Breast Pain: 10 Reasons Your Breasts May Hurt
Most women experience some form of breast pain at one time or another. Breast pain is typically easy to treat, but on rarer occasions it can be a sign of something more serious.
Medical director of the Suburban Hospital Breast Center Pamela Wright, M.D., discusses the most common causes of breast pain , their treatments and when to see a doctor:
Hormones are making your breasts sore.
Hormonal fluctuations are the number one reason women have breast pain. Breasts become sore three to five days prior to the beginning of a menstrual period and stop hurting after it starts. This is due to a rise in estrogen and progesterone right before your period. These hormones cause your breasts to swell and can lead to tenderness.
Its normal to have breast tenderness that comes and goes around the time of your period, says Wright. Its nothing to worry about.
If you become pregnant, your breasts may remain sore during the first trimester as hormone production ramps up. Breast tenderness is one of the earliest signs of pregnancy for many women.
Steps you can take to minimize sore breasts include:
Who Gets Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is the most common cancer among women other than skin cancer. Increasing age is the most common risk factor for developing breast cancer, with 66% of breast cancer patients being diagnosed after the age of 55.
In the US, breast cancer is the second-leading cause of cancer death in women after lung cancer, and its the leading cause of cancer death among women ages 35 to 54. Only 5 to 10% of breast cancers occur in women with a clearly defined genetic predisposition for the disease. The majority of breast cancer cases are sporadic, meaning there is no definitive gene mutation.
Read Also: How Do You Check For Male Breast Cancer
Breast Lumps Or Lumpiness
Many women find their breasts feel lumpy. Breast tissue naturally has a bumpy texture.
Some women have more lumpiness in their breasts than others. In most cases, this lumpiness is no cause to worry.
If the lumpiness can be felt throughout the breast and feels like your other breast, then its likely normal breast tissue.
Lumps that feel harder or different from the rest of the breast or that feel like a change should be checked. This type of lump may be a sign of breast cancer or a benign breast condition .
See a health care provider if you:
- Find a new lump that feels different from the rest of your breast
- Find a new lump that feels different from your other breast
- Feel something thats different from what you felt before
If youve had a benign lump in the past, dont assume a new lump will also be benign. The new lump may not be breast cancer, but its best to make sure.
Recommended Reading: How To Cure Breast Cancer With Baking Soda
Stress Anxiety And Breast Pain
During particularly harsh periods of anxiety, pressure and stress, you can experience breast pain.
What causes it? While the science isnt in on the ‘why’, once again it seems to come back to hormonal fluctuations. Research has found correlations between the impact of stress and oestrogen levels, meaning that increased stress during a specific time during the menstrual cycle could cause excess discomfort.
Whats the treatment for stress-related breast pain? Its easy for us to say dont stress so much but we know thats not as easy to do. Our stress health guide has lots of interesting articles and resources to help you better manage your stress. Youll also find programs and services we can offer if you need more help in getting on top of stress.
What Is Breast Cancer

Breast cancer is a type of cancer that starts in the breast. It starts when cells in the breast begin to grow out of control.
Breast cancer cells usually form a tumor that can often be seen on an x-ray or felt as a lump. Breast cancer is most common in women, but men can get breast cancer, too.
Breast cancer cells can spread to other parts of the body and grow there, too. When cancer cells do this, its called metastasis.
Cancer is always named based on the place where it starts. So even if breast cancer spreads to the bones , its still called breast cancer. Its not called bone cancer unless it starts from cells in the bone.
The breast
You May Like: Red Mill Baking Soda Cancer
Change In Size Shape Or Feel Of Your Breast
A cancer might cause your breast to look bigger or have a different shape than usual, it might feel different.
Many healthy women find that their breasts feel lumpy and tender just before their period.
It can help to be breast aware. This means getting to know the size, shape and feel of your breasts.
When To See Your Healthcare Provider
It’s important to talk to your healthcare provider if you have breast pain from any cause. Even if it’s not due to cancer, many women find that breast pain decreases their quality of life. In one study, 15% of women experienced breast pain at some time in their life that interfered with work and family activities. Make sure to talk to your healthcare provider if you are experiencing any unusual discomfort.
Read Also: Stage Four Breast Cancer Treatment
Breast Changes In Boys
In men, enlargement of male breast tissue is a non-cancerous breast change. Breast buds are common in teenage boys during puberty. The buds may last up to 2 years, but they tend to go away within the first year. Breast buds develop because of rapid changes in hormone levels.
Treatment of a breast problem depends on the cause of the problem.
Check your symptoms to decide if and when you should see a doctor.
Working With A Pain Management For Breast Cancer Team
Many hospitals and medical centers now have pain management programs, also called palliative care. These are staffed by a range of healthcare professionals specialized in assessing and treating pain. Palliative care is for anyone who needs help due to the physical pain, as well as the stress and anxiety, which cancer can cause.
