The Types Of Radiotherapy
The type of radiotherapy you have will depend on the type of breast cancer and the type of surgery you have. Some women may not need to have radiotherapy at all.
Types of radiotherapy include:
- breast radiotherapy after breast-conserving surgery, radiation is applied to the whole of the remaining breast tissue
- chest-wall radiotherapy after a mastectomy, radiotherapy is applied to the chest wall
- breast boost some women may be offered a boost of high-dose radiotherapy in the area where the cancer was removed however, this may affect the appearance of your breast, particularly if you have large breasts, and can sometimes have other side effects, including hardening of breast tissue
- radiotherapy to the lymph nodes where radiotherapy is aimed at the armpit and the surrounding area to kill any cancer that may be in the lymph nodes
Genetics And Family History
Treatment for breast cancer may depend partly on having a close relative with a history of breast cancer or testing positive for a gene that increases the risk of developing breast cancer.
Patients with these factors may choose a preventive surgical option, such as a bilateral mastectomy.
Clinical trials are studies in which patients volunteer to try new drugs, combinations of drugs, and methods of treatment under the careful supervision of doctors and researchers. Clinical trials are a crucial step in discovering new breast cancer treatment methods.
Emerging treatments for breast cancer being studied in clinical trials include:
- PARP inhibitors that block protein used to repair DNA damage that occurs during cell division are being used and tested for TNBC.
- Drugs that or prevent androgen production are being used and tested for TNBC.
If youre interested, ask your oncologist for information about available trials.
Immunotherapy As An Emerging Treatment
Immunotherapy is a relatively new treatment option, and while it hasnt been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for breast cancer yet, its a promising area.
Immunotherapy works by raising the bodys natural defenses to fight off the cancer. It has fewer side effects than chemotherapy and is less likely to cause resistance.
Pembrolizumab is an immune checkpoint inhibitor. Its a type of immunotherapy that has shown particular promise in the treatment of metastatic breast cancer.
It works by blocking specific antibodies that make it harder for the immune system to fight the cancer. This allows the body to fight back more efficiently. A 2016 study found 37.5 percent of patients with triple-negative breast cancer saw a benefit from the therapy.
Because immunotherapy isnt FDA approved yet, treatment is mostly available through clinical trials at this time.
Don’t Miss: Stage-three Cancer
What Are The Side Effects Of Chemo Versus Endocrine Therapy How Does Each Impact A Womans Health
Side effects of Chemotherapy include hair loss, nausea, damage to the heart and nerves, and an increased risk of both infection and rare leukemia later in life.
Less severe, Endocrine Therapy increases menopausal-type symptoms such as hot flashes. Occasionally it also increases joint pain, muscle pain, and weight gain. One of the Endocrine Therapy drug options Tamoxifen rarely may increase the chances of cancer in the uterus. Most patients tolerate it very well.
Read Also: Is Breast Cancer Curable In The 3 Stage
Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Neoadjuvant Her2
With neoadjuvant chemotherapy, all the chemotherapy to treat the breast cancer is usually given before surgery . If the tumor doesnt get smaller with the first combination of chemotherapy drugs, other combinations can be tried.
If your tumor is HER2-positive, you may get neoadjuvant trastuzumab and neoadjuvant pertuzumab , but not at the same time as the chemotherapy drug doxorubicin .
If your tumor is estrogen receptor-negative, progesterone receptor-negative and HER2-negative with a high risk of recurrence, you may get neoadjuvant pembrolizumab . Pembrolizumab is an immunotherapy drug.
Read Also: What Is A Malignant Neoplasm Of Breast
When Is Chemotherapy Used To Treat Early
The first treatment for early-stage breast cancer usually includes surgery and sometimes radiation. Your doctor may also talk to you about added treatment, such as chemotherapy and hormone therapy, that may help keep cancer from coming back.
It isnât possible for all women to know for sure who will benefit from added treatment. But if you have early-stage, estrogen receptor positive breast cancer with no cancer in the lymph nodes, you may have a gene test. Gene tests, such as the Oncotype DX, may be done on the cancerous tissue that was removed to look for tumor markers. These tests can give your doctor important information about whether chemotherapy will help you.
The type of added treatment you have depends on the stage and classification of your breast cancer:
Also Check: Metastatic Breast Adenocarcinoma
Is Early Menopause A Risk Of Chemotherapy For Breast Cancer
Yes. If you have not gone through menopause, chemotherapy may stop your ovaries from producing estrogen. You may go into early menopause. If you want to have children in the future, discuss the risks of infertility with your healthcare provider.
Some womens ovaries begin working again after chemotherapy treatment. Women who want to bear children in the future may also choose fertility preservation before starting chemotherapy.
