Is There A Genetic Test For Breast Cancer
If you suspect you have a genetic risk for breast cancer, such as BRCA mutation, you may decide to get tested.
The genetic test is simple a blood test covered by most insurance companies. It can take a couple weeks to get results. Ninan says, For those who have a family member who has tested positive for an abnormal breast cancer gene, the lab can look for that specific mutation. In these cases, results may take one week.
Who Should Be Tested For Brca
While BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene mutations may increase your odds of developing breast cancer, your odds of having either mutation are pretty small. An estimated 0.25% of the general population carries a mutated BRCA gene, or about one out of every 400 people.
For some people, though, the chances of having a BRCA gene mutation are much higher. Genes are inherited, which is why knowing your family history is important when determining breast cancer risks. If one of your parents has a BRCA mutation, you have a 50% chance of inheriting the mutated gene.
Odds can also vary depending on a persons ethnicity. For example, people of Ashkenazi Jewish descent have a 2.5% chance of inheriting a BRCA mutation, or about 10 times the rate of the general population.
Because the overall odds are so low, most experts recommend that only people with a heightened risk get tested for BRCA mutations. Likewise, insurance companies often only cover genetic counseling and testing for individuals who are at high risk. A person could be considered at high risk for BRCA mutations if they have a family history of:
There are also other gene mutations besides BRCA that could increase the risk of breast cancer. The most prominent of these is PALB2. As with BRCA1 and BRCA2, testing for other genetic mutations is recommended only if you are at high risk for that particular gene.
Risk Of Breast Cancer By Age
A womans risk of developing breast cancer based on her age is as follows:
- 30 years old: 0.49% or 1 in 204
- 40 years old: 1.55% or 1 in 65
- 50 years old: 2.4% or 1 in 42
- 60 years old: 3.54% or 1 in 28
- 70 years old: 4.09% or 1 in 24
About 5% of breast cancer cases occur in women under 40 years old. It may be more difficult to diagnose breast cancer in young women because their breast tissue is denser than that of older women. Young women and their doctors may also be more likely to ignore a breast lump because of their low risk.
Breast cancer that occurs in young women tends to be more aggressive and less likely to respond to treatment. Women who are diagnosed with breast cancer before age 40 are more likely to have a genetic mutation that puts them at higher risk. Screening for the BRCA gene mutation may begin at age 25.
Other signs for young women to be aware of include:
- A lump in the breast
- Nipple discharge
- Focal pain
- Skin changes on the breast
Mammogram screening is recommended to begin between ages 40 and 50 based on your individual risk factors.
Also Check: First Stage Breast Cancer Symptoms
Family History And Inherited Genes
Some people have a higher risk of developing breast cancer than the general population because other members of their family have had particular cancers. This is called a family history of cancer.
Having a mother, sister or daughter diagnosed with breast cancer increases the risk of breast cancer. This risk is higher when more close relatives have breast cancer, or if a relative developed breast cancer under the age of 50. But most women who have a close relative with breast cancer will never develop it.
Some people have an increased risk of breast cancer because they have an inherited gene fault. We know about several gene faults that can increase breast cancer risk and there are tests for some of them. Having one of these faulty genes means that you are more likely to get breast cancer than someone who doesnt. But it is not a certainty.
Two of these faulty genes are known as BRCA1 and BRCA2. These are not common. Only about 2 out of every hundred of breast cancers are related to a change in the BRCA1 or BRCA2 genes.
Ionising radiation includes tests such as x-rays and CT scans and treatment such as radiotherapy.
Yearly Screening Mammograms Are Not Recommended For Most Until Age 40 Most Patients Under 40 Who Learn They Have Breast Cancer Usually Sought An Exam Because They Have Felt A Lump Or Noticed Other Changes To Their Breasts
Laura Chamberlin first noticed a lump in her breast when she was a graduate student living in Seattle, Washington. She mentioned it to her primary care doctor, who told her not to worry.
She said, Youre young. You just have dense tissue, Laura recalled.
After moving to Louisville a year later to work as an art therapist, Laura went to an urgent care clinic for an ear infection. She mentioned the lump and was referred for a biopsy. Laura was 28 when she learned she had breast cancer.
It was definitely a shock, Laura said, though the diagnosis didnt feel real until she had made the difficult calls to family and friends to give them the news.
Patients under 40 like Laura make up 5% of breast cancer cases.
The numbers arent growing significantly. I think were doing a better job screening. Our screening has helped us find it earlier, said Blakely Kute, M.D., medical oncologist at Norton Cancer Institute Womens Cancer Center.
