What Is Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
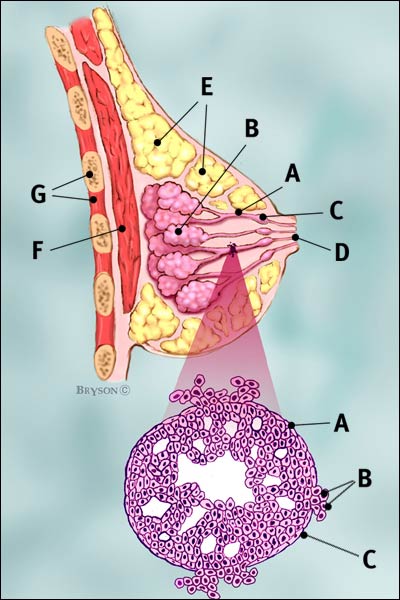
Breast ducts are the passageways where milk from the milk glands flows to the nipple.
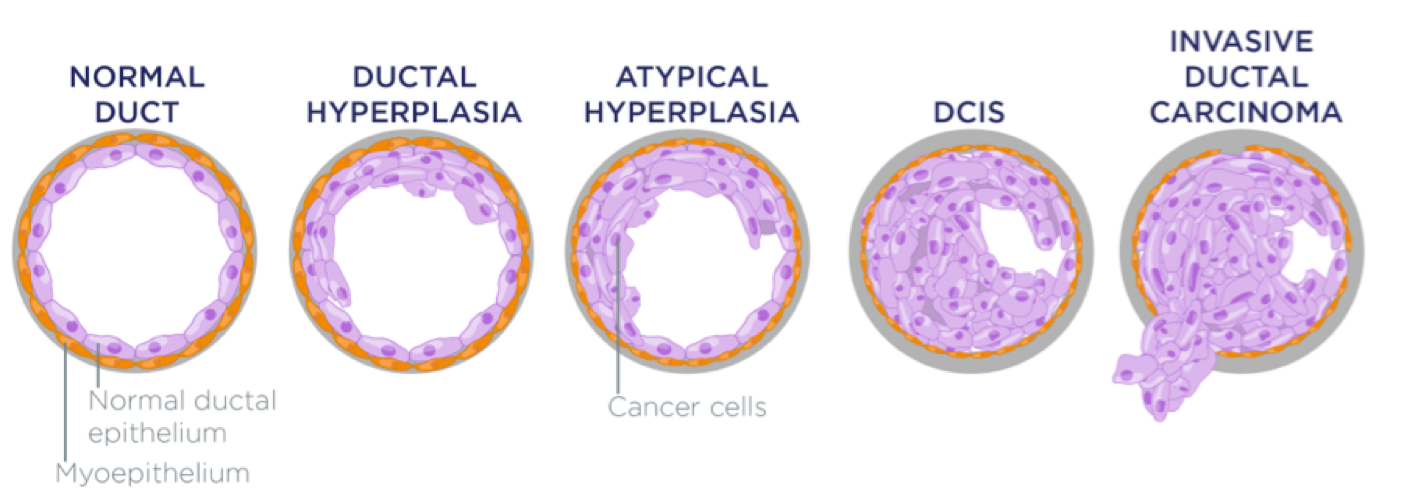
Invasive ductal carcinoma is cancer that happens when abnormal cells growing in the lining of the milk ducts change and invade breast tissue beyond the walls of the duct.
Once that happens, the cancer cells can spread. They can break into the lymph nodes or bloodstream, where they can travel to other organs and areas in the body, resulting in metastatic breast cancer.
Cancer Cure And All Clear
Many people who have cancer want to know if theyre cured. You may hear words like cure and all clear in the media.
Cured means theres no chance of the breast cancer coming back. However, its not possible to be sure that breast cancer will never come back. Treatment for breast cancer will be successful for most people, and the risk of recurrence gets less as time goes on. Recurrence, unfortunately, can happen even many years after treatment, so no one can say with certainty that youre definitely cured.
All clear, or in remission which is another term you may have heard used, means theres no obvious sign of cancer at the moment.
If your breast cancer has spread to other parts of your body this will affect your prognosis. Secondary breast cancer can be treated, sometimes for many years, but not cured. Find out more about secondary breast cancer.
In order to be as clear as possible, your treatment team is more likely to talk about your chances of survival over a period of time or the possibility of remaining free of breast cancer in the future.
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma: The Most Common Kind
The most common form of breast cancer is invasive ductal carcinoma , sometimes also called infiltrating ductal carcinoma. About 80 percent of all new breast cancer cases in women, and nearly all breast cancer in men, are IDC. The risk of IDC also increases as people grow older.
