What Is Inflammatory Breast Cancer
As its name suggests, inflammatory breast cancer often causes the breast to become red, swollen, and inflamed. Some women with IBC also notice thickened or discolored breast skin with tiny dimples, puckers, or ridges that make it look like an orange peel. While the symptoms may sound like an infection, the real culprit is cancer that is blocking lymphatic vessels in the skin and breast tissue, causing a buildup of fluid and, in some cases, pain, discoloration, and sudden swelling of the breast. Also called inflammatory breast carcinoma or locally advanced breast cancer, IBC can spread quickly, making prompt diagnosis and treatment essential.
Read Also: Low Grade Breast Cancer Prognosis
Her2 Positive Breast Cancer Risk Factors
The exact causes of breast cancers including HER2 positive breast cancer are not fully understood. Still, certain factors are known to increase an individuals risk of developing a breast malignancy. Not all of these risk factors can be controlled, but some can.
Here are a few of the most common risk factors associated with breast cancer:
- Being female
- Having a family history of breast cancer
- Giving birth for the first time after age 30
- Receiving radiation therapy to the chest
- Being overweight
- Living a sedentary lifestyle
- Using tobacco products
Additionally, HER2 positive cancer which makes up about 20 percent of breast cancer cases is more likely to affect younger women.
Its important to note that having one or more of these risk factors does not mean you will be diagnosed with breast cancer. On the other hand, not having any of these risk factors doesnt mean youll never develop cancer. Risk factors are just characteristics that may leave you slightly more susceptible to disease.
If any of these risk factors apply to you, be particularly mindful of any changes in your breasts and see a physician for regular breast cancer screenings. Your physician will be able to determine an optimal schedule of preventive care based on your health, age and other risk factors.
What Are Hormones And Hormone Receptors
Hormones are substances that function as chemical messengers in the body. They affect the actions of cells and tissues at various locations in the body, often reaching their targets through the bloodstream.
The hormones estrogen and progesterone are produced by the ovaries in premenopausal women and by some other tissues, including fat and skin, in both premenopausal and postmenopausal women and in men. Estrogen promotes the development and maintenance of female sex characteristics and the growth of long bones. Progesterone plays a role in the menstrual cycle and pregnancy.
Estrogen and progesterone also promote the growth of some breast cancers, which are called hormone-sensitive breast cancers. Hormone-sensitive breast cancer cells contain proteins called hormone receptors that become activated when hormones bind to them. The activated receptors cause changes in the expression of specific genes, which can stimulate cell growth.
Breast cancers that lack ERs are called ER negative, and if they lack both ER and PR they may be called HR negative.
Approximately 67%80% of breast cancers in women are ER positive . Approximately 90% of breast cancers in men are ER positive and approximately 80% are PR positive .
Also Check: Estrogen Induced Breast Cancer
How Herceptin Is Given
Herceptin is given during visits to a hospital or clinic.
It can be given in 2 ways:
The first time you have herceptin you will need to stay in hospital for around 6 hours so you can be monitored for any side effects. For further treatment sessions you’ll usually only need up to 2 hours in hospital.
If you have breast cancer, you’ll have treatment every 1 or 3 weeks. Stomach and oesophageal cancer are usually treated once every 3 weeks.
Early-stage breast cancer will need treatment for 1 year. For breast, oesophageal or stomach cancer that’s spread, treatment is used for as long as it is helpful.
Inclusion And Exclusion Criteria

This study enrolled female patients with invasive ductal carcinoma of no special type/no otherwise specified histology with overexpression/amplification of HER2. Patients were excluded according to the following criteria: synchronic metastatic disease missing histopathological data incomplete immunohistochemistry and/or indeterminate HER2 failure to perform surgery neoadjuvant radiation therapy the presence of a special component lysed/destroyed tumour bilateral cancer more than one primary cancer tumour progression during adjuvant treatment, except endocrine therapy unreported cause of death and follow-up time less than 180 days from diagnosis to event.
