Immunohistochemistry Criteria: Past Present And Future
The HER2 status assessment was establishment by The American Society of Clinical Oncology and the College of American Pathologists , with the publication of guidelines with recommendations for testing the level of HER2 protein overexpression by IHC and the HER2 gene amplification determined by ISH, both on FFPE breast tumor tissues. The first ASCO/CAP guideline was published in 2007 , and updated in 2013 and 2018 . In the last update, the experts refined some controversial criteria of the older guidelines and tried to systematize the testing algorithm for the unusual categories of HER2 ISH results . The results of these tests are graded semi-quantitatively as either 0 , 1+ , 2+ or 3+ by IHC, and classify as amplification , equivocal or negative by ISH. In all of these guidelines, when the HER2 status is negative by IHC and/or ISH, is not indicated the confirmation by an alternate assay. In contrast, the HER2 equivocal cases, by either HER2 IHC or HER2 ISH assays, must be analyzed with an secondary HER2 testing method, or on different tissue blocks with the same testing approach . The answer about which of the two methods is better for evaluating the HER2 status, continues to be unknown. Also, with the two latest updates, an important problem was added respecting the 2007 ASCO/CAP guidelines: more HER2 equivocal cases are diagnosed which an increase in reflex HER2 testing .
Table 3. 2018 ASCO/CAP summary recommendations .
Relative Survival Rates For Breast Cancer
The National Cancer Institute gives 5-year relative survival rates for breast cancer based on how far the disease had spread before a doctor found it.
- Localized : 99%
- Unknown stage: 55%
- All stages: 90%
While these numbers can give you a general idea, they are an average for women with any type of breast cancer. They arent specific to the HER2+ type. They also come from data that researchers collected from 2010 to 2016, so they dont reflect more recent treatment advances.
You May Like: How To Cure Breast Cancer
What Type Of Breast Cancer Do I Have
Breast cancers arent all the same. Doctors classify them in a number of different ways. The most basic place to start is where the cancer cells originate. Their origin is a key factor in whether or not your cancer may spread and helps dictate the kind of treatment youll get.
Most breast cancers 70% to 80% start in the milk ducts. Theyre known as infiltrating or invasive ductal carcinomas, meaning that theyve broken through the milk ducts wall and have proliferated into the breasts fatty tissue. Once there, its possible for the cancer cells to further spread to other parts of the body.
Another 10% of breast cancers start in the milk-producing glands, or lobules, and are called invasive lobular carcinomas. Theyre also capable of spreading.
Other rarer breast cancers may involve the nipple, the breasts connective tissue or the linings of blood vessels or lymph vessels.
Some breast cancers are non-invasive. They havent spread. Theyre contained within the milk ducts and are called ductal carcinoma in situ . Generally, the prognosis for patients with DCIS is very good, Dr. Abraham says.
Also Check: What Are The Side Effects Of Radiation After Breast Cancer
Recommended Reading: What Organs Does Breast Cancer Affect
What This Means For You
If youve been diagnosed with triple-negative breast cancer, this study offers some encouraging and interesting information. The results strongly suggest that triple-negative breast cancers are not all the same and that certain subtypes have better survival rates than hormone-receptor-positive breast cancer.
Determining the subtype of triple-negative breast cancer is not universally done. Still, many cancer centers do this type of testing. You may want to ask your doctor about this study, as well as whether subtype testing has been done as part of your pathology report and what it means for your prognosis and treatment.
Armed with the most complete information you can get, you and your doctor can make the best decisions for your unique situation.
What Is My Her2 Status
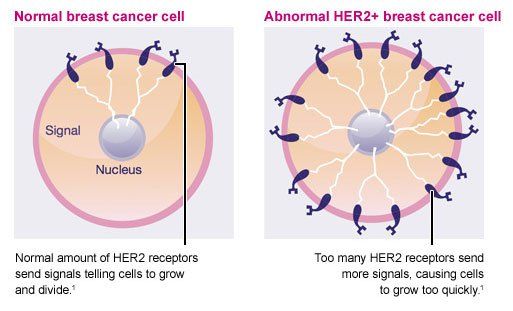
HER2 is another type of growth signal receptor which may be present on your breast cancer cells. About 25% of breast cancers are HER2-positive. HER2-positive cancers are a mix of good and bad news.