IDC starts in the ducts just as DCIS does, but the cancer then grows beyond the ducts and invades, or infiltrates, the fatty tissue surrounding the ducts. Without treatment, the cancer continues to metastasize, or spread, into the lymph nodes and bloodstream.
The options available to treat IDC depend on the type of breast cancer it is, what mutations it does or does not have, how aggressive it is, and other factors. One of the most important of those other factors is the cancer stage.
Also Check: Signs Of Breast Cancer Recurrence After Mastectomy
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Diagnosis
IDC is usually found as the result of an abnormal mammogram. To diagnose cancer, youâll get a biopsy to collect cells for analysis. The doctor will remove a bit of tissue to look at under a microscope. They can make a diagnosis from the biopsy results.
If the biopsy confirms you have cancer, youâll likely have more tests to see how large the tumor is and if it has spread:
- CT scan. It’s a powerful X-ray that makes detailed pictures inside your body.
- PET scan. The doctor injects a radioactive substance called a tracer into your arm. It travels through your body and gets absorbed into the cancer cells. Together with a CT scan, this test can help find cancer in lymph nodes and other areas.
- MRI. It uses strong magnets and radio waves to make pictures of the breast and other structures inside your body.
- Bone scan. The doctor injects a tracer into your arm. They take pictures to find out if cancer has traveled to your bones.
- Chest X-ray. It uses low doses of radiation to make pictures of the inside of your chest.
What If My Report On Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Mentions Margins Or Ink
When the entire area of DCIS is removed, the outside surface of the specimen is coated with ink, sometimes even with different colors of ink on different sides of the specimen. The pathologist looks at slides of the DCIS under the microscope to see how close the DCIS cells get to the ink . If DCIS is touching the ink , it can mean that some DCIS cells were left behind, and more surgery or other treatments may be needed. Sometimes, though, the surgeon has already removed more tissue to help make sure that this isnt needed. If your pathology report shows DCIS with positive margins, your doctor will talk to you about what treatment is best.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Early Stages Of Melanoma
Recommended Reading: Progesterone Positive Breast Cancer Treatment
Kinds Of Breast Cancer
The most common kinds of breast cancer are
- Invasive ductal carcinoma. The cancer cells begin in the ducts and then grow outside the ducts into other parts of the breast tissue. Invasive cancer cells can also spread, or metastasize, to other parts of the body.
- Invasive lobular carcinoma. Cancer cells begin in the lobules and then spread from the lobules to the breast tissues that are close by. These invasive cancer cells can also spread to other parts of the body.
What Are The Symptoms Of Breast Cancer Recurrence
You may experience different signs of breast cancer recurrence depending on where the cancer forms.
Local breast cancer recurrence may cause:
- Breast lump or bumps on or under the chest.
- Nipple changes, such as flattening or nipple discharge.
- Swollen skin or skin that pulls near the lumpectomy site.
- Thickening on or near the surgical scar.
- Unusually firm breast tissue.
- Biopsy of the site of suspected recurrence.
Recommended Reading: Hormone Receptor Positive Breast Cancer Prognosis
How Is Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Diagnosed
Several tests can help your doctor identify and diagnose IDC, including:
Physical exam. Manual examination of your breasts by your doctor can detect lumps and other changes. If your doctor feels a lump or thickening, he or she may recommend further tests to rule out IDC.
Digital mammography is an improved method for breast imaging that is performed much like a regular mammogram. However, it is better than conventional mammography in detecting cancer in younger patients and in those with dense breast tissue. Electronic images can be enhanced with computer-aided detection systems to spot masses, calcifications and abnormalities associated with cancer.
Breast ultrasound uses sound waves to examine the breast tissue and gauge blood flow. It is safe for examining pregnant patients, and does not use radiation.
Breast magnetic resonance imaging uses a large magnet, radio waves and a computer that can detect small breast lesions, and may be especially useful in examining patients with a high risk of breast cancer, such as those with BRCA1, BRCA2 or other gene mutations associated with cancer.
Schedule Your Mammogram
Biopsy. A breast biopsy involves taking a sample of breast tissue from a suspicious area and sending it to a laboratory for microscopic examination by a pathologist, a doctor who specializes in identifying signs of disease. A biopsy can confirm or rule out the presence of cancer and, if cancer is present, reveal its characteristics.
