Vitamin D And Breast Cancer Survival
There is some research to suggest that vitamin D has a positive link to breast cancer survival rates. One study, for example, published in JAMA Oncology, found an association between higher vitamin D levels and a lower risk of both breast cancer morbidity and mortality. Ultimately, though, more research is needed.
Can Vitamin D Reduce Breast Cancer Risk Heres What The Experts Have To Say
The advertiser paid a fee to promote this sponsored article and may have influenced or authored the content. The views expressed in this article are those of the advertiser and do not necessarily reflect those of this site or affiliated companies.
Its commonly known that vitamin D helps maintain strong bones, helps the body absorb calcium and can improve heart health. But a recent study indicates vitamin D specifically, vitamin D3 can even help reduce the risk of breast cancer.
Breast cancer is the most common non-skin type of cancer in women, and, the researchers of the study say, there has been progress in detecting and treating the disease. Although certain anti-hormonal therapies have been shown to reduce breast cancer risk, many patients do not complete these therapies due to the side effects. This study found that in some cases, vitamin D decreased the risk of breast cancer by 83%.
To understand how vitamin D can decrease the risk of breast cancer, lets look at the role of vitamin D in the body.
What is vitamin D?
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin, meaning it can dissolve along with fatty foods and be absorbed in the fatty tissues of the body. It is naturally present in a few foods, like salmon and tuna, and is fortified in milk, orange juice, yogurt, eggs and cereal. Two forms of vitamin D exist, based on the source.
Vitamin D can help reduce breast cancer by:
Questions about vitamin D
Vitamin D Deficiency And Breast Cancer
Among those diagnosed with breast cancer, low vitamin D levels are common, notes a review of research in Breast Cancer . The authors write that the vitamin helps regulate the expression of genes responsible for keeping breast cells from growing too quickly and may also play a role in autophagy, the process by which your body breaks down and recycles damaged cells.
You May Like: What Is Radiation Treatment Like For Breast Cancer
Epidemiological Studies Of Vitamin D And Breast Cancer
In the 1980s, the association between sunlight exposure and cancer incidence was suggested based on the observation that geographical areas located far from the equator have a higher incidence of cancer, which could be associated with a decrease in sunlight exposure or vitamin D status . This association was further analysed in epidemiological studies in which baseline 25D levels were measured before start of any treatment . Vitamin D deficiency is often seen in BC patients at diagnosis and can be correlated to BC subtype, as patients with higher tumour grade, non-luminal and ERâ BCs have lower serum 25D levels than their opposing groups .
So Should You Supplement

Vitamin D is important for everything from bone health to depressionnot just cancer risk. Plus, many Americans could be deficient.
A lot of us are vitamin D deficient because many people are not taking multivitamins, are overweight, and are not physically active , says Dr. Balija. If we’re not giving our body what it needs, our bodies can’t function optimally. We cant fight infection or disease optimally and we can’t fight cancer optimally.
Dr. Bao notes that checking vitamin D levels is a routine part of the cancer care she provides she recommends getting your D levels tested if you think you’re low. If you live in a Northern climate or notice symptoms such as fatigue, bone pain, or muscle weakness, you might be deficient.
If you decide to supplement, heres what that looks like: For people 19 to 70, the recommended dietary allowance of vitamin D is 600 international units . If youre older than 70, its 800 IU. But its usually fine to go highereven well above that level. The National Institutes of Health notes that the tolerable upper intake level of the vitaminbasically what you could take before you might see negative health effectsis 4,000 IU for adults.
Whether you take D supplements or not, its best to think about vitamin D as one piece of the health puzzle. Everybody wants that magic pill or quick fix when really whats going to optimize your immune system and help it fight cancer is a healthy lifestyle, says Dr. Balija.