From a total of 2,580 medical records, 1,685 were excluded for being metastatic or in situ tumours, or lack of adequate pathological examination, lack of surgery, neoadjuvant radiation therapy, development of another cancer and/or bilateral/contralateral breast cancer. Of the remaining 895 medical records, 737 were excluded for being Luminal A or B or TN. Three patients were subsequently excluded due to tumour progression during chemotherapy, trastuzumab or radiation therapy course.
Recommended Reading: Did Anne Hathaway Have Cancer
What Is Hormone Therapy
Hormone therapy slows or stops the growth of hormone-sensitive tumors by blocking the bodys ability to produce hormones or by interfering with effects of hormones on breast cancer cells. Tumors that are hormone insensitive do not have hormone receptors and do not respond to hormone therapy.
Hormone therapy for breast cancer should not be confused with menopausal hormone therapy treatment with estrogen alone or in combination with progesterone to help relieve symptoms of menopause. These two types of therapy produce opposite effects: hormone therapy for breast cancer blocks the growth of HR-positive breast cancer, whereas MHT can stimulate the growth of HR-positive breast cancer. For this reason, when a woman taking MHT is diagnosed with HR-positive breast cancer she is usually asked to stop that therapy.
What Happens During A Her2 Breast Cancer Test
Most HER2 testing involves taking a sample of tumor tissue in a procedure called a biopsy. There are three main types of biopsy procedures:
- Fine needle aspiration biopsy, which uses a very thin needle to remove a sample of breast cells or fluid
- Core needle biopsy, which uses a larger needle to remove a sample
- Surgical biopsy, which removes a sample in a minor, outpatient procedure
Fine needle aspiration and core needle biopsies usually include the following steps:
- You will lay on your side or sit on an exam table.
- A health care provider will clean the biopsy site and inject it with an anesthetic so you won’t feel any pain during the procedure.
- Once the area is numb, the provider will insert either a fine aspiration needle or core biopsy needle into the biopsy site and remove a sample of tissue or fluid.
- You may feel a little pressure when the sample is withdrawn.
- Pressure will be applied to the biopsy site until the bleeding stops.
- Your provider will apply a sterile bandage at the biopsy site.
In a surgical biopsy, a surgeon will make a small cut in your skin to remove all or part of a breast lump. A surgical biopsy is sometimes done if the lump can’t be reached with a needle biopsy. Surgical biopsies usually include the following steps.
Also Check: Fish Test Breast Cancer
Survival Rates And Statistics
A relative survival rate helps give an idea of how long a person with a particular condition will live after receiving a diagnosis compared with those without the condition.
For example, if the 5-year relative survival rate is 70%, it means that a person with the condition is 70% as likely to live for 5 years as someone without the condition.
It is important to remember that these figures are estimates. A person can talk with a doctor about how their condition is likely to affect them.
Some factors affecting a personâs survival rate with breast cancer include:
- individual factors, such as the personâs age and overall health
- the stage of the cancer at diagnosis
- the treatment the person receives
HER2-positive cancers are than HER2-negative cancers. With treatment, however, the chances of survival are high, especially with an early diagnosis. In some cases, they may be higher than for HER2-negative breast cancer due to effective targeted treatment.
According to the , the likelihood of living for another 5 years with HER2-positive cancer, compared with a person who does not have breast cancer, is as follows. These statistics are based on figures for the years 2011â2017.
| Stage |
|---|
Her2 Expression Patterns In Early Lesions
Notably, upregulation of HER2 levels can be readily detected in human breast tissues that show the early signs of transformation but have not been completely transformed. Completely transformed cells are able to grow in an anchorage independent fashion in vitro and also grow in vivo. Incompletely transformed cells display one, but not both, of these traits. Table 1 summarizes HER2 expression within breast lesions at various stages of cancer progression. Generally, HER2 is absent or expressed at low-levels in benign breast lesions . For instance, HER2 is not detected in terminal duct lobular units and has been detected rarely in atypical ductal hyperplasia .
Recommended Reading: Non Inflammatory Breast Cancer
How Her2+ Breast Cancer Is Diagnosed
There are many steps in the process of diagnosing breast cancer.
