Previous Breast Cancer Or Lump
You have a higher risk of developing breast cancer again if youve previously had breast cancer. The risk is also higher if youve had early non-invasive cancer cell changes in breast ducts. This could have been either in your other breast or in the same breast.
A benign breast lump doesnt mean you have breast cancer.
Certain changes in your breast tissue, such as cells growing abnormally in ducts , or abnormal cells inside your breast lobules , can make getting breast cancer more likely.
Reducing Your Risks For Breast Cancer
Women who breast-feed their children for the recommended length of time can reduce their risk of breast cancer by 25%. You can also reduce your risk by maintaining a low BMI and by getting exercise. You should also cut back on the amount of alcohol you drink. Birth control pills and some forms of hormone therapy after menopause can boost the odds. But the risk seems to go back to normal after you stop these medications. Good lifestyle choices can help survivors, too. Research says physical activity can lower the chances your cancer will return. And it’s a proven mood-booster, too.
26
What Are The Types Of Breast Cancer
The most common types of breast cancer are:
- Infiltrating ductal carcinoma. This cancer starts in the milk ducts of the breast. It then breaks through the wall of the duct and invades the surrounding tissue in the breast. This is the most common form of breast cancer, accounting for 80% of cases.
- Ductal carcinoma in situ is ductal carcinoma in its earliest stage, or precancerous . In situ refers to the fact that the cancer hasn’t spread beyond its point of origin. In this case, the disease is confined to the milk ducts and has not invaded nearby breast tissue. If untreated, ductal carcinoma in situ may become invasive cancer. It is almost always curable.
- Infiltrating lobular carcinoma. This cancer begins in the lobules of the breast where breast milk is produced, but has spread to surrounding tissues in the breast. It accounts for 10 to 15% of breast cancers. This cancer can be more difficult to diagnose with mammograms.
- Lobular carcinoma in situ is a marker for cancer that is only in the lobules of the breast. It isn’t a true cancer, but serves as a marker for the increased risk of developing breast cancer later, possibly in both or either breasts. Thus, it is important for women with lobular carcinoma in situ to have regular clinical breast exams and mammograms.
You May Like: Chemotherapy For Estrogen Positive Breast Cancer
Your Breast Looks Like It Has Been Bruised
If your breast is starting to have a bruised appearance with no other reason for the discoloration, the Mayo Clinic says it could be a sign of inflammatory breast cancersomething that can easily be confused with an infection. And for things you can do to improve your overall well-being, check out 100 Easy Ways to Be a Healthier Woman.
The Radiologist Decides Whether To Send A Breast Sample For Biopsy Or Not
It is usually up to the radiologist to determine if a mild or faintly suspicious finding on a breast X-ray is to require biopsy and histological evaluation with a pathologist. But there is a delicate balance for the radiologist between diagnosing too many things to be biopsied, and diagnosing too few. They have to self-tune in terms of their own thresholds in terms of image findings which actually turn out to be breast cancer and benign or insignificant findings.
Don’t Miss: What Is Stage 3a Breast Cancer
Can Exercise Help Reduce My Risk Of Developing Breast Cancer
Exercise is a big part of a healthy lifestyle. It can also be a useful way to reduce your risk of developing breast cancer in your postmenopausal years. Women often gain weight and body fat during menopause. People with higher amounts of body fat can be at a higher risk of breast cancer. However, by reducing your body fat through exercise, you may be able to lower your risk of developing breast cancer.
The general recommendation for regular exercise is about 150 minutes each week. This would mean that you work out for about 30 minutes, five days each week. However, doubling the amount of weekly exercise to 300 minutes can greatly benefit postmenopausal women. The longer duration of exercise allows for you to burn more fat and improve your heart and lung function.
The type of exercise you do can vary the main goal is get your heart rate up as you exercise. Its recommended that your heart rate is raised about 65 to 75% of your maximum heart rate during exercise. You can figure out your maximum heart rate by subtracting your current age from 220. If you are 65, for example, your maximum heart rate is 155.
Aerobic exercise is a great way to improve your heart and lung function, as well as burn fat. Some aerobic exercises you can try include:
- Walking.
- Dancing.
- Hiking.
