Precancer Or Noninvasive Cancer
There is some debate over whether to consider DCIS precancer or noninvasive cancer. Generally, DCIS is considered noninvasive cancer, while lobular carcinoma is considered a precancerous condition, also called lobular neoplasia.
Learning that your condition is precancerous may make you worry that it will inevitably progress to cancer. This is not always the case, however, precancerous conditions like LCIS should be monitored closely.
Insurance And Scheduling Problems
Some people find that the surgeon they’ve chosen under their insurance company isn’t available for longer than they would like to wait, or that it’s difficult to coordinate a surgeon and plastic surgeon on the same day in a reasonable amount of time. This can be more difficult some places than others. With the larger cancer centers, you may have a coordinator who will assist you in setting up appointments. In the community, you may need to do most of the legwork yourself.
Regardless, it’s important to be your own advocate. If you’re having difficulty, make sure to work with your insurance company. Sometimes they may cover a second or third tier provider if it’s the only option available for scheduling your surgery promptly . With some procedures, prior authorization is needed before scheduling can take place.
There are many breast cancer organizations that can assist you as well as help you make decisions. Support groups and online support communities are also an excellent option when it comes to questions and challenges along the way.
There are many options as well for those who are underinsured or uninsured, but again, it’s usually up to you to do the legwork. Programs such as the SAGE program are available, as well as many other assistance programs that can help with anything from transportation to childcare. Talking to a social worker at your cancer center can be invaluable in learning about your options.
Side Effects And Complications
All treatments have some side effects that range from mild to severe. Most clear up when treatment ends, but there can be some lasting complications.
Its important to tell your oncologist about all symptoms, even if they seem minor. Your healthcare team will work with you to ease side effects and deal with complications.
Recommended Reading: 3 Cm Tumor In Breast
Surgery For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Breast cancer treatment has evolved to offer patients more options. In addition to removing breast cancer, new aesthetic surgical approaches can enhance well-being and lessen the emotional impact of losing all or part of a breast to cancer. Comprehensive breast centers with coordinated teams of oncologic and plastic surgery practitioners can offer a wider array of options.
Surgery for IDC may include one of these procedures:
- Lumpectomy is removal of part of the breast. It is also known as breast-conserving surgery. Lumpectomy may be followed by radiation treatments to treat any remaining cancer cells.
- Mastectomy is removal of the breast. Mastectomy is a treatment for patients with multiple, very aggressive, or large invasive ductal tumors. It can be followed by breast reconstruction.
Grading Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
DCIS is also graded on how abnormal the cancer cells look and has a similar grading system to that used for invasive breast cancer .
- Grade 1 or low grade DCIS. The cells are growing slower, and look more like normal breast cells. These cells tend to have estrogen and progesterone receptors .
- Grade 2 or intermediate grade. The cells are growing at a speed of and look like cells somewhere between grades 1 and 3.
- Grade 3 or high grade. The cancer cells look very different from normal cells and are growing faster. These cells tend not to have estrogen and progesterone receptors . High grade DCIS is often more likely to turn into invasive breast cancer.
Necrosis is also noted. If there is necrosis, it means the tumor is growing quickly. The term comedo necrosis may be used if a breast duct is filled with dead and dying cells. Comedo necrosis is often linked to a high grade of DCIS and has a higher chance of developing into invasive breast cancer.
Don’t Miss: What Is Stage 3a Cancer
Diagnosis Of Invasive Lobular Carcinoma
The earlier youre diagnosed with ILC and start treatment, the better your outlook. As with other types of cancer, early stages of ILC are likely to be treated more easily with fewer complications. This typically but not always leads to a complete recovery and low recurrence rates.
But compared with the much more common IDC, early diagnosis of ILC can be a challenge. Thats because the growth and spread patterns of ILC are more difficult to detect on routine mammograms and breast exams. ILC tumors are likely to have multiple origins, and they grow in single-file lines rather than a lump.
The first step in a diagnosis of ILC is a breast examination. Your doctor will feel your breast for a thickening or hardening of the tissue. Theyll also look for any swelling in the lymph nodes under your arms or around your collarbone.
