What This Means For You
If youâve been diagnosed with early-stage breast cancer, your doctor may recommend treatments after surgery to reduce your risk of recurrence.
If you were diagnosed with hormone receptor-positive, early-stage breast cancer, itâs likely that your doctor will recommend you take some type of hormonal therapy medicine â either tamoxifen or an aromatase inhibitor depending on your menopausal status â for five to 10 years after surgery.
Chemotherapy after surgery is usually completed in three to six months. If youâre also receiving a targeted therapy, such as Herceptin , with chemotherapy, you may continue to receive the targeted therapy for up to a year after completing chemotherapy.
Radiation therapy after surgery can be completed in one to seven weeks.
So, hormonal therapy after surgery takes the longest to complete. Hormonal therapy medicines also can cause troubling side effects, such as hot flashes, night sweats, and joint pain. Less common but more severe side effects include heart problems and blood clots.
Research has shown that about 25% of women who are prescribed hormonal therapy to reduce the risk of recurrence after surgery either donât start taking the medicine or stop taking it early, in many cases because of side effects.
Learn more about Staying on Track With Treatment. You can read about why itâs so important to stick to your treatment plan, as well as ways to manage side effects after radiation, chemotherapy, and hormonal therapy.
What Are The Complications Of Breast Cancer Recurrence
Breast cancer that comes back can be harder to treat. The same therapy isnt always effective again. Tumors can develop a tolerance to certain treatments like chemotherapy. Your healthcare provider will try other therapies. You may be able to try drugs under development in clinical trials.
If breast cancer spreads to other parts of the body, your healthcare providers still treat it like breast cancer. For instance, breast cancer cells that move to the lungs cause breast cancer in the lungs not lung cancer. Metastatic breast cancer is more difficult to treat than cancer in only one part of the body.
You may feel stressed, depressed or anxious. A mental health counselor and support groups can help.
Systemic Treatments For Stage 1 Breast Cancer
Systemic treatments, often termed add-on or adjuvant treatments, treat breast cancer throughout your body and not just at the site of the tumor.
These treatments help destroy cancer cells that have spread beyond your breast but are still too small to be spotted. They include the therapies outlined below.
Chemotherapy
Doctors may recommend chemotherapy, also called chemo, after surgery to help destroy any undetected cancer cells. Chemotherapy may also lower your risk of the cancer coming back at a later stage.
Chemotherapy may be recommended for a smaller tumor if:
- Any cancer cells were found in the lymph nodes.
- You score high on a gene test such as Oncotype DX, which shows whether chemotherapy could help treat your breast cancer and if its likely to come back after surgery.
- The cancer cells are progesterone receptor- and estrogen receptor-negative.
- The breast cancer cells are positive for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 various therapies can target these receptors.
Hormone therapy
Hormone therapy can be used to help slow down the growth of cancer cells in people with estrogen receptor-positive or progesterone receptor-positive cancer cells. Hormone therapy works by blocking hormone receptors on the cancer cells or by lowering the amount of estrogen produced in your body.
Its important to ask your doctor about the potential side effects of hormone therapy before you begin this treatment, so can you know what to expect.
Targeted therapy
Also Check: How Quickly Does Breast Cancer Spread
Getting Support And Information
It can be very difficult to cope with the news that your cancer has come back. At first, you are likely to feel very upset, frightened and confused. Or you may feel that things are out of your control.
It is very important to get the right information about your type of cancer and how it is best treated. People who are well informed about their illness and treatment are more able to make decisions and cope with what happens. Your doctor or breast care nurse can give you information.
It can help to talk to family and friends about how you feel.
You can also contact one of the breast cancer organisations. They have free factsheets and booklets they can send to you. They might also be able to put you in touch with a support group.
What Does Stage 1a Breast Cancer Mean
Stage 1 breast cancer means the cancerous cells are invading the surrounding breast tissue. Stage 1 breast cancer has two subcategories â1A and 1B. People with stage 1A breast cancer have breast cancer with: A tumor measuring no more than 2 centimeters in diameter that has not spread outside the breast.