Remember, there are many benefits to working more exercise into your weekly routine. Some benefits of aerobic exercise can include:
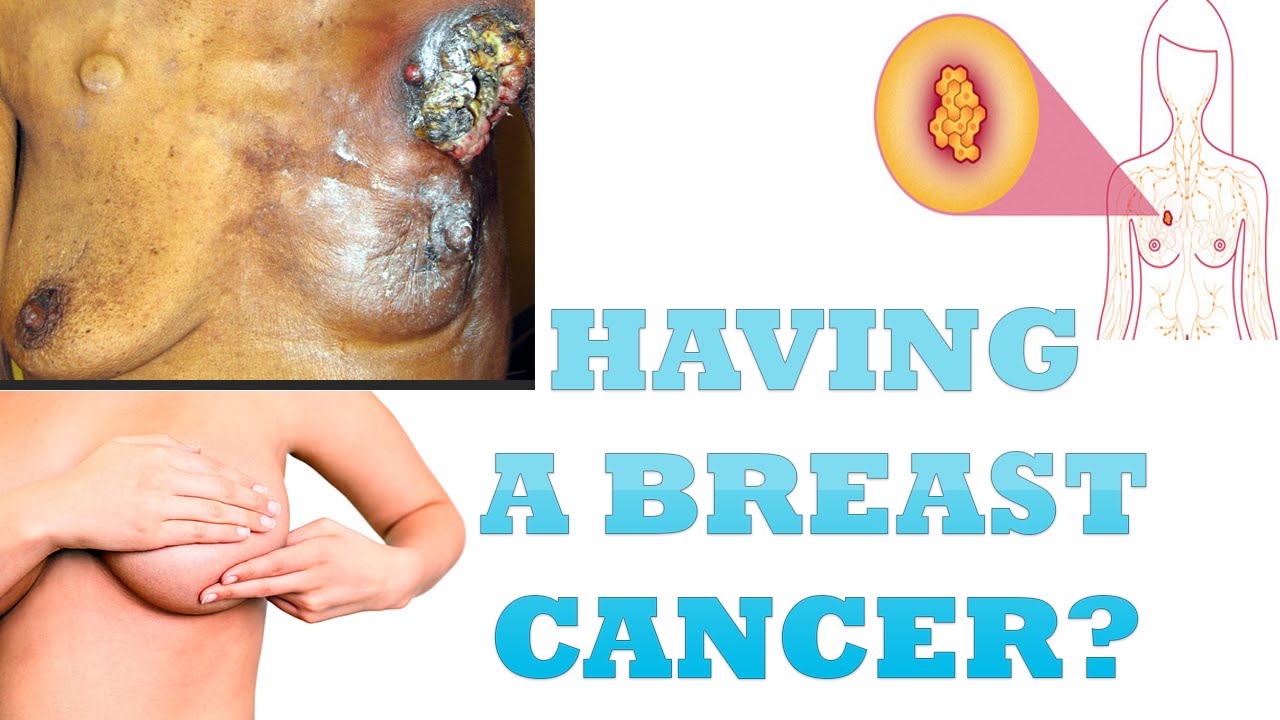
Changes To The Breast Or Chest Area
After breast-conserving surgery or a mastectomy, with or without reconstruction, be aware of any changes to either side, such as:
- swelling on your chest, in your armpit or around your collarbone
- a change in shape or size
- a change in skin texture, such as puckering or dimpling
- redness or a rash on or around the nipple or on the skin
- liquid that comes from the nipple without squeezing it
- the nipple has become inverted or looks different, for example changed its position or shape
- swelling in the arm or hand
- a lump or thickening that feels different
COVID-19 booster vaccinations
Some people report swelling in the armpit or to the lymph nodes under the arm after a COVID-19 booster vaccination. This seems to be more common with the Moderna booster vaccination. If you notice any swelling following your booster vaccination, it should disappear within about 10 days, if not, or you have any concerns, contact your GP or treatment team.
