What Are The Stages Of Breast Cancer
In India, one woman gets diagnosed with breast cancer every 4 minutes, and one woman dies of breast cancer every 13 minutes,making it the most prevalent cancer in the country. With such glaring statistics, the question that arises is how we can prevent or rather minimize incidences or occurrences of breast cancer among women.
For mostly all types of cancer, doctors need to know how much and where cancer has spread in the body to determine the best treatment options. For instance, the best treatment for early-stage cancer may be either surgery or radiation, while a more advanced stage of the disease may need another kind of treatment that can be effective for multiple body parts as well such as chemotherapy, targeted drug therapy, or immunotherapy as well.
Sometimes, early-stage cancer may create more health complications in the body as compared to advanced-stage cancer. However, it is very important to know the stage of cancer in the body to move forward with the treatment.
Managing Your Mental Health
When you learn you have stage 0 breast cancer, you have some big decisions to make. Its important to talk with your doctor about your diagnosis in depth. Ask for clarification if you dont quite understand the diagnosis or your treatment options. You can also take the time to get a second opinion.
Theres a lot to think about. If youre feeling anxious, stressed, or experiencing difficulty coping with the diagnosis and treatment, talk with your doctor. They can refer you to support services in your area.
Here are some other things to consider:
- Reach out to friends and family for support.
Stage 0 breast cancer can be very slow growing and may never progress to invasive cancer. It can be successfully treated.
According to the American Cancer Society, women whove had DCIS are approximately to develop invasive breast cancer than women whove never had DCIS.
In 2015, an observational study looked at more than 100,000 women who had been diagnosed with stage 0 breast cancer. The researchers estimated the 10-year breast cancer-specific negative outlook at 1.1 percent and the 20-year negative outlook at 3.3 percent.
For all these reasons, your doctor may recommend screening more frequently than if you never had DCIS.
After Dcis The Risk Of Another Cancer Is Higher
Stage 0 breast cancer still comes with risks. “When you have DCIS, it means your risk of developing another DCIS or an invasive breast cancer is higher than the general population,” says Dr. Meyers. Studies show that people with DCIS have a 1% to 2% chance of developing invasive breast cancer after a mastectomy and a slightly higher chance after a lumpectomy.
“Whatever caused the cells to mutate will generally occur in more than one ductand sometimes, those mutated cells can break through a duct and become invasive breast cancer,” adds Dr. Meyers. “We don’t know why some DCIS have the ability to do this while others don’t, so right now we want to treat all of them with at least surgery, and maybe more.”
You May Like: Tamoxifen Metastatic Breast Cancer
Pearls And Other Issues
Breast cancer patients are advised to be followed up for life to detect early recurrence and spread. Yearly or biannual follow-up mammography is recommended for the treated and the other breast. The patient must be informed that they must visit a breast clinic if they have any suspicious manifestations. Currently, there is no role for repeated measurements of tumor markers or doing follow-up imaging other than mammography.
What Is Stage Iii Breast Cancer
In stage III breast cancer, the cancer has spread further into the breast or the tumor is a larger size than earlier stages. It is divided into three subcategories.
Stage IIIA is based on one of the following:
- With or without a tumor in the breast, cancer is found in four to nine nearby lymph nodes.
- A breast tumor is larger than 50 millimeters, and the cancer has spread to between one and three nearby lymph nodes.
In stage IIIB, a tumor has spread to the chest wall behind the breast. In addition, these factors contribute to assigning this stage:
- Cancer may also have spread to the skin, causing swelling or inflammation.
- It may have broken through the skin, causing an ulcerated area or wound.
- It may have spread to as many as nine underarm lymph nodes or to nodes near the breastbone.
In stage IIIC, there may be a tumor of any size in the breast, or no tumor present at all. But either way, the cancer has spread to one of the following places:
- ten or more underarm lymph nodes
- lymph nodes near the collarbone
- some underarm lymph nodes and lymph nodes near the breastbone
- the skin
Read Also: Breast Cancer Life Expectancy Without Treatment
Should You Watch And Wait
Some experts believe âwatchful waitingâ is another valid option. About one third of the women with DCIS will likely get invasive cancer. Your doctor might suggest that you skip immediate treatment and keep a close eye on your condition instead.