The bad news is the tumors tend to grow more aggressively than those without the HER2 receptor. The good news is that like ER/PR-positive cancers, medicines can switch the HER2 growth receptor off.
New drugs such as trastuzumab, pertuzumab, T-DM1 and lapatinib are extremely effective at this and have dramatically improved the prognosis for HER2-positive patients, Dr. Abraham says. Treatment outcomes are now as good as those with HER2-negative tumors.
But HER2-positive tumors bigger than half a centimeter or that have spread into the lymph nodes may require treatment with chemotherapy and one of the medicines specifically targeting the HER2 receptor, such as trastuzumab.
Dont Miss: What Are Common Treatments For Breast Cancer
Read Also: Signs Of Breast Cancer Returning
Survival Rates And Statistics
A relative survival rate helps give an idea of how long a person with a particular condition will live after receiving a diagnosis compared with those without the condition.
For example, if the 5-year relative survival rate is 70%, it means that a person with the condition is 70% as likely to live for 5 years as someone without the condition.
It is important to remember that these figures are estimates. A person can talk with a doctor about how their condition is likely to affect them.
Some factors affecting a personâs survival rate with breast cancer include:
- individual factors, such as the personâs age and overall health
- the stage of the cancer at diagnosis
- the treatment the person receives
HER2-positive cancers are than HER2-negative cancers. With treatment, however, the chances of survival are high, especially with an early diagnosis. In some cases, they may be higher than for HER2-negative breast cancer due to effective targeted treatment.
According to the , the likelihood of living for another 5 years with HER2-positive cancer, compared with a person who does not have breast cancer, is as follows. These statistics are based on figures for the years 2011â2017.
| Stage |
|---|
How Her2+ Breast Cancer Is Diagnosed
There are many steps in the process of diagnosing breast cancer.
If a person has a symptom that is concerning to them, such as a lump in their breast, they should discuss it with their healthcare provider. The healthcare provider will likely start by taking a medical history and performing a physical exam. This can help them determine what is causing the symptoms. The next step in the process is imaging.
Recommended Reading: Stage 3 Breast Cancer Prognosis
Blocking Her2 Slows Or Stops Some Types Of Breast Cancer
NCI-funded researcher Dennis Slamon, M.D., was among the many scientists searching for genes that can lead to cancer. In 1987, he and his colleagues discovered that the growth factor receptor gene HER2, which produces HER2 proteins, might be a good candidate.
At the same time, a team of NCI researchers led by Stuart Aaronson, M.D., were among the first to show that the HER2 protein could cause normal cells to grow uncontrollably like aggressive cancer cells.
Dr. Slamons team found that the HER2 protein is present at high levels in about 30 percent of breast cancers. They also discovered that high levels of HER2 are linked to a greater likelihood of metastasis and relapse and an overall decrease in patient survival. The group concluded that HER2 might play a role in the development and growth of breast cancer.
NCI-funded researcher Dennis J. Slamon, M.D., discovered the genetic link between HER2 and breast cancer.
This led researchers to a groundbreaking hypothesis: If HER2 could be blocked, the growth of HER2-positive breast cancer might be slowed.
One way to block the action of a protein is to use laboratory-made monoclonal antibodies that attach to a specific protein and disrupt its function. With NCI support, Dr. Slamon and colleagues from the University of Texas Health Sciences Center had a breakthrough. They showed that an antibody specific to HER2 could slow the growth of metastatic breast cancer cells and other types of cancer in a laboratory dish.
What Does Testing Involve
If a doctor confirms an unusual growth, they will take a biopsy. To collect a sample, they may perform one of the following procedures:
- Use a fine needle to remove a sample of breast cells or a liquid in fine-needle aspiration.
- Use a larger needle in a core needle biopsy.
- Carry out minor surgery as an outpatient procedure.
According to the American Cancer Society , a core needle biopsy is often the preferred option.
The doctor will send the tissue samples to a laboratory to test whether or not breast cancer is present. If it is, the pathologist will test to see if the cancer is HER2-positive.
The two main tests for determining whether or not HER2-positive cancer is present are the fluorescent in situ hybridization test and the immunohistochemistry test.
