What Questions Should I Ask My Healthcare Provider
You may want to ask your provider:
- What type of breast cancer recurrence do I have?
- Has the cancer spread outside the breast?
- What stage is the breast cancer?
- What is the best treatment for this type of breast cancer?
- What are the treatment risks and side effects?
- Should I look out for signs of complications?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Most breast cancer recurrences respond well to treatments. You may be able to try new drugs or combination therapies in development in clinical trials. Your healthcare provider can discuss the best treatment option based on your unique situation.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 03/24/2021.
References
Tnm Staging And Stage 2 Classification
In addition to using the numerical stage classifications, healthcare professionals also describe tumors using the tumor, node, metastasis staging system that the American Joint Committee on Cancer issued.
In this system, T describes tumor size, N describes the presence of cancer cells in the lymph nodes, and M describes whether or not the cancer has spread to other areas of the body.
The classifications for tumor size are:
- TX: Healthcare professionals cannot measure primary tumor size.
- T0: Healthcare professionals cannot find a tumor.
- T1: The tumor is smaller than 2 centimeters .
- T2: The tumor measures 25 cm.
- T2: The tumor is larger than 5 cm.
- T4: The tumor has spread beyond the breast tissue and lymph nodes or is inflammatory.
The classifications for lymph node involvement are:
- NX: Healthcare professionals cannot assess the lymph nodes.
- N0: The cancer has not spread to the surrounding nodes.
- N1, N2, N3: These indicate the number of nodes involved.
The classifications for metastasis are:
- M0: There is no sign that the cancer has spread .
- M1: The cancer has spread to another area of the body.
- MX: The cancer spread is not measurable.
Examples Of Mortality Rates Versus Number Of Deaths
Say, town A has a population of 100,000 and town B has a population of 1,000. Over a year, say there are 100 breast cancer deaths in town A and 100 breast cancer deaths in town B.
The number of breast cancer deaths in each town is the same. However, many more people live in town A than live in town B. So, the mortality rates are quite different.
In town A, there were 10 breast cancer deaths among 100,000 people. This means the mortality rate was less than 1 percent .
In town B, the mortality rate was 10 percent .
Although the number of deaths was the same in town A and town B, the mortality rate was much higher in town B than in town A .
Lets look at another example. In 2022, its estimated among women there will be :
- 100 breast cancer deaths in Washington, D.C.
- 730 breast cancer deaths in Alabama
- 4,690 breast cancer deaths in California
Of the 3, California has the highest number of breast cancers. However, that doesnt mean it has the highest breast cancer rate. These numbers dont take into account the number of women who live in each place. Fewer women live in Alabama and Washington, D.C. than live in California.
Other factors may vary by place as well, such as the age and race/ethnicity of women. So, to compare breast cancer mortality rates, we need to look at mortality rates.
In 2022, the estimated mortality rates are :
- 25 per 100,000 women in Washington, D.C.
- 21 per 100,000 women in Alabama 22
- 19 per 100,000 women in California 20
Recommended Reading: Can Stage 1 Breast Cancer Metastasis
Stage 1b Breast Cancer Means One Of The Following Descriptions Applies:
Lymph nodes have cancer evidence with small clusters of cells between the approximate size of a pinprick to the approximate width of a grain of rice .
AND EITHER No actual tumor is found in the breast.
OR The tumor is smaller than the approximate size of a peanut .
Similar to stage 0, breast cancer at this stage is very treatable and survivable. When breast cancer is detected early, and is in the localized stage , the 5-year relative survival rate is 100%.
Breast Cancer: Types Of Treatment
Have questions about breast cancer? Ask here.
ON THIS PAGE: You will learn about the different types of treatments doctors use for people with breast cancer. Use the menu to see other pages.
This section explains the types of treatments that are the standard of care for early-stage and locally advanced breast cancer. Standard of care means the best treatments known. When making treatment plan decisions, you are strongly encouraged to consider clinical trials as an option. A clinical trial is a research study that tests a new approach to treatment. Doctors want to learn whether the new treatment is safe, effective, and possibly better than the standard treatment. Clinical trials can test a new drug and how often it should be given, a new combination of standard treatments, or new doses of standard drugs or other treatments. Some clinical trials also test giving less treatment than what is usually done as the standard of care. Clinical trials are an option to consider for treatment and care for all stages of cancer. Your doctor can help you consider all your treatment options. Learn more about clinical trials in the About Clinical Trials and Latest Research sections of this guide.