You May Like: What Body System Does Breast Cancer Affect
Disease Free Survival According To Clinicopathological Factors And 25d Groups
Among clinicopathological factors, stage and vitamin D groups were associated with worse DFS in univariate analysis . In multivariate analysis included age, menopausal status, luminal type and stage, vitamin D groups had statistically independent prognostic parameter for DFS. Among the four groups, only group 2 defined as initial insufficient 25D levels and insufficient after supplementation, showed worse DFS than group I . If sufficient 25D levels were achieved after vitamin D replacement in patients who had insufficient 25D level at baseline, better DFS was obtained, as in patients who had initial sufficient 25D level .
| 0.717.73 | 0.16 |
Group 1: adequate 25D level at baseline and follow-up Group 2: insufficient levels of 25D initially and insufficient after supplements Group 3: insufficient initially, but adequate 25D levels after supplementation Group 4: adequate 25D levels in the beginning but insufficient in follow-up. IDC: invasive ductal carcinoma ILC: invasive lobular carcinoma. OR: odds ratio, CI: confidence interval. Multivariate analysis was performed for 25D level groups, stage, luminal types, age, and menopausal status. Menopausal status and age were included because there was imbalance among 25D level groups as was shown in Table 1. Values in italic are p < 0.05 statistically significant values.
Overall Survival According To Clinicopathological Factors And Vitamin D Groups
Among clinicopathological factors, pre-perimenopausal status, luminal types, and four groups were associated with worse OS in univariate analysis . In the multivariate analysis, four groups were adjusted for age, because there was an imbalance between the four groups. Accordingly, pre-perimenopausal status, triple negative luminal types and 25 D groups had a statistically independent effect on OS. Among the four groups, only group 2, defined as initial insufficient 25D level and insufficient after supplementation, showed worse OS than group I . If sufficient 25D levels were achieved after vitamin D replacement in patients who had insufficient 25D levels at baseline, better OS was obtained, as in patients who had sufficient 25D level at baseline .
| 0.8410.6 | 0.091 |
Group 1: adequate 25D level at baseline and follow-up Group 2: insufficient levels of 25D initially and insufficient after supplements Group 3: insufficient initially, but adequate 25D levels after supplementation Group 4: adequate 25D levels in the beginning but insufficient in follow-up. IDC: invasive ductal carcinoma ILC: invasive lobular carcinoma. OR: odds ratio, CI: confidence interval. Multivariate analysis was performed for 25D level groups, luinal types, age, and menopausal status. Menopausal status and age were included because there was imbalance among 25D level groups as was shown in Table 1. Values in italic are p < 0.05 statistically significant values.
Also Check: Free Breast Cancer Stuff By Mail
Shoulder Range Of Motion
The range of active shoulder abduction in the side of surgery was measured by a Leighton flexometer . Participants stood near a pillar, and their head, trunk, and hip were fixed with straps. A flexometer was attached to their arm the dial at 0 degrees was considered when the hand hanged on the side of the body. Then, participants elevated their arms in the strict coronal plane as far as they could. At the end-range point, the measurement was documented. The best of the three trials was considered.
The Link Between Vitamin D3 And Breast Cancer
In short, the research on the link between breast cancer and vitamin D is conflicting, says Ting Bao, M.D., a breast medical oncologist and the director of Memorial Sloan Kettering’s integrative breast oncology program in New York City. While some research does suggest benefits, other studies do notand its tough for scientists to parse out cause and effect.
For instance, one of the best ways to get vitamin D is from the sun . So, it can be hard to tell whether the benefits of breast cancer risk reduction come from the vitamin D or healthy activities that also raise your D levels, like outdoor exercise, explains Tara Balija, M.D., a board-certified general surgeon with fellowship training in breast surgical oncology and an assistant professor of surgery at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City. Heres what we do know.
You May Like: How To Help Breast Cancer Awareness
Combination Therapies With 1252d3 Or Analogues
As 1,252D3 and vitamin D3 analogues reduce tumour progression by blocking different pathways, multiple studies investigated possible combinations of approved chemotherapies or other compounds with 1,252D3 or vitamin D3 analogues to find a synergistic combination therapy.
MTT, 3–2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide XTT, 2,3-bis–2H-tetrazolium-5-carboxanilide.