Recommended Reading: Stage 3 B Cancer
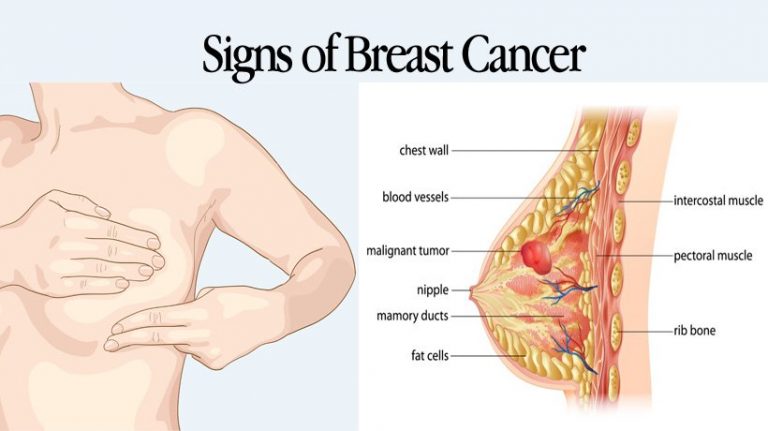
Signs And Symptoms Of Breast Cancer
In its early stages, breast cancer may not cause any symptoms. In many cases, a tumor may be too small to be felt, but an abnormality can still be seen on a mammogram.
If a tumor can be felt, the first sign is usually a new lump in the breast that was not there before. However, not all lumps are cancer.
Each type of breast cancer can cause a variety of symptoms. Many of these symptoms are similar, but some can be different. Symptoms for the most common breast cancers include:
- a breast lump or tissue thickening that feels different than surrounding tissue and has developed recently
- breast pain
- changes to the appearance of the skin on your breasts
- a lump or swelling under your arm
If you have any of these symptoms, it doesnt necessarily mean you have breast cancer. For instance, pain in your breast or a breast lump can be caused by a benign cyst.
Still, if you find a lump in your breast or have other symptoms, you should see your doctor for further examination and testing.
Dont Miss: Breast Cancer Spread To Brain Life Expectancy
Questions To Ask About Planning Follow
-
What is the chance that the cancer will come back? Should I watch for specific signs or symptoms?
-
What long-term side effects or late effects are possible based on the cancer treatment I received?
-
After my treatment has ended, what will my follow-up care plan be?
-
How often will I need to see a doctor?
-
If I move or need to switch doctors, how do I make sure to continue my recommended follow-up care schedule?
-
What follow-up tests will I need, and how often will those tests be needed?
-
Can I get copies of my laboratory test results?
-
How do I get a treatment summary and survivorship care plan to keep in my personal records?
-
Who will lead my follow-up care?
-
What survivorship support services are available to me? To my family?
The next section in this guide is Additional Resources. It offers more resources on this website that may be helpful to you. Use the menu to choose a different section to read in this guide.
Read Also: Hormone Therapy Metastatic Breast Cancer
Read Also: Estrogen Positive Breast Cancer Survival
Surgery That Removes All Of The Breast
Mastectomy procedures include:
- Total or simple mastectomy, which is the removal of the whole breast.
- Modified radical mastectomy, which is the removal of the whole breast and the lymph nodes under the arm .
- Radical mastectomy, which is the removal of the breast, chest muscles, and all of the lymph nodes under the arm . This surgery is rarely used.
Depending on the location of the tumour in the breast or other factors, some women may be able to have a skin-sparing or nipple-sparing mastectomy. Skin-sparing mastectomy leaves most of the skin, except for the nipple and the areola. Nipple-sparing mastectomy saves the skin as well as the nipple and areola.
Tests At The Breast Cancer Clinic
If you have suspected breast cancer you’ll be referred to a specialist breast cancer clinic for further tests. This referral will be because of your symptoms or because your mammogram has shown an abnormality,
Mammogram and breast ultrasound
If you have symptoms and have been referred to a specialist breast unit by your GP, you’ll probably be invited to have a mammogram if you are over 35 years old. This is an X-ray of your breasts. You may also need an ultrasound scan.
If your cancer was detected through the BreastCheck screening programme, you may need another mammogram or ultrasound scan.
Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to produce an image of the inside of your breasts. It helps to determine the nature of a lump or of the abnormality. It may be needed to find out if a lump in your breast is solid or contains liquid.
Your breasts are made up of thousands of tiny glands that produce milk. This glandular tissue contains a higher concentration of breast cells than other breast tissue, making it denser.
Dense breast tissue can make a mammogram difficult to read. Lumps or areas of abnormal tissue are harder to spot.
Younger women tend to have denser breasts. This is why mammography is not routinely performed in women under 35 years. As you get older, the amount of glandular tissue in your breasts decreases and is replaced by fat. This means your breasts become less dense.
Biopsy
Also Check: Estrogen Sensitive Cancer
Types Of Breast Cancer
There are two categories that reflect the nature of breast cancer:
- Noninvasive cancer is cancer that hasnt spread from the original tissue. This is referred to as stage 0.
- Invasive cancer is cancer thats spread to surrounding tissues. These are categorized as stages 1, 2, 3, or 4.
The tissue affected determines the type of cancer:
- Ductal carcinoma is a cancer that forms in the lining of the milk ducts. This is the most common type of breast cancer.
- Lobular carcinoma is cancer in the lobules of the breast. The lobules are where milk is produced.