The FISH test looks for additional copies of the HER2 gene in breast cancer cells. It uses special labels that attach to the HER2 proteins that glow in the dark.
The IHC test uses a chemical dye to stain HER2 proteins and can determine how much HER2 protein is present in breast cancer cells.
Often, the pathologist will carry out the IHC test and then the FISH test. IHC testing is faster and less costly than FISH testing. However, if the results of the IHC test are unclear, a person will need a FISH test to determine whether or not a tumor is HER2-positive.
Recommended Reading: Did Anne Hathaway Have Cancer
Immunohistochemistry: Er Pr And Her2
Via the characterization of ER, PR, and HER2 status, we can divide BC in three phenotypes or entities. Hormone receptor-positive breast cancers are defined as positive by expression of ER and/or PR receptor equal to 1% or higher of invasive cancer cells . ER and PR receptors are expressed around 80 and 65% of breast cancers, respectively . Although estrogen receptor-positive tumors co-express PR in the majority of breast cancers, some cases are ER+/PR and less frequently, ER/PR+. The response to hormonal therapy seems to be major in breast tumors with positivity for ER and PR, with lower rates in ER+/PR and ER/PR+ tumors .
Even so, this current and basic classification of human breast tumors presents a number of important limitations. The main one is the variability in therapeutic response and clinical outcomes, even for tumors with similar clinical and pathological features. Secondly, this classification provides limited knowledge into the biology and the molecular pathways that divide the BC in distinct subtypes and stages, stepping away from the personalized treatment paradigm.
What Are The Side Effects Of Treatment
Generally, the side effects of hormonal therapies tend to be mild and fairly well tolerated, says Brufsky. The most common side effects are menopausal symptoms , achiness in the joints and bones, and fatigue. AIs can cause some bone loss , but that can typically be well controlled with bone-modifying medications, Brufsky notes. CDK4/6 inhibitors may cause low white blood cell counts as well as some nausea and diarrhea.
Read Also: Signs And Symptoms Of Breast Cancer Stage 1
Hormone Receptor Status And Prognosis
Hormone receptor status is related to the risk of breast cancer recurrence.
Hormone receptor-positive tumors have a slightly lower risk of breast cancer recurrence than hormone receptor-negative tumors in the first 5 years after diagnosis .
After 5 years, this difference begins to decrease and over time, goes away .
|
For a summary of research studies on hormone receptor status and survival, visit the Breast Cancer Research Studies section. |
What Is The Treatment For Her2
Treatment for breast cancers is individualized depending on the type, grade, stage, HR and HER2 status, and any gene mutations. Treatment also depends on the age, overall health and whether the woman is menopausal or not. Treatment may be more complicated if the woman is pregnant. Patients also have the option of enrolling for clinical trials for new treatments.
Read Also: Stage 3a Cancer Lymph Nodes
What Clinical Trials Are Available For Women With Inflammatory Breast Cancer
NCI sponsors clinical trials of new treatments for all types of cancer, as well as trials that test better ways to use existing treatments. Participation in clinical trials is an option for many patients with inflammatory breast cancer, and all patients with this disease are encouraged to consider treatment in a clinical trial.
Descriptions of ongoing clinical trials for individuals with inflammatory breast cancer can be accessed by searching NCIs list of cancer clinical trials. NCIs list of cancer clinical trials includes all NCI-supported clinical trials that are taking place across the United States and Canada, including the NIH Clinical Center in Bethesda, MD. For information about how to search the list, see Help Finding NCI-Supported Clinical Trials.
People interested in taking part in a clinical trial should talk with their doctor. Information about clinical trials is available from NCIs Cancer Information Service at 18004CANCER and in the NCI booklet Taking Part in Cancer Treatment Research Studies. Additional information about clinical trials is available online.
Selected References
Anderson WF, Schairer C, Chen BE, Hance KW, Levine PH. Epidemiology of inflammatory breast cancer . Breast Diseases 2005 22:9-23.
Inform Her2 Dual Ish Test
This test is also conducted for identifying the presence of excessive copies of the HER2 gene in the breast cancer cells. The test report of the Inform HER2 Dual ISH test can help to determine the HER2 gene amplification or no HER2 gene amplification .