Other diagnostic tests may include:
What Are The Symptoms Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Like other breast cancers, IDC may present as a lump that you or your doctor can feel on a breast exam. But in many cases, at first, there may be no symptoms, Wright says.
That is why it is important to have screening mammograms to detect breast cancers such as invasive ductal carcinoma. A mammogram may detect a lump that is too small for you to feel, or suspicious calcifications in the breast, either of which will lead to further testing.
According to Wright, the following are possible signs of invasive ductal carcinoma and other breast cancers. If you notice any of these, you should contact your doctor right away for further evaluation:
- Lump in the breast
- Nipple discharge, other than breast milk
- Scaly or flaky skin on the nipple or an ulceration on the skin of the breast or nipple. These can be signs of Pagets disease, a different kind of breast cancer that can occur along with IDC.
- Lumps in the underarm area
- Changes in the appearance of the nipple or breast that are different from your normal monthly changes
Read Also: What Are The Symptoms Of Stage 1 Breast Cancer
What Is Stage 1 Breast Cancer
This breast cancer is the earliest stage of invasive breast cancer. In stage 1, the tumor measures up to 2 cm and no lymph nodes are involved. At this stage, the cancer cells have spread beyond the original location and into the surrounding breast tissue.
Because a stage 1 tumor is small, it may be difficult to detect. However, breast self-exams and routine screening are always important and can often lead to early diagnosis, when the cancer is most treatable.Stage 1 breast cancer is divided into two categories:
Stage 1A: The tumor measures 2 cm or smaller and has not spread outside the breast.
Stage 1B: Small clusters of cancer cells measuring no more than 2 mm, are found in the lymph nodes, and either there is no tumor inside the breast, or the tumor is small, measuring 2 cm or less.
At stage 1, TNM designations help describe the extent of the disease. For example, there may or may not be cancer cells in the lymph nodes, and the size of the tumor may range from 1 cm to 2 cm. Most commonly, stage 1 breast cancer is described as:
- T: T1, T2, T3 or T4, depending on the size and/or extent of the primary tumor
- N0: Usually, cancer has not spread to the lymph nodes.
- M0: The disease has not spread to other sites in the body.
Stage 1 breast cancer survival rate
The survival rate for stage 1A breast cancer may be slightly higher than for stage 1B. However, all women with stage 1 breast cancer are considered to have a good prognosis.
How Is Breast Cancer Diagnosed
During your regular physical examination, your doctor will take a thorough personal and family medical history. He or she will also perform and/or order one or more of the following:
- Breast examination: During the breast exam, the doctor will carefully feel the lump and the tissue around it. Breast cancer usually feels different than benign lumps.
- Digital mammography: An X-ray test of the breast can give important information about a breast lump. This is an X-ray image of the breast and is digitally recorded into a computer rather than on a film. This is generally the standard of care .
- Ultrasonography: This test uses sound waves to detect the character of a breast lump whether it is a fluid-filled cyst or a solid mass . This may be performed along with the mammogram.
Based on the results of these tests, your doctor may or may not request a biopsy to get a sample of the breast mass cells or tissue. Biopsies are performed using surgery or needles.
After the sample is removed, it is sent to a lab for testing. A pathologist a doctor who specializes in diagnosing abnormal tissue changes views the sample under a microscope and looks for abnormal cell shapes or growth patterns. When cancer is present, the pathologist can tell what kind of cancer it is and whether it has spread beyond the ducts or lobules .
Also Check: 4th Stage Breast Cancer Life Expectancy
Breast Cancer Survival Rates Are Affected By Tumor Grade
Breast cancer grade refers to the size and shape of the malignant breast cancer cells. If the breast cancer cells look very different than normal breast tissue cells, and somewhat random in appearance, they are called poorly differentiated and described as high grade.
There are three main breast cancer grades and these are as follows:-
- Grade 1: The cancer cells are well differentiated and look the most like normal cells. These type of cancers tend to be slow-growing.
- Grade 2: These cancer cells are moderately differentiated. This means that the cells look less like normal cells and tend to grow faster.
- Grade 3: Poorly differentiated cells do not appear like normal cells at all and tend to be very fast growing. Hence, the affect on prognosis.
Microscopic Images of Ductal cell carcinoma in Situ Grades 1, 2 and 3
Higher grade breast cancers tend to have a poorer prognosis.