Also, chloroquine, an inhibitor of autophagosome acidification, synergistically inhibited cell proliferation in combination with 1,252D3 in MCF7 cells not only in vitro but also in vivo. The size of tumour xenografts was substantially smaller after the combination treatment than after the mono-treatment .
Another target important in the process of inflammation is cyclooxygenase 2 . 1,252D3 was combined with the COX2 inhibitor, celecoxib, in MCF7 and MDA-MB-231 cells, causing a synergistic growth inhibitory effect in both BC cell lines . Interestingly, 1,252D3 regulated the production and secretion of cytokines such as IL-1β and TNF-α in TNBC SUM-229PE cells. Moreover, when combining 1,252D3 with TNF-α, the combination was more potent to reduce cell proliferation than either compound alone, probably by potentiating the cytotoxic effect of TNF-α on BC cells .
Effect Of Vitamin D Supplementation On Risk Of Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review And Meta
- 1Centre for Clinical Epidemiology and Methodology, Guangdong Second Provincial General Hospital, Guangzhou, China
- 2Department of Gynecology, Guangdong Second Provincial General Hospital, Guangzhou, China
- 3Department of Health Research Methods, Evidence, and Impact, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON, Canada
- 4St. Joseph’s Healthcare Hamilton, Hamilton, ON, Canada
Objective: Laboratory findings indicated that vitamin D might have a potent protective effect on breast cancer, but epidemiology studies reported conflicting results. The aim of the study was to conduct a systematic review and meta-analysis to clarify the efficacy of vitamin D supplementation on risk of breast cancer.
Methods: MEDLINE, EMBASE, The Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, ClinicalTrials.gov, and abstracts of three major conferences were searched . Parallel randomized controlled trials examining the efficacy of vitamin D supplementation on risk of breast cancer or change of mammography compared with placebo in females were included. Data were meta-analyzed using a random-effects model. Bayesian meta-analysis was conducted to synthesize the results using data from observational studies as priors.
There is insufficient evidence to support the efficacy of vitamin D supplementation in breast cancer risk and change of mammography density. The protective effect of vitamin D on risk of breast cancer from previous observational studies may be overestimated.
Read Also: 8 Cycles Of Chemotherapy For Breast Cancer
