Does Breast Cancer Affect Women Of All Races Equally
All women, especially as they age, are at some risk for developing breast cancer. The risks for breast cancer in general arent evenly spread among ethnic groups, and the risk varies among ethnic groups for different types of breast cancer. Breast cancer mortality rates in the United States have declined by 40% since 1989, but disparities persist and are widening between non-Hispanic Black women and non-Hispanic white women.
Statistics show that, overall, non-Hispanic white women have a slightly higher chance of developing breast cancer than women of any other race/ethnicity. The incidence rate for non-Hispanic Black women is almost as high.
Non-Hispanic Black women in the U.S. have a 39% higher risk of dying from breast cancer at any age. They are twice as likely to get triple-negative breast cancer as white women. This type of cancer is especially aggressive and difficult to treat. However, it’s really among women with hormone positive disease where Black women have worse clinical outcomes despite comparable systemic therapy. Non-Hispanic Black women are less likely to receive standard treatments. Additionally, there is increasing data on discontinuation of adjuvant hormonal therapy by those who are poor and underinsured.
In women under the age of 45, breast cancer is found more often in non-Hispanic Black women than in non-Hispanic white women.
What Do Cancer Stages And Grades Mean
The stage of a cancer describes the size of a tumour and how far it has spread from where it originated. The grade describes the appearance of the cancerous cells.
If you’re diagnosed with cancer, you may have more tests to help determine how far it has progressed. Staging and grading the cancer will allow the doctors to determine its size, whether it has spread and the best treatment options.
Stage 3 Breast Cancer
Stage 3 breast cancer is divided into three groups:
- Stage 3A
- Stage 3C
Stage 3A can mean:
No cancer is seen in the breast, but cancer is found in four to nine lymph nodes under the arm or near the breastbone
The cancer in the breast measures up to 5cm and cancer is found in four to nine lymph nodes under the arm or near the breastbone
The cancer in the breast is larger than 5cm, and cancer is found in up to three lymph nodes under the arm or near the breastbone.
Stage 3B means the cancer in the breast can be any size and has spread to the skin of the breast or chest wall. Cancer is found in up to nine lymph nodes under the arm or near the breast bone.
Stage 3C means the cancer in the breast can be any size, may have spread to the skin of the breast or chest wall and cancer is found in 10 or more lymph nodes under the arm or near the breastbone, or to nodes above or below the collarbone.
Read Also: Signs Of Stage 3 Breast Cancer
What Are The Types Of Breast Cancer
The most common types of breast cancer are:
- Infiltrating ductal carcinoma. This cancer starts in the milk ducts of the breast. It then breaks through the wall of the duct and invades the surrounding tissue in the breast. This is the most common form of breast cancer, accounting for 80% of cases.
- Ductal carcinoma in situ is ductal carcinoma in its earliest stage, or precancerous . In situ refers to the fact that the cancer hasn’t spread beyond its point of origin. In this case, the disease is confined to the milk ducts and has not invaded nearby breast tissue. If untreated, ductal carcinoma in situ may become invasive cancer. It is almost always curable.
- Infiltrating lobular carcinoma. This cancer begins in the lobules of the breast where breast milk is produced, but has spread to surrounding tissues in the breast. It accounts for 10 to 15% of breast cancers. This cancer can be more difficult to diagnose with mammograms.
- Lobular carcinoma in situ is a marker for cancer that is only in the lobules of the breast. It isn’t a true cancer, but serves as a marker for the increased risk of developing breast cancer later, possibly in both or either breasts. Thus, it is important for women with lobular carcinoma in situ to have regular clinical breast exams and mammograms.
How Can I Protect Myself From Breast Cancer
Follow these three steps for early detection:
- Get a mammogram. The American Cancer Society recommends having a baseline mammogram at age 35, and a screening mammogram every year after age 40. Mammograms are an important part of your health history. Recently, the US Preventive Services Task Force came out with new recommendations regarding when and how often one should have mammograms. These include starting at age 50 and having them every two years. We do not agree with this, but we are in agreement with the American Cancer Society and have not changed our guidelines, which recommend yearly mammograms starting at age 40.
- Examine your breasts each month after age 20. You will become familiar with the contours and feel of your breasts and will be more alert to changes.
- Have your breast examined by a healthcare provider at least once every three years after age 20, and every year after age 40. Clinical breast exams can detect lumps that may not be detected by mammogram.
