How Much Does Brca1 And Brca2 Mutation Testing Cost
The cost for BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation testing usually ranges from several hundred to several thousand dollars. Insurance policies vary as to whether the cost of testing is covered. People who are considering BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation testing may want to find out about their insurance companyâs policies regarding genetic tests.
Criteria For Insurance Coverage For Breast Cancer Genetic Testing
Health insurance providers, including Medicaid and Medicare, differ in the criteria for coverage for DNA tests for BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations. Generally speaking, the person should have a family history of cancer – breast or ovarian cancer. Genetic counseling is another prerequisite and recommendations by a genetic counselor not affiliated with a laboratory are also often necessary. A genetic counselor will perform a risk assessment to identify risk factors and susceptibility to developing the condition.
People of Ashkenazi Jewish descent have a high risk of breast cancer when compared to the general population. This is why most insurance companies will cover these individuals.
Those with a family history of breast cancer and have family members with genetic mutations are at higher risk of also suffering from it. Cancer treatment is much more expensive than a DNA test and the preventative strategies for those with BRCA gene mutations are also much more cost-effective. More on that below.
The only way to know for sure if a health insurance company will pay for genetic test results is to request health plan information. Many people have changed their insurance plans to include coverage for breast cancer genetic testing. Changing health plans may not always be the right decision, so weigh the pros and cons carefully before moving forward with this option. Remember, breast cancer genetic testing costs arent as expensive as you believe – lower cost options are available.
What Are The Next Steps After Brca Gene Testing
Once youve taken a BRCA gene test, there are three possible test results you can receive:
- Positive. A positive result indicates the presence of a harmful BRCA1 or BRCA2 variant, which places you at an increased risk of developing breast, ovarian, or other cancers.
- Negative. A negative result indicates one of two things: 1) that you did not inherit a harmful BRCA1 or BRCA2 variant from a close family member, or 2) that you do not have the specific variant tested for but may possibly have another variant.
- Variant of uncertain significance . A VUS result indicates the presence of another genetic variant that is rare but not currently associated with an increased risk of cancer.
Depending on your test results, your doctor or genetic counselor will advise you on the next steps. If you have tested positive for BRCA1 or BRCA2 variants, there are many ways that you can reduce your cancer risk, including annual screenings, certain medications, and preventative surgeries.
Read Also: What Is The Test For Breast Cancer Called
Can I Do Genetic Testing At Home
Some at-home genetic tests can help you determine breast cancer risk. These tests typically involve providing a sample of saliva or cheek cells and sending the sample by mail to be tested.
Its recommended that you seek genetic testing from a healthcare professional rather than using an at-home test for the following reasons:
- an incomplete result: At-home tests may not cover all known variants of a gene, such as BRCA1 or BRCA2. Because of this, a negative result can be misleading.
- unnecessary alarm: At-home tests may detect common genetic variants that are only associated with a slight increase in breast cancer risk, meaning that a positive result may cause unnecessary alarm.
- genetic counseling: With genetic testing through a healthcare professional, youll often also have access to genetic counseling both before and after you receive your result. This can help you better understand your result in the context of your overall health.
- privacy: Your privacy may not be ensured when you use an at-home test. If you do choose to use one, carefully review a companys disclosure policy beforehand.
Getting genetic testing for breast cancer risk has several benefits. But there are some risks involved as well.
Why Do Some People Decide Not To Have The Test
After looking at the advantages and disadvantages of testing, some people choose not to have a genetic test. They may feel that they dont want to know if they have a higher than normal cancer risk.
Some people decide they dont want any preventative treatment even if they have a faulty gene. So they may not feel they have anything to gain by having the test.
Only you can decide what is best for you.
Recommended Reading: How Many Breast Lumps Are Cancer
What Do The Results Of Genetic Testing Mean
Genetic testing can give several possible results: positive, negative, true negative, uninformative negative, variant of uncertain significance, or benign variant.
Positive result. A positive test result means that the laboratory found a genetic variant that is associated with an inherited cancer susceptibility syndrome. A positive result may:
- For a person who has cancer, confirm that the cancer was likely due to an inherited genetic variant and help guide treatment choices
- Indicate an increased risk of developing certain cancer in the future and guide future management to lower that risk
- Provide important information that can help other family members make decisions about their own health care, such as whether to have genetic testing to see if they have also inherited the variant.
