Neoadjuvant And Adjuvant Systemic Therapy
For women who have a hormone receptor-positive breast cancer, most doctors will recommend hormone therapy as an adjuvant treatment, no matter how small the tumor is. Women with tumors larger than 0.5 cm across may be more likely to benefit from it. Hormone therapy is typically given for at least 5 years.
If the tumor is larger than 1 cm across, chemo after surgery is sometimes recommended. A woman’s age when she is diagnosed may help in deciding if chemo should be offered or not. Some doctors may suggest chemo for smaller tumors as well, especially if they have any unfavorable features .
After surgery, some women with HER2-positive cancers will be treated with trastuzumab for up to 1 year.
Many women with HER2-positive cancers will be treated with trastuzumab followed by surgery and more trastuzumab for up to 1 year. If after neoadjuvant therapy, residual cancer is found during surgery, trastuzumab may be changed to a different drug, called ado-trastuzumab emtansine, which is given every 3 weeks for 14 doses. If hormone receptor-positive cancer is found in the lymph nodes, your doctor might recommend one year of trastuzumab followed by additional treatment with an oral drug called neratinib for 1 year.
Types Of Stage 1 And 2 Breast Cancer
The most common types of invasive breast cancers are named after the area of the breast where they begin. Types of early breast cancers include:
- Invasive ductal carcinoma IDC means that the cancer originated in the milk ducts of the breast, and has spread into the surrounding breast tissue. IDC is the most common type of breast cancer, accounting for 80% of all breast cancers.
- Invasive lobular carcinoma ILC means that the cancer originated in the milk-producing lobules of the breast, and has spread into the surrounding breast tissue. ILC is the second most common type of breast cancer, and accounts for 10% of breast cancers.
- There are also other less common forms of invasive breast cancer, such as inflammatory breast cancer and Pagets disease of the nipple. For more information on the various types of invasive breast cancer, including the less common forms, please visit Types of Breast Cancer page.
More Benefits Of The Birads Classification System
Another benefit of BIRADS to radiologists, that has indirectly benefited everyone else, is that the categorization scheme has helped to standardize the words used in mammographic reporting, and this has reduced the confusion and improved communication between radiologists, patients and physicians.
BI-RADS classifications have also helped in monitoring breast cancer treatment and supporting breast cancer research again by making statistics easier to calculate.
Following mammogram, a woman will usually see the BI-RADS assessment on the pathology report. So, if you do come across these terms in your report it may be useful to know what they mean.
Don’t Miss: When You Have Breast Cancer Does It Hurt
How The Breast Cancer Staging Process Starts
The breast cancer staging process begins with diagnostic testing. Depending on previous screening results, if any breast cancer symptoms are present, and other factors, your doctor may recommend one of the following tests:
- Diagnostic mammogram A mammogram involves using an X-ray to take photos of your breast tissue at different angles. To do this, your breasts are gently compressed between two plates so the X-ray can be taken.
- Ultrasound An ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging test that bounces soundwaves of your breast tissue to create a picture of the inside of your breast.
- MRI An MRI is another non-invasive imaging test that uses radio waves and a magnetic field to create an image of your breast tissue. This can help doctors determine the size and placement of tumors.
- Biopsy A biopsy removes small masses and growths from your breast so they can be examined under a microscope by a pathologist and determine if theyre cancerous.
If cancer is detected, a CT scan may be ordered to look for any distant metastasis or local invasion to other organs. And youll likely be connected with a breast surgeon right away, either through a nurse navigator or your doctor.
Survival Rates And Prognosis
The outlook for breast cancer is often described in terms of relative survival rates.
Relative survival rates are an estimate of the percentage of people who will survive their cancer for a given period of time after diagnosis. Survival among people with cancer is compared to survival among people of the same age and race who have not been diagnosed with cancer.
Five-year relative survival rates tend to be lower for triple-negative breast cancer than for other forms of breast cancer.
