Tnbc Targeted Therapy And Potential Treatment Regimens
Due to the high heterogeneity of TNBC, it is particularly difficult to discover new therapeutic targets and perform targeted therapy. Currently, there are a large number of ongoing clinical trials targeting specific receptors or on targeted therapies of TNBC based on immunohistochemical staining results.
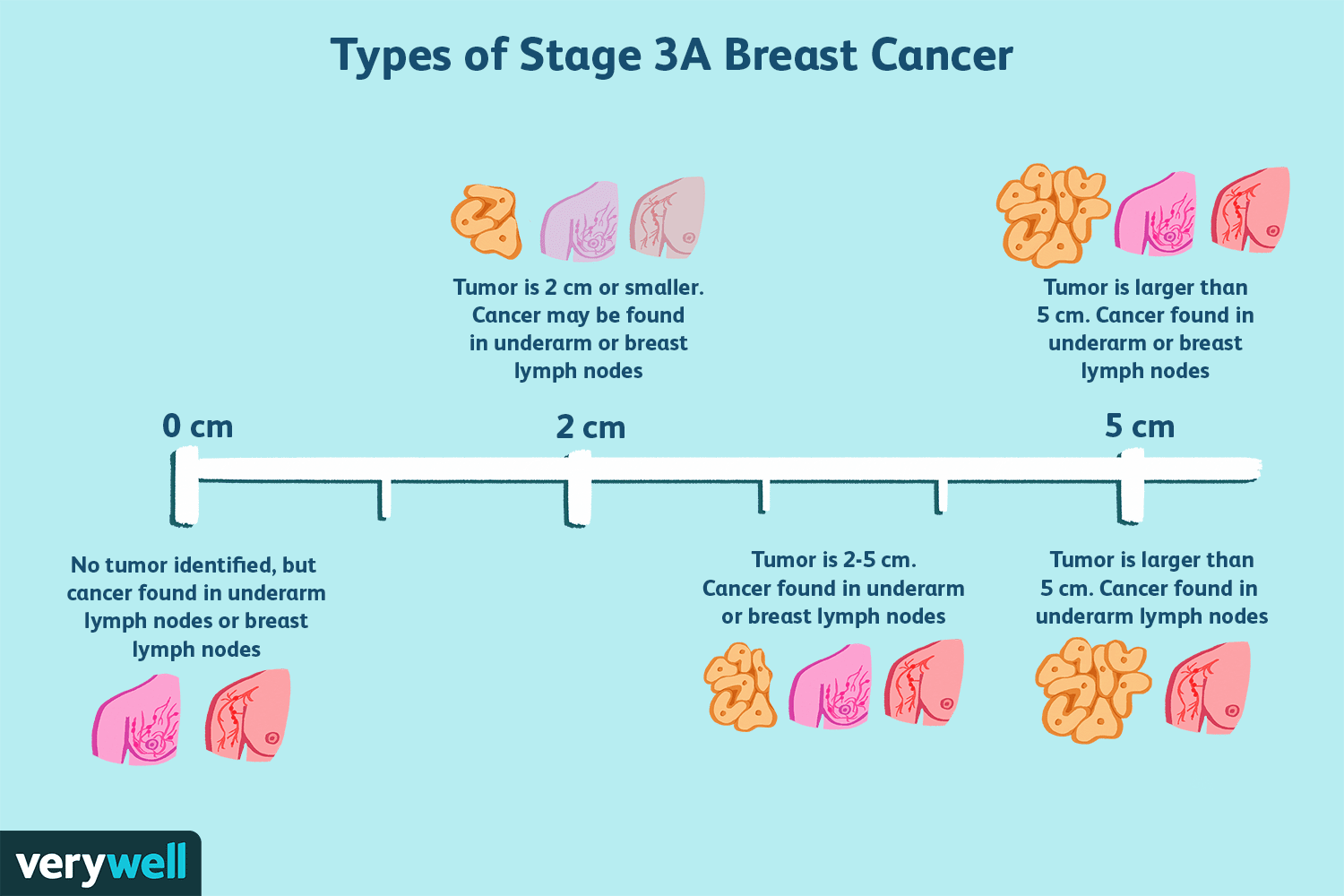
T Categories For Breast Cancer
T followed by a number from 0 to 4 describes the main tumor’s size and if it has spread to the skin or to the chest wall under the breast. Higher T numbers mean a larger tumor and/or wider spread to tissues near the breast.