Also, people who have a positive test result that indicates that they have an increased risk of developing cancer in the future may be able to take steps to lower their risk of developing cancer or to find cancer earlier, including:
- Being checked at a younger age or more often for signs of cancer
- Reducing their cancer risk by taking medications or having surgery to remove at-risk tissue.
- Changing personal behaviors to reduce the risk of certain cancers
- Getting help to guide decisions about fertility and pregnancy
What Should You Do If You Get A Positive Result For One Of The Concerning Genetic Mutations Should I Get A Mastectomy
While a mastectomy is proven to be the most effective way in reducing breast cancer risk, particularly for those with a gene mutation, we understand that this isnt an option for everyone. Other available options that may reduce the chance of developing cancer or improve the likelihood of detecting it earlier, include having yearly screening with breast MRIs and regular mammograms, clinical breast examinations, paying close attention to how your breasts normally look, and engaging in healthy behavior such as regular exercise. Make sure to discuss your results and your options with your GP/ health care professional, as they are best placed to give you advice based on your personal situation.
Don’t Miss: Is Breast Cancer In Both Breast
Disadvantages Of Genetic Testing
Some genetic test results identify a variation in a gene. But it may not be clear whether it increases your cancer risk or not. This can be difficult to cope with.
You may have a constant worry about developing cancer if the test finds a faulty gene. If the test is positive, you may also need to tell other relatives that they may have inherited the same gene.
Should I Get Genetic Counseling
You may want to talk with a genetic counselor before or after you have genetic testing.
If youre considering genetic testing to learn whether you have an inherited gene mutation related to breast cancer risk, its recommended you talk with a genetic counselor before genetic testing. A genetic counselor can help you determine whether genetic testing would give you useful information and can discuss the benefits and risks of testing with you.
If youre getting genetic testing to help guide your breast cancer treatment, talking with a genetic counselor before or after testing can help you learn whether your test results affect you and your familys risk of breast cancer and other cancers.
For more information on genetic counseling, visit the National Cancer Institutes website or visit the National Society of Genetic Counselors website.
The National Society of Genetic Counselors has an online directory to help you find a genetic counselor.
Learn more about genetic counseling and weighing the risks and benefits of genetic testing to learn about breast cancer risk.
Don’t Miss: How To Cure Breast Cancer Naturally And Effectively
Does Insurance Cover Brca Testing
In the United States, BRCA testing is usually covered by insurance if the patient meets certain criteria. Insurance coverage and criteria varies by insurance plan, and genetic counselors will review potential costs and insurance coverage with you during your appointment.
Some insurance companies have specific testing criteria or do not cover testing in certain situations, even when it is considered medically appropriate. For example, Medicare has specific BRCA testing criteria that only includes individuals with a personal history of cancer. Therefore, Medicare does not cover someone with a known mutation in the family who has no personal history of cancer. Medicaid coverage typically varies by state.
Genetic Testing Facilities And Costs
You can get a genetic test in your doctors office to see if you have inherited an abnormal BRCA1, BRCA2, or PALB2 gene mutation. The doctor takes a blood or saliva sample and sends it to a commercial laboratory, or sometimes a research testing facility. During testing, the genes are separated from the rest of the DNA and scanned for abnormalities.
Whether the genetic test is handled by a research testing facility depends on the type of test and the specific genes being tested. Research laboratories tend to perform free and anonymous tests. But research laboratories may provide limited results or require multiple family members to participate. It also may take many months or years for test results to be ready, if they are ever made available at all.
In the United States, several laboratories conduct commercial BRCA1, BRCA2, and PALB2 testing, including Myriad Genetic Laboratories, Ambry Genetics, and GeneDx. These facilities report results in two to four weeks.
The most common causes of hereditary breast cancer are BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations. But abnormalities in other genes also have been associated with breast cancer risk.
Although many insurance plans cover genetic testing, its smart to confirm whether your insurance plan does.
Also Check: Signs And Symptoms Of Metastatic Breast Cancer
What Percentage Of The Population Have The Brca Gene Mutation
It is estimated that in Australia today, about 1 in 400 women are at the highest risk of breast cancer because they carry a BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene mutation. For these people, carrying a BRCA1 gene mutation is associated with an approximate 72% risk of developing breast cancer over the course of their lifetime. And they can have a risk of up to 44% of developing ovarian cancer. BRCA2 is associated with around a 69% chance of breast cancer and 17% chance of ovarian cancer of a lifetime.