According to the American Cancer Society, the overall 5-year relative survival rate for TNBC is 77 percent. However, an individuals outlook depends on many factors, including the stage of the cancer and the grade of the tumor.
Your healthcare professional will be able to give you a more precise outlook based on:
- the stage of your TNBC
- your age
Read Also: Is There Stage 0 Breast Cancer
Category 4 Suspicious Or Indeterminate Abnormality
A BI-RADS category 4 mammogram is where concern for breast cancer risk begins to increase. Your breast cancer physician should recommend a biopsy with BI-RADS category 4. Typically, a lump is present, but does not initially appear to have the morphological characteristics of breast cancer.
Therefore, there are 3 sub-categories of BI-RADS category 4 and these are as follows:-
- BIRADS 4AThere is a low suspicion of malignancy.
- BI- RADS 4B There is a moderate suspicion of malignancy.
- BIRADS 4C There is a high suspicion of malignancy.
Findings typical of BIRADS category 4 include:
Scientists estimate that the positive predictive value of BI-RADS 4 mammograms to be around 20-40%.
| powderish microcalcifications are suggestive of BI-RADS classification of 4. |
| These powderish microcalcifications appear in large clusters. |
Stage 3 Breast Cancer
Stage 3 breast cancer is divided into three groups:
- Stage 3A
- Stage 3C
Stage 3A can mean:
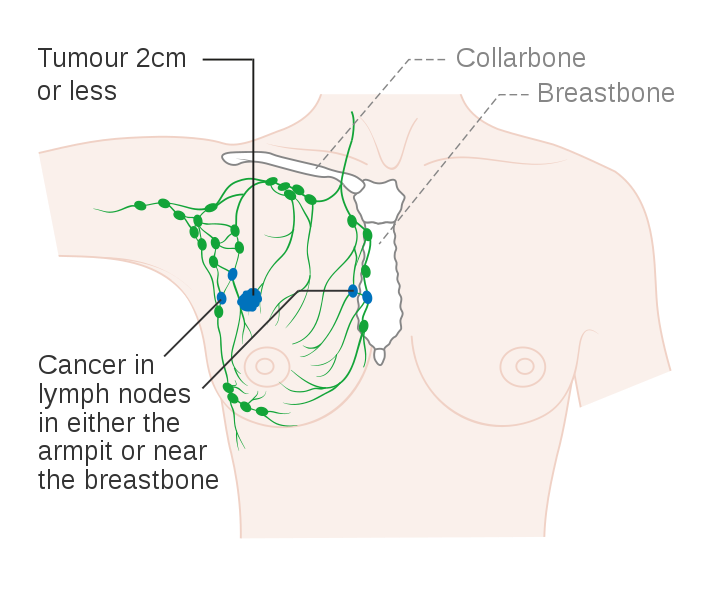
No cancer is seen in the breast, but cancer is found in four to nine lymph nodes under the arm or near the breastbone
The cancer in the breast measures up to 5cm and cancer is found in four to nine lymph nodes under the arm or near the breastbone
The cancer in the breast is larger than 5cm, and cancer is found in up to three lymph nodes under the arm or near the breastbone.
Stage 3B means the cancer in the breast can be any size and has spread to the skin of the breast or chest wall. Cancer is found in up to nine lymph nodes under the arm or near the breast bone.
Stage 3C means the cancer in the breast can be any size, may have spread to the skin of the breast or chest wall and cancer is found in 10 or more lymph nodes under the arm or near the breastbone, or to nodes above or below the collarbone.
You May Like: Can You Work During Breast Cancer Treatment
Determining The True Stage Of Breast Cancer
All the diagnostic tests and scans up to this point have been critical for helping your doctors understand your disease. But the exact stage of cancer cant be determined until surgery happens which is sometimes referred to surgical staging or pathological staging.
Breast surgery is usually the first step in Stages 0-2, and sometimes Stage 3 breast cancer. Surgery allows your surgeon to see whats happening inside your body. It also allows them to remove cancerous tissues which is an important step in preventing the cancer from spreading and determining next steps for your treatment.