TX: Primary tumor cannot be assessed.
T0: No evidence of primary tumor.
Tis: Carcinoma in situ
T1 : Tumor is 2 cm or less across.
T2: Tumor is more than 2 cm but not more than 5 cm across.
T3: Tumor is more than 5 cm across.
T4 : Tumor of any size growing into the chest wall or skin. This includes inflammatory breast cancer.
Symptoms Of Triple Negative Breast Cancer
The symptoms of triple negative breast cancer are similar to other breast cancer types.
Symptoms can include:
- a new lump or thickening in your breast or armpit
- a change in size, shape or feel of your breast
- skin changes in the breast such as puckering, dimpling, a rash or redness of the skin
- fluid leaking from the nipple in a woman who isnt pregnant or breast feeding
- changes in the position of nipple
Make an appointment to see your GP if you notice anything different or unusual about the look and feel of your breasts.
Also Check: Mbc Metastatic Breast Cancer
What Questions Should I Ask My Healthcare Provider
You may want to ask your provider:
- What type of breast cancer recurrence do I have?
- Has the cancer spread outside the breast?
- What stage is the breast cancer?
- What is the best treatment for this type of breast cancer?
- What are the treatment risks and side effects?
- Should I look out for signs of complications?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Most breast cancer recurrences respond well to treatments. You may be able to try new drugs or combination therapies in development in clinical trials. Your healthcare provider can discuss the best treatment option based on your unique situation.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 03/24/2021.
References
Survival Rates For Triple
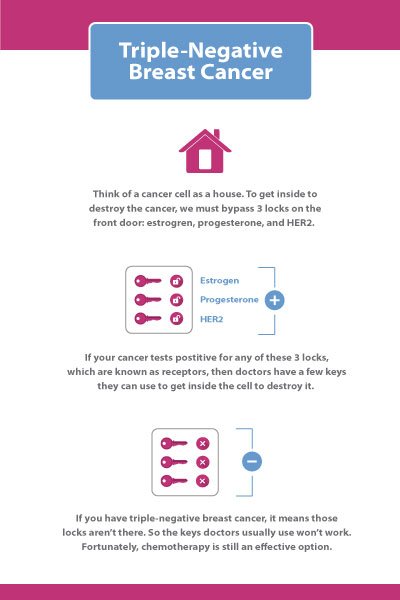
Triple-negative breast cancer is considered an aggressive cancer because it grows quickly, is more likely to have spread at the time its found, and is more likely to come back after treatment than other types of breast cancer. The outlook is generally not as good as it is for other types of breast cancer.
Survival rates can give you an idea of what percentage of people with the same type and stage of cancer are still alive a certain amount of time after they were diagnosed. They cant tell you how long you will live, but they may help give you a better understanding of how likely it is that your treatment will be successful.
Keep in mind that survival rates are estimates and are often based on previous outcomes of large numbers of people who had a specific cancer, but they cant predict what will happen in any particular persons case. These statistics can be confusing and may lead you to have more questions. Talk with your doctor about how these numbers may apply to you, as he or she is familiar with your situation.
Recommended Reading: Breast Cancer Spread To Brain Life Expectancy
Are There Any New Drugs For Triple Negative In The Pipeline
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence who decide which medicines will be available on the NHS in England is currently considering a new treatment for triple negative breast cancer called atezolizumab. Also known as Tecentriq, this drug targets a receptor called PD-L1 which is found in triple negative breast cancer. Atezolizumab, in combination with the chemotherapy drug nab-paclitaxel, may be an option for women with previously untreated locally advanced or secondary triple negative breast cancer. A decision on whether to make atezolizumab available on the NHS is due in late 2019.
Later this year, NICE is also likely to consider another targeted treatment called pembrolizumab. Also known as Keytruda, pembrolizumab can be used before surgery in women with triple negative early breast cancer, and may also be an option for women with previously treated secondary triple negative breast cancer. Decisions on whether to make these new options available on the NHS are expected in 2020.