Donât Miss: 3b Cancer
Recommended Reading: What Are The Chances Of Recurrence Of Breast Cancer
What Does It Mean To Have Stage 1 Breast Cancer
In Stage 1 breast cancer, cancer is evident, but it is contained to only the area where the first abnormal cells began to develop. The breast cancer has been detected in the early stages and can be very effectively treated.
Stage 1 can be divided into Stage 1A and Stage 1B. The difference is determined by the size of the tumor and the lymph nodes with evidence of cancer.
How Is Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Diagnosed
The sooner this type of cancer is found, the sooner it can be treated. The following tests or procedures are usually used to diagnose DCIS:
- Breast examination: A routine breast exam is usually part of a regular physical. It is the first step in detecting breast cancer. Although DCIS does not usually come with a noticeable lump, the doctor may be able to feel an abnormal growth in the breast, such as a small, hardened spot, during a physical examination. The doctor will also look for any skin changes, nipple changes or nipple discharge. Most times, though, the abnormal growth will show up on a mammogram.
- Mammogram: DCIS is usually found during a mammogram. As old cells die off and pile up within the milk duct, they leave tiny, hardened calcium spots which show up as a shadow or white spot on a mammogram.
- Biopsy: If a spot or a shadow is found on the mammogram, the doctor will recommend a biopsy.
- Core needle biopsy: With this procedure, the doctor inserts a large needle into the breast to get a big sample of the breast tissue that looked abnormal on the mammogram. The doctor will first numb the skin at the site of the biopsy and then make a small incision in the skin to help get the needle into the breast. Because the skin has been cut, there will be a tiny scar which will fade over time.
Biopsies are only used to diagnose that there is cancer within the breast. If cancer is found, surgery will be recommended to remove the abnormal cells.
Read Also: What Are Some Treatments For Breast Cancer
How Is A Local Recurrence After Lumpectomy Diagnosed
After a diagnosis of early stage breast cancer, any remaining breast tissue should be evaluated annually with scans .
Most local recurrences within the breast after lumpectomy are detected on routine annual breast imaging, which usually takes the form of mammography and ultrasound, and on occasions MRI.
If you have a local recurrence or new primary breast cancer, you may find symptoms similar to an initial breast cancer. This includes:
- A new lump in the breast, armpit area or around the collarbone
- A change in breast size or shape
- Changes to the nipple, such as sores or crusting, an ulcer or inverted nipple
- Clear or bloody nipple discharge
- Changes to the skin including redness, puckering or dimpling
- Breast tenderness or pain
Once a local recurrence has been diagnosed, we do tests to see whether there are signs of cancer elsewhere in the body. These may include a chest X-ray, CT scan, bone scan or PET scan, and blood tests , then we have to figure out how best to treat the tumour in the breast. Usually in these cases we do a mastectomy, as the prior less drastic surgery and radiation didnt take care of it.
Dont Miss: Malignant Neoplasm Of Breast Treatment
Lifestyle Changes Can Reduce The Risk Of Breast Cancer Returning
Surviving breast cancer diagnosis, treatment and recovery can cause uncertainty and concern that the cancer will come back or that a new cancer will occur. Addressing self-care after breast cancer and tending to your overall well-being can help restore a more positive outlook, and might even reduce your chances of facing cancer again.Does using deodorant increase your breast cancer risk? Learn about breast cancer myths and facts
We are experts in managing local breast cancer recurrence and metastatic disease, Lange says. As a comprehensive breast center, our patients range from the newly diagnosed to those with advanced metastatic disease.
Our goal is to find treatment and management options for all patients, using all the healing modalities that evidence-based medicine has proven to be beneficial in the treatment of breast cancer.
Breast Cancer: Moving Beyond the Fear of Recurrence
Being a Survivor
Lifestyle Changes After Breast Cancer
Read Also: How Effective Is Chemotherapy For Breast Cancer
What Are The Symptoms Of Breast Cancer Recurrence
You may experience different signs of breast cancer recurrence depending on where the cancer forms.
Local breast cancer recurrence may cause:
- Breast lump or bumps on or under the chest.
- Nipple changes, such as flattening or nipple discharge.
- Swollen skin or skin that pulls near the lumpectomy site.
- Thickening on or near the surgical scar.
- Unusually firm breast tissue.