Recommended Reading: Red Mill Baking Soda Cancer
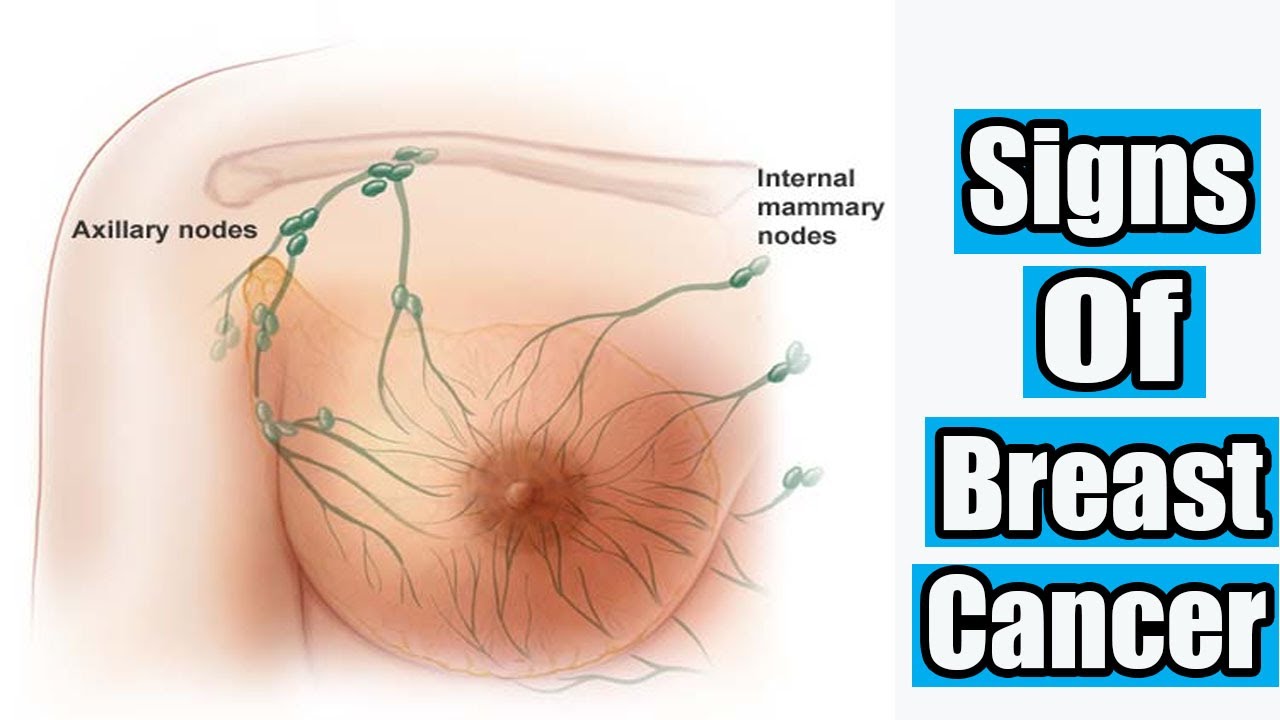
Your Armpit Lymph Nodes Are Swollen
Most people are always looking for bumps in their breasts, but don’t forget to check your lymph nodes for swelling, too. “Many patients who end up diagnosed with breast cancer that has spread to the lymph nodes have no symptoms in the breast, no changes in the structure of the breast, but they come in for a consult because they feel something under their arm,” says Alvarez. “This may mean that cancer from the breast has traveled to the lymph nodes, and now there is lymph node invasion.”
Breast Lumps Or Lumpiness
Many women find their breasts feel lumpy. Breast tissue naturally has a bumpy texture.
Some women have more lumpiness in their breasts than others. In most cases, this lumpiness is no cause to worry.
If the lumpiness can be felt throughout the breast and feels like your other breast, then its likely normal breast tissue.
Lumps that feel harder or different from the rest of the breast or that feel like a change should be checked. This type of lump may be a sign of breast cancer or a benign breast condition .
See a health care provider if you:
- Find a new lump that feels different from the rest of your breast
- Find a new lump that feels different from your other breast
- Feel something thats different from what you felt before
If youve had a benign lump in the past, dont assume a new lump will also be benign. The new lump may not be breast cancer, but its best to make sure.
