Targeted Chemotherapy In Early
Research has been performed on targeted chemotherapy agents, including the following:
- Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors
- Small-molecule epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors
- Blockade by antiangiogenic agents
- PI3K/Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors
- Poly polymerase inhibitors]
The CDK4/6 inhibitor abemaciclib has been approved for use in early breast cancer for use in hormone receptor positve, HER2-negative early breast cancer, for patients who have high-risk, node-positive disease and whose tumors have a Ki-67 score of 20%, as determined by a US Food and Drug Administration approved test.
Neoadjuvant Aromatase Inhibitors Tamoxifen: Which Is The Best Choice
The third-generation aromatase inhibitors anastrozole, letrozole, and exemestane are currently considered standard treatment for women with early or advanced BC, based on clinical trials that demonstrated their superiority over tamoxifen . In the neoadjuvant setting, four phase III randomised clinical trials addressed this same questionthree in postmenopausal and one in premenopausal women .
Table 1. Randomised clinical trials comparing different endocrine agents in the neoadjuvant setting.
Finally, a Russian study compared exemestane with tamoxifen in 151 women with HR T2-4, N0-2 BC, both given for three months. Clinical response rates were higher with exemestane , though ultrasound and mammographic response were not different. Higher rates of BCS were reported in the exemestane arm .
A meta-analysis of these studies, including a total of 1160 patients indicatedas expectedsuperior outcomes in terms of clinical objective response rate , ultrasound response rate , and BCS rate with AI as compared to tamoxifen. Furthermore, there was no difference in clinically relevant toxicities between the two treatments .
Dual Blockade With Trastuzumab Plus Lapatinib
In the phase III GeparQuinto trial , 620 patients with untreated HER2-positive operable or locally advanced breast cancer were randomly assigned at a 1:1 ratio to receive neoadjuvant treatment with epirubicin plus cyclophosphamide followed by docetaxel, with either trastuzumab or lapatinib. Patients completed post-surgery trastuzumab treatment for 1 year in both treatment groups. The rate of pCR was lower in the lapatinib arm , and the authors concluded that lapatinib should not be used outside of clinical trials as single anti-HER2 treatment in combination with neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
In the phase II NeoAltto trial , 529 patients with operable HER2-positive tumors were randomly assigned 1:1:1 to lapatinib, trastuzumab, or lapatinib plus trastuzumab for 6 weeks, followed by an additional 12 weeks of the assigned anti-HER2 therapy in combination with weekly paclitaxel . After surgery, women received FEC followed by 34 weeks of the same assigned neoadjuvant anti-HER2 therapy. pCR was achieved in 20% of the patients in the lapatinib arm, 27.6% in the trastuzumab arm , and 46.8% in the combination group . However, lapatinib plus trastuzumab did not significantly improve DFS compared with trastuzumab alone . Additionally, this combination has a higher rate of toxicities and a higher rate of interruption of the neoadjuvant treatment due to adverse events.
You May Like: Does Medicaid Cover Genetic Testing For Breast Cancer
Breast Cancer Recurrence And Survival With Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
A meta-analysis that combined the results of 12 studies found no difference in rates of breast cancer recurrence or overall survival in women who had neoadjuvant chemotherapy versus those who had adjuvant chemotherapy .
Learn more about lumpectomy versus mastectomy and survival.
Triple negative breast cancer
Some people with triple negative breast cancer have cancer remaining in their breast after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. In these cases, treatment with the chemotherapy drug capecitabine after breast cancer surgery may lower the risk of recurrence and improve survival .
