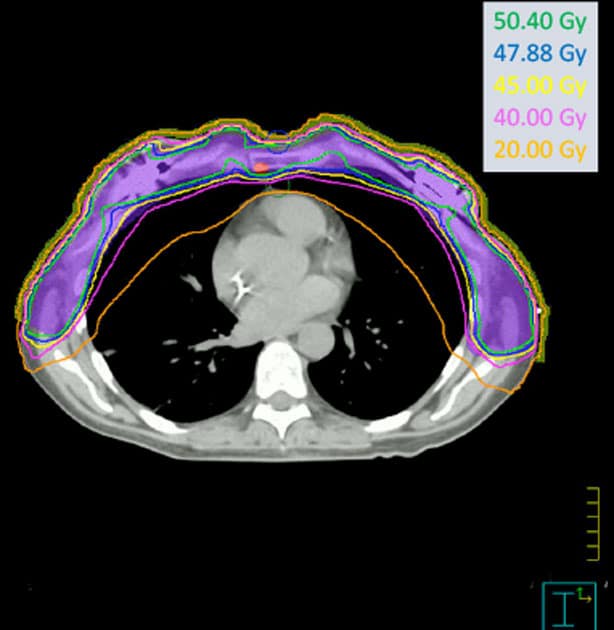
Predictors Of Heart And Lung Dose In Left
-
Contributed equally to this work with: Zheng Kang, Sijia Chen
Roles Conceptualization, Writing original draft
Affiliation Department of Radiation Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xiamen University, Xiamen, Fujian Province, China
-
Contributed equally to this work with: Zheng Kang, Sijia Chen
Roles Methodology, Writing review & editing
Affiliation Department of Radiation Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xiamen University, Xiamen, Fujian Province, China
Risk Of Cardiovascular Disease In Left Breast Cancer
In the entire patient group, the cumulative hazard of cardiovascular disease was numerically greater in patients treated with left-sided RT than those treated with right-sided RT, but the difference was not significant . The cumulative incidence of cardiovascular disease was 0.6% at 5 years and 1.9% at 10 years in patients treated with right breast RT and 1.0% at 5 years and 2.3% at 10 years in patients treated with left breast RT . Figure 2B shows the hazard plots for cardiovascular disease according to tumor laterality and hyperlipidemia. Regardless of hyperlipidemia, patients treated with left breast RT showed slightly higher incidence of cardiovascular disease than those treated with right breast RT, but the difference was not significant. Figure 2C shows the hazard plots for incidence of cardiovascular disease according to tumor laterality and smoking. Although smokers have a higher risk of cardiovascular disease, no difference was observed between left and right breast cancer in either group, the smokers or the nonsmokers. Table 4 indicates incidence rates and unadjusted HRs for cardiovascular disease in patients with left breast cancer relative to right breast cancer in various subgroups. None of the subgroups were identified to have a higher risk of cardiovascular disease in left breast cancer compared to right breast cancer.
Lt=left Rt=right HyL=hyperlipidemia.
Proton Therapy Is Our Focus
The New York Proton Center has a singular focusto provide adults and children with cancer the most sophisticated and advanced form of radiation therapy. While we do not provide surgery or chemotherapy, some of our patients do receive these important treatments from other healthcare providers in coordination with proton therapy.
You May Like: How Much Is Genetic Testing For Breast Cancer
Possible Side Effects Of External Beam Radiation
The main short-term side effects of external beam radiation therapy to the breast are:
- Swelling in the breast
- Skin changes in the treated area similar to a sunburn
Your health care team may advise you to avoid exposing the treated skin to the sun because it could make the skin changes worse. Most skin changes get better within a few months. Changes to the breast tissue usually go away in 6 to 12 months, but it can take longer.
External beam radiation therapy can also cause side effects later on:
What Is Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy is a commonly used therapy for many types of cancer. For breast cancer, radiation is typically used after surgery to help reduce the risk of cancer returning. It can also help treat a symptom, such as pain, in someone with cancer that has spread outside the breast.
During treatment, a dose of ionizing radiation is targeted at the tumor. It is often given each day, Monday through Friday, for one to six weeks. Each dose of radiation is referred to as a fraction.
