What Are Risk Factors For Pagets Disease
Factors that can put people at risk of Pagets disease include:
- Age. Older people, particularly people over age 55, are affected more often.
- Gender. Females are more likely to develop the condition.
- Obesity. Putting on extra pounds may increase the risk of the condition.
- Family or personal history. If a person or any of their parents or siblings have had breast cancer, it may increase their risk of Paget’s disease.
- Hormone therapy. Taking estrogen hormone treatments after menopause may put people at a greater risk of Pagets disease.
- Excessive drinking. Heavy alcohol drinking may trigger Paget’s disease.
What Is The Name Of The Cancer That Spreads Rapidly
Inflammatory breast cancer is an infrequent, aggressive type of breast cancer that spreads rapidly. Cancer initiates when normal cells in the breast alter and grow uncontrollably, forming a sheet of cells called a tumor. Breast cancer spreads when the cancer grows into other parts of the body through the blood vessels and lymph vessels.
What Is A Bilateral Mastectomy
Also called a double mastectomy, this is when both breasts are surgically removed. The term Contralateral Prophylactic Mastectomy is also used by the medical community for removal of the opposite, non-cancerous breast. Most of the time the decision to have a bilateral mastectomy is a personal one and is not required to treat a breast cancer that is on one side.
There are situations where a bilateral mastectomy may be offered for consideration by your breast surgeon. The medical aspects are more complicated than listed below, but we include some common scenarios.
- BRCA mutation or other high-risk genetic mutation
- Strong family history of breast cancer
- Younger than 35 with breast cancer
- High risk for developing a new cancer
- Radiation to your chest at a young age
Recommended Reading: Stage 3 Advanced Breast Cancer
Read Also: Signs Of Men Breast Cancer
How Much Do Tamoxifen And Raloxifene Lower The Risk Of Breast Cancer
Multiple studies have shown that both tamoxifen and raloxifene can reduce the risk of developing estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer in healthy postmenopausal women who are at high risk of developing the disease. Tamoxifen lowered the risk by 50 percent. Raloxifene lowered the risk by 38 percent. Overall, the combined results of these studies showed that taking tamoxifen or raloxifene daily for five years reduced the risk of developing breast cancer by at least one-third. In one trial directly comparing tamoxifen with raloxifene, raloxifene was found to be slightly less effective than tamoxifen for preventing breast cancer.
Both tamoxifen and raloxifene have been approved for use to reduce the risk of developing breast cancer in women at high risk of the disease. Tamoxifen is approved for use in both premenopausal women and postmenopausal women . Raloxifene is approved for use only in postmenopausal women.
Less common but more serious side effects of tamoxifen and raloxifene include blood clots to the lungs or legs. Other serious side effects of tamoxifen are an increased risk for cataracts and endometrial cancers. Other common, less serious shared side effects of tamoxifen and raloxifene include hot flashes, night sweats, and vaginal dryness.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Paget’s Disease

Signs and symptoms of Paget’s disease are usually mistaken for symptoms of common skin conditions such as eczema and dermatitis. These include:
- Redness or itching of the nipple or areola
- Burning sensation of the skin of nipple or areola
- Inverted nipple
- Bloody or yellowish discharge from the nipple
- Lump in the breast
Also Check: Can You Go Into Remission With Stage 4 Breast Cancer
The Grading System Is Used To Describe How Quickly A Breast Tumor Is Likely To Grow And Spread
The grading system describes a tumor based on how abnormal the cancer cells and tissue look under a microscope and how quickly the cancer cells are likely to grow and spread. Low-grade cancer cells look more like normal cells and tend to grow and spread more slowly than high-grade cancer cells. To describe how abnormal the cancer cells and tissue are, the pathologist will assess the following three features:
- How much of the tumor tissue has normal breast ducts.
- The size and shape of the nuclei in the tumor cells.
- How many dividing cells are present, which is a measure of how fast the tumor cells are growing and dividing.
For each feature, the pathologist assigns a score of 1 to 3 a score of 1 means the cells and tumor tissue look the most like normal cells and tissue, and a score of 3 means the cells and tissue look the most abnormal. The scores for each feature are added together to get a total score between 3 and 9.
Three grades are possible:
- Total score of 3 to 5: G1 .
- Total score of 6 to 7: G2 .
- Total score of 8 to 9: G3 .
Who Is Likely To Have Inflammatory Breast Cancer
Anyone can develop inflammatory breast cancer, but certain factors may raise your risk.