If a person has a symptom that is concerning to them, such as a lump in their breast, they should discuss it with their healthcare provider. The healthcare provider will likely start by taking a medical history and performing a physical exam. This can help them determine what is causing the symptoms. The next step in the process is imaging.
Heart Monitoring On Herceptin
Heart problems can sometimes develop while you’re taking herceptin and they can be serious.
Before treatment starts, you’ll have a test to see how well your heart is working for example, an echocardiogram or a multi-gated acquisition scan.
Your heart will also be regularly checked during treatment.
It’s important to tell your doctor if you’re being treated with herceptin and you get:
- shortness of breath during the day or night
- swollen ankles
If you develop a problem with your heart during treatment, it will usually improve if you have a short break from taking herceptin.
Also Check: Stage 3 Advanced Breast Cancer
Do Symptoms And Signs Of Her2
The signs and symptoms for HER2-positive breast cancers are the same as for HER2-negative breast cancers, except for the fact that HER2-positive cancers are likely to grow faster and are more likely to spread. The following are possible signs of breast cancer:
- Thickening or lump in the breast that feels different from the surrounding area
- Inverting of the nipple
The Overall Hormone Receptor Status Of A Breast Tumor Helps Predict Behaviour And Responsiveness To Treatment
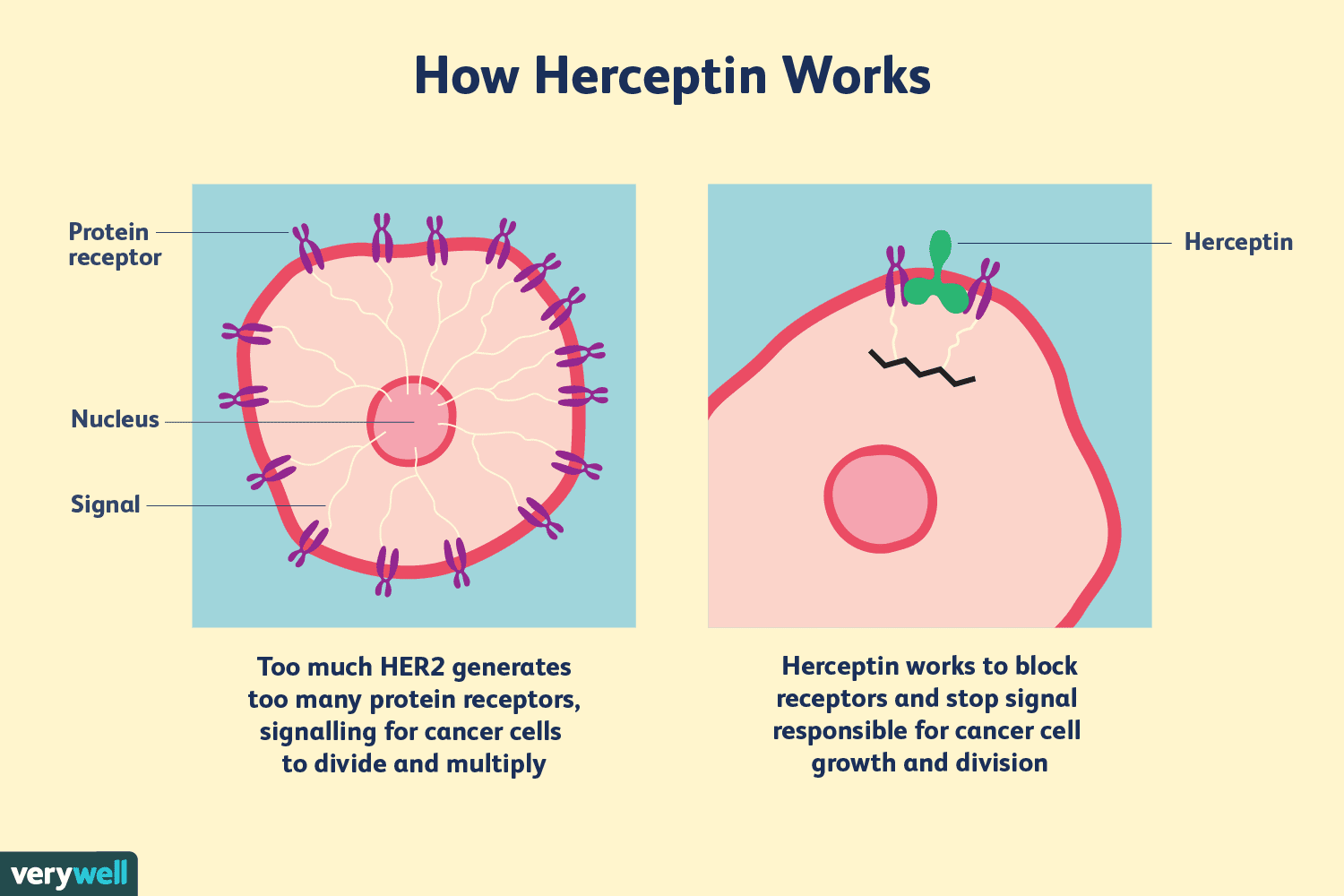
Indeed, specialists consider the hormone-receptor status of a tumor to be more of a predictive factor rather than a prognostic factor. It helps determine what you are up against, and how best to treat it.
However, research shows that the outlook for a particular breast cancer is more likely to be influenced by the histological type and grade of the breast cancer tumor at the time of discovery.
Also, whether or not there is lymphatic involvement is another important factor, and not the hormone receptor status.
It is true, however, that breast cancer tumors with a positive hormone receptor status have a more indolent course than do hormone receptor-negative tumors.
Indolent is kind of a strange term to use, but it means that a tumor is less responsive or lazy in response to treatment than hormone negative receptor status tumors. Some kind of extra intervention or boost is often necessary to really get a positive healing response from cancer.
However, the good news is that certain kinds of hormone-receptor-positive tumors are actually more responsive to endocrine therapy. So, there is a positive aspect to this as well.