Recommended Reading: Is Stage 3 Breast Cancer Curable
How Quickly Do Breast Cancer Tumors Grow From Stage To Stage
Cancer cells divide and multiply quickly in such a way that as a tumor gets bigger, it divides and grows even faster. The average doubling time for breast cancer tumors is between 50 and 200 days. Breast cancer tumor growth rate is impacted by hormonal factors, such as hormone receptor status and HER2 status.
The Number Staging System
Breast cancer can also be divided into four number stages. We have put these into a table to make them easier to understand. You can .
This information is about stage 1 to 3 breast cancer.
Stage 1 breast cancer is when the cancer is 2cm or smaller. There may be no cancer cells in the lymph nodes in the armpit or tiny numbers of cancer cells are found. Sometimes the cancer cannot be found in the breast, but cancer cells have spread to lymph nodes in the armpit.
Stage 2 breast cancer is when the cancer is up to or bigger than 5cm. It may or may not have spread to the lymph nodes under the arm. Sometimes the cancer cannot be found in the breast. But cancer cells have spread to 1 to 3 lymph nodes in the armpit or near the breast bone.
Stage 3 breast cancer is sometimes called locally advanced breast cancer. The cancer has spread to the lymph nodes in the armpit and sometimes to other lymph nodes nearby. It may have spread to the skin of the breast or to the chest muscle. The skin may be red, swollen or have broken down. Sometimes the cancer cannot be found in the breast or is small but has spread to 4 to 9 lymph nodes in the armpit.
Stage 4 breast cancer is also called secondary or metastatic breast cancer. This is when the cancer has spread to other parts of the body, such as the bones, the liver or lungs. We have separate information about secondary breast cancer.
You May Like: Invasive Ductal Breast Cancer Treatment
What Is Stage 1 Breast Cancer
This breast cancer is the earliest stage of invasive breast cancer. In stage 1, the tumor measures up to 2 cm and no lymph nodes are involved. At this stage, the cancer cells have spread beyond the original location and into the surrounding breast tissue.
Because a stage 1 tumor is small, it may be difficult to detect. However, breast self-exams and routine screening are always important and can often lead to early diagnosis, when the cancer is most treatable.Stage 1 breast cancer is divided into two categories:
Stage 1A: The tumor measures 2 cm or smaller and has not spread outside the breast.
Stage 1B: Small clusters of cancer cells measuring no more than 2 mm, are found in the lymph nodes, and either there is no tumor inside the breast, or the tumor is small, measuring 2 cm or less.
At stage 1, TNM designations help describe the extent of the disease. For example, there may or may not be cancer cells in the lymph nodes, and the size of the tumor may range from 1 cm to 2 cm. Most commonly, stage 1 breast cancer is described as:
- T: T1, T2, T3 or T4, depending on the size and/or extent of the primary tumor
- N0: Usually, cancer has not spread to the lymph nodes.
- M0: The disease has not spread to other sites in the body.
Stage 1 breast cancer survival rate
The survival rate for stage 1A breast cancer may be slightly higher than for stage 1B. However, all women with stage 1 breast cancer are considered to have a good prognosis.
What Is Stage 4 Breast Cancer
Also known as metastatic breast cancer, the cancer in this stage has spread beyond the breast, underarm and internal mammary lymph nodes to other parts of the body near to or distant from the breast. The cancer has spread elsewhere in the body. The affected areas may include the bones, brain, lungs or liver and more than one part of the body may be involved.
At stage 4, TNM designations help describe the extent of the disease. Higher numbers indicate more extensive disease. Most commonly, stage 4 breast cancer is described as:,
- T: T1, T2, T3 or T4 depends on the size and/or extent of the primary tumor.
- N1: Cancer has spread to the lymph nodes.
- M1: The disease has spread to other sites in the body.
Read Also: Do You Gain Weight With Breast Cancer
Grade And Rate Of Growth
Predicting the cancer cells speed and way of growing is an important consideration in categorizing a patients breast cancer.
Rate of growth S-phase fraction and Ki67 tests will likely be performed to measure cell growth. These tests are not always accurate, so other factors will also be used to make decisions.
Patterns of cell growth How a cancer grows is measured on a scale of one to three, one for a cancer that grows slowly or predictably and three for a cancer that is more irregular in its growth pattern.
Necrosis/dead cells The presence of dead cells is one sign that the tumor has aggressive growth.
Lymphatic invasion If the tumor cells have gotten into the fluid channels of the breast, they are categorized this way. These cancers have an increased risk of spreading beyond the breast to lymph nodes and/or to other organs within the body.