Jewish women of eastern European ancestry are more likely to carry a BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene mutation, estimated to be present in about 1 in 40 women. This is 20 times more common than in the general population.
Whos Eligible For The Breast Cancer Index Test
You may be eligible for the Breast Cancer Index test if:
- you were diagnosed with early-stage breast cancer
- the cancer was hormone-receptor-positive
- there was no cancer in your lymph nodes or the cancer is lymph-node positive and is in one, two, or three lymph nodes
- youve been taking hormonal therapy for 4 to 5 years and want to know if taking hormonal therapy for more time will be beneficial
Research has shown that extending hormonal therapy for 5 more years for a total of 10 years of hormonal therapy can offer benefits for some women diagnosed with early-stage, hormone-receptor-positive disease.
The Breast Cancer Index test is performed on preserved tissue that was removed during the original biopsy or surgery.
Because many women have troubling side effects, including hot flashes and joint pain, from hormonal therapy, they want to know if extending the time they take hormonal therapy is worth tolerating the side effects.
Also Check: How Long Do You Live With Breast Cancer
Does Medicare Pay For Genetic Testing For Breast Cancer
Medicare covers genetic testing for people with a cancer diagnosis. Cancer treatment alone does not qualify for full coverage for genetic testing by Medicare. The criteria cancer patients must meed depend on where they live. The criteria often include some or more of the following:
- Suffering from ovarian cancer, fallopian tube cancer, or primary peritoneal cancer
- Breast cancer diagnoses in women 45 to 50 years old
- Women with triple-negative breast cancer before 60 years old
- Those of Ashkenazi Jewish descent who suffer from breast cancer
- Men with breast cancer
- Those with pancreatic cancer
- People suffering from metastatic prostate cancer or prostate cancer with a Gleason score of more than 7
- People with a history of BRCA mutations in their family
Adopted individuals may receive Medicare coverage for breast cancer genetic testing. People with a limited family history or those coming from small families may receive financial assistance with the cost of genetic testing. This is especially true if the person has female relatives who:
- Suffered breast or ovarian cancer before the age of 45
- Received a triple-negative breast cancer diagnosis before or at the age of 60
- History of cancer that could have been related to a BRCA gene
Talking With Your Health Care Provider
If you have questions about BRCA1, BRCA2 or other high-risk inherited gene mutations related to breast cancer or are considering genetic testing, talk with your health care provider.
Your health care provider can help you understand your breast cancer risk and can refer you to a genetic counselor if needed.
|
My Family Health History Tool |
|
My Family Health History tool is a web-based tool that makes it easy for you to record and organize your family health history. It can help you gather information thats useful as you talk with your family members, doctor or genetic counselor. |
Don’t Miss: How Many Women Die Of Breast Cancer Every Year
The Cost Of Breast Cancer Treatment
When comparing the cost of genetic testing to the cost of breast cancer treatment, its plain to see the worth.
- Breast cancer has the highest treatment cost out of all cancer.
- Co-pays for breast cancer patients can be as much as $5,800 depending on insurance coverage. Thats nearly three times as much as the most expensive genetic testing for breast cancer.
- Its not even the cost of the treatment that is high – the loss of income and future productivity is huge as well. Most cancer survivors dont work the same job they did before their illness and usually take a pay cut. Some people have a difficult time performing after their treatment due to illness or distress, and that can lead to a loss of income as well.
For those who do not have insurance to pay for treatment, the financial demands of oncology care can be insurmountable. The stress of battling cancer is bad enough but add in the financial hardships that come from it and youll really be distressed. The good news is that there is a way to prevent all of this stress from happening.
Learn More: Breast Cancer Genetic Testing: Pros and Cons
Positive Test Results And Gina
Many people avoid genetic testing because they believe it will affect their health and life insurance. This should not be a concern for anyone in the United States. In 2008, an act was put into place to ensure people were not discriminated against based on their genetic makeup. The act is called GINA, and it stands for the Genetic Information Nondiscrimination Act.