|
For a summary of research studies on neoadjuvant chemotherapy, visit the Breast Cancer Research Studies section. |
Breast Surgery In The Context Of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
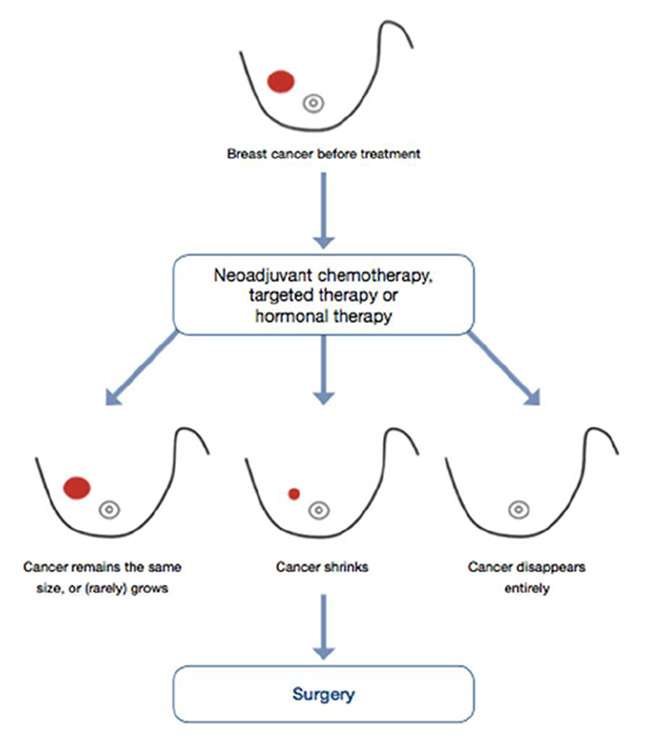
Conceived in the 1970s by forward thinking experts seeking to improve care for women with breast cancer, multidisciplinary breast care has revolutionized the way that breast cancer is treated today . Once mainly the province of expert surgeons, breast cancer treatment requires input from many specialties including diagnostic imaging, surgery, radiation oncology, medical oncology, anatomic and molecular pathology, medical genetics, oncoplastic reconstructive surgery and complementary therapy. Decision-making not only involves whether to utilize one or more of these specialty services, but how to use them and in what order. Through two landmark trials, the NSABP demonstrated that systemic chemotherapy could be administered preoperatively in a save and effective manner with one clear clinical benefit: the ability to increase the rate of breast conservation for women seeking that option . Other benefits, such as improved disease free survival and overall survival were not seen with pre-surgical chemotherapy however, neither did they suffer. The lessons learned were many, giving clinicians some new options in the struggle to cure patients diagnosed with breast cancer while improving the quality of survivorship. Better surgical options came with more time for decision making relative to surgical needs and hope that cumulative treatment would one day be risk adaptedthat is, defined by the personalized assessment of response of tumors to treatment .
Read Also: How Many Breast Cancer Survivors In The Us
Clinical And Relapse Features
BC is the most common tumor and the main cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide TNBC is about 1520% among all. Epidemiology, distribution and mortality from TNBC varies within populations based on race or country of origin. In the prospective population-based study in North Carolina, the Carolina Breast Cancer Study , designed to oversample Black and premenopausal women with newly diagnosed BC, it was observed that patients with TNBC were far more likely to be Black, younger than those with other subtypes, had tumors diagnosed at higher stage, and those tumors were mostly high-grade. This racial and age distribution was confirmed and extended in CBCS3, in which intrinsic subtyping revealed that a young Black woman was more than twice as likely to have a BL tumor as an older white woman.
The aggressive biological and clinical behavior of TNBC translates into more frequent and earlier relapses than other subtypes of BC. It is well established that the risk of early distant recurrence within five years of diagnosis is nearly three-fold higher for TNBC compared with non-TNBC. Conversely, the risk of late relapse after 5 years is less than 3%. The most common sites of relapses are lung, lymph nodes and brain . Optimizing treatment for patients with brain metastases remains an unmet need.
To Put That Into Context
Triple-negative breast cancer
Although there are no approved drugs specifically indicated for TNBC, this subtype is associated with relatively high pCR rates following chemotherapy, with many novel agents under investigation. The addition of the antivascular endothelial growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody bevacizumab to chemotherapy has been studied extensively in the setting of neoadjuvant treatment for breast cancer. The German Breast Group 44 study and the Avastin Randomized Trial With Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Patients With Early Breast Cancer found that in TNBC cohorts, the addition of bevacizumab improved the rates of ypT0N0 pCR by 11.4% and 14% , respectively. The recently presented Austrian Breast and Colorectal Cancer Study Group 32 study and the Southwestern Oncology Group S0800 study have also reported improvements in pCR rates, especially in patients with TNBC. The NSABP B-40 and CALGB 40603 studies found statistically significant improvements in ypT0Nx pCR in the breast with the addition of bevacizumab, but differences in ypT0N0 rates were not statistically significant . While these neoadjuvant studies demonstrated improvements in pCR, three large randomized studies in multiple breast cancer subtypes in the adjuvant setting have failed to demonstrate a survival advantage. These data demonstrate no role for bevacizumab at this time in unselected populations with early-stage breast cancer.