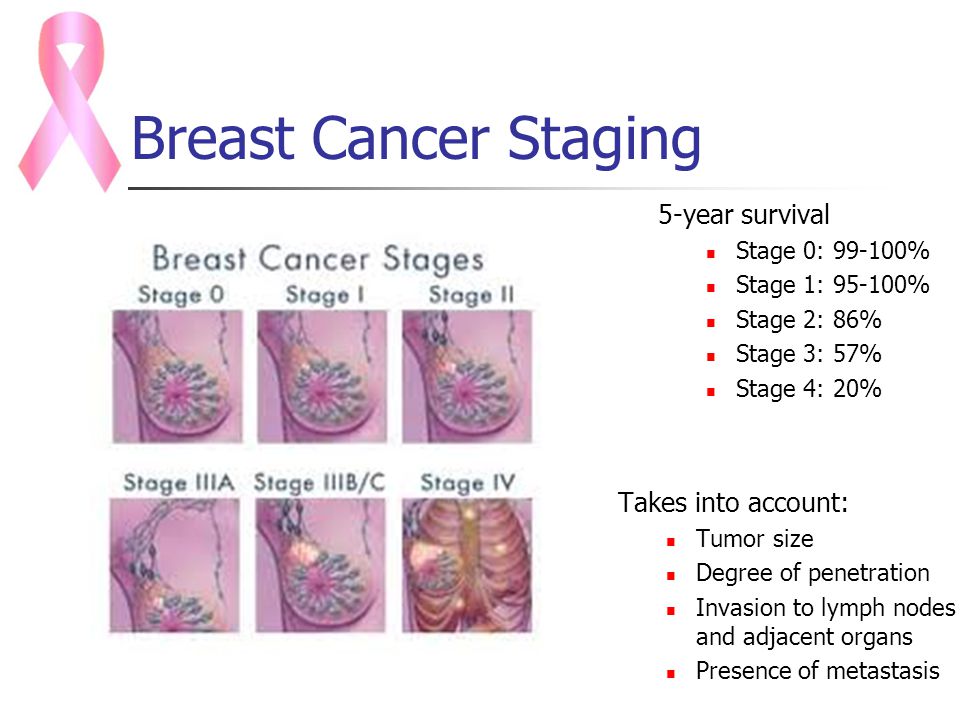
What Is Stage Ii Breast Cancer
Stage II describes cancer that is in a limited region of the breast but has grown larger. It reflects how many lymph nodes may contain cancer cells. This stage is divided into two subcategories.
Stage IIA is based on one of the following:
- Either there is no tumor in the breast or there is a breast tumor up to 20 millimeters , plus cancer has spread to the lymph nodes under the arm.
- A tumor of 20 to 50 millimeters is present in the breast, but cancer has not spread to the lymph nodes.
Stage IIB is based on one of these criteria:
- A tumor of 20 to 50 millimeters is present in the breast, along with cancer that has spread to between one and three nearby lymph nodes.
- A tumor in the breast is larger than 50 millimeters, but cancer has not spread to any lymph nodes.
Also Check: Can Nipple Piercing Cause Cancer
Checking The Lymph Nodes
The usual treatment is surgery to remove the cancer. Before your surgery you have an ultrasound scan to check the lymph nodes in the armpit close to the breast. This is to see if they contain cancer cells. If breast cancer spreads, it usually first spreads to the lymph nodes close to the breast.
Depending on the results of your scan you might have:
- a sentinel lymph node biopsy during your breast cancer operation
- surgery to remove your lymph nodes
What Is Stage Iv Breast Cancer
Stage IV is the most advanced stage of breast cancer. It has spread to nearby lymph nodes and to distant parts of the body beyond the breast. This means it possibly involves your organs such as the lungs, liver, or brain or your bones.
Breast cancer may be stage IV when it is first diagnosed, or it can be a recurrence of a previous breast cancer that has spread.
You May Like: Risk Factors For Metastatic Breast Cancer
Stage 2 Breast Cancer: Treatment Timeline Survival Rate
If you have stage 2 breast cancer, it means that the cancer hasnt spread beyond the breast tissue or nearby lymph nodes.
Cancer isnt a single disease. Its a group of diseases, and breast cancer is no different. Because there are different types, not all stage 2 breast cancers are treated the same way.
In this article, well explore how breast cancer is staged and treated, as well as the general outlook.
When its first confirmed that you have breast cancer, your doctor will assign a clinical stage to your cancer diagnosis. This is called clinical staging and its based on:
- a physical exam
- imaging tests
- biopsy results
If surgery is done to examine the breast tissue, laboratory test results on the tissue and lymph nodes will be able to provide more information. Based on these results, your doctor will be able to determine the pathologic stage, or surgical stage, of the cancer. This is more accurate than the clinical stage.