The Emerging Concept Of Triple Negative Breast Cancer
Breast cancers are commonly associated with a high incidence and a high mortality rate in the female population worldwide. However, at a microscopic and molecular level, breast cancer is not a homogeneous disease, thus being the focus of numerous ongoing studies. The molecular heterogeneity of the normal breast tissue has been previously documented and has outlined the different molecular profiles of epithelial and non-epithelial cells responsible for the existence of several molecular types of breast carcinomas, already characterized . Starting from the histopathological classification up to the molecular classification, breast cancer has been constantly redefined in order to ensure a better management of the patient. In 2012 Boyle et al. stated that the minimal characterization of breast cancer was a situation that had lasted for a century, until a quiet revolution has taken place so that in modern times breast cancer is characterized by its molecular and clinical heterogeneity .
Read Also: Stage 3 A Cancer
What Is The Treatment For Triple Negative Breast Cancer
Healthcare providers and researchers are making significant progress on TNBC treatments. Recent clinical trials are testing new combinations of drugs and new approaches to existing treatments. Some existing treatments are:
- Chemotherapy: Providers might combine chemotherapy and surgery, with chemotherapy being used to shrink your tumor before surgery or after surgery to kill cancer cells throughout your body.
- Surgery: This could be a lumpectomy to remove an individual lump, or a mastectomy to remove an entire breast. Providers then perform a sentinel node biopsy or axillary node surgery to look for signs your breast cancer has spread to your lymph nodes.
- Radiation therapy: Post-surgery radiation therapy helps reduce the chances your cancer will return or recur.
- Immunotherapy: This treatment stimulates your immune system to produce more cancer-fighting cells or help healthy cells identify and attack cancer cells. Immunotherapy can be added to chemotherapy to before surgery to shrink the tumor. You might also receive immunotherapy for about a year after your surgery and post-surgery radiation therapy.
Questionable Issues In Tnbcs
TNBCs are known to metastasize via hematogenous routes and this may be in contradiction with the study of Liu previously mentioned, a study which clearly stated that TNBCs have an active lymphangiogenic process which, normally may favour lymphovascular but not hematogenous dissemination. Currently, the molecular features that differentiate or are able to differentiate lymph node positive TNBCs from lymph node negative TNBCs still remain at a hypothetical level and none of them proved to be useful in the clinical and therapeutic approach of TNBCs patients. But most of the TNBCs cancers have preferentially hematogenous metastases. Besides the high mitotic rate and increased nuclear grade, TNBCs also include pushing border of invasion, frequent tumor necrosis and a large central acellular zone . TNBCs usually exhibit a solid/sheet-like growth pattern and may be associated with an increased lymphocytes infiltrate . Despite the fact that these tumors do not usually metastasize through the lymphatic pathways, TNBCs may be characterized by lymphatic invasion and by an increased LVD . However, not all TNBCs are associated with a poor long term survival, although in a low percentage . EGFR, Src kinase pathway and Cdc42-interacting protein 4 are known to promote TNBCs metastasis . CIP4 inhibition seems to decrease the rate of lung metastasis .
Also Check: Stage 1b Breast Cancer Prognosis
What Is The Staging Of Triple
Staging is the process of determining the extent of the cancer and its spread in the body. Together with the type of cancer, staging helps determine the appropriate therapy and predict the chances for survival.
To determine if the cancer has spread, medical professionals may use several different imaging techniques, including X-ray, CT scans, bone scans, and PET scans. Staging depends upon the size of a tumor and the extent to which it spread to lymph nodes or distant sites and organs in the body. Examination of lymph nodes removed at surgery and the results of ER, PR, and HER2 tests performed on the tumor tissue also help determine the stage of a tumor. Stage I is the lowest stage, while stage IV is the highest stage and refers to tumors that have metastasized, or spread to areas distant from the breast.
Most doctors specifically adjust breast cancer treatments to the type of cancer and the staging group.