- Sarcoma is cancer in the breasts connective tissue. This is a rare type of breast cancer.
When you visit your doctor with concerns about breast pain, tenderness, or a lump, there are common tests they might perform.
Can Breast Cancer Be Prevented
At this time, there is no sure way to prevent breast cancer.
Some risk factors, such as your age and being female, cannot be controlled. But you may be able to do things to stay as healthy as you can, such as having a healthy diet and being active. Knowing your risk of getting breast cancer also can help you choose what steps to take.
Talk to your doctor about your risk. Find out when to start having mammograms and how often you need one. If your doctor confirms that you have a high or very high risk, ask about ways to reduce your risk, such as getting extra screening, taking medicine, or having surgery.
If you have a strong family history of breast cancer, ask your doctor about genetic testing. The test can check for gene changes that increase your risk for getting breast cancer and ovarian cancer.
Recommended Reading: Breast Cancer Life Expectancy Without Treatment
How Much Do Tamoxifen And Raloxifene Lower The Risk Of Breast Cancer
Multiple studies have shown that both tamoxifen and raloxifene can reduce the risk of developing estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer in healthy postmenopausal women who are at high risk of developing the disease. Tamoxifen lowered the risk by 50 percent. Raloxifene lowered the risk by 38 percent. Overall, the combined results of these studies showed that taking tamoxifen or raloxifene daily for five years reduced the risk of developing breast cancer by at least one-third. In one trial directly comparing tamoxifen with raloxifene, raloxifene was found to be slightly less effective than tamoxifen for preventing breast cancer.
Both tamoxifen and raloxifene have been approved for use to reduce the risk of developing breast cancer in women at high risk of the disease. Tamoxifen is approved for use in both premenopausal women and postmenopausal women . Raloxifene is approved for use only in postmenopausal women.
Less common but more serious side effects of tamoxifen and raloxifene include blood clots to the lungs or legs. Other serious side effects of tamoxifen are an increased risk for cataracts and endometrial cancers. Other common, less serious shared side effects of tamoxifen and raloxifene include hot flashes, night sweats, and vaginal dryness.
What Are The 6 Symptoms Of Breast Lumps And Pain
- Breast lump: Although alarming when you find one, most breast lumps are not cancer.
- Breast pain: Most commonly associated with fibrocystic changes, pain may occur in both breasts, though one may be more painful than the other. With fibrocystic changes, the pain occurs about a week before your menstrual period. The pain usually goes away gradually with the onset of your period.
- Cyclic breast pain is typically most severe before your period and gets better during your period.
- It is usually described as bilateral , in the upper outer areas of your breast, and is often associated with lumpiness.
- Women tend to describe this pain as dull, aching, heavy, or sore, and it can radiate to your armpit or even down your arm.
- The intensity of pain can vary widely with the range of severity from mild to severe enough to limit clothing selections, sleep positions, or hugging.
You May Like: Prognosis Of Stage 3 Breast Cancer
What Are The Types Of Breast Cancer
The most common types of breast cancer are:
- Infiltrating ductal carcinoma. This cancer starts in the milk ducts of the breast. It then breaks through the wall of the duct and invades the surrounding tissue in the breast. This is the most common form of breast cancer, accounting for 80% of cases.
- Ductal carcinoma in situ is ductal carcinoma in its earliest stage, or precancerous . In situ refers to the fact that the cancer hasnt spread beyond its point of origin. In this case, the disease is confined to the milk ducts and has not invaded nearby breast tissue. If untreated, ductal carcinoma in situ may become invasive cancer. It is almost always curable.
- Infiltrating lobular carcinoma. This cancer begins in the lobules of the breast where breast milk is produced, but has spread to surrounding tissues in the breast. It accounts for 10 to 15% of breast cancers. This cancer can be more difficult to diagnose with mammograms.
- Lobular carcinoma in situ is a marker for cancer that is only in the lobules of the breast. It isnt a true cancer, but serves as a marker for the increased risk of developing breast cancer later, possibly in both or either breasts. Thus, it is important for women with lobular carcinoma in situ to have regular clinical breast exams and mammograms.
Questions To Ask The Doctor
- Do you know the stage of the cancer?
- If not, how and when will you find out the stage of the cancer?
- Would you explain to me what the stage means in my case?
- Based on the stage of the cancer, how long do you think Ill live?
- Do you know if my cancer has any of these proteins: estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, or the HER2 protein?
- What does it mean if my cancer has any of these proteins?
- What will happen next?
There are many ways to treat breast cancer.
Surgery and radiation are used to treat cancer in a specific part of the body . They do not affect the rest of the body.
Chemotherapy, hormone treatment, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy drugs go through the whole body. They can reach cancer cells almost anywhere in the body.
Doctors often use more than one treatment for breast cancer. The treatment plan thats best for you will depend on:
- The cancer’s stage and grade
- If the cancer has specific proteins, like the HER2 protein or hormone receptors
- The chance that a type of treatment will cure the cancer or help in some way
- Your age
- Other health problems you have
- Your feelings about the treatment and the side effects that come with it
Recommended Reading: Stage 2 Grade 3 Breast Cancer