Breast cancer staging involves the TNM system, which provides specific details about:
- T: the size of the tumor
- N: lymph node involvement
- M: whether the cancer has spread
These factors are combined to determine the cancer stage. Breast cancer is staged from 1 to 4.
Stage 2 breast cancer has two subcategories.
Stage 2B
Breast cancer is stage 2B if one of these is true:
- The breast tumor is between 2 and 5 cm and the cancer has reached 4 or fewer lymph nodes.
- The tumor is over 5 cm but theres no lymph node involvement.
Stage : One Of The Following Applies:
- Only the lining of a breast duct contains cancer cells. The medical term for this situation is ductal carcinoma in situ .
- Abnormal cells have accumulated in the lobules of the breast. This is known as lobular carcinoma in situ .
- Paget disease of the breast occurs when there is no invasive cancer, DCIS, or LCIS.
Also Check: Hormone Receptor Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer
Stage 2 Cancer Treatment Options
In general, stage 2 cancers tend to be treated locally with surgery and/or radiation. At times, chemotherapy or other drug therapies may also be a part of stage 2 cancer treatment. Below, find stage 2 cancer treatment options for the five most common cancers.
Stage 2 breast cancer treatment: Stage 2 breast cancer tends to be most commonly treated with surgerya lumpectomy or mastectomyand radiation treatment afterward. During the surgery, doctors check the nearby lymph nodes for cancer, too. Most patients also have medication as part of their treatment plan: either chemotherapy, breast cancer targeted therapy, hormone therapy or a combination.
Stage 2 lung cancer treatment: Stage 2 lung cancer is typically treated with surgery. Some people may also have chemotherapy after surgery. For patients who cant have surgery, radiation may be a treatment option.
Stage 2 prostate cancer treatment: For stage 2 prostate cancer, treatment depends on the patients symptoms, age and overall health. If the patient is older and isnt experiencing symptoms, doctors may simply keep an eye on how the tumor is doing and treat it if theres any drastic change. However, stage 2 cancers are more likely to spread without treatment than stage 1 cancers. Treatment options may include surgery, surgery followed by radiation, radiation only, or radiation with hormone therapy.
Expert
How Is Breast Cancer Diagnosed
During your regular physical examination, your doctor will take a thorough personal and family medical history. He or she will also perform and/or order one or more of the following:
- Breast examination: During the breast exam, the doctor will carefully feel the lump and the tissue around it. Breast cancer usually feels different than benign lumps.
- Digital mammography: An X-ray test of the breast can give important information about a breast lump. This is an X-ray image of the breast and is digitally recorded into a computer rather than on a film. This is generally the standard of care .
- Ultrasonography: This test uses sound waves to detect the character of a breast lump whether it is a fluid-filled cyst or a solid mass . This may be performed along with the mammogram.
Based on the results of these tests, your doctor may or may not request a biopsy to get a sample of the breast mass cells or tissue. Biopsies are performed using surgery or needles.
After the sample is removed, it is sent to a lab for testing. A pathologist a doctor who specializes in diagnosing abnormal tissue changes views the sample under a microscope and looks for abnormal cell shapes or growth patterns. When cancer is present, the pathologist can tell what kind of cancer it is and whether it has spread beyond the ducts or lobules .
Recommended Reading: First Stage Of Breast Cancer Symptoms
The Treatment Process For Stage Two Breast Cancer
After tests, the oncologist gives a proper diagnosis. People dont know that Can you die from stage 2 breast cancer? In stage two, breast cancer, the treatment methods are very similar to step one as cancer has not affected other parts of the body.
- In a surgical procedure, the tumor can be surgically removed through a lumpectomy or a mastectomy. After the surgery, the doctor may recommend radiation, which increases the effectiveness of the treatment. However, the radiation process may interfere with the reconstruction process.
- After the surgery and the radiation, one goes through systemic treatment, these treatment prevents the recurrence of cancer cells and depending on ones age, and health one goes through the following systemic treatment: lymph node involvement, chemotherapy, hormonal therapy including tamoxifen, an aromatase inhibitor, and HER2 targeted therapy.
- However, if the tumor is too large, the therapy treatment may be different. Your oncologist may suggest going through systemic treatment to reduce the size of the cancer before surgically removing it. Unfortunately, some tumors do not respond well to systemic therapy, and this results in mastectomy where you need to undergo breast reconstruction.
The treatment may take about 1 and a half years, after surgery, one goes through six weeks of chemotherapy and later follow-up.