Surgery
Many women with breast cancer will require surgery. Broadly, the surgical therapies for breast cancer consist of breast-conserving surgery and mastectomy .
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy destroys cancer cells with high-energy rays. Doctors commonly administer radiation therapy to patients after breast cancer surgery, most commonly after lumpectomy.
Chemotherapy
Types of chemotherapy include the following:
Other therapies for triple-negative breast cancer
Read Also: Anne Hathaway Breast Cancer
Survival Rates And Prognosis
The outlook for breast cancer is often described in terms of relative survival rates.
Relative survival rates are an estimate of the percentage of people who will survive their cancer for a given period of time after diagnosis. Survival among people with cancer is compared to survival among people of the same age and race who have not been diagnosed with cancer.
Five-year relative survival rates tend to be lower for triple-negative breast cancer than for other forms of breast cancer.
According to the American Cancer Society, the overall 5-year relative survival rate for TNBC is . However, an individuals outlook depends on many factors, including the stage of the cancer and the grade of the tumor.
Your healthcare professional will be able to give you a more precise outlook based on:
- the stage of your TNBC
- your age
Read Also: Secondaries Breast Cancer
Treatment For Triple Negative Breast Cancer
The main treatments for triple negative breast cancer are surgery, chemotherapy and radiotherapy. The treatment you need depends on:
- where the cancer is
- the size of the cancer and whether it has spread
- how abnormal the cells look under the microscope
- your general health
You might have surgery to remove:
- an area of the breast
- the whole breast
When you have your surgery, the surgeon usually takes out some of the lymph nodes under your arm. They test these nodes to see if they contain cancer cells. The surgeon might check the lymph nodes closest to the breast using a procedure called sentinel lymph node biopsy. Testing the lymph nodes helps to find the stage of the cancer and decide on further treatment.
After breast conserving surgery you usually have radiotherapy to the rest of the breast tissue.
A New Era Of Hope For Patients With Triple
Triple-negative breast cancer is a particularly devastating subtype of breast cancer, as it is often diagnosed in young women and is associated with an exceptionally poor prognosis. The triple-negative designation indicates that the three key features driving most breast cancers are lacking, but it provides no clues as to potential biologic drivers. In the absence of any biologic insights, tailored, targeted treatment decisions have historically not been possible.
Consequently, until as recently as 2018, we have relied exclusively on nonselective cytotoxic agents, with modest success. For example, conventional neoadjuvant chemotherapy confers a pathologic complete response in just 50% to 55% of patients with early-stage triple-negative breast cancer,1-4 and among those who do not achieve a pathologic complete response, approximately one-third will die within 3 years.5 Moreover, patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer treated with conventional chemotherapeutics have a median survival of 12 to 18 months and an estimated 5-year overall survival of 11%.6 Thus, therapeutic innovation for early and late triple-negative breast cancer has been desperately needed.
Biologic Insight Leads to Therapies
From biologic insight springs hope for therapeutic innovation. Heather L. McArthur, MD, MPHTweet this quote
Immune Modulation Via Checkpoint Blockade
Antibody-Drug Conjugates
Forecast Finally Changing in Triple-Negative Disease
REFERENCES
Also Check: Breast Cancer Staging Prognosis
Trials For Advanced Triple Negative Breast Cancer
Trials are comparing different types of chemotherapy to see which are better at treating advanced disease. For example, researchers are waiting for the results of the Triple Negative Trial to find out whether it is better to use carboplatin or docetaxel.
Research is looking at using targeted cancer drugs alongside other treatments. For example, a trial is using a drug called atezolizumab in combination with chemotherapy. Some trials are testing a drug called pembrolizumab. Researchers think that these targeted drugs on their own might help to control the growth of the cancer.
How The Breast Cancer Staging Process Starts
The breast cancer staging process begins with diagnostic testing. Depending on previous screening results, if any breast cancer symptoms are present, and other factors, your doctor may recommend one of the following tests:
- Diagnostic mammogram A mammogram involves using an X-ray to take photos of your breast tissue at different angles. To do this, your breasts are gently compressed between two plates so the X-ray can be taken.
- Ultrasound An ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging test that bounces soundwaves of your breast tissue to create a picture of the inside of your breast.