Radiation damages the DNA inside the cells it’s hitting, which causes the cell’s death. Unfortunately, radiation can also damage healthy cells, leading to side effects. Some body tissues can handle radiation better than others, so side effects may occur quickly or appear later, even after radiation is done.
Read Also: How Serious Is Breast Cancer
Comparison Of Deep Inspiration Breath Hold Versus Free Breathing In Radiotherapy For Left Sided Breast Cancer
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xian Jiaotong University, Xian, China
- 2Department of Radiation Oncology, Shaanxi Provincial Tumor Hospital, Affiliated Hospital of Xian Jiaotong University Health Science Center, Xian, China
- 3Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Xian Central Hospital, The Affiliated Hospital of Xian Jiaotong University, Xian, China
- 4Department of Thoracic Surgery, Second Affiliated Hospital of Air Force Medical University, Xian, China
- 5Department of Radiation Oncology, Weinan Central Hospital, Weinan, China
Objectives: Modern breast cancer techniques, such as the deep inspiration breath-hold technique has been applied for left-sided breast cancer. Whether the DIBH regimen is the optimal solution for left-sided breast cancer remains unclear. This meta-analysis aims to elucidate the differences of DIBH and free-breathing for patients receiving radiotherapy for left-sided breast cancer and provide a practical reference for clinical practice.
Methods: Relevant research available on PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, and the Web of Science published before November 30, 2021 was independently and systematically examined by two investigators. Data were extracted from eligible studies for assessing their qualities and calculating the standardized mean difference and 95% confidence intervals using Review Manager software 5.4 .
Risk Of Heart Disease Following Treatment For Breast Cancer Results From A Population
eLife11
Recommended Reading: What Does Breast Cancer Rash Look Like
What Is The Long Term Outlook For Patients Treated With Radiation Therapy
As more patients are surviving cancer and living longer, knowledge about the long-term effects of treatment is expanding. It is becoming clear that the longer a patient lives after cancer treatment, the more likely that damage to the heart will develop.
Patients who develop radiation-related cardiotoxicity should be under the care of a cardiologist who understands the relationship between cancer treatment and heart problems. Although cardiotoxicity can be life-threatening, many of these problems can be managed effectively with medication and minimally invasive treatments.
What Are The Effects Of Breast Radiation
Radiation may cause scar tissue buildup which results in the breast feeling hard. Shrinkage of breast tissue is one of the more common breast cancer radiation side effects.
What are the side effects of breast cancer radiation?
Common breast cancer radiation side effects may include redness, dryness or irritation of the skin in the treated area. Another common side effect is fatigue, especially in the later weeks of treatment and for some time afterward.
Can radiation damage the heart?
In other words, radiation can injury literally every part of the heart. This means that the pericardium , myocardium, heart valves and arteries can all be damaged by radiation therapy. The hearts electrical system can also be susceptible to damage, leading to arrhythmias.
Also Check: Do Men Get Breast Cancer
How We Protect Breast Cancer Patients Hearts During Radiation Therapy
Many breast cancer patients undergo radiation therapy as part of their treatment. While radiation therapy often comes with side effects, such as skin irritation and fatigue, patients with left-sided breast cancer have an added concern: potential for heart disease.
Years ago, researchers discovered that many patients who underwent radiation therapy to the left breast later developed heart conditions, including pericardial disease, conduction abnormalities, coronary artery disease, congestive heart disease, heart valve disease and even sudden cardiac death. Scientists linked these problems to the hearts exposure to radiation during treatment. Thats why MD Anderson now takes extra precautions to protect patients hearts during radiation therapy. Our goal is to offer state-of-the-art radiation therapy for breast cancer without increasing the risk of long-term heart issues.
How we protect the heart during radiation therapy
Here are four methods that we use at MD Anderson to reduce the risk of radiation-induced heart disease.
Multi-leaf collimation: Our linear accelerator machines are equipped with a special shield to protect the heart from radiation exposure. This shield has multiple leafs that can move independently in and out of the path of the radiation beam to allow the radiation to target cancer cells while protecting nearby healthy tissue.
