How To Check For Breast Cancer
Doru Paul, MD, is triple board-certified in medical oncology, hematology, and internal medicine. He is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Weill Cornell Medical College and attending physician in the Department of Hematology and Oncology at the New York Presbyterian Weill Cornell Medical Center.
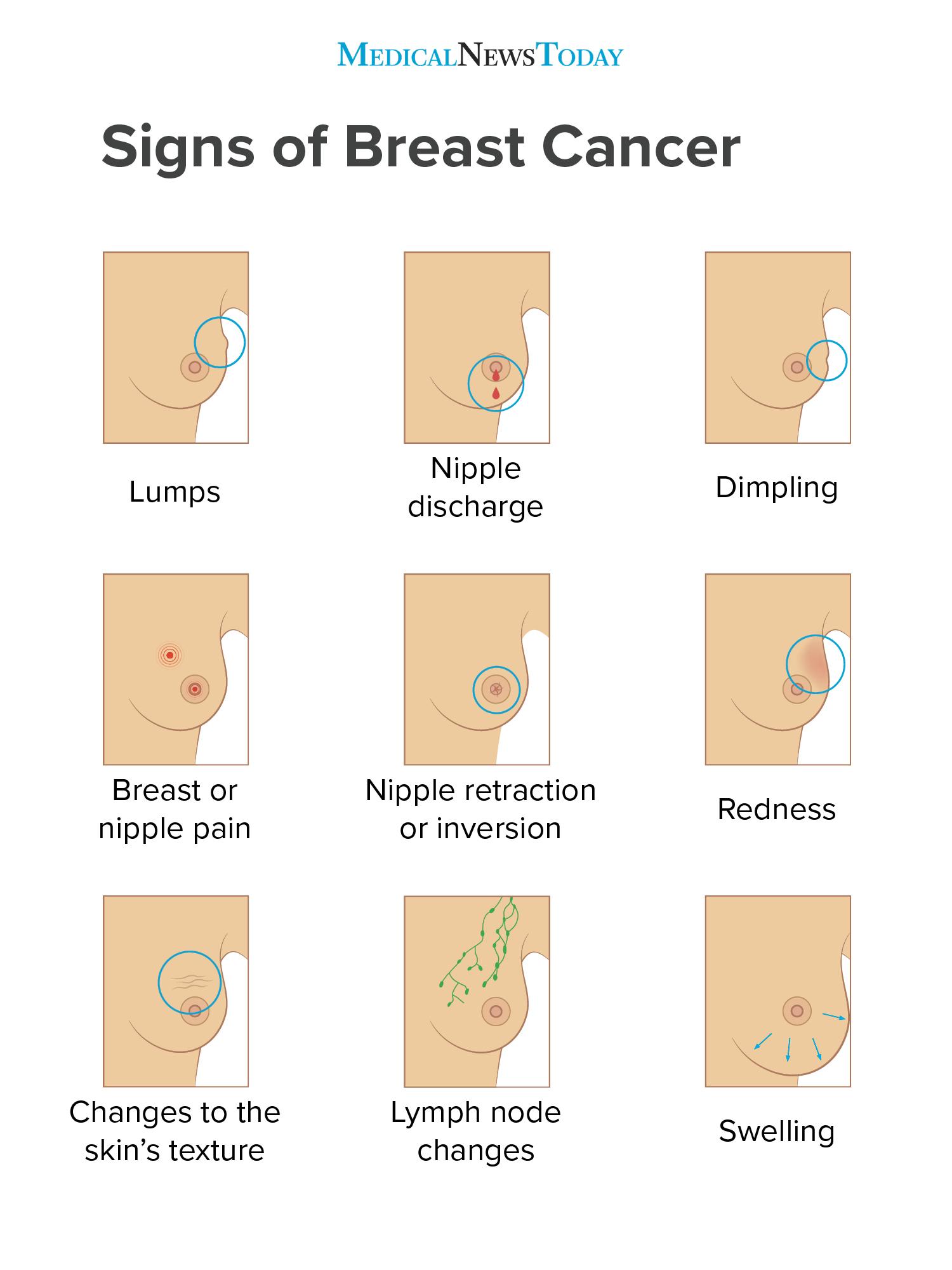
Itâs important that every woman knows how to do a breast self-examination , as it can help in early detection of breast cancer, such as lumps, nipple changes, and more.
Being familiar with what is normal for you will make it easier to recognize any new developments. Furthermore, knowing whatâs not normal for anyone can help prompt you to bring such issues to your doctorâs attention, should you notice them during your BSE.
This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing.
Medicare Coverage For Breast Cancer Screenings
Original Medicare Part B covers screenings you may need to detect breast cancer early, including mammograms and physical exams.