- Biopsy of the site of suspected recurrence.
Keep Up With Exercise
A recent study shows that if you regularly exercise even for at least 2.5 hours per week, you can improve your overall health. It may also lower the risk of your cancer coming back. Research also shows that if youâre overweight, cancer is more likely to come back. Physical activity can help you reduce or maintain your weight at a healthy range for your body type.
Exercise can include waking, running, cardio activities, strength training, and flexibility. Guidelines recommend:
- At least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise per week or 75 minutes per week of harder physical activity like running.
- 2 days of muscle training with weights per week.
Thatâs a lot to do if youâre not active now. Take it one step at a time, starting with even a few minutes. Gradually, youâll be able to do more.
Read Also: Are Breast Cancer Lumps Hard Or Soft
Treatment For Locally Advanced Breast Cancer
Treatment for locally advance breast cancer is likely to include a treatment that affects the whole body .
This might be chemotherapy, hormone therapy or targeted therapy.
Chemotherapy
If you have previously had chemotherapy, you may be offered different chemotherapy drugs this time.
Hormone therapy
If the cancer is oestrogen receptor positive you may be offered hormone therapy.
If you were already taking hormone therapy when your cancer returned, your doctor may consider switching you to a different drug.
Targeted therapy
Targeted therapies are a group of drugs that block the growth and spread of cancer.
The most widely used targeted therapies are for HER2 positive breast cancer. However, other targeted therapies are available to treat locally advanced breast cancer that is HER2 negative.
Radiotherapy and surgery
You may be offered radiotherapy if cancer cells are found in the lymph nodes above or below the collarbone, under the breastbone or between the ribs. Its not usually possible to remove the cancer using surgery in this situation.
If the recurrence has affected the muscles on the chest wall, surgery may be offered as well as radiotherapy.
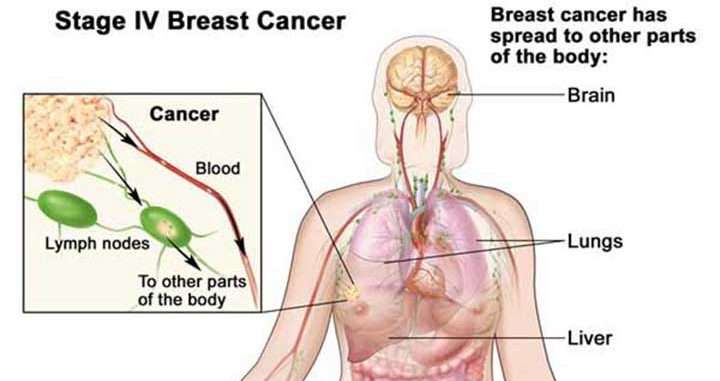
What Are The Signs Of Distant Breast Cancer Recurrence
If your breast cancer has spread to other parts to the body, known as distant recurrence, there are a number of possible symptoms, including:
- Fatigue
- Unexpected weight loss or change in appetite
- Severe or ongoing headaches
- Nausea
However, symptoms will vary depending on where the secondary cancer presents. Sometimes recurrence is identified on a scan or blood test that was done for a reason other than breast cancer.
Studies have shown that doctors are sometimes reluctant to mention the symptoms of metastatic disease. In medical school it was suggested that we shouldnt tell people who had been treated for cancer what to look for if they were worried about recurrences because theyd start imagining that they had every symptom we told them about, but that doesnt reassure people at all it just means theyll be afraid of everything instead of a few specific things. When youve had cancer, youre acutely aware of your body, and any symptom thats newor that you never noticed beforecan take on terrifying significance as you worry that your cancer may be back. Inevitably this will mean a lot of fear over symptoms that turn out to be harmless.
As I explain to my patients, there are good reasons these days to remain optimistic, even after cancer comes back. Newer, better treatments are becoming available all the time. And for women who were treated a long time ago, the options for treatment may have changed and improved significantly since the first time they were treated
Don’t Miss: What Is Er In Breast Cancer
Introduction To Breast Cancer Recurrence
Breast cancer can recur at any time, but most recurrences occur in the first three to five years after initial treatment. Breast cancer can come back as a local recurrence or as a distant recurrence somewhere else in the body. The most common sites of recurrence include the lymph nodes, the bones, liver, or lungs.