Recommended Reading: Baking Soda And Breast Cancer
How Has The Risk Of Being Diagnosed With Breast Cancer Changed In Recent Years
For a woman born in the 1970s in the United States, the lifetime risk of being diagnosed with breast cancer, based on breast cancer statistics from that time, was just under 10% .
The last five annual SEER Cancer Statistics Review reports show the following estimates of lifetime risk of breast cancer, all very close to a lifetime risk of 1 in 8:
- 12.83%, based on statistics for 2014 through 2016
- 12.44%, based on statistics for 2013 through 2015
- 12.41%, based on statistics for 2012 through 2014
- 12.43%, based on statistics for 2011 through 2013
- 12.32%, based on statistics for 2010 through 2012
SEER statisticians expect some variability from year to year. Slight changes may be explained by a variety of factors, including minor changes in risk factor levels in the population, slight changes in breast cancer screening rates, or just random variability inherent in the data.
Selected Reference
Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, et al. . SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 19752017, National Cancer Institute. Bethesda, MD, , based on November 2019 SEER data submission, posted to the SEER web site, April 2020.
Related Resources
- Reviewed:December 16, 2020
Want to use this content on your website or other digital platform? Our syndication services page shows you how.
Causes Of Breast Cancer: How Did This Happen
When youre told that you have breast cancer, its natural to wonder what may have caused the disease. But no one knows the exact causes of breast cancer. Doctors seldom know why one woman develops breast cancer and another doesnt, and most women who have breast cancer will never be able to pinpoint an exact cause. What we do know is that breast cancer is always caused by damage to a cells DNA.
Recommended Reading: Stage 3 Breast Cancer Prognosis
Who Gets Breast Cancer
All women can get breast cancer. Although the causes of breast cancer are still unknown, there are some factors that may increase a woman’s chances of getting the disease:
- Getting older – Most women are diagnosed when they are 50 years of age or older
- Having a first menstrual period at a young age
- Starting menopause at an older age
- Never giving birth, or giving birth to a first child after age 30
- Not breastfeeding
- Having had breast cancer or some non-cancerous breast diseases
- Having a close family member who has had breast cancer, especially at an early age
- Having certain gene mutations such as BRCA 1 or BRCA 2
- Being overweight or obese
- Exposure to high levels of ionizing radiation to the chest area early in life
- Long-term use of hormone replacement therapy
Even if women have one or more of these risk factors, it does not mean they will get breast cancer. Also, many women who get breast cancer do not have any risk factors. This is why screening is important for all women.
Women with a personal or family history of breast cancer may want to consider genetic counseling to find out if they are at greater risk for getting the disease.
While very rare, it is possible for men to get breast cancer. 2,3,4
Spotting Cancer Early Matters
Remember, spotting cancer at an early stage means treatment is more likely to be successful.