Study Population And Data
Out of a total of 1,513 women with breast cancer in the WCHS, women were excluded if they were diagnosed with pure DCIS , invasive carcinomas of other types , or cancers with unknown histology . Records of pure IDC patients were included only when medical reports clearly stated that there was no DCIS component, or included detailed descriptions of hyperplasia without mention of DCIS. In addition, slides of tumor samples from cases were reviewed by two breast pathologists to verify presence or absence of DCIS. Included in the final study were 831 women with IDC or mixed IDC/invasive lobular carcinoma and 1,620 controls.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Get Rid Of Breast Cancer
What Is The Difference Between Invasive Ductal Carcinoma And Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
DCIS means the cancer is still contained in the milk duct and has not invaded any other area. IDC is cancer that began growing in the duct and is invading the surrounding tissue. Cancer staging done by a physician, along with a physical exam and medical history can help identify the best treatment options.
Materials on this page courtesy of National Cancer Institute
What Can You Tell Me About Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Stages
Staging describes how advanced your cancer is, based on the location, size and how far it has spread. There are five stages of ductal carcinoma:
- Stage 0: The cancer is localized to your milk ducts. This stage is also known as non-invasive ductal carcinoma in situ.
- Stage 1: The cancer has spread outside of your milk ducts to the breast tissue, but it hasnt spread to your lymph nodes. In some cases, the cancer may have spread to your lymph nodes, but not to your surrounding breast tissue.
- Stage 2: The tumor is small and has spread to one to three of your lymph nodes. Or, the tumor is larger, but hasnt spread to any of your lymph nodes.
- Stage 3: The cancer has often spread to more than three of your lymph nodes or is causing inflammation of most of your breast skin, but hasnt spread to other areas of your body.
- Stage 4: The cancer has spread to your other organs, which may include your bones, liver, lungs, brain, chest wall or distant lymph nodes.
Also Check: What Are The Side Effects Of Breast Cancer
Rare Types Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Medullary ductal carcinoma accounts for only 3%5% of breast cancers. It may appear on a mammogram, and it does not always feel like a lump rather, it can feel like an abnormally spongy area in the breast tissue.
Mucinous ductal carcinoma is also called colloid breast cancer. It occurs when cancer cells within the milk duct of the breast produce mucous, which also contains breast cancer cells. The cells and mucous combine to form a tumor. Pure mucinous ductal carcinoma tends to grow slowly, and has a better prognosis than some other types of IDCs.
Papillary carcinoma forms finger-like projections that can be seen under a microscope. Many papillary tumors are benign, but even those that become cancerous are usually very treatable with a good prognosis. Papillary carcinoma most commonly occurs in people older than 60.
Tubular ductal carcinoma is a rare diagnosis of IDC, comprising only 2% of breast cancer diagnoses. The name comes from how the cancer looks under the microscope like hundreds of tiny tubes. Tubular breast cancer has an excellent prognosis.
What Is The Significance Of The Stage Of The Tumor
The stage of a cancer is a measurement of the extent of the tumor and its spread. The standard staging system for breast cancer uses a system known as TNM, where:
- T stands for the main tumor
- N stands for spread to nearby lymph nodes
- M stands for metastasis
If the stage is based on removal of the cancer with surgery and review by the pathologist, the letter p may appear before the T and N letters.
The T category is based on the size of the tumor and whether or not it has spread to the skin over the breast or to the chest wall under the breast. Higher T numbers mean a larger tumor and/or wider spread to tissues near the breast. Since the entire tumor must be removed to learn the T category, this information is not given for needle biopsies.
The N category indicates whether the cancer has spread to lymph nodes near the breast and, if so, how many lymph nodes are affected. Higher numbers after the N indicate more lymph node involvement by cancer. If no nearby lymph nodes were removed to be checked for cancer spread, the report may list the N category as NX, where the letter X is used to mean that the information is not available .
The M category is usually based on the results of lab and imaging tests, and is not part of the pathology report from breast cancer surgery. In a pathology report, the M category is often left off or listed as MX .
Don’t Miss: Did Anne Hathaway Get A Nose Job
What Are Breast Cancer Stages
The stage of a cancer describes the size of the cancer and how far it has spread.
Your breast cancer may be described as stage 1, stage 2, stage 3 or stage 4.
An early form of breast cancer called DCIS is sometimes referred to as stage 0 breast cancer.
The stage takes into account:
- The size of the cancer
- Whether the lymph nodes are affected
- If the cancer has spread to other parts of the body
The stage of your cancer may not be fully known until after you have had surgery.
Infiltrating/invasive Lobular Breast Carcinoma
Infiltrating lobular carcinoma usually appears as a subtle thickening in the upper-outer breast quadrant.