Also Check: Stage 3 Advanced Breast Cancer
The Radiologist And Surgeon Work Together To Plan Surgeries
If it has been determined that some degree of surgery is required to treat the breast cancer, the radiologist plays a key role in planning the surgery. Additional imaging may be required, possibly an MRI scan. One of the advantages of MR images is the ability to more clearly see the extent of a given best cancer. Most importantly, the surgeon and radiologist want to gain a clear understanding of exactly where the malignant tissue is, and how best to make sure that all of it is removed.
Sometimes the wording of the ultrasound or mammogram report can be a little bit ambiguous, so the surgeon may ask the radiologist to clarify the exact location of the tumor. The surgeon also needs to know if the tumor is something like a small lump that can completely removed, or if it might be multifocal.
They might also ask the radiologist to clarify exactly where the edges of the tumor are. The surgeons need to decide if they can do a small procedure and remove a small amount of tissue, or whether they need to remove a lot of tissue. In other words, do they need to remove the entire breast or can it be conserved. These are important discussions between the surgeon and radiologist.
How A Breast Cancers Stage Is Determined
Your pathology report will include information that is used to calculate the stage of the breast cancer that is, whether it is limited to one area in the breast, or it has spread to healthy tissues inside the breast or to other parts of the body. Your doctor will begin to determine this during surgery to remove the cancer and look at one or more of the underarm lymph nodes, which is where breast cancer tends to travel first. He or she also may order additional blood tests or imaging tests if there is reason to believe the cancer might have spread beyond the breast.
The breast cancer staging system, called the TNM system, is overseen by the American Joint Committee on Cancer . The AJCC is a group of cancer experts who oversee how cancer is classified and communicated. This is to ensure that all doctors and treatment facilities are describing cancer in a uniform way so that the treatment results of all people can be compared and understood.
In the past, stage number was calculated based on just three clinical characteristics, T, N, and M:
- the size of the cancer tumor and whether or not it has grown into nearby tissue
- whether cancer is in the lymph nodes
- whether the cancer has spread to other parts of the body beyond the breast
Numbers or letters after T, N, and M give more details about each characteristic. Higher numbers mean the cancer is more advanced. Jump to more detailed information about the TNM system.
Jump to a specific breast cancer stage to learn more:
Recommended Reading: Malignant Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Causes Of Breast Cancer: How Did This Happen
When youre told that you have breast cancer, its natural to wonder what may have caused the disease. But no one knows the exact causes of breast cancer. Doctors seldom know why one woman develops breast cancer and another doesnt, and most women who have breast cancer will never be able to pinpoint an exact cause. What we do know is that breast cancer is always caused by damage to a cells DNA.
Tests To Determine Specific Types Of Treatment
You’ll also need tests that show whether the cancer will respond to specific types of treatment. The results of these tests can give your doctors a more complete picture of the type of cancer you have and how best to treat it. The types of test you could be offered are discussed below.
In some cases, breast cancer cells can be stimulated to grow by hormones that occur naturally in your body, such as oestrogen and progesterone.
If this is the case, the cancer may be treated by stopping the effects of the hormones, or by lowering the level of these hormones in your body. This is known as “hormone therapy”.
During a hormone receptor test, a sample of cancer cells will be taken from your breast and tested to see if they respond to either oestrogen or progesterone. If the hormone is able to attach to the cancer cells , they’re known as “hormone receptor positive”.
While hormones can encourage the growth of some types of breast cancer, other types are stimulated by a protein called human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 .
These types of cancer can be diagnosed using a HER2 test, and treated with medication to block the effects of HER2. This is known as “biological” or “targeted” therapy.
You May Like: Hormone Induced Cancer
When Is The Best Time Of Month To Do A Breast Self
A) At the start of your period
B) Mid-cycle
C) Right before your period is about to start
D) Its not advisable to do breast self-exams
Answer: B, Mid-cycle
Breast self-exams are a good way to get to know your breasts, Dr. Morris says, so that you can recognize any changes that develop. Mid-cycle, breasts are the least swollen and tender, making for an easier exam.
Stomach Upset Loss Of Appetite And Weight Loss
Cancer can cause nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation. Anxiety and lack of sleep can also upset the digestive system.