If surgery cant be done right away or at all, a clinical stage is given instead based on diagnostic imaging test results, biopsy pathology results, and a physical exam.
The Tnm System The Grading System And Biomarker Status Are Combined To Find Out The Breast Cancer Stage
Here are 3 examples that combine the TNM system, the grading system, and the biomarker status to find out the Pathological Prognostic breast cancer stage for a woman whose first treatment was surgery:
If the tumor size is 30 millimeters , has not spread to nearby lymph nodes , has not spread to distant parts of the body , and is:
- Grade 1
- PR-
The cancer is stage IV .
Don’t Miss: What Does Triple Negative Breast Cancer Look Like
Certain Microcalcifications Might Even Be Directly Associated With Breast Cancer
BI-RADS mammogram classifications are generalizations and tend to revolve around the presence and type of microcalcifications. Within the range of observations about the various types and patterns of breast tissue microcalcifications present, it may be suggested that coarse heterogeneous microcalcifications are positively associated with breast cancer about 7% of the time and amorphous microcalcifications about 13% of the time.
Fine pleomorphic breast microcalcifications have a positive predictive value for breast cancer of about 30%, while fine linear microcalcifications are associated with confirmed breast cancer in over 50% of cases.
BI-RADS mammogram classifications are not intended as a diagnostic tool, but only as a means of standardizing communications and helping to identify situations where follow-up is required, and the most appropriate type of follow-up. The fastest and most economical way to arrive at a positive or confirmed diagnosis of breast cancer is by core needle biopsy.
Where Do These Numbers Come From
The American Cancer Society relies on information from the SEER* database, maintained by the National Cancer Institute , to provide survival statistics for different types of cancer.
The SEER database tracks 5-year relative survival rates for breast cancer in the United States, based on how far the cancer has spread. The SEER database, however, does not group cancers by AJCC TNM stages . Instead, it groups cancers into localized, regional, and distant stages:
- Localized: There is no sign that the cancer has spread outside of the breast.
- Regional: The cancer has spread outside the breast to nearby structures or lymph nodes.
- Distant: The cancer has spread to distant parts of the body such as the lungs, liver or bones.
Read Also: How Long Can You Live With Stage Four Breast Cancer
The Use Of Certain Medicines And Other Factors Decrease The Risk Of Breast Cancer
Anything that decreases your chance of getting a disease is called a protective factor.
Protective factors for breast cancer include the following:
- Taking any of the following:
What Are Risk Factors For Breast Cancer Recurrence
Anyone with a breast cancer diagnosis can have a recurrence. Your risk of cancer recurrence depends on several factors:
- Age: Women who develop breast cancer before age 35 are more likely to get breast cancer again.
- Cancer stage: Cancer stage at the time of diagnosis correlates with the risk of the cancer being able to recur. Several factors determine cancer stage: tumor size, cancer grade and cancer spread to lymph nodes or other parts of the body. Cancer grade indicates how unusual cancer cells look in comparison to healthy cells.
- Cancer type: Aggressive cancers like inflammatory breast cancer and triple-negative breast cancer are harder to treat. Theyre more likely to come back and spread.
Don’t Miss: Why Is Left Breast Cancer More Common
Bi Rads Mammographic Assessment Categories
The BI-RADS assessment categories are:
- 0- incomplete
- 5-highly suspicious of malignancy
- 6-known biopsy with proven malignancy
After the initial breast cancer screening, a follow-up or diagnostic mammography is often recommended if the BI-RADS category is 3 or higher. By a huge majority, the radiologist will classify most breast cancer screening mammograms as either BI-RADS 1 or BI-RADS 2. However, these categories are nothing to worry about and require no further treatment. A lot of women over 40 will have BIRADS categories 1 and 2 following their annual mammogram.
Survival Rates Of Stage 1 And Stage 2 Breast Cancer
According to data from the Australian Institute of Health and Welfare, the earlier breast cancer is first diagnosed, the better the outcome. The survival rates of people diagnosed with breast cancer have also improved over time due to earlier detection and improvements in treatment. Most people with early stage breast cancer can be treated successfully.
