Stage 3 Breast Cancer
- Stage 3A:
- The cancer has spread to 49 axillary lymph nodes or has enlarged the internal mammary lymph nodes, and the primary tumor can be any size.
- Tumors are greater than 5 cm, and the cancer has spread to 13 axillary lymph nodes or any breastbone nodes.
Consider A Second Opinion
You might feel the urge to start treatment right away. But usually, people with early-stage breast cancer have a little time to take everything in. In fact, you might not be sure about your diagnosis or care plan. Itâs OK to ask another doctor what they think before you make any decisions.
Get a referral to a breast cancer specialist. They might agree with your first doctor. But sometimes they can give you other options to think about. Check with your health insurance provider to make sure the visit is covered. Ask your doctor to send over all the medical records the new doctor will need.
A breast cancer diagnosis can change your life. Itâll also affect those around you. But there are ways you and your loved ones can prepare for whatâs ahead.
Show Sources
Breast Exam By Your Doctor
The same guidelines for self-exams provided above are true for breast exams done by your doctor or other healthcare professional. They wont hurt you, and your doctor may do a breast exam during your annual visit.
If youre having symptoms that concern you, its a good idea to have your doctor do a breast exam. During the exam, your doctor will check both of your breasts for abnormal spots or signs of breast cancer.
Your doctor may also check other parts of your body to see if the symptoms youre having could be related to another condition.
Recommended Reading: Stage 3 Invasive Breast Cancer
What Is Stage 1 Breast Cancer
This breast cancer is the earliest stage of invasive breast cancer. In stage 1, the tumor measures up to 2 cm and no lymph nodes are involved. At this stage, the cancer cells have spread beyond the original location and into the surrounding breast tissue.
Because a stage 1 tumor is small, it may be difficult to detect. However, breast self-exams and routine screening are always important and can often lead to early diagnosis, when the cancer is most treatable.Stage 1 breast cancer is divided into two categories:
Stage 1A: The tumor measures 2 cm or smaller and has not spread outside the breast.
Stage 1B: Small clusters of cancer cells measuring no more than 2 mm, are found in the lymph nodes, and either there is no tumor inside the breast, or the tumor is small, measuring 2 cm or less.
At stage 1, TNM designations help describe the extent of the disease. For example, there may or may not be cancer cells in the lymph nodes, and the size of the tumor may range from 1 cm to 2 cm. Most commonly, stage 1 breast cancer is described as:
- T: T1, T2, T3 or T4, depending on the size and/or extent of the primary tumor
- N0: Usually, cancer has not spread to the lymph nodes.
- M0: The disease has not spread to other sites in the body.
Stage 1 breast cancer survival rate
The survival rate for stage 1A breast cancer may be slightly higher than for stage 1B. However, all women with stage 1 breast cancer are considered to have a good prognosis.
What Is A Primary Tumor

The primary tumor refers to the original breast tumor. So, any metastases are either secondary tumors, or simply metastatic breast cancer.
Note, when breast cancer spreads to the bones, it is not bone cancer, it is metastatic breast cancer in the bones.
Metastatic describes a breast cancer that has already spread to distant areas and organs of the body. Metastatic cancer is the most advanced stage of breast cancer. Furthermore, the most common sites for breast cancer to metastasize to are the:-
- bones
- liver
- lungs.
Once breast cancer is at this most advanced metastatic stage, the odds of completely curing the breast cancer are quite low. .
The treatment of metastatic breast cancer, after a reasonable effort, will often focus on the quality of life and relieving symptoms rather than a cure.
Recommended Reading: Baking Soda And Honey Cancer
Also Check: Breast Cancer Medications After Surgery
When To Consider Joining A Clinical Trial
If youre newly diagnosed with early or locally advanced breast cancer, consider joining a clinical trial before starting treatment. For most people, treatment doesnt usually start right after diagnosis. So, theres time to look for a clinical trial that youre eligible for and fits your needs.
Once youve begun standard treatment for early or locally advanced breast cancer, it can be hard to join a clinical trial.
Learn more about clinical trials.
Whats Next After An Early
A cancer diagnosis affects everyone differently. It may take a little time to adjust to the news. You might deny your illness at first. Or you could feel strong sadness, anger, or worry. But a sense of hope might come over you, too, once you accept the diagnosis. All these feelings are normal.
You may also wonder what comes next. Hereâs what you need to know.
Don’t Miss: 3 Cm Tumor In Breast
Metastatic Breast Cancer Symptoms And Diagnosis
The symptoms of metastatic breast cancer can vary greatly depending on the location of the cancer. This section covers the symptoms of breast cancer that has spread to the bone, lung, brain, and liver, and the tests used to diagnose metastatic breast cancer.