Itâs controversial. If you have surgery right away, you might protect yourself from ever getting invasive cancer. On the other hand, you could end up going through painful procedures for no good reason.
But if you skip surgery and radiation at first and choose to get more frequent screening tests, there’s a chance you’ll end up with cancer that’s more advanced by the time doctors find it. It’s a choice only you and your doctor can make.
Show Sources
American Cancer Society: âBreast Cancer Survival Rates, by Stage,â “How is Breast Cancer Classified?” âHow is Breast Cancer Staged?â âUnderstanding Your Pathology Report,â “Breast Cancer.”
NIH National Cancer Institute: âNCI Dictionary of Cancer Terms,â âPaget Disease of the Breast.â
National Breast Cancer Foundation: âStages 0 and 1.â
Mayo Clinic: âDuctal Carcinoma In Situ .â
National Comprehensive Cancer Network: âNCCN Guidelines for Patients: Breast Cancer Carcinoma in Situ.â
UT Southwestern Medical Center: âPersonalized Treatment is Key for Stage 0 Breast Cancer.â
Prescrire International, December 2013.
A Vaccine May Be Helpful
Patients diagnosed with DCIS may one day get a vaccine to help reduce their risk of developing an invasive breast cancer in the future, according to a 2016 study published in Clinical Cancer Research.
More clinical trials are underway, but researchers hope that a vaccine may be able to stimulate the immune system and keep early DCIS from progressing beyond the milk duct. If trials are successful, experts say it could eventually be an alternative to surgery and radiation for some patients.
To get our top stories delivered to your inbox, sign up for the Healthy Living newsletter
Read Also: Estrogen Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer
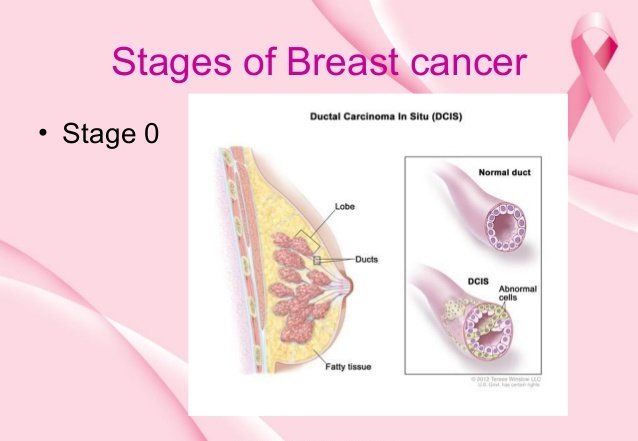
What Is Stage 0 Breast Cancer
Also called carcinoma in situ, stage 0 is the earliest breast cancer stage. At stage 0, the breast mass is noninvasive, and there is no indication that the tumor cells have spread to other parts of the breast or other parts of the body. Often, stage 0 is considered a precancerous condition that typically requires close observation, but not treatment.
Stage 0 breast cancer is difficult to detect. There may not be a lump that can be felt during a self-examination, and there may be no other symptoms. However, breast self-exams and routine screening are always important and can often lead to early diagnosis of breast cancer, when the cancer is most treatable. Stage 0 disease is most often found by accident during a breast biopsy for another reason, such as to investigate an unrelated breast lump.
There are two types of stage 0 breast cancer:
Ductal carcinoma in situ occurs when breast cancer cells develop in the breast ducts. Today, stage 0 DCIS is being diagnosed more often because more women are having routine mammogram screenings. DCIS can become invasive, so early treatment can be important.
Early Diagnosis And Treatment Are Key
Although DCIS is not an invasive cancer, early diagnosis and treatment can be life changing.
Cynthia Whiteman, who is in her 60s, explains, “When I first was diagnosed with DCIS, I was shocked. I didn’t realize there was a stage 0 cancer.” An Indiana resident, Jan had her routine mammogram in Indiana when her provider recommended a biopsy. Shortly afterward, she learned she had DCIS. “At that point I thought I would seek out the best treatment in the area.” This led her to drive to Chicago and consult with providers at Northwestern Medicine Prentice Women’s Hospital about her options.
This medication could offer women with DCIS another option for treatment.
