Lifestyle Also Plays A Role
Some risk factors for DCIS are modifiable. Eating lots of fruits and vegetables, maintaining a healthy weight, and limiting alcohol intake have all been linked to lower breast cancer rates, says Dr. Meyers, and they are smart habits to develop no matter what type of breast cancer you’re trying to avoid.
For women who have already had DCIS, cutting back on drinking may reduce their risk of a recurrence, according to a 2014 study in the journal Cancer, Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention. “It is possible that alcohol consumption may increase risk of second breast cancer incidence,” the authors wrote in their paper, “but may not substantially increase the likelihood of aggressive second diagnoses that result in death, particularly among DCIS survivors.”
Morphological Features Of Carcinoma In Situ
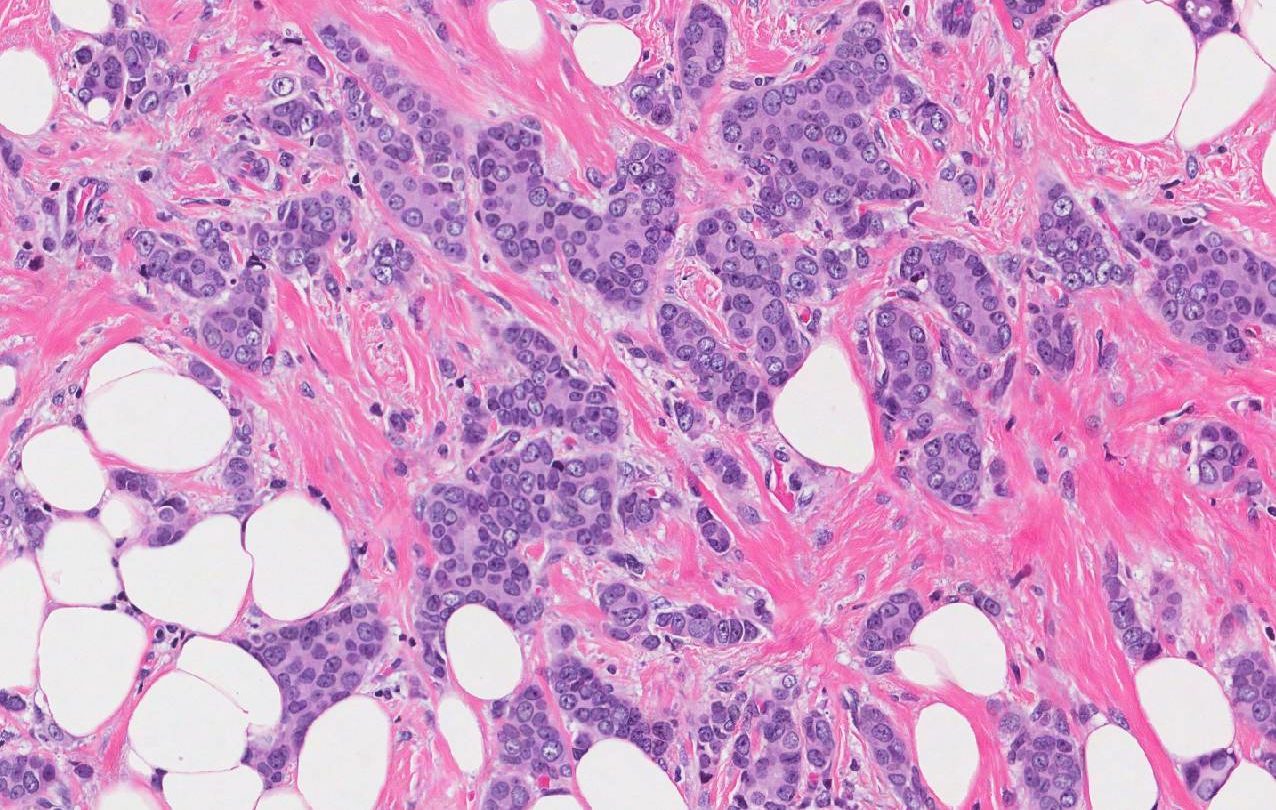
Features of a low-grade DCIS. Low-grade DCIS in a core needle biopsy intermediate and high-magnification of the lesion showing a cribriform growth pattern DCIS with negative margins, but the distance between neoplasia and inked margin is < 2 mm ER positivity in a low-grade DCIS Her-2 positivity in a low-grade DCIS.