Could Your Overall Health Benefit From Vitamin D
Make sure you know your vitamin D level, and take steps to keep it within a target of 40-60 ng/ml or 100-150 nmol/L! Through GrassrootsHealth Nutrient Research Institute, you can also test your essential elements magnesium, copper, zinc and selenium, toxins such as lead, mercury and cadmium, as well as your omega-3 levels, inflammation levels and thyroid stimulating hormone level. Find out your levels today! Log on to the test selection page to get your tests and see for yourself if your levels can be improved.
Make sure you track your results before and after, about every 6 months!
Vitamin D Through Sunlight Exposure And Diet
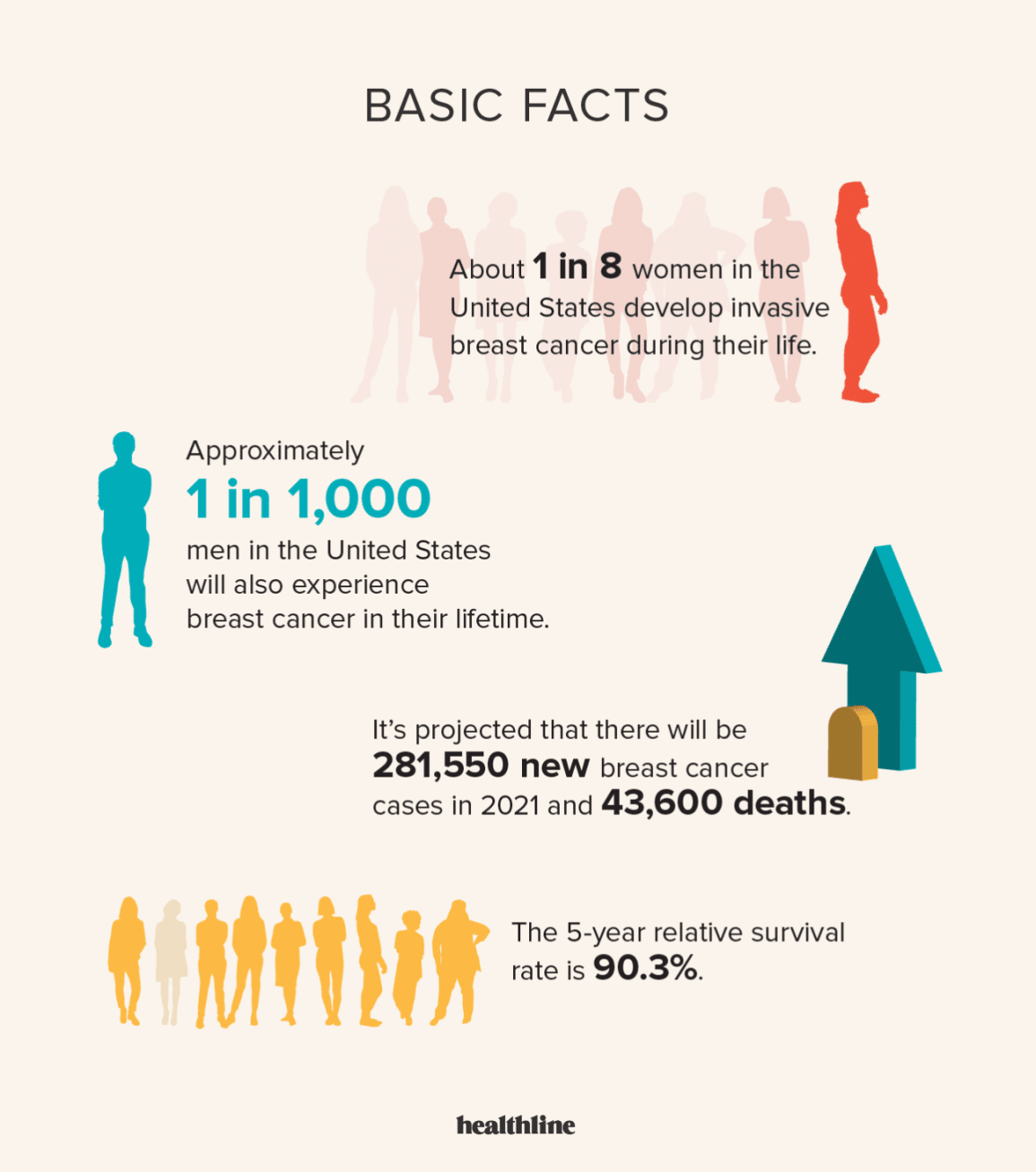
Findings from studies on vitamin D and decreased breast cancer risk are mixed.
Studying vitamin D with measures of sunlight exposure and diet has some challenges. Its hard to measure sunlight exposure. And, because so many foods that contain vitamin D also contain calcium, its hard to single out the effects of vitamin D alone.
You May Like: Breast Cancer Chemo Port Picture
Vitamin D As A Potential Preventative Therapeutic For Postpartum Breast Cancer
While vitamin D supplementation targeted to premenopausal women is a strategy anticipated to increase prevention efficacy, a complimentary approach is to specifically target transient, developmental windows of elevated breast cancer risk. The window of weaning-induced breast involution represents a key developmental window that contributes to breast cancer risk, and which may be particularly poised for vitamin D supplementation. In support of a prevention strategy targeted to the postpartum window, studies consistently find a transient increased risk for breast cancer following childbirth. The peak incidence has been reported at 5 years postpartum , with a long tail of increased risk persisting up to 15 years postpartum . It has been proposed that postpartum breast cancers account for approximately 50% of all young women’s breast cancer cases . Furthermore, these cancers have worse prognosis compared with age-, stage-matched cases in nulliparous women. A breast cancer diagnosis within 510 years of a recent pregnancy independently associates with a 2- to 3-fold increased risk of death, for both ER+ and ER disease . Conversely, a breast cancer diagnosis during pregnancy is not associated with poorer outcomes . Combined, these studies implicate the existence of a postpartum event that negatively impacts breast cancer.