Don’t Miss: Men’s Breast Cancer Symptoms
The Types Of Radiotherapy
The type of radiotherapy you have will depend on the type of breast cancer and the type of surgery you have. Some women may not need to have radiotherapy at all.
Types of radiotherapy include:
- breast radiotherapy after breast-conserving surgery, radiation is applied to the whole of the remaining breast tissue
- chest-wall radiotherapy after a mastectomy, radiotherapy is applied to the chest wall
- breast boost some women may be offered a boost of high-dose radiotherapy in the area where the cancer was removed however, this may affect the appearance of your breast, particularly if you have large breasts, and can sometimes have other side effects, including hardening of breast tissue
- radiotherapy to the lymph nodes where radiotherapy is aimed at the armpit and the surrounding area to kill any cancer that may be in the lymph nodes
Stage 2 Breast Cancer Survival Rate
According to the American Cancer Society findings, the 5-year-survival rate is 99% if cancer has not spread outside the breast tissue. But, it is 86% if cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes. However, now with the addition of targeted therapy in the treatment of breast cancer, the survival rate has also increased significantly.
Read Also: Can Smoking Weed Cause Breast Cancer
Outlook By Seer Stage
In the United States, healthcare professionals typically calculate the outlook for people with cancer using the SEER database.
All cases of stage 2 cancer are localized or regional, with cancer that has not spread beyond the breast tissue or nearby lymph nodes.
The relative survival rate for people with cancer compares their likelihood of survival during a given period with that of the general population.
For example, if the 5-year relative survival rate for a stage of cancer is 90%, people with that stage of cancer are 90% as likely as people without cancer to live for a minimum of 5 years after diagnosis, according to the
Receiving a cancer diagnosis can be frightening and overwhelming. However, it is important to get as much information as possible about the cancer itself, the next steps, and the treatment options available.
If Chemo Killed Everything
Then that would be a cure â it isnât! THe different types are different. ER/PR/Her2 status is different for each of us as is Stage/grade/etc.
Very simplistically as it was explained to me for me â chemo neo-adjuvant to try to get it to shrink and form margins so surgeon had a chance of getting it. Then surgery to remove all that surgeon could find. Then another chemo to attack any that was âfloatingâ around in the lymph system or anywhere. Then rads to re-hit the direct area effected âjust in caseâ.
Only you can decide what you want to do.
Winyan â The Power Within
Don’t Miss: What Are Some Warning Signs Of Breast Cancer
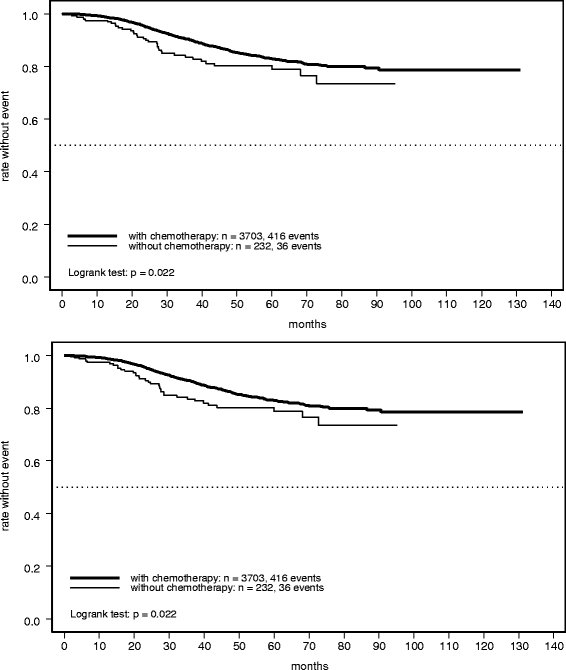
Endpoint Evaluation And Statistical Analyses
Relapse-free survival and overall survival were calculated as the time between the baseline assessment before the first trastuzumab administration and the respective event. Surviving patients were censored at the last valid observation point. Event-related endpoints were analyzed using Kaplan-Meier methodology, with 95% confidence intervals for event-free proportions at specific time points. Univariate analyses comparing the treatment subgroups were performed using the log-rank test, while hazard ratios with 95% CIs were derived from Cox proportional hazards models . In order to analyze the association between patient characteristics and the decision to withhold chemotherapy, t tests, Fishers exact tests, or appropriate trend tests for ordered categories were applied. All factors with an associated P-value < 0.1 in univariate analysis were included in a multivariable logistic regression model.