Reporting stromal reaction and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes is also recommended. High-grade DCIS is predominantly associated with a desmoplastic reaction of the periductal stroma and seems to correlate with a higher risk of recurrence . TIL is a dense, chronic inflammatory infiltrate surrounding DCIS. Several studies demonstrated that breast carcinomas with a marked intra-tumoral stromal lymphocytic infiltrate have a better prognosis than carcinomas with lymphocyte depletion . Triple-negative and HER2-positive DCIS lesions are the subgroups of breast carcinomas that show the greatest degree of enrichment of the stroma by lymphocytes . A shorter recurrence-free interval is seen if TILs are associated with younger age, larger size, comedonecrosis and ER negative, and HER2 overexpression. However, no significant association was identified for longer follow-ups . It should be noted that the evaluation of TILs has a prognostic value and not a predictive value of response to therapies, therefore, this criterion is not used to decide whether or not to administer chemotherapy or other systemic therapies.
New Imaging Technique Can Detect Skin Cancers Without Invasive Biopsy
Researchers funded by the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering have developed a non-invasive imaging technique that accurately detects skin cancer without surgical biopsy. Multiphoton microscopy of mitochondriasmall organelles that produce energy in cellsaccurately identified melanomas and basal cell carcinomas by detecting abnormal clusters of mitochondria in both types of skin cancer.
A group of international collaborators led by co-senior author Irene Georgakoudi, Ph.D., in the Department of Biomedical Engineering at Tufts, found that mitochondria behave very differently in healthy versus cancerous tissue. They used a laser microscopy technique that takes advantage of the characteristics of a key molecule in mitochondria, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide , that is central to energy production. They found that NADH, which naturally fluoresces without injecting any dye or contrast agent into the individuals being screened, can be detected using multiphoton microscopy to provide diagnostically useful information about the organization of the mitochondria in skin cells.
This research was funded by the National Institutes of Health through grant # P41EB015890 from the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering. Additional funding was provided by the American Cancer Society, the Alexander S. Onassis Public Benefit Foundation, and the Arnold and Mabel Beckman Foundation.
Also Check: Breast Cancer Mayo
Whats The Difference Between Invasive And Metastatic Breast Cancer
Invasive breast cancer simply refers to breast cancer that has spread away from the tissue in which it originated and into healthy breast tissue. It can be either localized or metastatic.
For example, if a cancer that began in the milk ducts breaks through the lining of the milk ducts and spreads into healthy breast tissue, that cancer is considered to be invasive. However, its not metastatic because its still localized to the breast.
If cancer cells break away from that tumor and spread to other areas of the body, such as the liver or lungs, the cancer is now metastatic. In this case, the breast cancer is both invasive and metastatic.