You will be able to find the Grade of your tumor on your pathology report.
Oncogene Expression May Negatively Affect Breast Cancer Outcome
A relatively new addition to the discussion of breast cancer survival statistics and prognosis is oncogene expression.
An oncogene is a tiny fragment of genetic material which is carried in a chromosome and can cause normal cells to become malignant.
The oncogene HER-2, in particular, has been linked to more aggressive breast cancers.
Around one-third of all breast tumours produce the HER-2 oncogene, and these patients tend to have higher rates of recurrence and lower overall breast cancer survival rates.
According to a 2013 Canadian scientific study, the overall 5-year survival rate of HER-2 positive breast cancer is 88.6%. Furthermore, the relapse-free survival rate for 5 years is 79.4%.
Read Also: Is Breast Cancer Curable At Stage 3
How Treatment Can Impact Survival Of Early Stage Breast Cancer
In most cases, the earlier breast cancer is first diagnosed and treated, the better the chance of survival. Cancer cells often become more difficult to treat and may develop drug resistance once they spread. The aim of treatment for Stage 1 and 2 breast cancer is to remove the breast cancer, and any other cancer cells that remain in the breast, armpit or other parts of the body but cannot be detected. Having treatment at this stage can also reduce the risk of the cancer coming back.
Read more:
Nonsurgical Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Treatment

Radiation. Radiation therapy might be part of your treatment plan if you are undergoing a lumpectomy. Studies show that lumpectomy followed by radiation can be as effective in treating IDC as mastectomy. We dont usually treat patients with radiation after a mastectomy unless theres some cancer in the lymph nodes, Wright says.
Chemotherapy. Deciding on whether to treat invasive ductal breast cancer with chemotherapy, or chemo, depends on features of the tumor cells themselves their genes and proteins. The more the doctor can learn about the characteristics of the cancer cells, the easier it is to determine what type of chemotherapy is likely to be effective.
Hormone therapy. Breast cancers with positive hormone receptors can be treated with estrogen or progesterone. These medications come in pill form, and may be prescribed for several years.
Biologic therapy. This approach uses antibodies or small molecule drugs to activate your bodys immune system to fight the invasive ductal cancer cells.
Also Check: Symptoms Of Stage 2 Breast Cancer
Bc Death By Ihc Subtype Grade And Ptn Status
To assess the independent contribution of each factor to breast cancer death, we stratified by all three variables IHC subtype, grade and pTN status in models adjusted for age, year and surgery type . Among ER+ subtypes, an increasing grade was associated with increased mortality in all subtypes and levels of pTN status. Larger tumour size and positive nodal status were consistently associated with increased mortality in all ER+ subtypes and levels of grade, and larger size was associated with increased mortality also among node-negative tumours . Among small tumours with no nodal spread, ER+PRHER2 subtype of grade III was associated with a particularly high mortality and of similar magnitude to TNBC grade III tumours . Women with larger tumours and any nodal spread had the highest mortality although numbers were low for this group. Among ER subtypes, high-grade tumours were associated with higher mortality than intermediate-grade tumours for pT1pN0 tumours, while for other pTN status the mortality rates were similarly elevated for intermediate- and high-grade tumours.
Table 2 Adjusted hazard ratios for breast cancer death by IHC subtypes, grade and pTN
Treatments For Stage 2 Breast Cancer
The following are treatment options for ductal carcinoma and lobular carcinoma. Doctors consider stage 2A to be early stage breast cancer. Stage 2B is considered to be locally advanced breast cancer. Your healthcare team will suggest treatments based on your needs and work with you to develop a treatment plan.
Don’t Miss: Early Symptoms Of Secondary Breast Cancer
Reasons To Wait A Short While
While information suggests having surgery within a few weeks and chemotherapy within a month is ideal, there are some very good reasons why you may wish to wait a few days or a few weeks to begin treatment.
Most surgeons and oncologists will reassure you that you have some time, though there are always exceptions to that general rule . Advantages of taking some time include:
Breast Cancer Doctor Discussion Guide
Get our printable guide for your next doctor’s appointment to help you ask the right questions.