In fact, there is often a kind of inverse relationship between the HER-2 hormone receptor status, and the ER and PR status of a tumor.
Recommended Reading: Breast Cancer Medications After Surgery
Her2 Positive Breast Cancer Recurrence
HER2 positive breast cancer is an aggressive disease with an elevated risk of metastatic spread if appropriate treatment or therapy is not administered. While HER2 positive breast cancer recurrence affects some patients, recent advancements in targeted therapies and long-term treatment approaches have made relapse less likely than ever before. The majority of patients with HER2 positive cancer do not experience recurrence.
Despite these odds, you may still feel nervous about your chances of cancer recurrence if you have a history of HER2 positive breast cancer. This is completely understandable. The best way to calm your fears and reduce your risk is to be proactive about your breast health, complete all recommended treatments or therapies, and maintain regular follow-up with your breast cancer clinical care team.
Actin Fiber Staining And Confocal Microscopy
Tzm-resistant SKBR3 cells were seeded and incubated on Matrigel-coated 4-well chamber slides in complete EBM-2 medium for 30min. Then, the medium was replaced with Hanks balanced salt solution supplemented with 0 or 4M salinomycin, and the cells were further incubated for 2h. The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 10min at room temperature. After permeabilization with 0.2% Triton X-100 for 2min, filamentous actin was stained with ActinGreen 488 Ready Probe for 30min. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI, and confocal images were obtained using an FV10i confocal laser scanning microscope . The amount of F-actin in a cell was quantified using ImageJ software and was represented as integrated density.
Read Also: How To Donate To Breast Cancer Charity
You May Like: How Fast Do Breast Cancer Tumors Grow
What Does Testing Involve
If a doctor confirms an unusual growth, they will take a biopsy. To collect a sample, they may perform one of the following procedures:
- Use a fine needle to remove a sample of breast cells or a liquid in fine-needle aspiration.
- Use a larger needle in a core needle biopsy.
- Carry out minor surgery as an outpatient procedure.
According to the American Cancer Society , a core needle biopsy is often the preferred option.
The doctor will send the tissue samples to a laboratory to test whether or not breast cancer is present. If it is, the pathologist will test to see if the cancer is HER2-positive.