Survival rates for breast cancer indicate the percentage of people, on average, that are still alive 5 years after their diagnosis.
According to the American Cancer Society, the 5-year survival rates for breast cancer are determined based on how far the cancer has spread at the time of diagnosis. For instance:
Its important to remember that these numbers are derived from a great number of people diagnosed with breast cancer. While these numbers can be informative, they cannot predict what will happen to you.
Every person is different. While factors like stage and characteristics of the cancer certainly impact outlook, individual factors like age and overall health are also important. Additionally, newer, more effective treatments continue to be developed, which helps improve the prognosis for breast cancer.
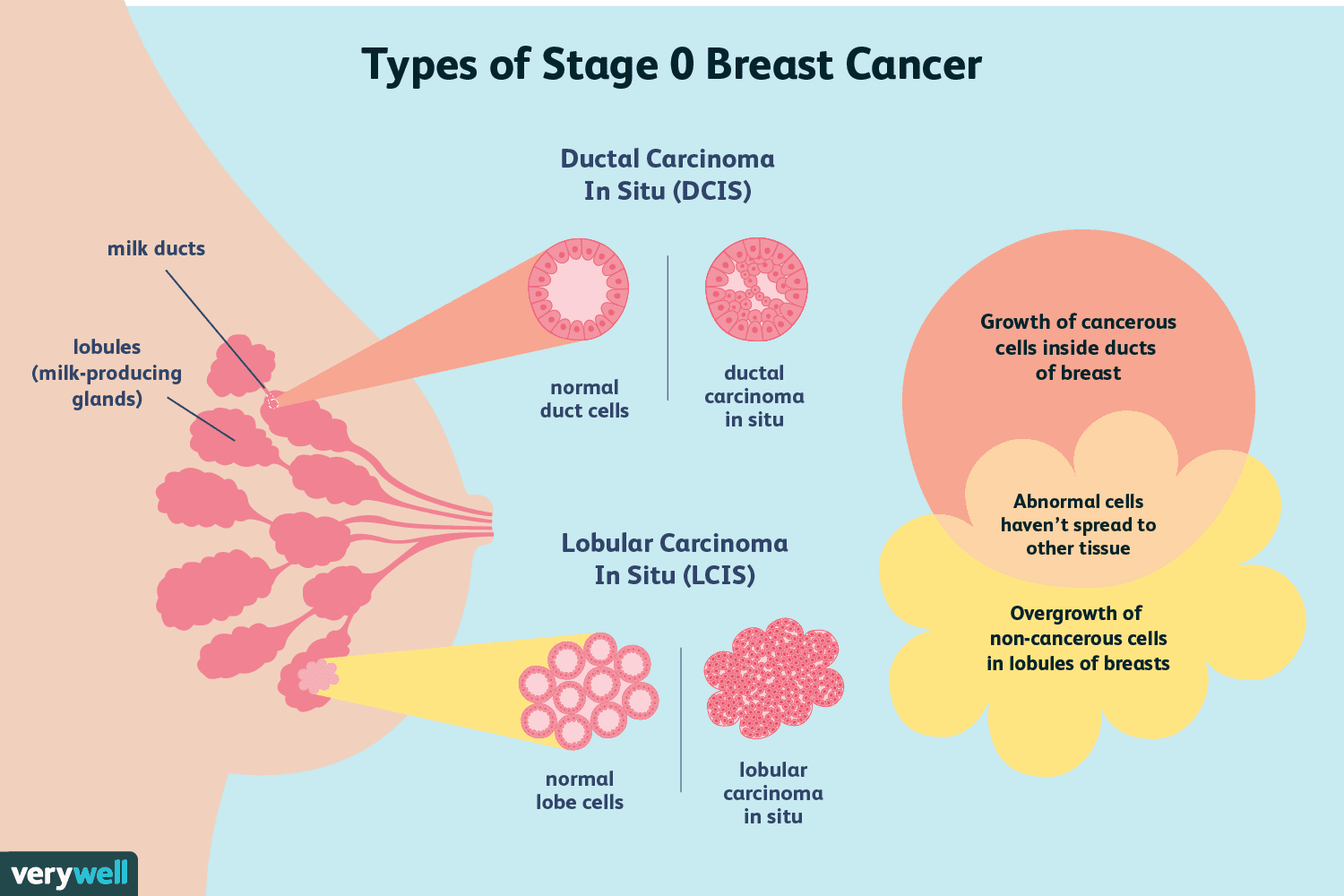
Precancer Or Noninvasive Cancer
There is some debate over whether to consider DCIS precancer or noninvasive cancer. Generally, DCIS is considered noninvasive cancer, while lobular carcinoma is considered a precancerous condition, also called lobular neoplasia.
Learning that your condition is precancerous may make you worry that it will inevitably progress to cancer. This is not always the case, however, precancerous conditions like LCIS should be monitored closely.
Also Check: Stage 3 Breast Cancer Aggressive
What Is Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
According to the American Cancer Society, DCIS is non-invasive orpre-invasive breast cancer, which means the cells that line the ductshave changed to cancer cells but havent spread through the walls ofthe ducts into the nearby breast tissue.
DCIS is considered a pre-cancer because sometimes it can become aninvasive cancer. This means that over time, DCIS may spread out of theducts into nearby tissue, and could metastasize. Currently, theres nogood way to predict which will become invasive cancer and which wont.Therefore, almost all women with DCIS will be treated.
In most cases, a woman with DCIS can choose betweenbreast-conserving surgery and simple mastectomy. In cases wherethe area of DCIS is very large, the breast has several areas of DCIS,or BCS cannot remove the DCIS completely, mastectomy might be a better option.
When Helen Spencer learned she had DCIS,she began a journey of decisions ranging from which hospital tochoose, to the type of surgery, to whether adjuvant hormone therapywould be worth the potential side effects. Readher story.
How Often Does Stage 1 Breast Cancer Come Back After Treatment
If stage 1 cancer is treated comprehensively, it rarely comes back. A new, unrelated breast cancer is more likely to emerge after stage 1 breast cancer is treated than a recurrence. Your healthcare provider will recommend a surveillance schedule for you so that new breast cancer or a recurrence can be identified and treated as quickly as possible.
Read Also: Is Breast Cancer Considered Internal Cancer
What Does It Mean To Have Stage 3 Breast Cancer
Stage 3 cancer means the breast cancer has extended to beyond the immediate region of the tumor and may have invaded nearby lymph nodes and muscles, but has not spread to distant organs. Although this stage is considered to be advanced, there are a growing number of effective treatment options.