Mammogram coverage includes:
- One baseline mammogram if you’re a woman between the ages of 35 and 59
- Screening mammograms once every 12 months if you’re a woman aged 40 or older
For these screenings, you’d pay $0 as long as the provider accepts assignment. Diagnostic mammograms are covered more frequently if medically necessary and you’d pay 20% of the Medicare-approved amount .
Medicare also covers one Pap test and pelvic exam every 24 months and as part of that exam, Medicare covers a clinical breast exam.
There Are Ways To Find Low
If you dont have health insurance, dont assume that means you cant get screened. There may be more ways to get good, affordable health care than you think. Each October, during Breast Cancer Awareness Month, many mammography centers offer mammograms at reduced rates. Year round, there are organizations working to help women get screened whatever their financial and insurance status.
Getting screened for breast cancer is a crucial part of breast healthbut its not enough on its own. Heres everything you should know to take charge of your breast health.
You May Like: Recurring Breast Cancer Symptoms
Breast Examination After Treatment For Breast Cancer
After surgery
The incision line may be thick, raised, red and possibly tender for several months after surgery. Remember to examine the entire incision line.
If there is redness in areas away from the scar, contact your physician. It is not unusual to experience brief discomforts and sensations in the breast or nipple area .
At first, you may not know how to interpret what you feel, but soon you will become familiar with what is now normal for you.
After breast reconstruction
Following breast reconstruction, breast examination for the reconstructed breast is done exactly the same way as for the natural breast. If an implant was used for the reconstruction, press firmly inward at the edges of the implant to feel the ribs beneath. If your own tissue was used for the reconstruction, understand that you may feel some numbness and tightness in your breast. In time, some feeling in your breasts may return.
After radiation therapy
After radiation therapy, you may notice some changes in the breast tissue. The breast may look red or sunburned and may become irritated or inflamed. Once therapy is stopped, the redness will disappear and the breast will become less inflamed or irritated. At times, the skin can become more inflamed for a few days after treatment and then gradually improve after a few weeks. The pores in the skin over the breast also may become larger than usual.
What to do
Choosing The Right Surgical Oncologist
Doru Paul, MD, is triple board-certified in medical oncology, hematology, and internal medicine. He is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Weill Cornell Medical College and attending physician in the Department of Hematology and Oncology at the New York Presbyterian Weill Cornell Medical Center.
If you have been diagnosed with breast cancer, often the first thing you will want to do find a surgical oncologist. A surgical oncologist is trained to treat cancer by removing tumors and other cancerous tissues. They can also perform breast biopsies to confirm the diagnosis or stage the disease.
A surgical oncologist may be one of several healthcare providers you will turn to when faced with breast cancer. Others may include a medical oncologist who treats cancer with medicine and a radiation oncologist who treats cancer with radiation.
Also Check: Difference Between Stage 3 And 4 Cancer
‘i Had Fevers And Difficulty Breastfeeding’
I was misdiagnosed with mastitis twice because I had high fevers and trouble breastfeeding. It turned out to be cancer. Tumors were blocking the milk ducts. I was diagnosed with stage 3 breast cancer at age 32, five weeks after I had my first child. It didnt look like mastitis at all. So many people told me ‘100% chance’ it is nothing. No one thought of any alternative, however, until multiple courses of treatment failed.
Melissa Thompson, healthcare policy advocate, Stamford, Connecticut
What Happens If I Find A Lump
âIf a person feels a new lump in their breasts, they should absolutely inform their physician,â says Fishman. If you discover some symptoms, breast changes that concern you, or changes that persist after your menstrual cycle, see a doctor for evaluation.
Younger women are more likely to have dense breasts, the appearance of having more dense tissue than fatty tissue in the breast when viewed on a mammogram. This is a risk factor for breast cancer because dense tissue can hide cancers. The difference between a lump and having dense breasts is that dense breast tissue will often feel rubbery and usually without discrete edges around, says Abe.
âNot all breast lumps are indicative of breast cancer,â says Fishman. Most lumps are usually not cancer, and the most common benign and non-cancerous lumps are cysts and fibroadenomas.
According to Abe, âcancerous lumps are rarely painful, while benign, non-cancerous lumps can be painful. Still, not all lumps feel the same, so notify your doctor of any breast mass that doesnât feel normal. If you find a lump, the next step is to get a mammogram or ultrasound to better characterize it, she says.
Also Check: Does Taking Estrogen Cause Cancer
Other Screening Tests Have Been Or Are Being Studied In Clinical Trials
Studies have been done to find out if the following breast cancer screening tests are useful in finding breast cancer or helping women with breast cancer live longer.