Residual disease
Recommended Reading: What Is 2a Breast Cancer
Combination Regimens For Breast Cancer
Combination chemotherapy regimens are standard recommendations in the adjuvant setting. The most commonly used regimens are shown in Table 1 below.
Table 1. Adjuvant Chemotherapy Regimens for Breast Cancer
Major chemotherapy clinical trials by the Cancer and Leukemia Group B from the last few decades have consistently shown that chemotherapy produces significantly better disease-free and overall survival in patients with estrogen receptor negative disease. These trials included the following:
- C8541 – Comparison of various doses of CAF
- C9344 – Addition of paclitaxel to standard-dose Adriamycin-cyclophosphamide )
- C9741 – Comparison of 3- and 2-week dosing in patients with ER-positive and ER-negative disease
A comparison of the inferior-dose arm of C8541 with the dose-dense arm of C9741 demonstrated a remarkable 63% improvement in disease-free survival and a 59% improvement in overall survival in patients with ER-negative disease, compared with 32% improvement in disease-free survival and 18% improvement in overall survival in patients with ER-positive disease. Overall, the advantages of chemotherapy, particularly in ER-negative disease, were observed across all three trials, irrespective of the chemotherapy regimen used.
The randomized, prospective phase III CALGB 9741 study assigned 2005 subjects to one of 4 arms:
- Conventional AC x 4 cycles T x 4 cycles
- AC × 4 cycles T x 4 cycles
- A × 4 cycles T x 4 cycles C x 4 cycles
- A × 4 cycles T x 4 cycles C x 4 cycles
Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy May Be Recommended:
- If you have inflammatory breast cancer
- If you have inoperable locally advanced breast cancer involving skin
- To reduce the size of the tumour so that you can have breast conserving surgery instead of mastectomy
- To reduce the size of the tumour so that a smaller amount of tissue can be removed this may give you a better cosmetic outcome
- To give you time to have genetic testing if you have a strong family history of breast cancer you may decide to have a different type of surgery if you are found to have an inherited breast cancer gene mutation
- To delay surgery if you are pregnant so that you can deliver your baby as near to full term as possible
- To give you time to consider your surgical options, including breast reconstruction.
Recommended Reading: Does Breast Cancer Spread To Bones
Are There Any Validated Biomarkers To Predict Short And/or Long
In NCT studies, pCR is considered a validated endpoint of long term outcomes, especially in more biologically aggressive subtypes such as triple negative and HER-2 positive BC . However, in patients with luminal BC treated with NCT, the end point appears to be less useful because of the low frequency of pCR in this setting. Interestingly, the prognostic/predictive value of pCR after NCT also appears to be lower in luminal than in HER-2 positive or triple negative BC, suggesting the implication of factors other than simply the low frequency of pCR . In addition, even with a careful selection of patient candidacy for NET, a small fraction of them will develop disease progression on treatment . Therefore, the identification of powerful biomarkers of short and long-term response to NET is a matter of great interest.
Table 2. Clinical utility of on-treatment Ki67 level measured in NET trials at different time-points.
Table 3. The preoperative endocrine prognostic index score and validation studies.
Initial Assessment Of The Patient
Breast evaluation
Locoregional assessment should be performed with careful physical examination and the use of mammography and ultrasound as recommended by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines. Magnetic resonance imaging of the breast is more sensitive in determining the extent of the tumor but it may also overestimate the tumor size. MRI may be performed if there are other areas of concern on initial imaging that may warrant additional evaluation. A baseline MRI has been shown to decrease re-excision rates, and this procedure also allows for assessment of the contralateral breast, where there is a 3% to 10% likelihood of synchronous disease. The decision to pursue an MRI should be tailored to each patients specific clinical situation and needs, particularly if BCS is desired.
Axillary evaluation
For patients with clinically node-negative breast cancer at diagnosis, the role of performing an SLNB prior to or following neoadjuvant chemotherapy is controversial. In the SENTINA study, 35% of clinically node-negative patients were found to have pathologically node-positive disease on SLNB performed prior to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Among these patients, repeat SLNB after neoadjuvant chemotherapy detected additional sentinel lymph nodes in 61% of patients, with a high false-negative rate of 51.6%. Thus, SLNB performed after excision of a positive node prior to neoadjuvant therapy has poor reliability.