A DNA test revealing a cancer gene should not have any influence on insurance. Insurance companies know this and if you ever feel as though youve been discriminated against based on your genes, contact a legal professional.
Also Check: What Is Triple Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer
What Are The Limitations Of Gina
GINA does not generally apply to employers with fewer than 15 employees, the military, Veteran’s Administration, Indian Health Service, or the Federal Employee Health Benefits Plan. However, all but small employers have similar protections in place.
Currently, GINA does not address concerns about disability, long-term care, or life insurance. It is important to understand that genetic non-discrimination laws do not protect people from discrimination based on having had a cancer diagnosis.
Acknowledgements Of Research Support
This project was supported by the Weill Cornell Medicine Clinical & Translational Science Center and Invitae Genetics. Paul Christos was partially supported by the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences of the National Institutes of Health under Award Number UL1TR000457. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
You May Like: Breast Cancer And Birth Control
Multigene Breast And Ovarian Cancer Panels
Aetna considers multigene hereditary cancer panels that accompany BRCA testing , BRCAPlus , BRCAvantage Plus , High Risk Hereditary Breast Cancer , OncoGeneDx Comprehensive Cancer Panel , and OncoGeneDx High/Moderate Risk Panel) experimental and investigational because there is insufficient published evidence of their clinical validity and utility. However, the BRCA testing portion of these panels are considered medically necessary if the above outlined criteria are met.
Aetna members may NOT be eligible under the Plan for genetic testing for breast and/or ovarian cancer susceptibility for indications or tests other than those listed above including, but may not be limited to, the following:
- Any of the following genes, alone or as part of a panel: ATM, BARD1, BRIP1, CHEK2, Mre11 complex, NBN, RAD50, or RAD51 paralogs , and STK11.
- Any of the following genes as part of a breast or ovarian cancer panel: CDH1, MUTYH .
- Multigene panels for breast and/or ovarian cancer susceptibility including, but may not be limited to, the following:
- Single nucleotide polymorphism genotyping tests .
When To Get Testing Done
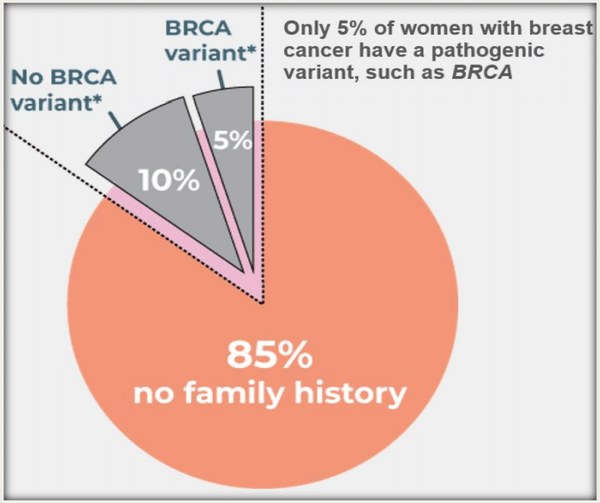
Not everyone is a candidate for genetic testing. In fact, only about 5% to 10% of all cancers are considered hereditary, although it varies by the specific cancer.
About one in 400 women have a BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation, although those of Ashkenazi Jewish heritage have a higher risk: one in 40. Lynch syndrome affects approximately one in 270 people and causes about 3% to 5% of colon cancers and 2% to 3% of uterine cancers.
To determine if you have a gene mutation, first gather your family history and see your doctor, said Susan Brown, senior director of education and support at Susan G. Komen.
If your health-care provider thinks you might have a hereditary mutation, you’ll be referred to a genetic counselor, who may order a blood or saliva test.
“It’s an easy test,” Brown said. “The ramifications of the results can be a little more complicated.
“If you have a positive mutation, then you have to think about what you are going to do with that information.”
Testing costs anywhere from a couple hundred dollars to several thousand dollars and may be covered by insurance. The multigene panel is pricey, since it surveys a number of genes.
If someone in your family has already been diagnosed with a specific mutation, you can be tested for that mutation alone, which is a lot cheaper. For those who don’t have health insurance, many of the gene-testing companies have programs that bring the cost down to $250 to $300.
Some tests may only check for a few mutations.
Also Check: How You Know If You Have Breast Cancer