It can be more difficult to eat a healthy diet as these symptoms occur, setting up a vicious cycle. As women avoid certain foods because of stomach upset, the digestive system may lack the fiber and nutrients it needs to function optimally.
Over time, women may lose their appetite and have difficulty taking in the calories they need. Not eating regularly may cause significant weight loss and nutritional imbalances.
Don’t Miss: Stage 1 Grade 3 Breast Cancer
Breast Examination After Treatment For Breast Cancer
After surgery
The incision line may be thick, raised, red and possibly tender for several months after surgery. Remember to examine the entire incision line.
If there is redness in areas away from the scar, contact your physician. It is not unusual to experience brief discomforts and sensations in the breast or nipple area .
At first, you may not know how to interpret what you feel, but soon you will become familiar with what is now normal for you.
After breast reconstruction
Following breast reconstruction, breast examination for the reconstructed breast is done exactly the same way as for the natural breast. If an implant was used for the reconstruction, press firmly inward at the edges of the implant to feel the ribs beneath. If your own tissue was used for the reconstruction, understand that you may feel some numbness and tightness in your breast. In time, some feeling in your breasts may return.
After radiation therapy
After radiation therapy, you may notice some changes in the breast tissue. The breast may look red or sunburned and may become irritated or inflamed. Once therapy is stopped, the redness will disappear and the breast will become less inflamed or irritated. At times, the skin can become more inflamed for a few days after treatment and then gradually improve after a few weeks. The pores in the skin over the breast also may become larger than usual.
What to do
Also Check: Stage 3 A Cancer
Risk Factors For Breast Cancer
There are several risk factors that increase your chances of getting breast cancer. However, having any of these doesnt mean you will definitely develop the disease.
Some risk factors cant be avoided, such as family history. You can change other risk factors, such as quitting smoking, if you smoke. Risk factors for breast cancer include:
- Age. Your risk for developing breast cancer increases as you age. Most invasive breast cancers are found in women over age 55 years.
- Drinking alcohol. Alcohol use disorder raises your risk.
- Having dense breast tissue. Dense breast tissue makes mammograms hard to read. It also increases your risk for breast cancer.
- Gender. White women are
While there are risk factors you cant control, following a healthy lifestyle, getting regular screenings, and taking any preventive measures your doctor recommends can help reduce your risk for developing breast cancer.
You May Like: Positive Lymph Nodes Breast Cancer
Radiologists And Computer Aided Detection Of Breast Cancers
Quite a lot of research interest in breast cancer radiology these days centers around the use of computer aideddetection systems for breast cancers. Essentially, these programs operate with a simple artificial intelligence which compares measured parameters of the scanned breast tumor to a database of known diagnostic results for previously scanned tumors. Generally speaking, the computer aided detection system has proven to be useful as a second-opinion, but is not suitable to provide the sole interpretation of the breast X-ray or other image.
CAD systems are really not that much help to an experienced breast cancer radiologist, but can be quite beneficial for inexperienced radiologists, or perhaps in more remote settings where breast cancer may not be the primary area of expertise for the attending radiologist. Using computer aided detection systems has tended to result in a higher recall rate for screening patients. Computer-suggested interpretations can often psych-out a less experienced radiologist, resulting in many more biopsies than are really necessary. Incidentally, the rate of accurate radiologically detected breast cancer is usually around 91% or higher.
For further reading, I recommend visiting this page involving information on a multidisciplinary team approach to breast cancer treatment.
References
Invasive Breast Cancer Symptoms
Most breast cancers start in the ducts, or the tubes that carry milk to the nipple, or in the lobules, the little clusters of sacs where breast milk is made. Invasive breast cancer refers to breast cancer that spreads from the original site to other areas of the breast, the lymph nodes or elsewhere in the body. In these cancers that form in the ducts or lobules, invasive ductal carcinoma or invasive lobular carcinoma , the cancer spreads from the ducts or lobules to other tissue. Depending on the stage, you may notice symptoms.
Invasive breast cancer symptoms may include:
- A lump or mass in the breast
- Swelling of all or part of the breast, even if no lump is felt
- Skin irritation or dimpling
- A lump or swelling in the underarm lymph nodes
Recommended Reading: Honey And Baking Soda Cancer Treatment