As the name suggests, these tumours originate mostly in the breast lobules rather than the lining of the breast ducts.
Invasive lobular cancer is a less common type of breast cancer than invasive ductal cancer. This cancer accounts for about 10% of all invasive breast cancer cases.
Prognosis for infiltrating and invasive lobular breast carcinomas will naturally be influenced by tumor size, grade, stage and hormone receptor status..
However, lobular breast cancers, when positive for estrogen and progesterone receptors, tend to respond very well to hormone therapy.
The overall breast cancer survival rates for infiltrating lobular carcinoma, when matched by stage, are a little higher than for ductal carcinoma for the first 5 years.
Survival rates range from about 77% to 93%, but on average, the 5-year survival rate was estimated at about 90%.
90%2010
You May Like: What Causes Hormonal Breast Cancer
Less Common Invasive Breast Cancers
- Inflammatory breast cancer is an aggressive form of locally advanced breast cancer. Its called inflammatory breast cancer because the main warning signs are swelling and redness in the breast.
With inflammatory breast cancer, warning signs tend to arise within weeks or months. With other breast cancers, warning signs may not occur for years.
- Paget disease of the breast is a cancer in the skin of the nipple or in the skin closely surrounding the nipple. Its usually found with an underlying breast cancer.
- Metaplastic breast cancers tend to be larger and have a higher tumor grade than more common breast cancers. Metaplastic breast cancers can be hard to diagnose because the tumor cells can look very different from the tumor cells of more common breast cancers.
Stage Iia & Iib Treatment Options
Stage II is divided into subcategories known as IIA and IIB.
In general, stage IIA describes invasive breast cancer in which:
- no tumor can be found in the breast, but cancer is found in 1 to 3 axillary lymph nodes or in the lymph nodes near the breast bone or
- the tumor measures 2 centimeters or smaller and has spread to the axillary lymph nodes or
- the tumor is larger than 2 cm but not larger than 5 cm and has not spread to the axillary lymph nodes
Still, if the cancer tumor measures between 2 and 5 cm and:
- has not spread to the lymph nodes or parts of the body away from the breast
it will likely be classified as stage IB.
Similarly, if the cancer tumor measures between 2 and 5 cm and:
- has not spread to the lymph nodes
- has an Oncotype DX Recurrence Score of 9
it will likely be classified as stage IA.
In general, stage IIB describes invasive breast cancer in which:
- the tumor is larger than 2 cm but no larger than 5 cm small groups of breast cancer cells larger than 0.2 mm but not larger than 2 mm are found in the lymph nodes or
- the tumor is larger than 2 cm but no larger than 5 cm cancer has spread to 1 to 3 axillary lymph nodes or to lymph nodes near the breastbone or
- the tumor is larger than 5 cm but has not spread to the axillary lymph nodes
Still, if the cancer tumor measures between 2 and 5 cm and:
- cancer is found in 1 to 3 axillary lymph nodes
Also Check: Does Cancer Hurt In Breast
Tests To Determine The Need For Chemotherapy
If the cancer is early-stage and has certain characteristics, you may be eligible for a genomic test, which looks at specific genes in the cancer to predict how likely the cancer is to recur . If a cancer is not very likely to come back, you might not need chemotherapy. If the cancer is more likely to come back, you and your doctor might decide that chemotherapy is right for you. Oncotype DX, MammaPrint, and the Prosigna Breast Cancer Prognostic Gene Signature Assay are some examples of genomic tests. Learn more about breast cancer tests.
What Is Invasive Breast Cancer
Invasive breast cancer means that the cancer cells have grown through the lining of the ducts into the surrounding breast tissue. NST stands for No Special Type.
Most invasive breast cancers have no special features and are classed as No Special Type. NST is sometimes called NOS . It was previously known as invasive ductal carcinoma. Around 70 out of 100 invasive breast cancers are this type.
Special type means that when the doctor looks at the cancer cells under a microscope the cells have particular features. Breast cancers that are classed as special type include some rare types of breast cancer.
Remember that if your doctor has told you that you have ductal carcinoma in situ , you don’t have invasive breast cancer.
Also Check: Does Taking Estrogen Cause Cancer
Symptoms Of Invasive Breast Cancer
Make an appointment to see your doctor if you notice anything different or unusual about the look and feel of your breasts.
The symptoms of breast cancer include:
- a new lump or thickening in your breast or armpit
- a change in size, shape or feel of your breast
- skin changes in the breast such as puckering, dimpling, a rash or redness of the skin
- fluid leaking from the nipple in a woman who isnt pregnant or breast feeding
- changes in the position of nipple