You May Like: Stage 4 Invasive Breast Cancer
How Long After Cancer Diagnosis Does Treatment Start
In general, most breast cancer treatments should start soon after a diagnosis. What does soon mean? This depends on the type of cancer, how aggressive it is, if additional testing is needed and if you plan to seek a second opinion.
A few days or a week may go by without treatment as your doctors put a plan in place. If this occurs, you may feel antsy and wonder if those lost days will cause your cancer to spread. Most cancers grow slowly, though, so waiting a short amount of time wont typically alter the outcome.
Timeline After Breast Cancer Diagnosis
Receiving a breast cancer diagnosis can create many feelings and emotions. Since some breast cancer diagnoses come with a bleak outlook, its common to want to start a treatment plan as soon as possible.
This article is designed to give you a comprehensive understanding of which factors play a role in your prognosis and what you should expect in the coming days, weeks and months following your diagnosis.
You May Like: What Is Stage 3 Cancer Mean
How Is Chemotherapy For Breast Cancer Given
Chemo drugs for breast cancer are typically given into a vein , either as an injection over a few minutes or as an infusion over a longer period of time. This can be done in a doctors office, infusion center, or in a hospital setting.
Often, a slightly larger and sturdier IV is required in the vein system to administer chemo. These are known as central venous catheters , central venous access devices , or central lines. They are used to put medicines, blood products, nutrients, or fluids right into your blood. They can also be used to take out blood for testing.
There are many different kinds of CVCs. The most common types are the port and the PICC line. For breast cancer patients, the central line is typically placed on the side opposite of the breast cancer. If a woman has breast cancer in both breasts, the central line will most likely be placed on the side that had fewer lymph nodes removed or involved with cancer.
Chemo is given in cycles, followed by a rest period to give you time to recover from the effects of the drugs. Chemo cycles are most often 2 or 3 weeks long. The schedule varies depending on the drugs used. For example, with some drugs, chemo is given only on the first day of the cycle. With others, it is given one day a week for a few weeks or every other week. Then, at the end of the cycle, the chemo schedule repeats to start the next cycle.
What Does Cancer Grade Mean
Breast cancers are given a grade according to:
- How different the cancer cells are to normal breast cells
- How quickly they are growing
The grade of a cancer is different to the cancer stage.
A cancers grade is determined when a doctor looks at the cancer cells under a microscope, using tissue from a biopsy or after breast cancer surgery.
Don’t Miss: Fish Test Breast Cancer
The Pressure Of Patient Expectations
A majority of surveyed physicians reported that patients want the most aggressive treatment, even if the benefit is small, and that it takes more effort to tell patients that they do not need radiation than it does to recommend it.
Its important to recognize that this is a controversial area, says Shumway. You cant say that offering radiation to older women is wrong. It really is a patient-driven decision, and it depends on the patients own values and preferences, in addition to her risk of recurrence and overall health.
As the point of first contact for breast cancer patients, surgeons have a tremendous influence on how patients choose treatment options.
Which is why Shumway thinks they could play a crucial role in counseling older women about options for less aggressive therapy.
The population is aging, and this is going to be an issue that affects more women, says Shumway. There is increasing attention given to considerations that are unique to older patients and in this case, their vulnerability for overtreatment.
Shumways future work will focus on developing interventions to help patients make fully informed decisions and understand the concept of competing causes of mortality.
Learn more about breast cancer and breast cancer treatment:
Is Chemotherapy Necessary Before Or After Breast Cancer Surgery Or At All
A recent study found that breast cancer has been highly over treated with chemotherapy and doctors can now confidently provide an alternative treatment known as Endocrine Therapy.
However, each patient is different with a unique set of circumstances. Chemotherapy is necessary in advanced stages, as well as early stages when specific characteristics are present, such as spreading to the lymph nodes or other body parts.
Recommended Reading: Side Effects Of Hormone Blockers For Breast Cancer
Chemo Drugs For Breast Cancer That Has Spread
- Taxanes: Paclitaxel , docetaxel , and albumin-bound paclitaxel
- Ixabepilone
- Gemcitabine
- Antibody drug conjugates
Although drug combinations are often used to treat early breast cancer, advanced breast cancer often is treated with single chemo drugs. Still, some combinations, such as paclitaxel plus gemcitabine, are commonly used to treat metastatic breast cancer.
For cancers that are HER2-positive, one or more drugs that target HER2 may be used with chemo.
Chemotherapy For Breast Cancer
Chemotherapy uses anti-cancer drugs that may be given intravenously or by mouth. The drugs travel through the bloodstream to reach cancer cells in most parts of the body. Sometimes, if cancer spreads to the spinal fluid, which surrounds and cushions the brain and spinal cord, chemo may be given directly into in this area .