Does Vitamin D Deficiency Increase The Risk Of Breast Cancer
Research suggests that women with low levels of vitamin D have a higher risk for breast cancer. Vitamin D may control normal breast cells growth and stop breast cancer cells from growing. Studies have also shown that vitamin D deficiency can lead to tumor progression and metastasis .
A strong link has been noted in women with recurrent breast cancer and a vitamin D level below 20 ng/mL. One study showed that women with vitamin D deficiency when their breast cancer was diagnosed had poorer outcomes with higher chances of cancer coming back and death. However, these findings are associative, meaning other factors could have contributed to the poor outcomes.
Don’t Miss: Can You Have Radiation More Than Once For Breast Cancer
Vitamin D And Breast Cancer
Home » Reduce Your Risk » Alcohol, Diet and weight » Diet » Vitamin D and breast cancer
Most studies have found low levels of vitamin D are linked to an increased breast cancer risk.
The body produces adequate levels of vitamin D if the skin is exposed to sufficient sunlight. Other sources include diet or supplements.
Studies have not shown that taking vitamin D supplements reduces breast cancer risk. Although taking them can restore serum vitamin D levels to a healthy state and are recommended for people unable to achieve sufficiency through sunshine and diet.
The main function of vitamin D is maintaining calcium levels.
Vitamin D may help prevent breast cancer by reducing breast cell growth and the production of oestrogen in the body.
Overview Of Vitamin D
The metabolism of vitamin D is a tightly regulated process , which is consistent with its known role as a key transcription factor that regulates varied and complex developmental and physiologic responses . The actions of vitamin D are mediated through the binding of its active form 1,252D to the vitamin D receptor , a transcription factor belonging to the steroid hormone receptor superfamily. Binding of 1,252D to VDR stimulates heterodimerization with the retinoid X receptor . The VDR-RXR heterodimer subsequently binds vitamin D-responsive DNA elements and regulates expression of VDR target genes .
The vitamin D receptor, VDR, is expressed in most tissues throughout the body, including immune, nervous, muscle, reproductive, and glandular tissue . This widespread expression profile broadly implicates vitamin D signaling in the maintenance of cell and tissue health. Indeed, impaired vitamin D signaling is implicated in the development and progression of various diseases, including inflammation and autoimmune disorders , chronic kidney disease , cardiovascular disease , hypertension , obesity , diabetes mellitus , as well as various types of cancer . Together, these studies reflect the numerous biologic functions of vitamin D, including mineral homeostasis, immune regulation, and epithelial cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. Importantly, many of these vitamin D functions interface with the hallmarks of cancer .
Recommended Reading: Survival Rate Inflammatory Breast Cancer
What Is Vitamin D
Vitamin D is also known as calciferol or the sunshine vitamin.” It is a fat-soluble vitamin that helps with teeth and bone development. The human body produces vitamin D naturally through exposure to sunlight. When ultraviolet rays from the sun are on the skin, it triggers the body to make vitamin D. The vitamin is also present in certain foods and can be taken as a supplement.
Can You Take Vitamin D After Breast Cancer
Individuals who have had breast cancer often take dietary supplements to improve overall nutrition and regain strength after treatment, as well as reduce their risk of getting breast cancer again. Many people living with breast cancer take vitamin D supplementation hoping to slow down or reverse the course of the disease.
The truth is that the role of vitamin D in breast cancer prevention is known by association but remains unproven. Meaning, researchers cannot say with certainty that if patients with breast cancer or other cancers take vitamin D supplements, it will lower their risk of cancer recurrence. However, doctors may recommend supplementation for overall health. This can be achieved through foods naturally rich in vitamin D, fortified foods, or a dietary supplement.
You May Like: Can You Have Breast Cancer With No Symptoms