The two main tests for determining whether or not HER2-positive cancer is present are the fluorescent in situ hybridization test and the immunohistochemistry test.
The FISH test looks for additional copies of the HER2 gene in breast cancer cells. It uses special labels that attach to the HER2 proteins that glow in the dark.
The IHC test uses a chemical dye to stain HER2 proteins and can determine how much HER2 protein is present in breast cancer cells.
Often, the pathologist will carry out the IHC test and then the FISH test. IHC testing is faster and less costly than FISH testing. However, if the results of the IHC test are unclear, a person will need a FISH test to determine whether or not a tumor is HER2-positive.
Tests To Detect Spread
If you notice signs that your HER2-positive breast cancer may have spread, talk to your doctor. This is especially important if your symptoms are new, wonât go away, or you canât tell why they may be happening.
But itâs important not to panic. Keep in mind that symptoms such as bone pain can happen from arthritis, getting older, or even from your breast cancer treatment. Meanwhile, a cough and shortness of breath could just mean you have a cold or the flu. And itâs normal to feel tired and to not be hungry after youâve had cancer treatment.
To figure out if your breast cancer has spread, your doctor might do a variety of tests. These can include:
- Blood tests, some of which may look for tumor âmarkersâ
- Bone scan
Recommended Reading: First Stage Breast Cancer Symptoms
Its A Hopeful Time For Her2
If you or a loved one are diagnosed with this cancer, remember this: There are more effective treatments available than ever. The big take-home point about HER2-positive tumors is that while this is very aggressive tumor, these very targeted treatments are incredibly effective, Dr. Kulkarni says. So while prognosis used to be poor, with the introduction of targeted treatments and more to come, people see much better outcomes, she says. Its very exciting times for HER2-positive breast cancer research, Dr. Czerniecki says.
Mechanisms Of Resistance To Her2
Intrinsic and acquired mechanisms of resistance to HER2-targeted agents have been described. HER2 reactivation or signaling downstream from the HER2 receptor are some of the commonly described mechanisms of resistance. HER2 mutations are a well-known intrinsic and acquired mechanisms of resistance,. Different types of mutations have been described, including activating mutations and mutations that modify the receptor preventing binding of monoclonal antibodies,,. L755S is the most frequently identified acquired activating mutation of HER2 which is more commonly seen in metastatic tumors. L755S has been described as an acquired mechanism of resistance to lapatinib and cross resistance to tucatinib has been reported in vitro. However, the resistant cells appear to be sensitive to neratinib, which is a pan-HER2 TKI,. More studies are needed to determine the clinical significance of this mutations to allow us to tailor treatment based on the specific mutations.
Don’t Miss: What Does Her2 Negative Mean In Breast Cancer
How Are Breast Tumors Tested For Her2
Either a test called an immunohistochemistry test or fluorescence in situ hybridization test is used to find out if cancer cells have a high level of the HER2 protein.
See Testing Biopsy and Cytology Specimens for Cancer and Understanding Your Pathology Report: Breast Cancerto get more details about these tests.
Targeted Therapies Prevent Pre

Since HER2 plays such an important role in early metastasis, targeted therapies may be critical to prevent pre-malignant lesions from developing into IBC. We have shown that HER2 targeted antibodies not only inhibit growth of already established tumors, but also can prevent tumor development in transgenic mice over-expressing the activated neu oncogene in mammary epithelial cells . In this study, treatment of transgenic animals after 20 weeks of age but before tumor emergence led to a dose-dependent reduction in tumor incidence, and the tumor-free mice seemed to be protected for life.
These studies indicated that cells expressing p185neu must still undergo further genetic changes to progress to fully transformed cells. Human cells over-expressing HER2 proteins also require additional allelic and adaptive changes to become fully transformed. Therefore, prevention of tumor emergence can occur by down-regulating HER2 proteins prior to complete transformation. This finding facilitated the use of the antibodies as an adjuvant to prevent tumor emergence .
Don’t Miss: Breast Cancer Return Symptoms