Evaluation of distant disease
Additional considerations
Read Also: How To Determine What Stage Breast Cancer
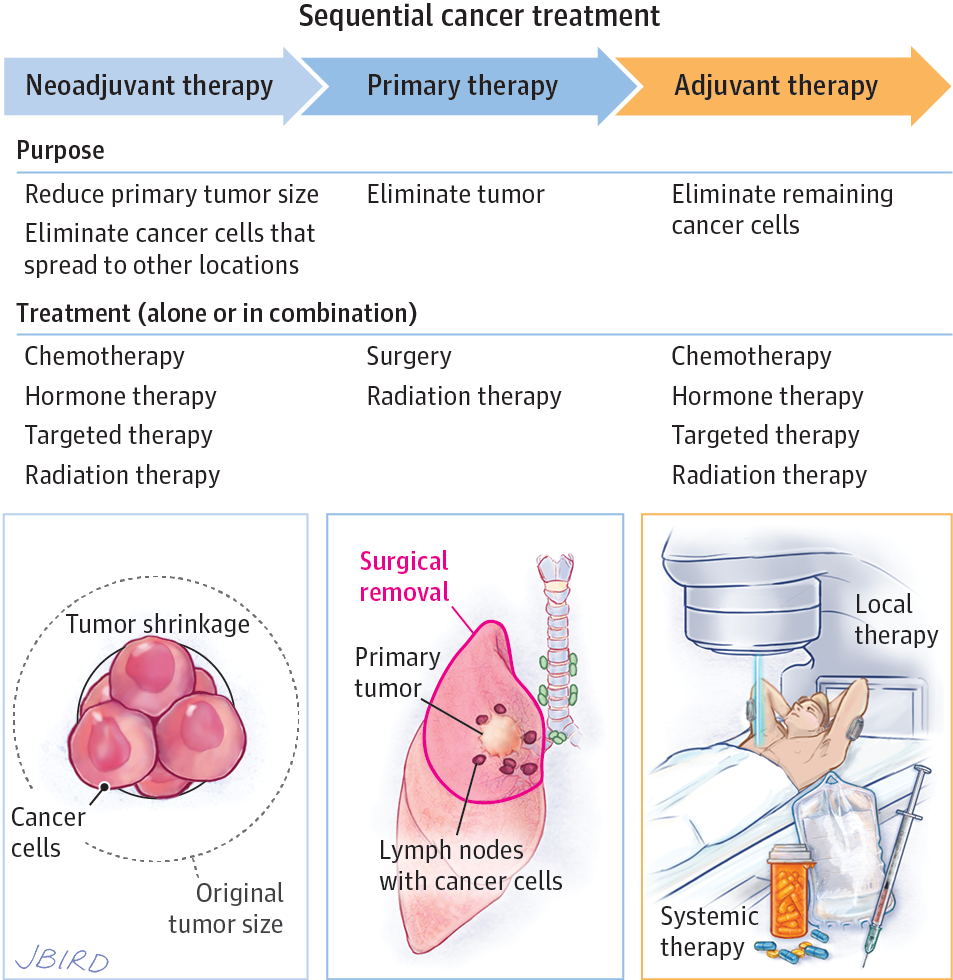
Overviewneoadjuvant Therapy In Early Breast Cancer: Treatment Considerations And Common Debates In Practice
Neoadjuvant treatment is an increasingly important part of early breast cancer management.
-
Multidisciplinary teams play a key role in the decision process for neoadjuvant treatment.
-
Neoadjuvant therapy practice still varies widely.
-
Expert discussion on current evidence to support neoadjuvant treatment decisions for patients.
Intrinsic Molecular Subtypes In Tnbc
Distinct molecular portraits of breast cancer, originally identified as Luminal, HER2-Enriched, Basal-like , and Normal-like breast cancer, were based unsupervised gene expression analysis. Luminal A and B subtypes express keratins 8/18 and ER-related gene clusters, the BL has overexpression of keratin 5, 17 and epithelial grown factor receptors -related genes, and the HER2-Enriched subtype is characterized by expression of Erb-B2-related genes each of these molecular subtypes can be found within clinical subsets . About 80% of TNBC are BL, and BL tumors cluster biologically far from the other BC subtypes, making intrinsic subtyping less useful for meaningful subclassification than in the other clinical subtypes. More detailed confirmation of BC heterogeneity has come from multiple efforts to examine DNA, RNA, microRNA, and protein expression patterns through cross-platform analyses such as The Cancer Genome Atlas and METABRIC,.
Fig. 1: Intrinsic molecular subtypes of breast cancer.