Bone Metastasis: Symptoms and DiagnosisThe most common symptom of breast cancer that has spread to the bone is a sudden, noticeable new pain. Breast cancer can spread to any bone, but most often spreads to the ribs, spine, pelvis, or the long bones in the arms and legs. Learn more.
Lung Metastasis: Symptoms and DiagnosisWhen breast cancer moves into the lung, it often doesnt cause symptoms. If a lung metastasis does cause symptoms, they may include pain or discomfort in the lung, shortness of breath, persistent cough, and others. Learn more.
Brain Metastasis: Symptoms and DiagnosisSymptoms of breast cancer that has spread to the brain can include headache, changes in speech or vision, memory problems, and others. Learn more.
Liver Metastasis: Symptoms and DiagnosisWhen breast cancer spreads to the liver, it often doesnt cause symptoms. If a liver metastasis does cause symptoms, they can include pain or discomfort in the mid-section, fatigue and weakness, weight loss or poor appetite, fever, and others. Learn more.
Does Breast Cancer Affect Women Of All Races Equally
All women, especially as they age, are at some risk for developing breast cancer. The risks for breast cancer in general arent evenly spread among ethnic groups, and the risk varies among ethnic groups for different types of breast cancer. Breast cancer mortality rates in the United States have declined by 40% since 1989, but disparities persist and are widening between non-Hispanic Black women and non-Hispanic white women.
Statistics show that, overall, non-Hispanic white women have a slightly higher chance of developing breast cancer than women of any other race/ethnicity. The incidence rate for non-Hispanic Black women is almost as high.
Non-Hispanic Black women in the U.S. have a 39% higher risk of dying from breast cancer at any age. They are twice as likely to get triple-negative breast cancer as white women. This type of cancer is especially aggressive and difficult to treat. However, it’s really among women with hormone positive disease where Black women have worse clinical outcomes despite comparable systemic therapy. Non-Hispanic Black women are less likely to receive standard treatments. Additionally, there is increasing data on discontinuation of adjuvant hormonal therapy by those who are poor and underinsured.
In women under the age of 45, breast cancer is found more often in non-Hispanic Black women than in non-Hispanic white women.
Read Also: Type 3 Breast Cancer
Soothe Skin And Nails
Cancer treatment can make your skin dry, itchy, or red. Radiation therapy can also make you more sensitive to the sun. Ask your cancer care team what products to use. Theyâll know which over-the-counter choices are mild and gentle. Here are some other things they might suggest:
- Use a fragrance-free moisturizer and soap
- Avoid tight clothes and underwire bras
- Keep skin clean to prevent infection
- Wear sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher on your body and lips
You might notice some nail changes. They could crack or turn yellow. Your cuticles may swell and hurt. To help, you can:
- Cut your nails short
What Is Breast Cancer
Cancer occurs when changes called mutations take place in genes that regulate cell growth. The mutations let the cells divide and multiply in an uncontrolled way.
Breast cancer is cancer that develops in breast cells. Typically, the cancer forms in either the lobules or the ducts of the breast.
Lobules are the glands that produce milk, and ducts are the pathways that bring the milk from the glands to the nipple. Cancer can also occur in the fatty tissue or the fibrous connective tissue within your breast.
The uncontrolled cancer cells often invade other healthy breast tissue and can travel to the lymph nodes under the arms. The lymph nodes are a primary pathway that help the cancer cells move to other parts of the body.
You May Like: Tubular Breast Cancer Symptoms
Don’t Miss: What Organs Are Affected By Breast Cancer
The Breast Cancer Stages: From 0 To 4
The stage of your cancer will appear on your pathology report, a report that details the size, shape and look of the cancer cells under a microscope. . Most cancers, including invasive breast cancer, have four stages.
Stage 0 is abnormal cells that have not spread beyond the ducts or lobules of the breast, such as DCIS or LCIS, respectively.
Stage I cancer is invasive and spreading beyond where it started.
In Stage IA, the cancer is 2 cm or smaller and has not spread into the lymph nodes or outside of the breast.
In Stage IB, small clumps of cancer cells ranging from 0.2 to 2 mm exist in the lymph nodes. There may not be a tumor in the breast, but if there is, it measures no bigger than 2 cm.
Stage II cancer also has two subcategories. Stage IIA describes a cancer that has spread to 1 to 3 lymph nodes under your arms with or without a tumor up to 2 cm large in the breast, or the breast tumor measures 2 to 5 cm without cancer cells in the axillary lymph nodes.
Stage IIB refers to a tumor between 2 and 5 cm along with cancer in 1 to 3 axillary lymph nodes or lymph nodes near the breastbone, or the tumor is larger than 5 cm when no cancer cells exist in the axillary lymph nodes.
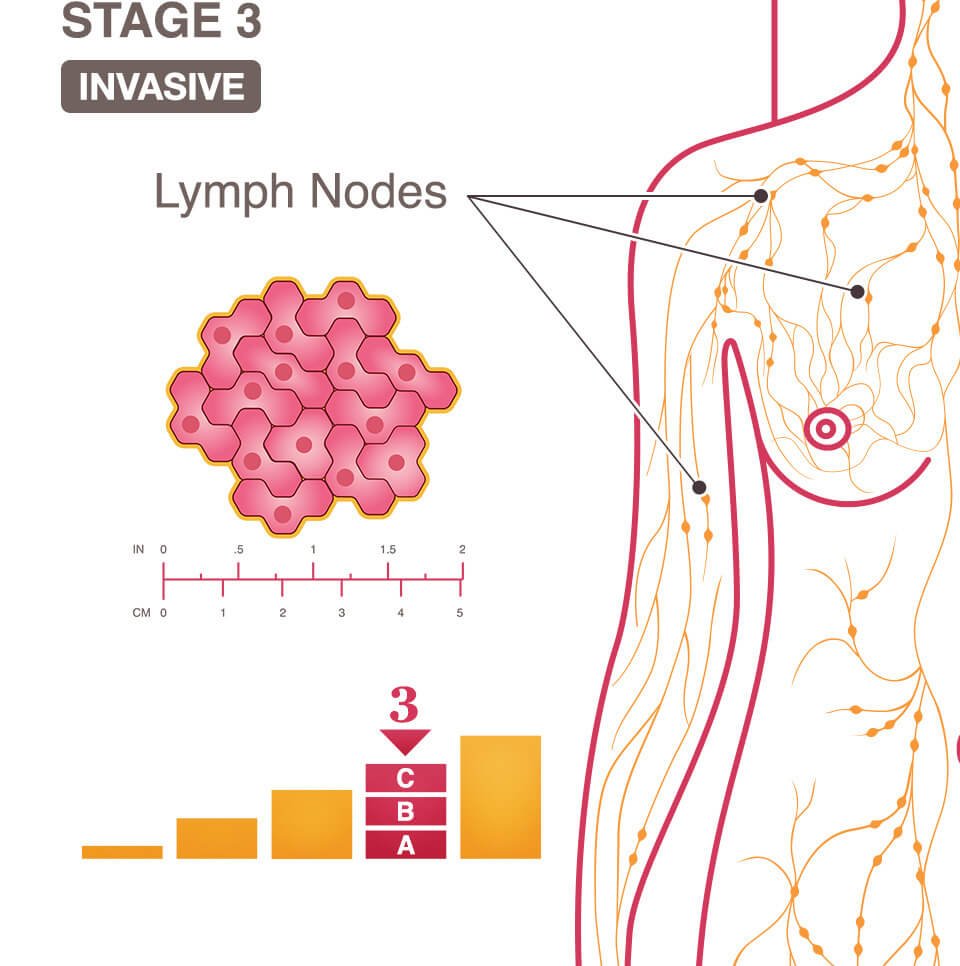
In Stage IIIB, the tumor has reached the skin of your breast and/or your chest wall and up to 9 lymph nodes under your arms or near your breastbone.
Inflammatory breast cancer is automatically Stage IIIB or a later stage.
Stage IIIC involves three behaviors of the cancer:
Using Knowledge To Guide Your Choices
Understanding these stages of early breast cancer can help you make better decisions for yourself. Although the treatment recommended to you will depend on the stage of your early breast cancer, you do have choices. Dont hesitate to have an open and honest discussion with your oncologist about your preferences and goals for treatment, and how those dovetail with the treatment options available to you.
Also Check: Stage 3a Breast Cancer Prognosis
What Should A Person With Stage 0 Or Stage 1 Breast Cancer Expect Regarding Treatment
Even though Stage 0 breast cancer is considered non-invasive, it does require treatment, typically surgery or radiation, or a combination of the two. Chemotherapy is usually not part of the treatment regimen for earlier stages of cancer.
Stage 1 is highly treatable, however, it does require treatment, typically surgery and often radiation, or a combination of the two. Additionally, you may consider hormone therapy, depending on the type of cancer cells found and your additional risk factors. Like stage 0, Chemotherapy is often not necessary for earlier stages of cancer.
Material on this page courtesy of National Cancer Institute
Types Of Stage 1 And 2 Breast Cancer
The most common types of invasive breast cancers are named after the area of the breast where they begin. Types of early breast cancers include:
- Invasive ductal carcinoma IDC means that the cancer originated in the milk ducts of the breast, and has spread into the surrounding breast tissue. IDC is the most common type of breast cancer, accounting for 80% of all breast cancers.
- Invasive lobular carcinoma ILC means that the cancer originated in the milk-producing lobules of the breast, and has spread into the surrounding breast tissue. ILC is the second most common type of breast cancer, and accounts for 10% of breast cancers.
- There are also other less common forms of invasive breast cancer, such as inflammatory breast cancer and Pagets disease of the nipple. For more information on the various types of invasive breast cancer, including the less common forms, please visit Types of Breast Cancer page.
Don’t Miss: 2cm Breast Cancer
Starting With Neoadjuvant Therapy
Most often, these cancers are treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy . For HER2-positive tumors, the targeted drug trastuzumab is given as well, sometimes along with pertuzumab . This may shrink the tumor enough for a woman to have breast-conserving surgery . If the tumor doesnt shrink enough, a mastectomy is done. Nearby lymph nodes will also need to be checked. A sentinel lymph node biopsy is often not an option for stage III cancers, so an axillary lymph node dissection is usually done.
Often, radiation therapy is needed after surgery. If breast reconstruction is done, it is usually delayed until after radiation is complete. In some cases, additional chemo is given after surgery as well.
After surgery, some women with HER2-positive cancers will be treated with trastuzumab for up to a year. Many women with HER2-positive cancers will be treated first with trastuzumab followed by surgery and then more trastuzumab for up to a year. If after neoadjuvant therapy, any residual cancer is found at the time of surgery, trastuzumab may be changed to a different drug, called ado-trastuzumab emtansine, which is given every 3 weeks for 14 doses. For people with hormone receptor-positive cancer in the lymph nodes who have completed a year of trastuzumab, the doctor might also recommend additional treatment with an oral drug called neratinib for a year.
You May Like: Breast Cancer Receptor Testing
What Does It Mean To Have Stage 2 Breast Cancer
Stage 2 means the breast cancer is growing, but it is still contained in the breast or growth has only extended to the nearby lymph nodes.
This stage is divided into groups: Stage 2A and Stage 2B. The difference is determined by the size of the tumor and whether the breast cancer has spread to the lymph nodes.
For Stage 2 breast cancer, chemotherapy is usually done first, followed by surgery and radiation therapy.
Dont Miss: Malignant Neoplasm Of Breast Definition
Also Check: What Organs Does Breast Cancer Affect
The Number Staging System
Breast cancer can also be divided into four number stages. We have put these into a table to make them easier to understand. You can .
This information is about stage 1 to 3 breast cancer.
Stage 1 breast cancer is when the cancer is 2cm or smaller. There may be no cancer cells in the lymph nodes in the armpit or tiny numbers of cancer cells are found. Sometimes the cancer cannot be found in the breast, but cancer cells have spread to lymph nodes in the armpit.
Stage 2 breast cancer is when the cancer is up to or bigger than 5cm. It may or may not have spread to the lymph nodes under the arm. Sometimes the cancer cannot be found in the breast. But cancer cells have spread to 1 to 3 lymph nodes in the armpit or near the breast bone.
Stage 3 breast cancer is sometimes called locally advanced breast cancer. The cancer has spread to the lymph nodes in the armpit and sometimes to other lymph nodes nearby. It may have spread to the skin of the breast or to the chest muscle. The skin may be red, swollen or have broken down. Sometimes the cancer cannot be found in the breast or is small but has spread to 4 to 9 lymph nodes in the armpit.
Stage 4 breast cancer is also called secondary or metastatic breast cancer. This is when the cancer has spread to other parts of the body, such as the bones, the liver or lungs. We have separate information about secondary breast cancer.
N Categories For Breast Cancer
N followed by a number from 0 to 3 indicates whether the cancer has spread to lymph nodes near the breast and, if so, how many lymph nodes are involved.
Lymph node staging for breast cancer is based on how the nodes look under the microscope, and has changed as technology has gotten better. Newer methods have made it possible to find smaller and smaller groups of cancer cells, but experts havent been sure how much these tiny deposits of cancer cells influence outlook.
Its not yet clear how much cancer in the lymph node is needed to see a change in outlook or treatment. This is still being studied, but for now, a deposit of cancer cells must contain at least 200 cells or be at least 0.2 mm across for it to change the N stage. An area of cancer spread that is smaller than 0.2 mm doesnt change the stage, but is recorded with abbreviations that indicate the type of special test used to find the spread.
If the area of cancer spread is at least 0.2 mm , but still not larger than 2 mm, it is called a micrometastasis . Micrometastases are counted only if there arent any larger areas of cancer spread. Areas of cancer spread larger than 2 mm are known to influence outlook and do change the N stage. These larger areas are sometimes called macrometastases, but are more often just called metastases.
NX: Nearby lymph nodes cannot be assessed .
N0: Cancer has not spread to nearby lymph nodes.
N1c: Both N1a and N1b apply.
N3: Any of the following:
N3a: either:
N3b: either:
Also Check: How Long Is Breast Cancer Treatment