Breast Exam
A clinical breast exam is an exam of the breast by a doctor or other health professional. He or she will carefully feel the breasts and under the arms for lumps or anything else that seems unusual. It is not known if having clinical breast exams decreases the chance of dying from breast cancer.
Breast self-exams may be done by women or men to check their breasts for lumps or other changes. If you feel any lumps or notice any other changes in your breasts, talk to your doctor. Doing regular breast self-exams has not been shown to decrease the chance of dying from breast cancer.
Thermography
Thermography is a procedure in which a special camera that senses heat is used to record the temperature of the skin that covers the breasts. Tumors can cause temperature changes that may show up on the thermogram.
There have been no randomized clinical trials of thermography to find out how well it detects breast cancer or the harms of the procedure.
Tissue sampling
Breast tissue sampling is taking cells from breast tissue to check under a microscope.Breast tissue sampling as a screening test has not been shown to decrease the risk of dying from breast cancer.
How Breast Cancer Spreads
Breast cancer can spread when the cancer cells get into the blood or lymph system and then are carried to other parts of the body.
The lymph system is a part of your body’s immune system. It is a network of lymph nodes , ducts or vessels, and organs that work together to collect and carry clear lymph fluid through the body tissues to the blood. The clear lymph fluid inside the lymph vessels contains tissue by-products and waste material, as well as immune system cells.
The lymph vessels carry lymph fluid away from the breast. In the case of breast cancer, cancer cells can enter those lymph vessels and start to grow in lymph nodes. Most of the lymph vessels of the breast drain into:
- Lymph nodes under the arm
- Lymph nodes inside the chest near the breastbone
- Lymph nodes around the collar bone
If cancer cells have spread to your lymph nodes, there is a higher chance that the cells could have traveled through the lymph system and spread to other parts of your body. Still, not all women with cancer cells in their lymph nodes develop metastases, and some women with no cancer cells in their lymph nodes might develop metastases later.
Recommended Reading: Can Stage 1 Breast Cancer Be Cured
Risk Factors For Breast Cancer
There are several risk factors that increase your chances of getting breast cancer. However, having any of these doesnt mean you will definitely develop the disease.
Some risk factors cant be avoided, such as family history. You can change other risk factors, such as quitting smoking, if you smoke. Risk factors for breast cancer include:
- Age. Your risk for developing breast cancer increases as you age. Most invasive breast cancers are found in women over age 55 years.
- Drinking alcohol. Alcohol use disorder raises your risk.
- Having dense breast tissue. Dense breast tissue makes mammograms hard to read. It also increases your risk for breast cancer.
- Gender. White women are
While there are risk factors you cant control, following a healthy lifestyle, getting regular screenings, and taking any preventive measures your doctor recommends can help reduce your risk for developing breast cancer.
What Happens After The Local Breast Cancer Treatment
Following local breast cancer treatment, the treatment team will determine the likelihood that the cancer will recur outside the breast. This team usually includes a medical oncologist, a specialist trained in using medicines to treat breast cancer. The medical oncologist, who works with the surgeon, may advise the use of the drugs like tamoxifen or anastrozole or possibly chemotherapy. These treatments are used in addition to, but not in place of, local breast cancer treatment with surgery and/or radiation therapy.
After treatment for breast cancer, it is especially important for a woman to continue to do a monthly breast examination. Regular examinations will help you detect local recurrences. Early signs of recurrence can be noted in the incision area itself, the opposite breast, the axilla , or supraclavicular region .
Maintaining your follow-up schedule with your physician is also necessary so problems can be detected when treatment can be most effective. Your health care provider will also be able to answer any questions you may have about breast self-examination after the following procedures.
Recommended Reading: Chest Cancer In Female
What Should I Do If I Find A Lump
Donât panic. It could be many things other than cancer. But do check in with your doctorâs office if you notice any new breast changes, such as:
- An area that is different from any other area on either breast
- A lump or thickening in or near the breast or in the underarm that lasts through your menstrual cycle
- A change in the size, shape, or contour of the breast
- A mass or lump
- A marble-like area under the skin
- A change in the feel or appearance of the skin on the breast or nipple
- Bloody or clear fluid discharge from the nipples
- Redness of the skin on the breast or nipple
Show Sources
Recommended Reading: Breast Cancer Stage 4 Life Expectancy
External Beam Radiation Therapy
The following three sections refer to treatment using x-rays.
Conventional external beam radiation therapy
Historically conventional external beam radiation therapy was delivered via two-dimensional beams using kilovoltage therapy x-ray units, medical linear accelerators that generate high-energy x-rays, or with machines that were similar to a linear accelerator in appearance, but used a sealed radioactive source like the one shown above. 2DXRT mainly consists of a single beam of radiation delivered to the patient from several directions: often front or back, and both sides.