Within each clinical subtype there are multiple molecular subtypes. ER endocrine receptor TNBC triple negative breast cancer HER2 Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2.
Recommended Reading: Why Do Breast Cancer Patients Lose Their Nipples
Endocrine Therapy Versus Chemotherapy
Direct comparisons of neoadjuvant chemotherapy against neoadjuvant endocrine therapy inER-positive breast cancer are rare. This, in part, reflects the considerable differencesin expected toxic effects between the two arms and the evidence that chemotherapies workless well in the neoadjuvant setting against ER-positive disease. a pCR to chemotherapymay be achieved in only 8% of ER-positive cancers compared with 24% in ER-negative tumours. However, in postmenopausal women withER-positive cancers, response rate and time to response may be similar betweenchemotherapy and hormonal therapies , andthe results are awaited with interest for the Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy versus ENdocrineTherapy trial comparing letrozole to FEC100 for the treatment of postmenopausalwomen with ER-positive breast cancers.
Window Of Opportunity Trials
Window of opportunity trials present clinicians and scientists with the opportunity tostudy the effects of novel agents against breast cancer in vivo for the 2-to 4-week window between diagnosis and surgery. Key to this model is the patient consent toallow core biopsy material from the primary, untreated cancer to becompared with postdrug tumour material, preferably also core biopsy material rather thanresected tissue , to seek evidence ofefficacy of the agent against breast cancer in vivo. a clear idea of thetarget involved is important and early-phase evidence of safety is needed before a windowof opportunity trial can proceed. Such trials may encompass new uses for established drugs , molecular-targetedtherapies or novelmechanistic approaches.
The first demonstration of antitumour activity for metformin in women with breast cancer was in this window of opportunitysetting and established the antidiabetes drug as having both antiproliferative and insulinsuppressing activities in vivo in women with breast cancer. Suchproof-of-principle activity was predicted by epidemiological and laboratory studies andsupports the current adjuvant trial of metformin in breast cancer.
Also Check: What Chemotherapy Is Used For Metastatic Breast Cancer
Expert Shows Promise Of Neoadjuvant Endocrine Therapy In Er
Neoadjuvant endocrine therapy trials are feasible with relatively low toxicity, Kelly K. Hunt, MD, FACS, FSSO, said during the 38th Annual Miami Breast Cancer Conference®.
Neoadjuvant endocrine therapy trials are feasible with relatively low toxicity for older women with estrogen receptor positive breast cancer, according to a presentation at the 38th Annual Miami Breast Cancer Conference®.1
At the conference, Kelly K. Hunt, MD, FACS, FSSO, Department of Breast Surgical Oncology, Division of Surgery, The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, discussed the role of neoadjuvant endocrine therapy in ER-positive breast cancer.
So typically, the traditional approach for breast cancer management has been surgery first followed by chemotherapy however, the neoadjuvant approach has been popularized in order to provide systemic therapy for a short period of time before surgery, where you can then assess response and perhaps improve local regional therapy treatments, Kelly explained.
Neoadjuvant Therapy in Breast Cancer
In breast cancer treatment, neoadjuvant therapy has not shown any survival difference from adjuvant approaches however, it does decrease the rate of mastectomies and the incidence of nodal metastasis, while improving pathologic complete responses and long-term outcomes.
Aromatase Inhibitors
In the ACOSOG Z1031 study , researchers compared 3 AIsexemestane , letrozole , and anastrozole for 16 weeks prior to surgery.2
Tumor Volume
When Neoadjuvant Therapy May Be Recommended
Neoadjuvant therapy may be recommended:
- To reduce the size of the tumour so that you can have breast conserving surgery instead of removal of the whole breast .
- To reduce the size of the tumour so that a smaller amount of tissue can be removed this may give you a better cosmetic outcome.
- If you have a fast-growing breast cancer such as inflammatory breast cancer, triple negative breast cancer or HER2 positive breast cancer.
- To reduce the number of lymph nodes that need to be removed from the armpit you may be able to have a sentinel lymph node biopsy that removes 1-3 nodes rather than more extensive axillary lymph node dissection.
- To give you time to have genetic testing if you have a strong family history of breast cancer you may decide to have a different type of surgery if you are found to have an inherited breast cancer gene mutation.
- To determine how effective systemic therapy is in treating your breast cancer.
- To provide more information about the risk of the cancer coming back
- To allow you to be eligible to participate in a neoadjuvant clinical trial.
Read Also: What Is The Test For Breast Cancer Called