Its important to listen to your body. If something doesnt look or feel quite right, speak to your doctor dont wait to see if it gets worse. And dont assume unusual changes are down to just getting older, or part of another health condition you may have.
If its not normal for you or wont go away, get it checked out.
Also Check: How Serious Is Stage 3 Cancer
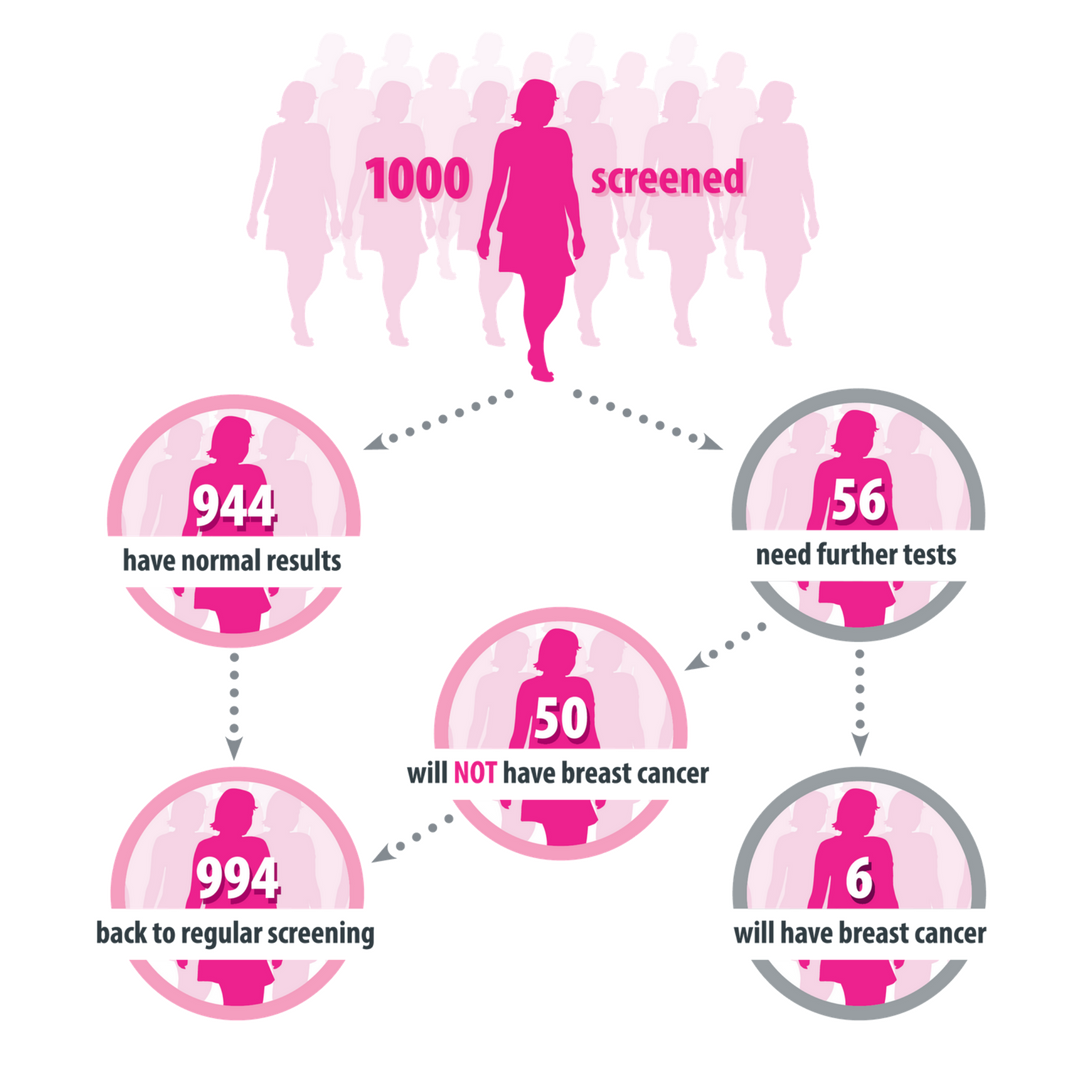
What Screening Tests Are Done For Breast Cancer
Breast cancer screening means checking the breasts for cancer before there are signs or symptoms of sickness. Three main tests are used to screen the breasts for cancer. Talk to your health care provider about which tests are right for you, and when you should have them.
At this time, guidelines suggest that the best way to find breast cancer is with a mammogram. Clinical breast exams or self-exams alone are not enough to detect breast cancer. Women who choose to have clinical breast exams and to perform breast self-exams should also get regular mammograms.7
Can I Get Treatment For Breast Cancer If I Don’t Have Insurance
Women in need of treatment for breast cancer may be eligible for coverage through the New York State Medicaid Cancer Treatment Program . Coverage lasts for the entire time you are being treated and includes medications.
To learn if you are eligible for this program or to get more information, visit the NYS MCTP website.
Don’t Miss: Average Age Of Breast Cancer Onset
Can I Get A Mammogram If I Have Breast Implants
Yes. If you have breast implants, you should still get regular screening mammograms as recommended. Be sure to inform them when scheduling your appointment. The implants can make it more difficult for the doctor to detect breast cancer, so more pictures are taken during the screening mammogram. If you have had both or one breast removed before getting an implant, you typically wonât need a mammogram on the reconstructed breast.
Types Of Breast Cancer

There are several different types of breast cancer, which develop in different parts of the breast.
Breast cancer is often divided into either:
- non-invasive breast cancer found in the ducts of the breast which has not spread into the breast tissue surrounding the ducts. Non-invasive breast cancer is usually found during a mammogram and rarely shows as a breast lump.
- invasive breast cancer where the cancer cells have spread through the lining of the ducts into the surrounding breast tissue. This is the most common type of breast cancer.
Other, less common types of breast cancer include:
- invasive lobular breast cancer
- inflammatory breast cancer
It’s possible for breast cancer to spread to other parts of the body, usually through the blood or the axillary lymph nodes. These are small lymphatic glands that filter bacteria and cells from the mammary gland.
If this happens, it’s known as secondary, or metastatic, breast cancer.
Read Also: Hormone Therapy For Metastatic Breast Cancer
What Clinical Trials Are Available For Women With Inflammatory Breast Cancer
NCI sponsors clinical trials of new treatments for all types of cancer, as well as trials that test better ways to use existing treatments. Participation in clinical trials is an option for many patients with inflammatory breast cancer, and all patients with this disease are encouraged to consider treatment in a clinical trial.