- Gender: IBC can affect people of all genders, but its more common in women and people assigned female at birth .
- Age: People with IBC tend to be younger than people with other forms of breast cancer. Inflammatory breast cancer is most commonly diagnosed in women and people AFAB who are younger than 40. The median age of diagnosis is 57.
- Race: People who are Black are more likely to get diagnosed with IBC than people who are white.
- Weight: People with obesity or overweight are more likely to get diagnosed than people with a BMI that falls within the normal range.
Don’t Miss: Invasive Lobular Breast Cancer Prognosis
What Are The Symptoms Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Like other breast cancers, IDC may present as a lump that you or your doctor can feel on a breast exam. But in many cases, at first, there may be no symptoms, Wright says.
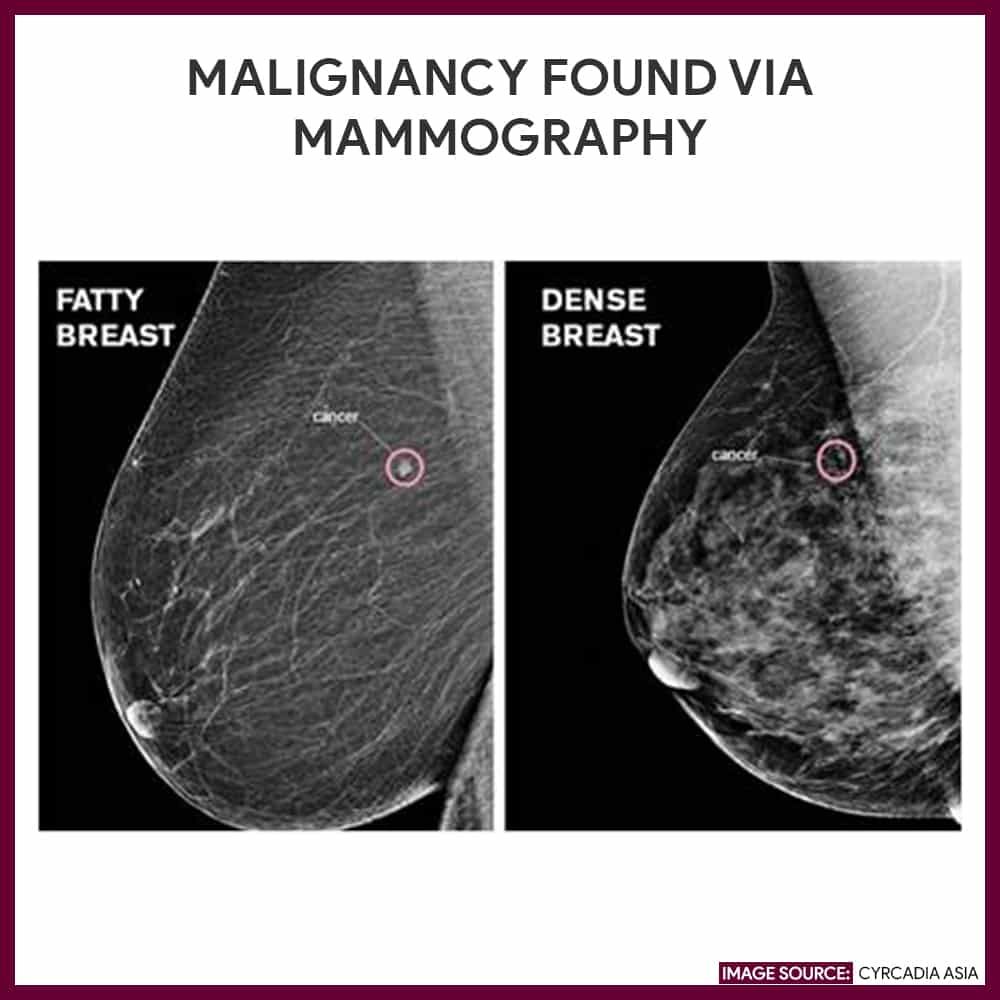
That is why it is important to have screening mammograms to detect breast cancers such as invasive ductal carcinoma. A mammogram may detect a lump that is too small for you to feel, or suspicious calcifications in the breast, either of which will lead to further testing.