- MRI An MRI is another non-invasive imaging test that uses radio waves and a magnetic field to create an image of your breast tissue. This can help doctors determine the size and placement of tumors.
- Biopsy A biopsy removes small masses and growths from your breast so they can be examined under a microscope by a pathologist and determine if theyre cancerous.
If cancer is detected, a CT scan may be ordered to look for any distant metastasis or local invasion to other organs. And youll likely be connected with a breast surgeon right away, either through a nurse navigator or your doctor.
Read Also: Stage 3 Cancer
Is Breast Cancer Now Funding Research Into Triple Negative Breast Cancer
We have a dedicated Research Unit at Kings College London which is the only research unit in the UK focusing solely on understanding triple negative breast cancer and finding better ways to treat it.
Under the leadership of Professor Andrew Tutt, there are currently 29 researchers based at the unit, including Professor Ng and his team who study the role of immune cells in triple negative breast cancer. They are using imaging techniques to look at how immune cells enter the tumour environment and how this contributes to the growth and spread of triple negative breast cancer.
We also fund triple negative research elsewhere in the UK. For example, Professor Claire Lewis at the University of Sheffield is testing whether targeting two molecules called CXCR4 and VEGFA could prevent triple negative breast cancers from spreading around the body.
Dr Walid Khaled at the University of Cambridge is trying to understand how a protein called BCL11A, present in large amounts in triple negative breast cancer cells, is interacting with other proteins in these cells. He hopes that we may be able to kill triple negative breast cancer cells by using treatments to target these interactions.
Although this research may take some time to reach patients, its hoped these projects could lead to new treatment options for people with triple negative breast cancer.
More Benefits Of The Birads Classification System
Another benefit of BIRADS to radiologists, that has indirectly benefited everyone else, is that the categorization scheme has helped to standardize the words used in mammographic reporting, and this has reduced the confusion and improved communication between radiologists, patients and physicians.
BI-RADS classifications have also helped in monitoring breast cancer treatment and supporting breast cancer research again by making statistics easier to calculate.
Following mammogram, a woman will usually see the BI-RADS assessment on the pathology report. So, if you do come across these terms in your report it may be useful to know what they mean.
Recommended Reading: Malignant Neoplasm Of Breast Treatment
Tnbc Chemotherapy Drugs And Efficacy Evaluation
Compared to other types of breast cancer, TNBC has limited treatment options, is prone to recurrence and metastasis, and has a poor prognosis. The main reason is that the expression of ER, PR, and HER2 are all negative, making specific endocrine therapies and targeted therapies ineffective. Therefore, chemotherapy has become the main approach for the treatment of TNBC. In recent years, a large body of literature has shown that the use of neoadjuvant chemotherapy regimens in the treatment of TNBC has a significantly higher pathological remission rate than for hormone receptor-positive breast cancer and can significantly improve the prognosis of TNBC patients. The national comprehensive cancer network guidelines recommend using combination regimens based on taxane, anthracycline, cyclophosphamide, cisplatin, and fluorouracil. At present, taxel/docetaxel + adriamycin + cyclophosphamide , docetaxel + cyclophosphamide , adriamycin + cyclophosphamide , cyclophosphamide + methotrexate + fluorouracil , cyclophosphamide + adriamycin + fluorouracil , and cyclophosphamide + epirubicin + fluorouracil + paclitaxel/docetaxel are the preferred adjuvant regimens for TNBC. Therefore, the selection of appropriate chemotherapy drugs and the optimization of chemotherapy regimens are important for ensuring good treatment outcome and prognosis of TNBC patients.
How Common Is Triple Negative Breast Cancer
15% of all breast cancers over 8,000 cases a year in the UK are triple negative.
Triple negative breast cancer is more common in:
- women who have inherited an altered BRCA gene
- black women
- women who have not yet reached the menopause
- women under 40
Some types of breast cancer are more likely to be triple negative than others. These include medullary and metaplastic breast cancer. However, most people with triple negative breast cancer have invasive ductal breast cancer as this is the most common type of breast cancer in general.
Also Check: Stage 3b Breast Cancer