Descriptions of ongoing clinical trials for individuals with inflammatory breast cancer can be accessed by searching NCIs list of cancer clinical trials. NCIs list of cancer clinical trials includes all NCI-supported clinical trials that are taking place across the United States and Canada, including the NIH Clinical Center in Bethesda, MD. For information about how to search the list, see Help Finding NCI-Supported Clinical Trials.
People interested in taking part in a clinical trial should talk with their doctor. Information about clinical trials is available from NCIs Cancer Information Service at 18004CANCER and in the NCI booklet Taking Part in Cancer Treatment Research Studies. Additional information about clinical trials is available online.
Selected References
Anderson WF, Schairer C, Chen BE, Hance KW, Levine PH. Epidemiology of inflammatory breast cancer . Breast Diseases 2005 22:9-23.
Living With Breast Cancer
Dealing with breast cancer can be very hard for a woman and her family. A woman who has breast cancer surgery or treatment may not feel well for a while. She may be depressed if she had her breast removed. If a woman needs chemotherapy, she may lose her hair and she may feel sick to her stomach. She also may worry that the cancer will return and shell get sick again.
The good news is that many times, especially if a lump is caught early, women with breast cancer go on to live full, healthy lives after treatment. Some join support groups so they can talk to other women with breast cancer who are feeling the same emotions.
There are even groups that kids or other family members can join to talk about their feelings when someone they love has breast cancer. Find a trusted adult to talk with if youre worried about a loved one.
You May Like: What Does Pt1c Mean In Breast Cancer
Read Also: How Fast Can Breast Cancer Grow
Tips For Preparing For A Mammogram
Mammograms are conducted in breast clinics, hospital radiology departments, private radiology offices, and doctorâs offices. Below are some tips on how to best prepare for a mammogram:
- Go to the same facility every year or bring the images from your last mammogram to the upcoming one
- Schedule when breasts are less tender
- Plan accordingly as mammograms usually take 30 minutes to complete
Breast Lumps In Teenagers
It can be normal to feel lumps when your breasts are developing and these often disappear on their own.
If a lump causes you any discomfort, appears to get bigger or youre worried about it, talk to someone such as your GP. You may also want to talk to someone in your family or a school nurse.
Although its very unlikely that theres anything wrong, a doctor can check it out and should put your mind at rest. You can ask to see a female doctor or the practice nurse if this will make you feel more comfortable.
Very occasionally lumps are a sign of a benign breast condition. Benign means harmless, and a benign condition will not become a breast cancer. The most common benign lump as the breasts are developing is known as a fibroadenoma.
Read Also: How Long Does Breast Cancer Take To Kill
Reproductive History Estrogen Is The Main Hormone Associated With Breast Cancer Estrogen Affects The Growth Of Breast Cells Experts Believe That It Plays An Important Role In The Growth Of Breast Cancer Cells As Well The Type Of Exposure And How Long Cells Are Exposed To Estrogen Affects The Chances That Breast Cancer Will Develop
Early menarche
The start of menstruation is called menarche. Early menarche is when menstruation starts at an early age . Starting your period early means that your cells are exposed to estrogen and other hormones for a greater amount of time. This increases the risk of breast cancer.
Late menopause
Menopause occurs as the ovaries stop making hormones and the level of hormones in the body drops. This causes a woman to stop menstruating. If you enter menopause at a later age , it means that your cells are exposed to estrogen and other hormones for a greater amount of time. This increases the risk for breast cancer. Likewise, menopause at a younger age decreases the length of time breast tissue is exposed to estrogen and other hormones. Early menopause is linked with a lower risk of breast cancer.
Late pregnancy or no pregnancies
Pregnancy interrupts the exposure of breast cells to circulating estrogen. It also lowers the total number of menstrual cycles a woman has in her lifetime.
Women who have their first full-term pregnancy after the age of 30 have a slightly higher risk of breast cancer than women who have at least one full-term pregnancy at an earlier age. Becoming pregnant at an early age reduces breast cancer risk.
The more children a woman has, the greater the protection against breast cancer. Not becoming pregnant at all increases the risk for breast cancer.
What Happens If My Test Is Positive For Hereditary Breast Cancer Risk
If testing confirms you are at risk, your care provider can work with you on a plan to safeguard your health, which could include:
- High-risk evaluation and monitoring
- Screening schedules, including digital mammography and clinical breast exams
- Hormonal therapy medications designed to prevent the development of breast cancer
Preventive surgery, such as mastectomy with breast reconstruction, is necessary only for patients at very high risk for aggressive breast cancer.
A comprehensive breast center offers a safe and supportive environment where you can ask questions and get the best answers for you, Ninan says. Every patients decision about how to handle their risk of developing breast cancer is managed with sensitivity and an understanding about the complexity of these decisions.
You May Like: Stage 2 Breast Cancer