According to Wright, the following are possible signs of invasive ductal carcinoma and other breast cancers. If you notice any of these, you should contact your doctor right away for further evaluation:
- Lump in the breast
- Nipple discharge, other than breast milk
- Scaly or flaky skin on the nipple or an ulceration on the skin of the breast or nipple. These can be signs of Pagets disease, a different kind of breast cancer that can occur along with IDC.
- Lumps in the underarm area
- Changes in the appearance of the nipple or breast that are different from your normal monthly changes
What About Other Treatments That I Hear About
When you have cancer you might hear about other ways to treat the cancer or treat your symptoms. These may not always be standard medical treatments. These treatments may be vitamins, herbs, special diets, and other things. You may want to know more about these kinds of treatments.
Some of them are known to help, but many have not been tested. Some have been shown not to help and a few have even been found to be harmful. Talk to your doctor before you use anything , whether its a vitamin, a diet, or anything else.
Don’t Miss: Best Breast Cancer Hospitals In Ohio
Breast Changes And Conditions
As you await follow-up test results, remember that most breast changes are not cancer.
You may have just received an abnormal mammogram result, or perhaps you or your health care provider found a breast lump or other breast change. Keep in mind that breast changes are very common, and most are not cancer. This page can help you learn about symptoms during your lifetime that are not cancer as well as follow-up tests used to diagnose breast conditions and treatments for specific breast conditions.
Can Breast Cancer Return After A Double Mastectomy
During the course of breast cancer treatment, a woman may decide, after discussion with her doctors, to have both of her breasts removed.
She might choose to have a double mastectomy in the hope that it will reduce the risk of breast cancer recurring in the remaining tissue or a new cancer developing in the opposite, unaffected breast.
A woman who has had breast cancer does not inherently or automatically face an increased risk of being diagnosed with another type of cancer, says Ellis Levine, MD, Chief of Breast Medicine at Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center.
Unless they have an underlying hereditary genetic mutation, I do not consider them at exquisite risk to develop another type of cancer, he says. The cancer that is most often genetically linked to breast cancer is ovarian, due to mutations in the BRCA 1 or BRCA 2 genes.
When mastectomies are performed, surgeons will remove as much of the cancerous tissue as possible. If a woman, in consultation with her doctors, decides to have a skin-sparing or nipple-sparing mastectomy, a small amount of healthy breast tissue may be left behind on the skin to allow for reconstruction of her breasts.
Even if the full breast is removed, surgeons will not have removed 100% of the breast cells, explains Jessica Young, MD, a breast surgeon at Roswell Park. The risk of cancer recurring is lower if the whole breast is removed, but it is not zero percent.
Breast Cancer Treatment
Also Check: Can Breast Cancer Be Passed On Genetically
How Long Can You Have Breast Cancer Without Knowing
Breast cancer has to divide 30 times before it can be felt. Up to the 28th cell division, neither you nor your doctor can detect it by hand. With most breast cancers, each division takes one to two months, so by the time you can feel a cancerous lump, the cancer has been in your body for two to five years.
Treatment Of Locoregional Recurrent Breast Cancer
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment of locoregional recurrentbreast cancer , may include the following:
- Targeted therapy .
- A clinical trial of a new treatment.
For information about treatment options for breast cancer that has spread to parts of the body outside the breast, chest wall, or nearby lymph nodes, see the Treatment of Metastatic Breast Cancer section.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Also Check: What To Ask Oncologist Breast Cancer
The Tnm System The Grading System And Biomarker Status Are Combined To Find Out The Breast Cancer Stage
Here are 3 examples that combine the TNM system, the grading system, and the biomarker status to find out the Pathological Prognostic breast cancer stage for a woman whose first treatment was surgery:
If the tumor size is 30 millimeters , has not spread to nearby lymph nodes , has not spread to distant parts of the body , and is:
The cancer is stage IV .
What Is Multicentric Breast Cancer
Multifocal breast cancer occurs when there are two or more tumors in the same breast. All of the tumors begin in one original tumor. The tumors are also all in the same quadrant or section of the breast. Multicentric breast cancer is a similar type of cancer. More than one tumor develops, but in different quadrants of the breast.
Also Check: How Can Males Get Breast Cancer
Getting A Breast Biopsy
In a breast biopsy, the doctor takes out small pieces of breast tissue to check them for cancer cells. A biopsy is the only way to tell for sure if you have breast cancer.
There are many types of biopsies. Ask your doctor what kind you will need. Each type has risks and benefits. The choice of which type to use depends on your case.