Certain Breast Cancer Subtypes Have A Better Statistical Prognosis
In general, tubular, mucinous and medullary breast carcinomas have a better prognosis than the other sub-types.
The table below gives a very general approximation of the survival rates that may be associated with the different breast cancer subtypes.
However, please bear in mind that these figures are a rough generalization only and survival will always be determined by the individual characteristics of each breast cancer and each patient.
Nonetheless, the relative aggressiveness of the different breast cancer subtypes can be interpreted from the table.
and is almost always near 100% curable.)
| breast cancer sub-type |
Read Also: What Stage 3 Cancer Means
Does Breast Cancer Affect Women Of All Races Equally
All women, especially as they age, are at some risk for developing breast cancer. The risks for breast cancer in general arent evenly spread among ethnic groups, and the risk varies among ethnic groups for different types of breast cancer. Breast cancer mortality rates in the United States have declined by 40% since 1989, but disparities persist and are widening between non-Hispanic Black women and non-Hispanic white women.
Statistics show that, overall, non-Hispanic white women have a slightly higher chance of developing breast cancer than women of any other race/ethnicity. The incidence rate for non-Hispanic Black women is almost as high.
Non-Hispanic Black women in the U.S. have a 39% higher risk of dying from breast cancer at any age. They are twice as likely to get triple-negative breast cancer as white women. This type of cancer is especially aggressive and difficult to treat. However, it’s really among women with hormone positive disease where Black women have worse clinical outcomes despite comparable systemic therapy. Non-Hispanic Black women are less likely to receive standard treatments. Additionally, there is increasing data on discontinuation of adjuvant hormonal therapy by those who are poor and underinsured.
In women under the age of 45, breast cancer is found more often in non-Hispanic Black women than in non-Hispanic white women.
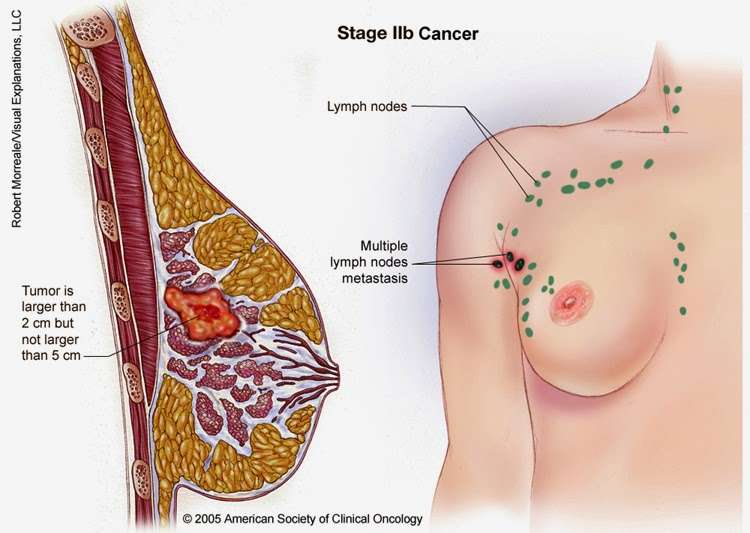
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Stages
Invasive ductal carcinoma stages provide physicians with a uniform way to describe how far a patients cancer may have spread beyond its original location in a milk duct. This information can be helpful when evaluating treatment options, but it is not a prognostic indicator in and of itself. Many factors can influence a patients outcome, so the best source of information for understanding a breast cancer prognosis is always a physician who is familiar with the patients case.
In general, breast cancer stages are established based on three key variables: the size of a tumor, the extent of lymph node involvement and whether the cancer has spread to other areas of the body. This information may be obtained through a combination of clinical examinations, imaging studies, blood tests, lymph node removal and tissue samples . If, based on the initial test results, a physician believes that the cancer may have spread to other parts of the body, further testing may be ordered, such as a bone scan, positron emission tomography scan or liver function test.
Invasive ductal carcinoma is usually described through a numeric scale ranging from 1 to 4 . Specifically, the invasive ductal carcinoma stages are:
If youd like to learn more about invasive ductal carcinoma stages and treatment options, call or complete a new patient registration form online.
- BROWSE
Also Check: Estrogen Receptive Breast Cancer Prognosis