All statistical analyses were of an exploratory nature, with P 0.05 termed significant, without any adjustments for multiplicity applied. All reported P-values are two-sided.
What Does Cancer Grade Mean
Breast cancers are given a grade according to:
- How different the cancer cells are to normal breast cells
- How quickly they are growing
The grade of a cancer is different to the cancer stage.
A cancers grade is determined when a doctor looks at the cancer cells under a microscope, using tissue from a biopsy or after breast cancer surgery.
Recommended Reading: What Are The First Signs Of Breast Cancer
Stage 1 Breast Cancer Survival Rate Without Chemotherapy
In patients with LABC and clinically negative nodes, SLN biopsy following induction chemotherapy has been shown to have a similar detection rate as in early-stagebreastcancerwithout induction.
Rate of New Cases and Deaths per 100,000: The rate of new cases of female breastcancer was 128.3 per 100,000 women per year. The death rate was 19.9 per 100,000 women per year. These rates are age-adjusted and based on 2015-2019 cases and deaths. Lifetime Risk of Developing Cancer: Approximately 12.9 percent of women will be diagnosed with.
Inflammatory breastcancer is a rare and fatal form of breastcancer. It accounts for only 2-5% of all newly diagnosed breastcancer cases and 7% of all breastcancer-specific mortality .Despite the lack of randomized clinical trial evidence for optimal chemotherapy in IBC, the chemotherapy regimens recommended for non-IBC are equally effective for IBC .
Residual cancer burden after neoadjuvant chemotherapy and long-term survival outcomes in breastcancer: a multicentre pooled analysis of 5161 patients. The Lancet Oncology. Elsevier BV 2021 10.1016/s1470-204500589-1. What is the chance I could die in the next 5 years? The average 5-year survivalrate for all people with breastcancer is 89%. The 10-year rate is 83%, and the 15-year rate is 78%. If the cancer is located only in the breast , the 5-year survivalrate is 99%. More than 70% of breastcancers are diagnosed at an Early Stage.
Outcome Analysis Of Breast Cancer Patients Who Declined Evidence
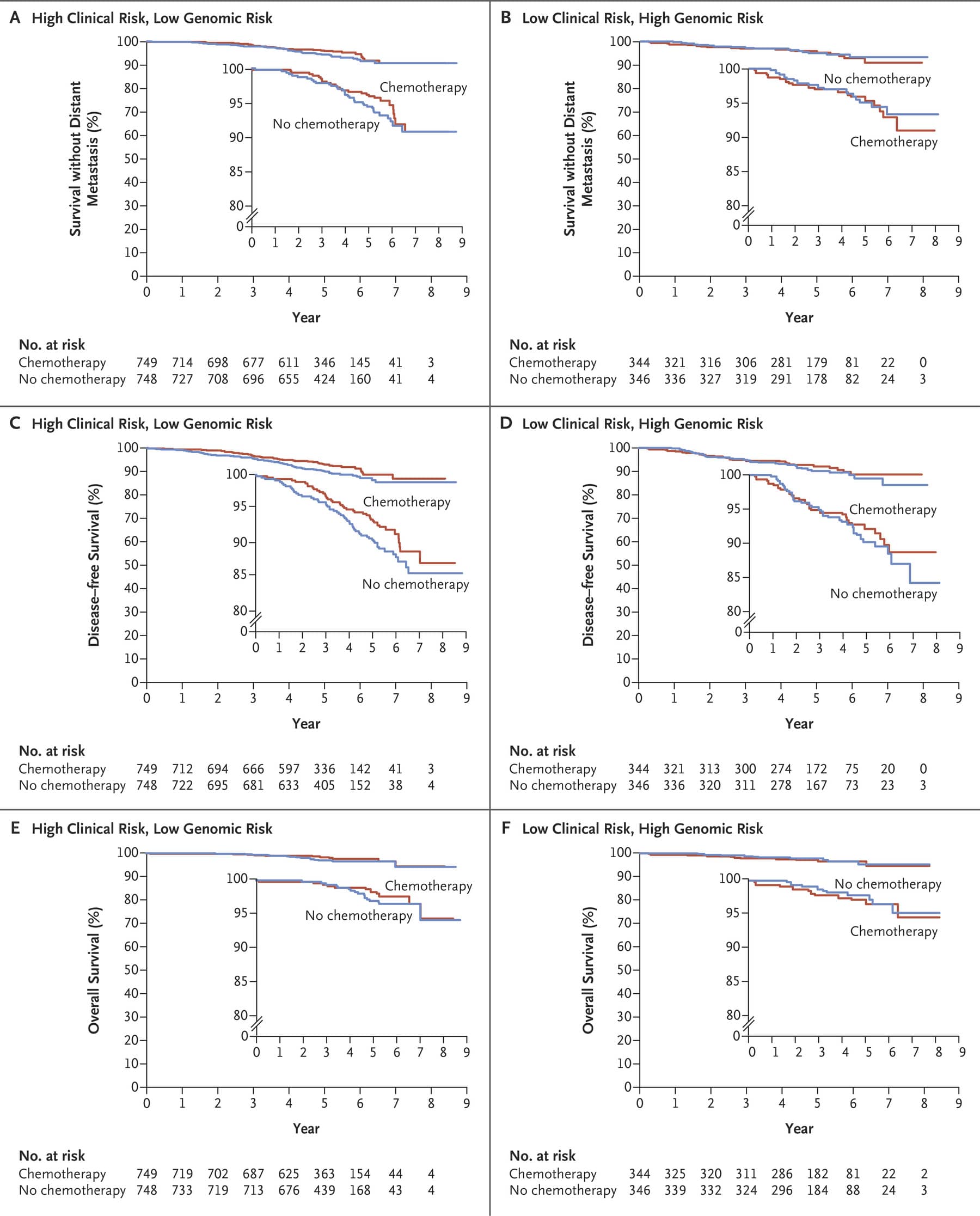