Treatment for DCIS will differ based on the patient and care plan. However, it can include surgery, radiation or hormone therapy. If it is not found and treated, DCIS can spread outside of its place in the breast milk duct and into surrounding tissue to become invasive breast cancer. “Early detection is so important. I tell everyone to get their annual mammogram. By doing so, I feel like I dodged a bullet,” states Jan.
Recommended Reading: What Is Stage 3a Breast Cancer
Dcis Has The Same Risk Factors As Invasive Breast Cancers
“The same things that increase a woman’s risk for DCIS are really the same things that increase her risk of invasive breast cancer,” says Dr. Meyers. For example, having a strong family history can be a factorespecially if a woman tests positive for a high-risk BRCA gene mutation.
Women who have a longer period of estrogen stimulation, meaning they started menstruation early and/or entered menopause late, also have an increased risk of DCIS as well as invasive cancer. That also goes for women who don’t have children, or who have their first pregnancy after age 30.
What Therapies Should You Initiate Immediately Ie Emergently
Therapy for DCIS and LCIS is not needed emergently. There is always time for appropriate work-up and evaluation to characterize the lesion and ascertain which treatments will be most appropriate. Consultations can be obtained with radiation oncology, plastic surgery, and surgical oncology services so that the patient fully understands her options and their benefits and risks.
Recommended Reading: Prognosis Of Stage 3 Breast Cancer
Stage 1b Breast Cancer Means One Of The Following Descriptions Applies:
Lymph nodes have cancer evidence with small clusters of cells between the approximate size of a pinprick to the approximate width of a grain of rice .
AND EITHER No actual tumor is found in the breast.
OR The tumor is smaller than the approximate size of a peanut .
Similar to stage 0, breast cancer at this stage is very treatable and survivable. When breast cancer is detected early, and is in the localized stage , the 5-year relative survival rate is 100%.
Personalized Treatment Is Key For Stage 0 Breast Cancer

An early form of breast cancer called ductal carcinoma in situ has stirred controversy in the medical community nationwide.
DCIS, also known as Stage 0 breast cancer, is abnormal cells that are confined to the milk ducts of the breast. The debate is whether all cases of DCIS should be treated immediately with surgery and additional therapy, or if patients should be monitored instead and treated only if the cancer spreads.
A New York Times article from August 2015 has fanned the flames of this controversy. The article features DCIS patients reacting with a mix of gratitude and outrage about their cancer treatment. Some felt their treatment was unnecessary or too severe others were glad they received proactive care.
Both sides of the debate have a viable argument: of course we dont want to perform surgeries that arent needed or expose women to radiation or hormonal therapy unnecessarily, and DCIS in some women will never spread beyond the milk ducts.
But this is our concern: DCIS has a significant chance of turning into invasive cancer. There is currently no way to know which cases will become invasive. Until we have a way to determine that, we cant just sit back and watch women develop breast cancer. We favor a personalized, case-by-case approach to treating Stage 0 breast cancer over watching and waiting.
Ive asked four of our breast cancer experts to explain our position and clear up some misconceptions about the treatment of DCIS.
Also Check: Recurring Breast Cancer Symptoms
The Tnm System For Staging Breast Cancer
The AJCCs addition of the letters T, N, and M for anatomic breast cancer staging adds more information to a breast cancer diagnosis. Heres what they mean:
- T : The tumor grade shows a higher number for a larger size or density.
- N : Nodes refers to lymph nodes and uses the numerals 0 to 3 to give information about how many lymph nodes are involved in the cancer.
- M : This refers to how the cancer has spread beyond the breast and lymph nodes.
The AJCC also added clarifications in staging for ER, PR, and HER2 expression and also genetic information.
Ultimately, this means someone diagnosed with stage 3 breast cancer can receive more information from their breast cancer staging than ever before.
No matter the stage, the best source of information about your individual outlook is your own oncology team.
Make sure you understand your breast cancer stage and subtype so that you can better understand treatment options and individual outlook.
Getting the right treatment and the support you need can help you navigate the challenges of being diagnosed with stage 3 breast cancer.