This stage is divided into three groups: Stage 3A, Stage 3B, and Stage 3C. The difference is determined by the size of the tumor and whether cancer has spread to the lymph nodes and surrounding tissue.
What Does Triple Negative Mean In Terms Of Breast Cancer
Normal breast cells have receptors that respond to hormones such as estrogen and progesterone, which allows them to grow and regress in response to the hormone level. Hormone receptors may or may not be present in breast cancer. About two-thirds of breast cancers are positive and contain these receptors like normal breast cells do. These are less aggressive cancers that are less likely to need chemo and are often treated with hormone therapy and surgery. Radiation may or may not be needed.
HER2/neu , is a protein molecule that has a role in cell proliferation in normal cells. In some breast cancers, this protein is overly produced or positive. For HER2-positive tumors, there a specific medication that targets this protein.
Triple-negative breast cancers are not positive for estrogen receptors, progesterone receptors or HER2 protein. Since these targets are absent in triple-negative breast cancer, chemotherapy is needed, Sun says. Triple-negative breast cancer is often very sensitive to chemotherapy, which, despite the side effects, is an effective treatment that can save lives. Because this is an aggressive cancer, treatment is aggressive also. But there are several ways we can address it.
Also Check: Can Nipple Piercings Cause Breast Lumps
How Is Dcis Different From Invasive Cancer
Invasive Breast Cancer can threaten your life because it may have the capacity to spread to other organs of the body. DCIS does not yet have this ability to spread, but it might if it evolves into invasive breast cancer in the future. So we treat DCIS very seriously in order to lessen the risk of it developing into an invasive, life-threatening problem. Learn more about Invasive Breast Cancer with our video lesson .
A Vaccine May Be Helpful
Patients diagnosed with DCIS may one day get a vaccine to help reduce their risk of developing an invasive breast cancer in the future, according to a 2016 study published in Clinical Cancer Research.
More clinical trials are underway, but researchers hope that a vaccine may be able to stimulate the immune system and keep early DCIS from progressing beyond the milk duct. If trials are successful, experts say it could eventually be an alternative to surgery and radiation for some patients.
To get our top stories delivered to your inbox, sign up for the Healthy Living newsletter
Recommended Reading: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Symptoms
Removal Of The Whole Breast
You might have a mastectomy if:
- the area of the DCIS is large
- there are several areas of DCIS
- you have small breasts and too much of the breast is affected by DCIS to make breast conserving surgery possible
You may have surgery to your armpit called a sentinel lymph node biopsy if you have a mastectomy. This means having about 1 to 3 lymph nodes removed.
If you want to, you can choose to have a new breast made at the time of the mastectomy, or some time afterwards.
Hormone therapy is recommended for 5 years if you have breast conserving surgery for DCIS and:
- your cancer calls have oestrogen receptors
- you do not have radiotherapy
Research shows that taking hormone therapy after breast conserving surgery for DCIS reduces the risk of it coming back .
Trials show that hormone therapy can reduce the number of further invasive breast cancers or DCIS. But in these trials, the people taking a hormone therapy tablet called tamoxifen did not live any longer than those who didn’t take it.
What Are The Symptoms Of Dcis
DCIS usually has no symptoms. Most cases of DCIS are found during routine breast screening or if a mammogram is done for some other reason.
Occasionally DCIS is found when someone has a breast change such as a lump or discharge from the nipple. However, if someone with DCIS has a breast change its more likely they will also have an invasive breast cancer.
Some people with DCIS also have a type of rash involving the nipple known as Pagets disease of the nipple, although this is rare.
Also Check: Difference Between Stage 3 And 4 Cancer
Contact Us To Learn More About Ig
Have further questions about how to treat Squamous cell carcinoma or Basal cell cancer with IG-SRT technology? Please call us at 312-987-6543 to learn more. The skin cancer information specialists at GentleCure can provide all the details you need to feel confident about making your non-melanoma skin cancer treatment decision. Need help finding a treatment center that offers IG-SRT near you? Our Find a Practice tool makes it quick and easy to find the nearest location to you.
Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer impacts the lives of 4 million Americans each year. GentleCure is committed to raising awareness of IG-SRT and is a trademark owned by SkinCure Oncology, LLC.
The information on this website is provided without any representations or warranties. You should not rely on this website as an alternative to medical advice from your doctor or healthcare provider. The information on this site, as well as any information provided by the skin cancer information specialists on our educational hotline, is intended to help you make a better-informed treatment decision in conjunction with trained and licensed medical professionals.