Here is the recent paper I referred to above, which studied women with breast cancer in Northern Alberta who refused standard treatments. It was also a chart review with a matched pair analysis that compared survival with those that received conventional cancer care. Between 1980 and 2006 they identified 185 women that refused cancer care following diagnosis by biopsy. Women older than 75 were excluded from the analysis because this population is generally not included in clinical trials and active treatment regimens. In addition, women that accepted surgery, but rejected chemotherapy/radiation were excluded from the analysis. To qualify, women had to have rejected all conventional care. The final population studied was 87 women, most of whom presented with early disease. Most were married, over the age of 50, and urban residents. In this group, the primary treatment was CAM in 58%, and was unknown in the remainder. Some women in this group eventually accepted cancer care, and the average delay was 20-30 weeks due to CAM use.
The results were grim. The 5 year overall survival was 43% for women that declined cancer care, and 86% for women that received conventional cancer care. For cancer-specific survival survival was 46% vs. 85% in those that took cancer care. The survival curves are ugly:
All causes of deaths and deaths due to breast cancer only
The authors compared the CAM group to those where treatment plan was not known:
Also Check: What Is Negative 3 Breast Cancer
Prognosis And Survival For Breast Cancer
If you have breast cancer, you may have questions about your prognosis. A prognosis is the doctors best estimate of how cancer will affect someone and how it will respond to treatment. Prognosis and survival depend on many factors. Only a doctor familiar with your medical history, the type, stage and characteristics of your cancer, the treatments chosen and the response to treatment can put all of this information together with survival statistics to arrive at a prognosis.
A prognostic factor is an aspect of the cancer or a characteristic of the person that the doctor will consider when making a prognosis. A predictive factor influences how a cancer will respond to a certain treatment. Prognostic and predictive factors are often discussed together. They both play a part in deciding on a treatment plan and a prognosis.