Sometimes, surgery is needed to take out all or part of the lump to find out if its cancer. This is often done in a hospital. You will be given local anesthesia and you might be given medicine to make you sleepy.
Why Is Breast Cancer Called Inflammatory
It is characteristically aggressive disease and is called inflammatory because the cancer cells block the lymphatic vessels, resulting in changes in the breast. In inflammatory breast cancer, the cancer cells block the lymph vessels within the breast, which causes fluid backup and swelling of the breast and overlying skin.
Read Also: Is Breast Cancer Common In 18 Year Olds
What Are The Early Signs Of Breast Cancer
Breast cancer symptoms can vary for each person. Possible signs of breast cancer include:
- A change in the size, shape or contour of your breast.
- A mass or lump, which may feel as small as a pea.
- A lump or thickening in or near your breast or in your underarm that persists through your menstrual cycle.
- A change in the look or feel of your skin on your breast or nipple .
- Redness of your skin on your breast or nipple.
- An area thats distinctly different from any other area on either breast.
- A marble-like hardened area under your skin.
- A blood-stained or clear fluid discharge from your nipple.
Some people dont notice any signs of breast cancer at all. Thats why routine mammograms and are so important.
What Is A Normal Breast
No breast is typical. What is normal for you may not be normal for another woman. Most women say their breasts feel lumpy or uneven. The way your breasts look and feel can be affected by getting your period, having children, losing or gaining weight, and taking certain medications. Breasts also tend to change as you age. For more information, see the National Cancer Institutes Breast Changes and Conditions.external icon
Recommended Reading: Do Silicone Breast Implants Cause Cancer
Checking For Ductal Breast Cancer In Lymph Nodes
The goal of invasive ductal carcinoma treatment is to get the cancer out of the breast. But we also may need to remove lymph nodes if the cancer has spread there, Wright explains.
Your lymph nodes are part of your immune system. Lymph fluid from the breast drains into the axillary lymph nodes. The number and location of axillary lymph nodes may be different from person to person.
A sentinel lymph node biopsy is a test that can help your doctor determine if removing lymph nodes may be part of your cancer surgery.
The sentinel lymph node is where cancer from invasive ductal carcinoma is likely to show up first. Your doctor can identify the sentinel lymph node by injecting dye into the breast and seeing which node takes up the dye first: This is the sentinel. A sample of tissue from this node can reveal if cancer has spread there.
If theres no cancer in the sentinel node, the other nodes are OK and dont need to be removed, says Wright. If theres a small amount of cancer present, well leave nodes in place and treat the area with radiation or use chemotherapy.
If we see a lot of cancer in the lymph nodes or if four or more lymph nodes are affected, we perform an axillary lymph node dissection: surgery to remove the nodes.
The Use Of Certain Medicines And Other Factors Decrease The Risk Of Breast Cancer

Anything that decreases your chance of getting a disease is called a protective factor.
Protective factors for breast cancer include the following:
- Taking any of the following:
Read Also: Does Early Menopause Cause Breast Cancer
Money And Financial Support
If you have to reduce or stop work because of your cancer, you may find it difficult to cope financially.
If you have cancer or you’re caring for someone with cancer, you may be entitled to financial support, for example:
- if you have a job but can’t work because of your illness, you’re entitled to Statutory Sick Pay from your employer
- if you don’t have a job and can’t work because of your illness, you may be entitled to Employment and Support Allowance
- if you’re caring for someone with cancer, you may be entitled to Carers Allowance
- you may be eligible for other benefits if you have children living at home, or if you have a low household income
Find out what help is available to you as soon as possible. The social worker at your hospital will be able to give you the information you need.
Surgery For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Breast cancer treatment has evolved to offer patients more options. In addition to removing breast cancer, new aesthetic surgical approaches can enhance well-being and lessen the emotional impact of losing all or part of a breast to cancer. Comprehensive breast centers with coordinated teams of oncologic and plastic surgery practitioners can offer a wider array of options.
Surgery for IDC may include one of these procedures:
- Lumpectomy is removal of part of the breast. It is also known as breast-conserving surgery. Lumpectomy may be followed by radiation treatments to treat any remaining cancer cells.
- Mastectomy is removal of the breast. Mastectomy is a treatment for patients with multiple, very aggressive, or large invasive ductal tumors. It can be followed by breast reconstruction.
Recommended Reading: How Dangerous Is Breast Cancer