You may wish to discuss your prognosis and treatment options with your doctors. However, it is not possible to predict the exact course of your cancer and how long you will live. The length of survival can vary from person to person. Factors that influence this include:
- Response to treatment
- The type of breast cancer that you have
- The rate of tumour growth
- Other factors such as your age, medical history and overall health.
Read Also: Does Breast Cancer Make You Lose Hair
Treatment Of Metastatic Breast Cancer
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment options for metastaticbreast cancer may include the following:
Hormone therapy
In postmenopausal women who have just been diagnosed with metastatic breast cancer that is hormone receptor positive or if the hormone receptor status is not known, treatment may include:
- A clinical trial of high-dose chemotherapy with stem cell transplant.
- Clinical trials testing new anticancer drugs, new drug combinations, and new ways of giving treatment.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Stage 1 Or 2 Early Breast Cancer
Stage 1 and 2 breast cancer refers to invasive breast cancer that is contained within the breast, and may or may not have spread to the lymph nodes in the armpit. These stages are also known as early stage breast cancer.
At Stage 1 and 2, some cancer cells may have spread outside the breast and armpit area, but at this stage these cannot be detected.
You May Like: Can Cancer Spread To The Breast
When Is Radiation Usually Used To Treat Stage 2 Breast Cancer
According to the American Cancer Society, radiation therapy may be used after a breast-conserving surgery, or lumpectomy, to mitigate the risk of cancer cells recurring in the same breast or nearby lymph nodes. After a mastectomy, an oncologist may determine that radiation is necessary if the tumor was larger than 5 cm, if there was lymph node involvement, or if cancer was found outside of surgical margins.
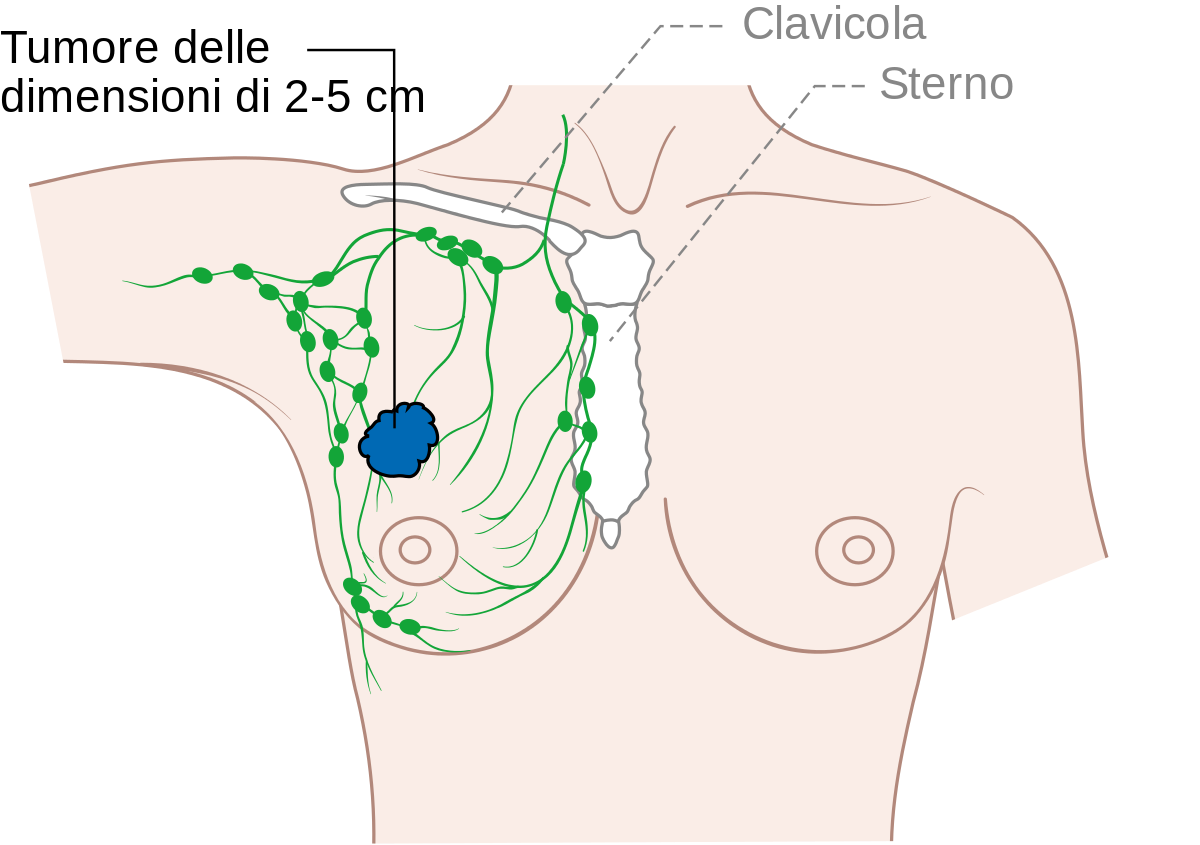
What Is Stage 2 Breast Cancer
Also known as invasive breast cancer, the tumor in this stage measures between 2 cm to 5 cm, or the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes under the arm on the same side as the breast cancer. Stage 2 breast cancer indicates a slightly more advanced form of the disease. At this stage, the cancer cells have spread beyond the original location and into the surrounding breast tissue, and the tumor is larger than in stage 1 disease. However, stage 2 means the cancer has not spread to a distant part of the body.