Doctors use different prognostic and predictive factors for newly diagnosed and recurrent breast cancers.
Read Also: Can Ovarian Cancer Spread To Breast
How Treatment Can Impact Survival Of Early Stage Breast Cancer
In most cases, the earlier breast cancer is first diagnosed and treated, the better the chance of survival. Cancer cells often become more difficult to treat and may develop drug resistance once they spread. The aim of treatment for Stage 1 and 2 breast cancer is to remove the breast cancer, and any other cancer cells that remain in the breast, armpit or other parts of the body but cannot be detected. Having treatment at this stage can also reduce the risk of the cancer coming back.
Read more:
Dont Miss: What Cancer Spreads To The Breast
Also Check: How Many People Have Died From Breast Cancer
Stage 4 Breast Cancer
What is Stage 4 breast cancer?
In Stage 4, the breast cancer has metastasized, which means the disease has spread to distant parts of your body. When breast cancer spreads, it can often invade the lungs, liver and bones, sometimes making its way to the brain or other organs.
What are the options for Stage 4 breast cancer treatment?
- Systemic therapies A combination of systemic therapies are often recommended at specific times during the treatment of Stages 1-3. But in stage four, these therapies are the primary treatment and include:
- Hormone therapy When you have Stage 4 breast cancer, hormone therapy can help slow or stop the growth of cancerous cells.
- Chemotherapy This therapy can destroy cancerous cells throughout your body.
- Targeted drug therapies Like chemotherapy, these targeted drugs help reach cancer in distant areas of the body. But depending on your type of cancer, HER2 status and hormone receptor status, different targeted drugs can work alongside chemotherapy or even better than chemotherapy.
- Immunotherapy for breast cancer This therapy helps raise your bodys natural immune response to fight of the cancer.
Lumpectomy With And Without Radiation For Early
Leonard R. Prosnitz, MDOncology
Breast-conserving therapy with lumpectomy and breast irradiation is an accepted standard treatment for patients with early-stage invasive breast cancer or ductal carcinoma in situ . For both diseases, investigators have tried to identify subgroups of patients who can be safely treated with lumpectomy without radiation. Some data suggest that it may be reasonable to omit radiation therapy in patients with small, low-grade invasive or noninvasive tumors and/or in elderly patients. Additional studies are needed to better identify criteria to prospectively select appropriate patients for treatment with lumpectomy alone.
Breast-conserving therapy with lumpectomy and breast irradiation is an accepted standard treatment for patients with early-stage invasive breast cancer or ductal carcinoma in situ . For both diseases, investigators have tried to identify subgroups of patients who can be safely treated with lumpectomy without radiation. Some data suggest that it may be reasonable to omit radiation therapy in patients with small, low-grade invasive or noninvasive tumors and/or in elderly patients. Additional studies are needed to better identify criteria to prospectively select appropriate patients for treatment with lumpectomy alone.
Recommended Reading: Does Chemo Really Work For Breast Cancer
Prognostic And Predictive Factors
Breast cancer is commonly treated by various combinations of surgery, radiationtherapy, chemotherapy, and hormone therapy. Prognosis and selection of therapymay be influenced by the following clinical and pathology features :
- Menopausal status of the patient.
- Stage of thedisease.
- Grade of the primary tumor.
- Estrogen receptor and progesterone receptor status of the tumor.
- Human epidermal growth factor type 2 receptor overexpression and/or amplification.
- Histologic type. Breastcancer is classified into a variety of histologic types, some of which haveprognostic importance. Favorable histologic types includemucinous, medullary, and tubular carcinomas.
The use of molecular profiling in breast cancer includes the following:
- ER and PR status testing.
- HER2/neu receptor status testing.
- Gene profile testing by microarray assay or reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction .
On the basis of ER, PR, and HER2/neu results, breast cancer is classified as one of the following types:
- Hormone receptor positive.
- HER2/neu positive.
- Triple negative .
ER, PR, and HER2 status are important in determining prognosis and in predicting response to endocrine and HER2-directed therapy. The American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists consensus panel has published guidelines to help standardize the performance, interpretation, and reporting of assays used to assess the ER-PR status by immunohistochemistry and HER2 status by immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization.