Why Do Other People In My Family Need This Information
Genetic information is different from most medical information an individual receives, because it is not only relevant to the individual but also to their family members. Genetic information can provide an explanation as to why someone has a particular health problem, but it also can predict future poor health or the risk of having a child affected with a particular genetic problem. If someone is aware that they have an increased risk of developing cancer, they have the chance to make choices about genetic testing, cancer surveillance or risk-reducing surgery. They may also decide to make changes to their lifestyle to help decrease their risk of developing cancer. Knowing about the risk gives your relatives a chance to take action to reduce their risk of getting cancer or help ensure that cancer is detected at an early stage so it may be treated more effectively.
How Do Certain Genes Affect Breast Cancer
Cancer is a health condition that can be caused by changes to your genes. Your genes carry instructions that tell the proteins in your cells how to behave.
When your genes cause proteins and cells to develop in abnormal ways, it can become cancer. This can happen because of a gene mutation.
Its possible to be born with certain gene mutations. This is called an inherited mutation. Somewhere between 5 to 10 percent of breast cancers are currently thought to be hereditary. Your genes may also mutate later in life due to environmental or other factors.
A few specific mutations can play a role in developing breast cancer. Affected genes tend to be ones that control things like cell growth and the DNA in your reproductive organs and breast tissue.
BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes typically make proteins that can repair your DNA when it gets damaged, particularly in your breasts and ovaries. When these genes are mutated, it can cause abnormal cell growth. These cells can then become cancerous.
About
People born with a penis and who have the BRCA2 mutation have an increased risk of developing male breast cancer.
Your risk for having BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations may be higher if you have:
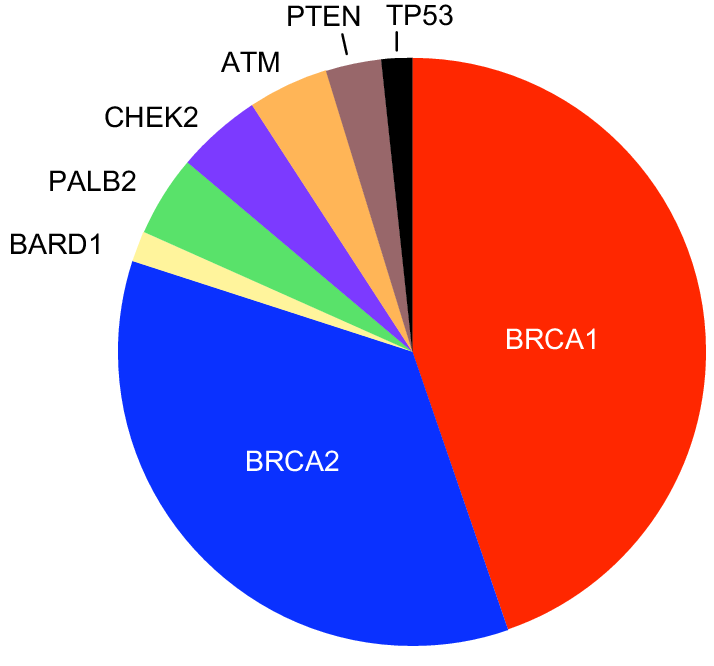
In addition to BRCA and BRCA2, there are other genes that can increase your risk of developing breast cancer if you inherit a mutation.
These genes include:
The Genetics Of Cancer
Cancer is a genetic diseasethat is, cancer is caused by certain changes to genes that control the way our cells function, especially how they grow and divide.
Genes carry the instructions to make proteins, which do much of the work in our cells. Certain gene changes can cause cells to evade normal growth controls and become cancer. For example, some cancer-causing gene changes increase production of a protein that makes cells grow. Others result in the production of a misshapen, and therefore nonfunctional, form of a protein that normally repairs cellular damage.
Genetic changes that promote cancer can be inherited from our parents if the changes are present in germ cells, which are the reproductive cells of the body . Such changes, called germline changes, are found in every cell of the offspring.
Cancer-causing genetic changes can also be acquired during ones lifetime, as the result of errors that occur as cells divide or from exposure to carcinogenic substances that damage DNA, such as certain chemicals in tobacco smoke, and radiation, such as ultraviolet rays from the sun. Genetic changes that occur after conception are called somatic changes.
Sometimes the changes are not in the actual sequence of DNA. For example, the addition or removal of chemical marks, called epigenetic modifications, on DNA can influence whether the gene is expressedthat is, whether and how much messenger RNA is produced.
You May Like: Symptoms Of Breast Cancer In Teenagers
Who Is At Risk Of Having The Faulty Brca Gene In My Family
If you are a BRCA mutation carrier, your close relatives have a 50/50 risk of having the faulty BRCA gene. The faulty gene would have been present in your family for many generations it is not new within your family. It is only that we are now able to identify who actually carries the faulty gene. You would have inherited the BRCA gene from either your mother or your father. This faulty BRCA gene causes the increased risk of developing cancer.
Yourbrothersandsisters:
Your brothers and sisters each have a 50/50 risk of having the faulty BRCA gene. Each person would need to have genetic testing to determine if they have the faulty BRCA gene or not. You cannot predict if someone has the gene on the basis of their brothers or sisters genetic test results or if people look alike in the family.
Yourchildren:
Your children each have a 50/50 risk of having the faulty BRCA gene. We do not offer predictive testing to children because screening or risk-reducing treatment is not generally needed or available for children. Once they are over eighteen, each of your children could choose to have genetic testing to find out if they have inherited the faulty BRCA gene or not.
Yourextendedfamily:
The faulty BRCA gene would either have come down through your mothers or your fathers family. So if you inherited the faulty BRCA gene from your mother, for example, then only your aunts, uncles and cousins on your mothers side of the family are at risk of having the faulty BRCA gene.
What Causes Breast Cancer
We dont know what causes each case of breast cancer. But we do know many of the risk factors for these cancers . For example, lifestyle-related risk factors, such as what you eat and how much you exercise, can increase your chance of developing breast cancer, but its not yet known exactly how some of these risk factors cause normal cells to become cancer. Hormones also seem to play a role in many cases of breast cancer, but just how this happens is not fully understood.
We do know that normal breast cells can become cancer because of changes or mutations in genes. But only about 1 in 10 breast cancers are linked with known abnormal genes that are passed on from parents . Many genes have not yet been discovered, so women with a family history of breast cancer might have inherited an abnormal gene that doesn’t show on a genetic test. Most breast cancers develop from acquired gene changes that have not yet been identified.
Don’t Miss: Breast Cancer Tumor Growth Rate
Causes Of Hereditary Breast Ovarian Cancer Syndrome
Both copies of a tumor suppressor gene must be altered or mutated before a person will develop cancer. In HBOC, the first mutation is inherited from either the mother or father and is therefore present in all cells of the body. This is called a germline mutation.
Whether a person who has a germline mutation will develop cancer and where the cancer will develop depends upon where the second mutation occurs. For example, if the second mutation is in the ovary, then ovarian cancer may develop. If it is in the breast, breast cancer may develop. The process of tumor development actually requires mutations in multiple growth control genes. Loss of both copies of BRCA1 or BRCA2 is just the first step in the process. What causes these additional mutations to be acquired is unknown. Possible causes include chemical, physical, or biological environmental exposures, or chance errors in cell replication.
Some individuals who have inherited a germline BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation never develop cancer because they never get the second mutation necessary to knock out the function of the gene and start the process of tumor formation. This can make the cancer appear to skip generations in a family, when, in reality, the mutation is present. Persons with a mutation, regardless of whether they develop cancer, however, have a 50/50 chance to pass the mutation on to the next generation.
See also: Founder’s Effect
Breast Cancer Genes And Inheritance
Viviana Rivera-Varas
Copyright 1998
Breast cancer is the most common cancer that affects women in the United States. There are at least two majors genes that when they mutate can causebreast cancer. These genes can be passed from parent to child, increasing the risk ofdeveloping cancer in those child that have parent carrying these genes. BRCA1 and BRCA2genes are located on chromosome 17 and chromosome 13 respectively. There is a 90% chance of developing breast cancer for a woman that has these mutated genes. In contrast,men carrying BRCA1 have no risk to develop breast cancer, but those carrying BRCA2 geneshave high risk. It is important to note that mutations in these genes can be passed on tochildren by either parent. A man with a mutation is just as likely to pass this gene to hischildren as a woman with a mutation. Hereditary cancer occurs at young age, for instance awoman in her 20’s with breast cancer is more likely to have hereditary type of cancer that awoman in her 50’s.
BRCA1 and BRCA2 are tumor suppressor genes, these genes also called “Anti-Oncogenes” which normally are involved in regulating cell growth, the proteins inhibit theproliferation of cell, which is crucial for the normal cell development and differentiation. .
The second similarity is that both BRCA1 and BRCA2 bind to Rad5 protein that isinvolved in maintain the integrity of the genome .
Literature Cited
Recommended Reading: Stage Three Breast Cancer
What Your Breast Cancer Genetic Tests Results Mean
Having a positive genetic test result doesnt mean youll get cancer. It means you have a higher risk of getting breast cancer than people without the mutation.
- Women without breast cancer gene mutations have a 12% lifetime risk of breast cancer.
- Women with a BRCA mutation have up to an 80% lifetime risk of breast cancer.
- Women with the PTEN mutation have an 85% lifetime risk.
- Men with the BRCA2 mutation have about an 8% lifetime risk, 80 times greater than males without the mutation.
Even if you get tested and get a negative result, dont skip mammograms or other health screenings, and continue to follow the American Cancer Societys guidelines.
Most cases of breast cancer arent hereditary, says Dr. Eng. A negative result means you dont have the known gene mutations for breast cancer. But you can still get breast cancer.
Can Hboc Be Avoided
There are options available for people with HBOC who are interested in having a child and reducing that childs risk of this hereditary syndrome. Preimplantation genetic diagnosis is a medical procedure done along with in-vitro fertilization . It allows people who carry a specific known genetic mutation to reduce the likelihood that their children will inherit the condition. For PGD, a womans eggs are removed and fertilized in a laboratory. When the embryos reach a certain size, 1 cell is removed and tested for the specific hereditary condition. The parents can then choose to transfer the embryos that do not have the mutation. PGD has been used for over 2 decades for several hereditary cancer syndromes. However, it is a complex procedure with financial, physical, and emotional factors to consider before starting. For more information, talk with an assisted reproduction specialist at a fertility clinic.
Recommended Reading: Chemotherapy Cycles For Breast Cancer
Brca1 And Brca2 Mutations And Treatment Strategies For Breast Cancer
Inês Godet
Department of Oncology, The Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center, The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, USA
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, The Johns Hopkins University, USA
E-mail :
Daniele M. Gilkes
Department of Oncology, The Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center, The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, USA
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, The Johns Hopkins University, USA
DOI: 10.15761/ICST.1000228
What Is Hereditary Breast And Ovarian Cancer
A diagnosis of Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer Syndrome is considered when there are multiple cases of breast cancer and/or ovarian cancer on the same side of the family. The chance that a family has HBOC increases in any of these situations:
-
1 or more women are diagnosed at age 45 or younger
-
1 or more women are diagnosed with breast cancer before age 50 with an additional family history of cancer, such as prostate cancer, melanoma, and pancreatic cancer
-
There are breast and/or ovarian cancers in multiple generations on the same side of the family, such as having both a grandmother and an aunt on the fathers side both diagnosed with these cancers
-
A woman is diagnosed with a second breast cancer in the same or the other breast or has both breast and ovarian cancers
-
A male relative is diagnosed with breast cancer
-
There is a history of breast cancer, ovarian cancer, prostate cancer, and/or pancreatic cancer on the same side of the family
-
Having Ashkenazi Jewish ancestry
Read Also: Will I Survive Breast Cancer
What Do Brca1 And Brca2 Genetic Test Results Mean
BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation testing can give several possible results: a positive result, a negative result, or a variant of uncertain significance result.