Breast Cancer: The Problem
Breast cancer is a major health problem that affects the lives of millions. For the year 2012, it was estimated that 226,870 women in the United States will be diagnosed with breast cancer and that 39,510 women will succumb to it . With these numbers, breast cancer is the leading cancer diagnosed in the US women and is second only to lung cancer in terms of total fatalities . It is generally recognized that much scientific advancements have been made in the area of breast cancer research, and it is because of these efforts that the chances of disease-free survival of breast cancer survivors have increased tremendously over the last few decades. However, this applies only if the breast cancer is diagnosed at an early stage and is limited to the primary organ. Once breast cancer metastasizes to other organs, the therapeutic options are very limited and the success rate of managing such patients in clinics is dismal.
As mentioned previously, a breast cancer patient has very good chances of a disease-free survival if the cancer is caught and treated early. It is important to mention that the term early is very subjective. In many cases, the cancer is thought to have been treated early only to discover its reappearance years after the first intervention . This phenomenon is tumor recurrence and the subject of our discussion here.
You May Like: Can Breast Cancer Return After Mastectomy
Molecular Factors That Influence Breast Cancer Recurrence
It is evident that breast cancer is particularly lethal when it recurs. The causes for such breast cancer recurrence remain completely unknown, except for many putative molecular markers that are under active investigation for their possible role in determining the recurrence. This section discusses many such factors with emphasis on studies that have linked individual molecules/signaling factors with breast cancer recurrence and/or disease-free survival.
Overall Breast Cancer Survival Rate For All Stages Of Breast Cancer
The overall 5 year survival rate for women with breast cancer was 89.7%. That is 89.7 out of 100 women were still alive 5 years after diagnosis, regardless of the stage of the cancer. This figure was taken from the SEERS statistics between the years of 2006 and 2012, so could well be even higher now.
Also Check: How To Donate To Breast Cancer Awareness
Treatment For Stage 4 Breast Cancer
Typically, treatment for stage 4 breast cancer includes a combination of chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and hormone therapy .
Targeted therapy is a treatment that targets the protein that allows cancer cells to grow and this type of therapy may also be an option for people with stage 4 breast cancer.
Sometimes, surgeons will operate to try and remove tumors though this is not usually the first option for treatment.
Doctors, however, may recommend surgery to help with pain relief by treating some of the issues that may develop as a result of having stage 4 breast cancer. These include spinal cord compression, removing single masses caused by metastasis, and fixing any broken bones.
A doctor may also prescribe medication to treat related symptoms such as:
- antidepressants to help mood
- anticonvulsants to manage pain or neurologic conditions
- local anesthetics to manage pain
New treatments and therapies are emerging all the time, and anyone who has breast cancer at any stage can volunteer to try out these new treatments. People considering this should talk to their doctor to see whether any trials are available in their area.
Trials for a new treatment called immunotherapy are currently taking place. Immunotherapy works by raising the bodys natural ability to fight off cancer and has fewer side effects than chemotherapy.
As well as numbers, a zero or an X often follow the letters T, N, and M. According to the AJCC, the meanings are as follows:
These include:
Age And Stage For Breast Cancer Survival
Research over the years has generally shown that women under 40 years have a poorer than average prognosis. Interestingly, this factor is particularly relevant when the breast cancer is axillary node negative.
A medical study published in 2015 examined 4,453 Swedish women diagnosed with invasive breast cancer between 1961 and 1991 regarding age at diagnosis.
This research showed that women under 40 years had a higher mortality rate both for 5 year and 10 year survival rate.
However, older ladies between ages 70 and 79 and over 80 years had a higher mortality rate in both the 5 and 10 year follow up periods. The statistically worst outcome, after all adjustments for other factors, is for ladies over 80 years.
Furthermore, an earlier taken from SEER statistics between the years of 1988 to 2003 found that women under 40 years had lower rates of survival for stage I and II breast cancers.
Conversely, younger women tended to have a more favourable chance of survival at stage III and IV compared with those over 70 years of age.
Read Also: What To Eat During Breast Cancer Treatment