Dont Miss: How Many Forms Of Skin Cancer Are There
Do I Need Genetic Counseling And Testing
Your doctor may recommend that you see a genetic counselor. Thats someone who talks to you about any history of cancer in your family to find out if you have a higher risk for getting breast cancer. For example, people of Ashkenazi Jewish heritage have a higher risk of inherited genetic changes that may cause breast cancers, including triple-negative breast cancer. The counselor may recommend that you get a genetic test.
If you have a higher risk of getting breast cancer, your doctor may talk about ways to manage your risk. You may also have a higher risk of getting other cancers such as ovarian cancer, and your family may have a higher risk. Thats something you would talk with the genetic counselor about.
Links with this icon indicate that you are leaving the CDC website.
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website’s privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance on other federal or private website.
Also Check: Red Mill Baking Soda Cancer
What Is Stage 1 Breast Cancer
This breast cancer is the earliest stage of invasive breast cancer. In stage 1, the tumor measures up to 2 cm and no lymph nodes are involved. At this stage, the cancer cells have spread beyond the original location and into the surrounding breast tissue.
Because a stage 1 tumor is small, it may be difficult to detect. However, breast self-exams and routine screening are always important and can often lead to early diagnosis, when the cancer is most treatable.Stage 1 breast cancer is divided into two categories:
Stage 1A: The tumor measures 2 cm or smaller and has not spread outside the breast.
Stage 1B: Small clusters of cancer cells measuring no more than 2 mm, are found in the lymph nodes, and either there is no tumor inside the breast, or the tumor is small, measuring 2 cm or less.
At stage 1, TNM designations help describe the extent of the disease. For example, there may or may not be cancer cells in the lymph nodes, and the size of the tumor may range from 1 cm to 2 cm. Most commonly, stage 1 breast cancer is described as:
- T: T1, T2, T3 or T4, depending on the size and/or extent of the primary tumor
- N0: Usually, cancer has not spread to the lymph nodes.
- M0: The disease has not spread to other sites in the body.
Stage 1 breast cancer survival rate
The survival rate for stage 1A breast cancer may be slightly higher than for stage 1B. However, all women with stage 1 breast cancer are considered to have a good prognosis.
In Situ Breast Cancers
Ductal carcinoma in situ
Considered pre-cancer, DCIS is the most common type of non-invasive breast cancer. It starts in a milk duct and is highly treatable. Nearly all women with this early stage of breast cancer can be cured, according to the American Cancer Society. Over time, DCIS may progress to invasive breast cancer.
Lobular carcinoma in situ
Also known as lobular neoplasia, LCIS is not cancer . Instead, cells that look like cancer cells grow in the milk-producing lobules of the breast.
Read Also: Stage 3 C Breast Cancer
What Should A Person With Stage 3 Breast Cancer Expect From Treatment
Stage 3 treatment options vary widely and may consist of mastectomy and radiation for local treatment and hormone therapy or chemotherapy for systemic treatment. Nearly every person with a Stage 3 diagnosis will do best with a combination of two or more treatments.
Chemotherapy is always given first with the goal to shrink the breast cancer to be smaller within the breast and within the lymph nodes that are affected. This is known as neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
Other possible treatments include biologic targeted therapy and immunotherapy. There may be various clinical trial options for interested patients with Stage 3 breast cancer.
Can I Avoid Surgery Completely For Lower Risk Dcis
Again, a lumpectomy followed by radiation for DCIS is felt to be the best way to reduce the risk of breast cancer returning within the breast. If it does recur in the breast, the new growth can be an invasive cancer that will require more surgery and could possibly threaten your life. There are active debates and ongoing clinical trials to see if we can safely identify women with low risk DCIS who can be treated with surgery alone or even no surgery with close follow up. This is a complex topic, but received great media attention in 2015 after a Time Magazine cover article outlined the question, Are we overtreating DCIS and breast cancer? A good medical overview of this dilemma by researcher Dr. Laura Esserman is located . It will take years to better determine how we can identify and treat lower risk DCIS less aggressively with the same good cancer outcomes. At this point in time, observation is not considered a successful treatment option.
This is a detailed outline of treatment options for women with DCIS written specifically for patients. The NCCN is a consortium of organizations and governmental agencies to promote quality breast cancer care.
Their information on DCIS is directed towards up-to-date treatment options. It contains some of the most relevant information about breast cancer. This site is created for patients by the American Society of Breast Surgeons.
Recommended Reading: 3rd Stage Breast Cancer