Positive result. A positive test result indicates that a person has inherited a known harmful variant in BRCA1 or BRCA2 and has an increased risk of developing certain cancers. However, a positive test result cannot tell whether or when the tested individual will develop cancer. Some people who inherit a harmful BRCA1 or BRCA2 variant never develop cancer.
A positive test result may also have important implications for family members, including future generations.
- Both men and women who inherit a harmful BRCA1 or BRCA2 variant, whether or not they develop cancer themselves, may pass the variant to their children. Each child has a 50% chance of inheriting a parents variant.
- All blood relatives of a person who has inherited a harmful BRCA1 or BRCA2 variant are at some increased risk of having the variant themselves. For example, each of that persons full siblings has a 50% chance of having inherited the variant as well.
- Very rarely, an individual may test positive for a harmful variant not inherited from either parent. This is called a de novo variant. Such a variant is one that arose in a germ cell of one of the parents and is present in all the cells of the person who grew from that cell. The children of someone with a de novo variant are at risk of inheriting the variant.
Breast Cancer And Genetic Testing

At the current time, testing is available for BRCA gene mutations, as well as mutations ATM, CDH1, CHEK2, MRE11A, MSH6, NBN, PALB2, PMS2, PTEN, RAD50, RAD51C, SEC23B, and TP53, with this area expected to expand dramatically in the near future.
Having these tests available, however, raises many questions. For example, who might have hereditary breast cancer and who should be tested? What should you do if you test positive for one of these genes?
Ideally, any testing should be done only with the guidance and help of a genetic counselor. There are two reasons for this.
One is that it can be devastating to learn that you carry a mutation that may increase your risk, and the guidance of someone who is aware of recommended management and screening is invaluable.
As noted earlier, some mutations confer a high risk and others a much lower risk. Some mutations might be of more concern earlier in life , whereas others might not require early screening. A genetic counselor can help you learn about what is currently recommended with regard to screening for your particular mutation while taking into account any other risk factors you might have.
The other reason genetic counseling is so important is that you may have a significant risk of developing breast cancer even if your tests are negative. There is much yet to learn, and a genetic counselor can help you look at your family history to see if you may carry a high risk despite negative testing, and plan screening accordingly.
You May Like: What Is Stage 2 Breast Cancer
How Can I Avoid Upsetting My Relative
Many people are concerned that sharing this information will cause their relative to feel very anxious or guilty and then feel responsible for causing this upset. It is always difficult to share bad news. It might be useful to think of other times that you have had to share bad news, how you did it and what you learned from that experience. The knowledge of a BRCA mutation in a family will explain why there have been cancers in the family and gives your relatives an opportunity to choose to have testing and reduce their risks of cancer. It is important to remember that if someone has this BRCA gene mutation it is nobodys fault we cannot control which genes were passed on to our children. It is also important to remember that if someone has a faulty BRCA gene they have always had it since the moment they were conceived, so what is different now is that we can identify it and give people options to manage their risk.
What Genes Are Linked To Breast Cancer
The term breast cancer genes means genes that, when altered , increase your risk of getting breast cancer. These gene mutations shut down some of your natural cancer-fighting genes. When you dont have your full army of genes fending off cancer, your risk of certain cancers goes up.
BRCA1 and BRCA2 are the most common breast cancer genes when mutated, followed closely by PTEN mutations, says Dr. Eng. But several other breast cancer gene mutations exist. We know of at least 14 different genes right now, and we are currently exploring several others, too.
These gene mutations arent limited to breast cancer risk. Some of these gene mutations may also increase the risk of:
Don’t Miss: Prognosis For Stage 3 Breast Cancer