How we determine the best method for you
Focus on a healthy lifestyle
Heart Issues After Breast Cancer Radiation: Left Side Has Twice The Risk
Coronary artery disease was far more common in young women with breast cancer who had radiation to their left breast than in those who had it to their right.
Young women who receive radiation therapy to their left breast where their heart is located have more than twice the risk of developing coronary artery disease than those who had radiation to their right side.
Coronary heart disease is something that increases in risk as women age, generally in the population. Most previous studies have focused on the average breast cancer survivor population that is a bit older in their 60s and 70s, on average. We were interested in whether this effect among younger, typically healthier women was also present. And we found that it was, said Gordon P. Watt, a postdoctoral research fellow in the department of epidemiology and biostatistics at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, in an interview with CURE®. Watt is a co-author of recent research that analyzed the risk of coronary artery disease in women with breast cancer between the ages of 25 and 54.
The study included 972 women who underwent radiation therapy for breast cancer: 466 had it on the right side and 506 on the left. Average age at diagnosis for both groups was 46, and each group was followed up with for 14 years.
Given these findings, women of all ages may want to advocate for continued follow-up and survivorship care after radiation treatment for breast cancer.
Related Content:
Read Also: What Screening Is Used To Test For Breast Cancer
Ssgrt Helps Us Make Sure Your Heart Is In The Right Place
During treatment planning, youll lie on your back for 3D images to be taken of your body. Well ask you to take and hold a deep breath usually for 15-25 seconds so that your breast is as far from your heart as it can be. This is called Deep Inspiration Breath Hold, or DIBH. DIBH will protect your heart during treatment.
Then, during treatment, youll take and hold a deep breath in the same way as before. When your breast surface is at the right position, the display lights turn green and the SGRT system turns the radiation beam on.
Using three cameras to monitor thousands of points on your skin, SGRT technology can detect any motion as you hold your breath side to side, up and down, forward and back and more with submillimeter accuracy. So if you move out of position, the radiation beam is turned off.
Your cancer is treated. And your heart is protected.
Breast Cancer Radiation Side Effects
Doru Paul, MD, is triple board-certified in medical oncology, hematology, and internal medicine. He is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Weill Cornell Medical College and attending physician in the Department of Hematology and Oncology at the New York Presbyterian Weill Cornell Medical Center.
If someone is diagnosed with breast cancer, radiation therapy is likely to be part of their treatment plan. Radiation therapy consists of high beams of energy directed at cancer cells to kill them. Side effects of radiation can include skin changes and feeling tired.
Today’s radiation therapy is more advanced than earlier forms of radiation therapy that were known to cause lasting cell or organ damage, but risks exist and should be discussed with your healthcare provider.
This article will review the side effects of radiation for breast cancer and discuss the types and benefits of radiation therapy.
Don’t Miss: Why Is Breast Cancer So Common
Effects On The Lung Or Heart
Sometimes after treatment to the breast or chest wall area, part of the lung behind the treatment area can become inflamed, causing a dry cough or shortness of breath. This usually heals by itself over time.
More rarely, fibrosis of the upper lung can occur, causing similar side effects.
Although particular care is taken to avoid unnecessary radiotherapy to the tissues of the heart, if radiotherapy is given on the left side you may be at risk of heart problems in future.
Breath hold technique is thought to reduce the risk of any possible damage to the heart and lungs.
The Link Between Breast Cancer And Heart Disease
Breast cancer treatments may increase the risk of heart disease. So wrote the American Heart Association in a scientific statement earlier this year.
For the 3 million U.S. women who are survivors of breast cancer not to mention the 266,000 women expected to be diagnosed this year understanding the links between breast cancer and heart disease is critical. After all, heart disease causes more women’s deaths each year than anything else, and 90 percent of women already have at least one risk factor for heart disease.
We asked oncologists at OHSU’s Knight Cancer Institute about the connection between breast cancer treatment and heart disease, and how they take this into account in treating their patients. Zahi Mitri, M.D., M.S., focuses on breast cancer treatments like chemotherapy, and Sophia Bornstein, M.D., Ph.D., is a radiation oncologist.