Conventional refers to the way the treatment is planned or simulated on a specially calibrated diagnostic x-ray machine known as a simulator because it recreates the linear accelerator actions , and to the usually well-established arrangements of the radiation beams to achieve a desired plan. The aim of simulation is to accurately target or localize the volume which is to be treated. This technique is well established and is generally quick and reliable. The worry is that some high-dose treatments may be limited by the radiation toxicity capacity of healthy tissues which lie close to the target tumor volume.
Intensity-modulated radiation therapy
Also Check: Natural Cures For Breast Cancer
Breast Cancer Screening & Early Detection
After the age of 45, women should go for annual mammograms, breast exams, and cancer screenings to be proactive in detecting an abnormality. Catching cancer in its early stages is crucial for increasing a patient’s survival rate. If women are at a high risk due to family history or risk factors such as being overweight or having a previous exposure to chest radiation, they may want to consider scheduling mammograms earlier. If something irregular is detected, doctors may also order a breast ultrasound or a needle biopsy to further inspect the area. Patients should understand the proper protocols for detection, and doctors should communicate recommendations and offer insights about potential concerns.
If a doctor fails to order age-based cancer screenings, ignores a patient’s symptoms and concerns that may align with a breast cancer diagnosis, or fails to consider previous health conditions and red flags, a patient may not be receiving the standard of care that is to be expected. If a breast cancer diagnosis is delayed, leading to a more invasive breast cancer in its later stages, patients may be eligible to file a breast cancer misdiagnosis lawsuit and be awarded compensation for costly cancer treatments, pain, and suffering.
How Breast Cancer Starts
The breast is a highly complex part of the human body. The female breast goes through many changes over a lifetime from birth, puberty, pregnancy and breastfeeding, right through to menopause.
If you have been diagnosed with breast cancer, understanding the anatomy of the breast and the role each part has to play can be helpful to understand your diagnosis. It can also help you talk to your doctor about surgery and other treatment options.
In this piece we cover:-Understanding Breast Anatomy-Normal Breast Changes Through Life-How Does Cancer Start in the Breast?-How Does Cancer Spread Beyond the Breast?-Symptoms of Breast Cancer
You May Like: Malignant Neoplasm Of Breast Definition
What About Other Treatments That I Hear About
When you have cancer you might hear about other ways to treat the cancer or treat your symptoms. These may not always be standard medical treatments. These treatments may be vitamins, herbs, special diets, and other things. You may wonder about these treatments.
Some of these are known to help, but many have not been tested. Some have been shown not to help. A few have even been found to be harmful. Talk to your doctor about anything youre thinking about using, whether its a vitamin, a diet, or anything else.
Inflammatory Breast Cancer Symptoms
Unlike other breast cancers, inflammatory breast cancer rarely causes breast lumps and may not appear on a mammogram. Inflammatory breast cancer symptoms include:
- Red, swollen, itchy breast that is tender to the touch
- The surface of the breast may take on a ridged or pitted appearance, similar to an orange peel
- Heaviness, burning, or aching in one breast
- One breast is visibly larger than the other
- Inverted nipple
- No mass is felt with a breast self-exam
- Swollen lymph nodes under the arm and/or above the collarbone
- Symptoms unresolved after a course of antibiotics
Unlike other breast cancers, inflammatory breast cancer usually does not cause a distinct lump in the breast. Therefore, a breast self-exam, clinical breast exam, or even a mammogram may not detect inflammatory breast cancer. Ultrasounds may also miss inflammatory breast cancer. However, the changes to the surface of the breast caused by inflammatory breast cancer can be seen with the naked eye.
Symptoms of inflammatory breast cancer can develop rapidly, and the disease can progress quickly. Any sudden changes in the texture or appearance of the breast should be reported to your doctor immediately.
For women who are pregnant or breast-feeding, redness, swelling, itchiness and soreness are often signs of a breast infection such as mastitis, which is treatable with antibiotics. If you are not pregnant or nursing and you develop these symptoms, your doctor should test for inflammatory breast cancer.
Read Also: Baking Soda Drink For Cancer
If You Have An Abnormal Cbe:
If youre under 30 and your CBE reveals a lump, your doctor may recommend starting with observation. This means waiting 1-2 menstrual periods to see if the lump goes away on its own, then getting checked again. If youre not comfortable waiting, let your doctor know or ask for a second opinion.
If youre 30 or older and your CBE reveals a lump or other change, the most likely next step is a follow-up mammogram and maybe a breast ultrasound.
Read Also: Breast Cancer Metastasis Prognosis