All the above-mentioned tests are conducted for the purpose of identifying the HER2 gene amplification or HER2 protein over-expression which is indicated by HER2-positive in the pathology report. The finding of this assists in determining HER2-positive Breast cancer. The aggressive nature of the HER2-positive breast cancers have a faster growth tendency and also spread faster and tend to relapse, which are not similar in HER2-negative breast cancers.
Different research results showed that the test report is not always correct to determine the status of HER2 protein due to the variation of the laboratory markers to classify positive and negative HER2 status. The pathologist who study the test report also follows different criteria to fix on whether the results are positive or negative. Most of the time confusion is created when the test report showed borderline and that cannot provide strong HER2-positive or HER2-negative. This lacuna needs to keep in mind during treating a patient with breast cancer, as Inaccurate HER2 test results may cause ineffective treatment prognosis. Therefore, repetition of test or alternative test must be performed to get an accurate result.
You May Like: Malignant Breast Cancer Survival Rate
What Do The Test Results Mean
The results of HER2 testing will guide you and your cancer care team in making the best treatment decisions.
It is not clear if one test is more accurate than the other, but FISH is more expensive and takes longer to get the results. Often the IHC test is done first.
- If the IHC result is 0 or 1+, the cancer is considered HER2-negative. These cancers do not respond to treatment with drugs that target HER2.
- If the IHC result is 3+, the cancer is HER2-positive. These cancers are usually treated with drugs that target HER2.
- If the IHC result is 2+, the HER2 status of the tumor is not clear and is called “equivocal.” This means that the HER2 status needs to be tested with FISH to clarify the result.
Triple-negative breast tumors dont have too much HER2 and also dont have estrogen or progesterone receptors. They are HER2-, ER-, and PR-negative. Hormone therapy and drugs that target HER2 are not helpful in treating these cancers. See Triple-negative Breast Cancer to learn more.
Triple-positive breast tumorsare HER2-, ER-, and PR-positive. These cancers are treated with hormone drugs as well as drugs that target HER2.
Our team is made up of doctors and oncology certified nurses with deep knowledge of cancer care as well as journalists, editors, and translators with extensive experience in medical writing.
Last Revised: November 8, 2021
Breast Cancer Cell Lines
Part of the current knowledge on breast carcinomas is based on in vivo and in vitro studies performed with cell lines derived from breast cancers. These provide an unlimited source of homogenous self-replicating material, free of contaminating stromal cells, and often easily cultured in simple standard media. The first breast cancer cell line described, BT-20, was established in 1958. Since then, and despite sustained work in this area, the number of permanent lines obtained has been strikingly low . Indeed, attempts to culture breast cancer cell lines from primary tumors have been largely unsuccessful. This poor efficiency was often due to technical difficulties associated with the extraction of viable tumor cells from their surrounding stroma. Most of the available breast cancer cell lines issued from metastatic tumors, mainly from pleural effusions. Effusions provided generally large numbers of dissociated, viable tumor cells with little or no contamination by fibroblasts and other tumor stroma cells.Many of the currently used BCC lines were established in the late 1970s. A very few of them, namely MCF-7, T-47D, MDA-MB-231 and SK-BR-3, account for more than two-thirds of all abstracts reporting studies on mentioned breast cancer cell lines, as concluded from a Medline-based survey.
Metabolic markers
Recommended Reading: Define Stage 3 Cancer
Tell Us About Your Research And The Novelty It Brings
M-A.G.: We observed a known phenomenon called hypoxia, present in HER2-positive cancers. Hypoxia is manifested by a lack of oxygen caused by the rapid growth of the tumour. This phenomenon leads to the production of metastases, weakening of the immune response against the tumour, and provoking resistance to treatment. In short, hypoxia makes tumours more aggressive, while reducing the body’s ability to defend itself.
In a preclinical model, our team demonstrated that the presence of a protein called AXL was crucial in hypoxia. By blocking the action of this protein in the tumour, we observed blood vessel recovery and a revitalization of the immune system surrounding the tumour. This in turn reduced the tumour’s ability to metastasize.
It is as if we had succeeded, on the one hand, in breaking down the protective walls of the tumour against the immune system, thus making it more vulnerable to immunological treatments, and, on the other hand, in preventing the tumour from moving elsewhere.