Chemotherapy and Heart Disease
There are many types of chemotherapy, but one very common and effective type is the anthracycline doxorubicin. Part of how it works is by binding to cancer cells’ DNA to stop them from replicating. This is great for treating breast cancer, but anthracyclines can cause irreversible damage to the heart.
“It’s extremely rare. It’s just a one or two percent risk, but it’s devastating if it happens,” says Dr. Mitri. “We talk to our patients about this risk, and some patients choose chemotherapy options that are potentially less effective but don’t have anthracyclines.”
Radiation and Heart Disease
Don’t Miss: Can Breast Cancer Cause Headaches
Heart Or Lung Problems
Some women experience lung inflammation years after radiation therapy. This is especially true if they have also had chemotherapy. If there is significant heart exposure because of left breast radiation, in some cases injury to the heart can occur, causing heart conditions or heart disease. This is not as common these days, thanks to greater understanding of this potential link.
Does Cancer Cause Heart Palpitations
Heart palpitations are a relatively rare symptom of leukaemia. According to our 2018 patient survey, palpitations or heart irregularities occur as a symptom of leukaemia in 6% of all patients before they are diagnosed, making it one of the least reported symptoms in our survey.
How can you protect your heart from radiation?
This is called Deep Inspiration Breath Hold, or DIBH. DIBH will protect your heart during treatment. Then, during treatment, youll take and hold a deep breath in the same way as before. When your breast surface is at the right position, the display lights turn green and the SGRT system turns the radiation beam on.
Can radiation cause enlarged heart?
Radiation therapy aimed at the chest region for breast cancer or lung cancer, for example, can prompt a thickening of the blood vessels and heart valves, inflammation, and artery blockages. Heart problems due to radiation often impact younger people, too.
Read Also: Refusing Hormone Therapy For Breast Cancer Premenopausal
Accelerated Partial Breast Irradiation
After whole breast radiation or even after surgery alone, most breast cancers tend to come back very close to the area where the tumor was removed . For this reason, some doctors are using accelerated partial breast irradiation in selected women to give larger doses over a shorter time to only one part of the breast compared to the entire breast . Since more research is needed to know if these newer methods will have the same long-term results as standard radiation, not all doctors use them. There are several different types of accelerated partial breast irradiation:
- Intraoperative radiation therapy : In this approach, a single large dose of radiation is given to the area where the tumor was removed in the operating room right after BCS . IORT requires special equipment and is not widely available.
- 3D-conformal radiotherapy : In this technique, the radiation is given with special machines so that it is better aimed at the tumor bed. This spares more of the surrounding normal breast tissue. Treatments are given twice a day for 5 days or daily for 2 weeks.
- Intensity-modulated radiotherapy : IMRT is like 3D-CRT, but it also changes the strength of some of the beams in certain areas. This gets stronger doses to certain parts of the tumor bed and helps lessen damage to nearby normal body tissues.
- Brachytherapy: See brachytherapy below.
Radiation Therapy For Breast Cancer May Have Long
HealthDay Reporter
WEDNESDAY, Sept. 22, 2021 — Younger women who undergo radiation for cancer in the left breast have a heightened risk of heart disease years later, a new study finds.
Among women who received radiation therapy for left-sided breast cancer, 10.5% developed coronary artery disease over the next 27 years, researchers found. That was close to double the rate among women who had radiation for tumors in the right breast.
Experts said the findings, published recently in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology: CardioOncology, are not unexpected.
Because of the heart’s anatomical position, the organ and its arteries are exposed to more radiation when a woman receives treatment for cancer in the left breast.
And previous studies have found that those women do have a higher long-term rate of coronary artery disease compared to women who receive treatment to the right breast.
But the new study focused on younger women, diagnosed before age 55, said researcher Gordon Watt, a postdoctoral fellow at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City.
Those women are likely to live for many years after their breast cancer treatment, so it’s important to understand what kinds of long-term follow-up they will need for their overall health, according to Watt.
He stressed that the point is not to deter women from receiving radiation therapy.
The study included 972 women who received radiation for stage 1 or stage 2 breast cancer between 1985 and 2008.
Also Check: Can You Work During Breast Cancer Treatment