On this page
You May Like: What Happens If You Get Hit In The Breast
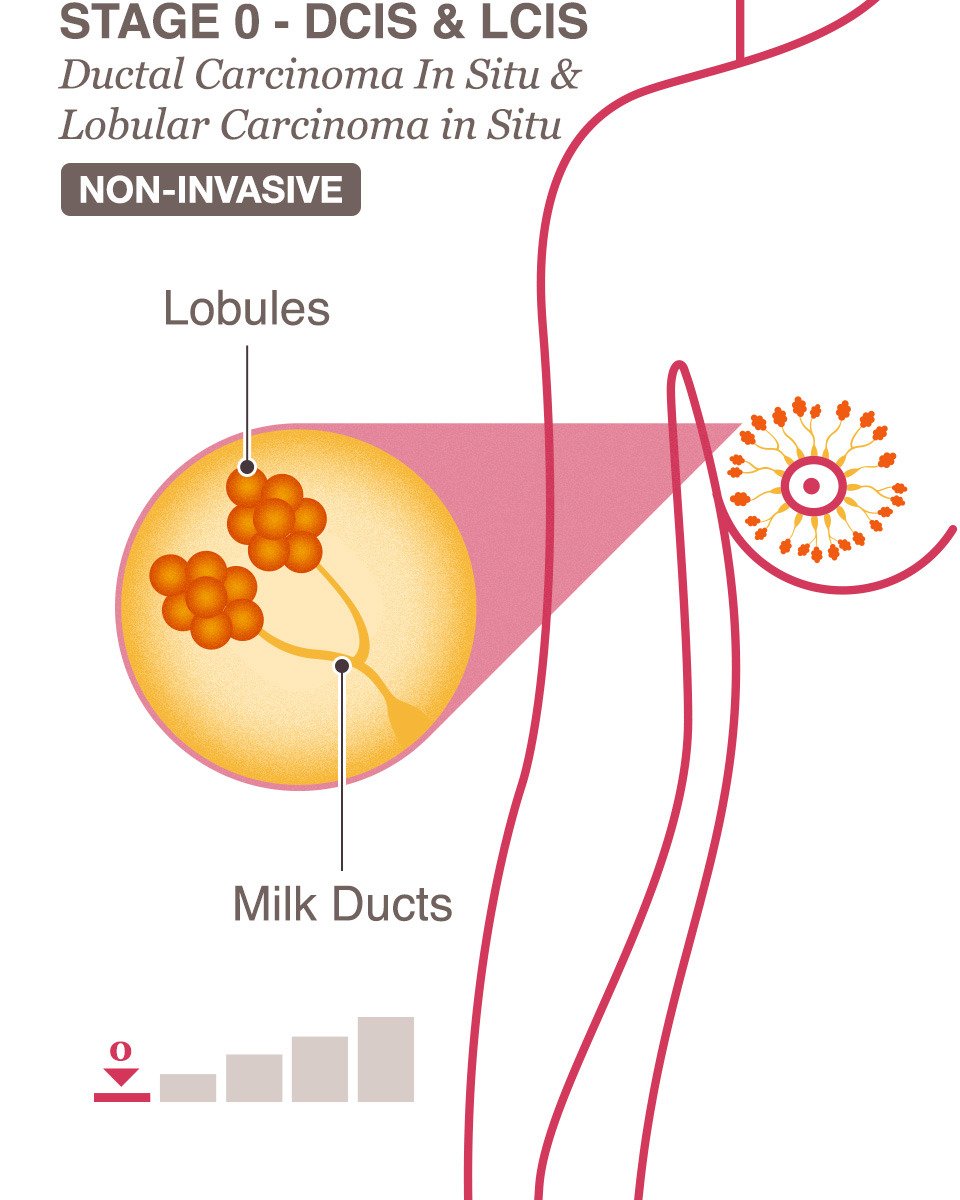
What Should A Person With Stage 0 Or Stage 1 Breast Cancer Expect Regarding Treatment
Even though Stage 0 breast cancer is considered non-invasive, it does require treatment, typically surgery or radiation, or a combination of the two. Chemotherapy is usually not part of the treatment regimen for earlier stages of cancer.
Stage 1 is highly treatable, however, it does require treatment, typically surgery and often radiation, or a combination of the two. Additionally, you may consider hormone therapy, depending on the type of cancer cells found and your additional risk factors. Like stage 0, Chemotherapy is often not necessary for earlier stages of cancer.
Material on this page courtesy of National Cancer Institute
Treatment For Stage 2 Breast Cancer
The most common for stage 2 breast cancer is surgery.
