exams. Theres little evidence that these exams help reduce deaths from breast cancer in women at average risk for the condition.
However, these exams may still be performed in certain scenarios.
For instance, some healthcare professionals may choose to perform clinical breast exams and counsel women on risk and early detection, in particular those at a higher-than-average risk for cancer. In addition, some women might prefer to use routine breast self-exams as a way to track possible changes to their breasts.
Understanding Your Risk Of Breast Cancer

Several breast cancer risk assessment tools have been developed to help a woman estimate her chance of developing breast cancer. The best studied is the Gail model, which is available on the National Cancer Institutes website at www.cancer.gov/bcrisktool. After you enter some personal and family information, including race/ethnicity, the tool provides you with a 5-year and lifetime estimate of the risk of developing invasive breast cancer. Because it only asks for information about breast cancer in first-degree family members and does not include their ages at diagnosis, the tool works best at estimating risk in women without a strong inherited breast cancer risk. For some women, other ways of determining the risk of breast cancer may work better. For example, women with a strong family history of breast cancer risk should consider talking to a genetic counselor.
It is important to talk with your doctor about how to estimate your personal risk of breast cancer and to discuss risk-reducing or prevention options .
Also Check: Hormone Receptor Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer
How Is Breast Cancer Treated
Treatment for breast cancer usually depends on the type of cancer and whether the cancer has spread outside of the breast to other parts of the body.
Here are some common treatments:
- lumpectomy , which removes the cancerous tumor from the breast. A woman usually has this surgery when the cancer is found early and when the lump is small and in only one part of the breast.
- mastectomy , which removes the whole breast. This surgery is done when cancer cells have spread through the breast or into other parts of the body. It’s a good way to remove all or most of the cancer, and can help prevent the cancer from spreading or coming back. Sometimes, a woman who has a mastectomy may choose to have an operation to reconstruct the breast, so her shape will be more like it was before.
- radiation therapy and chemotherapy, which are often used after lumpectomy or mastectomy to make sure that all the cancer cells are destroyed and do not grow back. Radiation therapy uses high-energy X-rays to kill the cancerous cells. Chemotherapy , or chemo, is special medicine that travels throughout the entire body and kills cancer cells.
Page 3
Breast Cancer Doubling Time
An easier way to envision how fast a breast cancer grows is by looking at the growth rate or volume doubling time. Tumor doubling time is the period of time that it takes for the tumor to double in size.
Since it would be unethical to leave a cancer untreated to see how rapidly it grew, doubling time is estimated in a number of ways. Looking at these estimates, however, doubling times have varied widely from study to study.
A 2019 study estimated doubling time by looking at serial ultrasounds between diagnosis and surgery. It was found that growth varied significantly based on the estrogen receptor status of the breast tumors.
During an average interval of 57 days, 36 percent of tumors did not change in size, while 64 percent grew. Of those tumors that increased in size, the average gain in volume was 34.5 percent.
Tumors that were triple negative had greater increases in volume and shorter doubling times than those that were estrogen receptor positive and HER2 negative tumors.
In a 2016 study that similarly looked at growth based on ultrasound between diagnosis and surgery over a 31 day period, tumors increased from 1.47 centimeters to 1.56 centimeters in diameter. Daily growth rate based on type was:
- 1.003 percent per day increase for triple negative tumors
- 0.859 percent per day increase for HER2 positive/estrogen receptor negative tumors
- 0.208 percent per day increase for estrogen receptor-positive tumors
Don’t Miss: Did Anne Hathaway Have Cancer
What Do Lumps In My Breast Mean
Many conditions can cause lumps in the breast, including cancer. But most breast lumps are caused by other medical conditions. The two most common causes of breast lumps are fibrocystic breast condition and cysts. Fibrocystic condition causes noncancerous changes in the breast that can make them lumpy, tender, and sore. Cysts are small fluid-filled sacs that can develop in the breast.
Links with this icon indicate that you are leaving the CDC website.
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website’s privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance on other federal or private website.
Questions To Ask The Doctor
- Do you know the stage of the cancer?
- If not, how and when will you find out the stage of the cancer?
- Would you explain to me what the stage means in my case?
- Based on the stage of the cancer, how long do you think Ill live?
- Do you know if my cancer has any of these proteins: estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, or the HER2 protein?
- What does it mean if my cancer has any of these proteins?
- What will happen next?
There are many ways to treat breast cancer.
Surgery and radiation are used to treat cancer in a specific part of the body . They do not affect the rest of the body.
Chemotherapy, hormone treatment, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy drugs go through the whole body. They can reach cancer cells almost anywhere in the body.
Doctors often use more than one treatment for breast cancer. The treatment plan thats best for you will depend on:
- The cancer’s stage and grade
- If the cancer has specific proteins, like the HER2 protein or hormone receptors
- The chance that a type of treatment will cure the cancer or help in some way
- Your age
- Other health problems you have
- Your feelings about the treatment and the side effects that come with it
Read Also: How To Cure Breast Cancer With Baking Soda
Breast Cancer Statistics In Young Adults
Although breast cancer in young adults is rare, more than 250,000 living in the United States today were diagnosed under age 40. In young adults, breast cancer tends to be diagnosed in its later stages. It also tends to be more aggressive. Young adults have a higher mortality rate. As well as a higher risk of metastatic recurrence .
Cancers Linked To Radiation Treatment
Lung cancer: The risk of lung cancer is higher in women who had radiation therapy after a mastectomy as part of their treatment. The risk is even higher in women who smoke. The risk does not seem to be increased in women who have radiation therapy to the breast after a lumpectomy.
Sarcoma: Radiation therapy to the breast also increases the risk of sarcomas of blood vessels , bone , and other connective tissues in areas that were treated. Overall, this risk is low.
Certain blood cancers: Breast radiation is linked to a higher risk of leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome . Overall, though, this risk is low.
Read Also: How Likely Am I To Get Breast Cancer
How Long Does It Take For Stage 1 Breast Cancer To Develop Into Stage 2
It is not possible to determine exactly how long it will take for newly diagnosed breast cancer to progress from stage 1 to stage 2. It can happen within months if it is an aggressive high-grade tumor, or it can take longer. It’s important to know that stage 1 breast cancer could have already been present for a while before being detected, so it may progress quickly.
How Quickly Breast Cancer Develops

You may have heard remarks that cancer has been present for five years before it is diagnosed, and this may sometimes be true.
The actual time it takes for breast cancer to grow from a single cancer cell to a cancerous tumor is unknown, as estimates based on doubling time assume that this is constant throughout the duration of tumor growth.
If doubling time were constant, cancer with a doubling time of 200 days would take 20 years to develop into a detectable tumor, and a doubling time of 100 days would take 10 years to be evident on exam.
In contrast, a breast tumor with a doubling time of 20 days would take only 2 years to develop.
Since the majority of studies have found the average doubling time to be between 50 days and 200 days, it’s likely that most breast cancers that are diagnosed began at least 5 years earlier .
Also Check: What Are The Chances Of Getting Breast Cancer Twice