At stage 2, a tumor may be detected during a breast self-exam as a hard lump within the breast. Breast self-exams and routine screening are always important and can often lead to early diagnosis, when the cancer is most treatable.
Stage 2 breast cancer is divided into two categories:
Stage 2A: One of the following is true:
- There is no tumor within the breast, but cancer has spread to the axillary lymph nodes, or
- The tumor in the breast is 2 cm or smaller and cancer has spread to the axillary lymph nodes, or
- The tumor in the breast measures 2 cm to 5 cm but cancer has not spread to the axillary lymph nodes.
Stage 2B: One of the following is true:
- The tumor measures 2 cm to 5 cm and cancer has spread to the axillary lymph nodes, or
- The tumor is larger than 5 cm but cancer has not spread to the axillary lymph nodes.
At stage 2, TNM designations help describe the extent of the disease. Most commonly, stage 2 breast cancer is described as:
You May Like: Can Breast Cancer Spread To Bones
Stage Iia & Iib Treatment Options
Stage II is divided into subcategories known as IIA and IIB.
In general, stage IIA describes invasive breast cancer in which:
- no tumor can be found in the breast, but cancer is found in 1 to 3 axillary lymph nodes or in the lymph nodes near the breast bone or
- the tumor measures 2 centimeters or smaller and has spread to the axillary lymph nodes or
- the tumor is larger than 2 cm but not larger than 5 cm and has not spread to the axillary lymph nodes
Still, if the cancer tumor measures between 2 and 5 cm and:
- has not spread to the lymph nodes or parts of the body away from the breast
it will likely be classified as stage IB.
Similarly, if the cancer tumor measures between 2 and 5 cm and:
- has not spread to the lymph nodes
- has an Oncotype DX Recurrence Score of 9
it will likely be classified as stage IA.
In general, stage IIB describes invasive breast cancer in which:
- the tumor is larger than 2 cm but no larger than 5 cm small groups of breast cancer cells larger than 0.2 mm but not larger than 2 mm are found in the lymph nodes or
- the tumor is larger than 2 cm but no larger than 5 cm cancer has spread to 1 to 3 axillary lymph nodes or to lymph nodes near the breastbone or
- the tumor is larger than 5 cm but has not spread to the axillary lymph nodes
Still, if the cancer tumor measures between 2 and 5 cm and:
- cancer is found in 1 to 3 axillary lymph nodes