Surgery
In most cases, treatment involves removing the cancer. The person may undergo a lumpectomy or mastectomy. The doctors and the individual can decide based on the size and location of the tumor. The surgeon may also remove one or more lymph nodes.
Combination therapy
A doctor may recommend a combination of radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and hormone therapy to people with stage 2A or 2B breast cancer.
Neoadjuvant therapy
In some cases, a doctor may recommend neoadjuvant therapy, which is chemotherapy before surgery to reduce the size of a tumor.
are 3A, 3B, and 3C.
3A breast cancer is an invasive breast cancer where:
- There is no tumor in the breast, or a tumor of any size is growing alongside cancer found in four to nine axillary lymph nodes or the lymph nodes by the breastbone.
- A person has a tumor greater than 5 cm. They also have clusters of breast cancer cells in the lymph nodes that are between 0.22 mm in diameter.
- The tumor is larger than 5 cm. The cancer has also spread to one to three axillary lymph nodes or the lymph nodes near the breastbone.
Stage 3B breast cancer is invasive breast cancer where:
- A tumor of any size has spread into the chest wall or skin of the breast, causing swelling or an ulcer to develop.
- Cancer cells may also be present in to up to nine axillary lymph nodes.
- They may be present in lymph nodes by the breastbone.
Recommended Reading: Effects Of Breast Cancer On A Person
What Are The Risks Of Chemotherapy
Different chemotherapy medicines tend to cause different side effects. Many women do not have problems with these side effects, while other women are bothered a lot. There are other medicines you can take to treat the side effects of chemo.
Talk to your doctor about the type of chemotherapy medicine that he or she is planning to give you. Ask about any side effects that the chemo may cause.
Short-term side effects can include:
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Hair thinning or hair loss.
- Mouth sores.
- Increased chance of bruising, bleeding, and infection.
- Memory and concentration problems.
Long-term side effects of chemotherapy can include:
- Early menopause, which means not being able to have children anymore. It also can include symptoms like hot flashes, vaginal dryness, and thinning bones .
- Concentration problems that may last for many months after your treatments are finished.
- In rare cases, heart damage and a higher risk of other types of cancers, such as leukemia.
Answers From The Community
-
Carool
First, I believe that, when it is said that, say, 95% of Stage 1 breast cancer patients have a 5-year survival rate, it means that 95% of those with Stage 1 breast cancer will survive for AT LEAST 5 years. Most of those people will go on to live for many years after that.
With regard to chemo, I was Stage 1 , but my breast cancer was HER2-positive , so my oncologist recommended four rounds of chemo . Nowadays, there is Herceptin for HER2+ patients, but 15 years ago, when I was diagnosed, Herceptin was given to treat only metastatic disease. Many factors are involved in whether or not chemo is recommended .
See what your oncologist recommends. I’d advise not making up your mind until you know more. Chemo is doable, and it’s best to use all tools in the toolbox, even though some of them aren’t very appealing. All the best to you – Carool
cbanks
These are great questions and suggest talking with your oncologist. For me, I support what our friends above have mentioned. I wanted the cancer gone so I did and still do whatever the doc recommends. For me I asked allot of questions, asked for advise and made the decions . It is important to have comfort level and trust with your doctor. I found by having that It really made treatment and after treatment less stressful. Good luck with your decisions and look forward to hearing more of your journey. Peace!
Don’t Miss: Stage 3 Of Breast Cancer
What Is Stage 1 Cancer
Stage 1 cancer typically means the cancer is small and localized to one area, and that it has not spread to the lymph nodes or other parts of the body. Even if the cancer spreads or improves, it will still be referred to by the stage at which it was diagnosed. Cancers at the same stage are often treated similarly. For example, treatment for stage 1 cancer generally includes surgery.
Stage 1 cancer is determined in the five most common cancers in the following ways:
Breast Cancer: Types Of Treatment

Have questions about breast cancer? Ask here.
ON THIS PAGE: You will learn about the different types of treatments doctors use for people with breast cancer. Use the menu to see other pages.
This section explains the types of treatments that are the standard of care for early-stage and locally advanced breast cancer. Standard of care means the best treatments known. When making treatment plan decisions, you are strongly encouraged to consider clinical trials as an option. A clinical trial is a research study that tests a new approach to treatment. Doctors want to learn whether the new treatment is safe, effective, and possibly better than the standard treatment. Clinical trials can test a new drug and how often it should be given, a new combination of standard treatments, or new doses of standard drugs or other treatments. Some clinical trials also test giving less treatment than what is usually done as the standard of care. Clinical trials are an option to consider for treatment and care for all stages of cancer. Your doctor can help you consider all your treatment options. Learn more about clinical trials in the About Clinical Trials and Latest Research sections of this guide.
You May Like: Can Breast Cancer Be Cured