Read Also: Can You Get Breast Cancer At 20
How A Breast Cancers Stage Is Determined
Your pathology report will include information that is used to calculate the stage of the breast cancer that is, whether it is limited to one area in the breast, or it has spread to healthy tissues inside the breast or to other parts of the body. Your doctor will begin to determine this during surgery to remove the cancer and look at one or more of the underarm lymph nodes, which is where breast cancer tends to travel first. He or she also may order additional blood tests or imaging tests if there is reason to believe the cancer might have spread beyond the breast.
The breast cancer staging system, called the TNM system, is overseen by the American Joint Committee on Cancer . The AJCC is a group of cancer experts who oversee how cancer is classified and communicated. This is to ensure that all doctors and treatment facilities are describing cancer in a uniform way so that the treatment results of all people can be compared and understood.
In the past, stage number was calculated based on just three clinical characteristics, T, N, and M:
- the size of the cancer tumor and whether or not it has grown into nearby tissue
- whether cancer is in the lymph nodes
- whether the cancer has spread to other parts of the body beyond the breast
Numbers or letters after T, N, and M give more details about each characteristic. Higher numbers mean the cancer is more advanced. Jump to more detailed information about the TNM system.
Jump to a specific breast cancer stage to learn more:
Recommended Reading: Signs Of Breast Cancer Recurrence After Mastectomy
Waiting And Watching With Stage 0 Breast Cancer Put To Nationwide Test
Barbara Nickles and Ligia Toro de Stefani are both women in their early 60s who were diagnosed with abnormal cells in a breast, or Stage 0 breast cancer, as its sometimes labeled. Nickles decided to have a double mastectomy. Toro de Stefani opted for active surveillance and a twice-yearly battery of tests.
I wish I had breasts, but I am also happy they are gone so that I dont have to worry so much about breast cancer, says Nickles, whose grandmother had the disease.
Quality of life is the most important thing to me, says Toro de Stefani, an avid traveler and scuba diver.
The two illustrate the vexing questions facing the 60,000 women a year diagnosed in this country with ductal carcinoma in situ , a condition in which cancerous-looking cells are found in the breast duct. What exactly is it a pre-cancer, cancer or more a risk factor? How much treatment is too much? Too little? Which women can safely skip surgery? What about those who want more treatment than their doctors recommend?
But a growing group of oncologists, worried about overtreatment, is stepping up efforts to add another approach active surveillance to the anti-DCIS arsenal. Proponents are launching COMET, the nations first prospective, randomized clinical trial to test whether such close monitoring is safe and effective for many women.
If the answer is yes, backers say, it could spare thousands the pain, trauma and cost of intrusive therapies.
Cancer Staging After 2018
After 2018, breast cancer staging was updated to include information about hormone receptor status. This additional information allows doctors to customize treatments more precisely for specific types of breast cancer.
Post-2018 Staging includes TNM status but also adds in
Tumor Grade How much the cells look like cancer
- Grade 1 Cells look Mostly normal and are slow-growing
- Grade 2 Middle of the road with about half cancer and half regular
- Grade 3 Cells look most abnormal and are faster growing
Hormone Receptor Status Each one can be positive or negative
- ER Estrogen receptor
- PR Progesterone Receptor
- HER2 Status HER2 is a protein on the outside of all breast cells. If a tumor is HER2 positive, it will grow faster
Recommended Reading: Neoplasm Breast Cancer
What Laboratory And Imaging Studies Should You Order To Characterize This Patient’s Tumor How Should You Interpret The Results And Use Them To Establish Prognosis And Plan Initial Therapy
Ductal carcinoma in situ
The diagnosis of DCIS is usually made on core needle biopsy of a mammographic abnormality. Suspicious findings on mammogram are typically evaluated further with spot compression and magnified mammogram views of the abnormality to better characterize the lesion and to assess the extent of the lesion.
The most common mammographic abnormality is the finding of fine microcalcifications which are clustered and pleomorphic in shape The calcifications are sometimes oriented in a linear array representing the course of the ductal system. Less common mammographic findings include spiculated densities. A careful physical exam should be done to confirm there are no breast abnormalities or regional adenopathy.
Figure 1.
Fine pleomorphic microcalcifications left breast with DCIS on excision. Compression magnification mammographic view.
Figure 3.
Pleomorphic numerous calcifications suspicious for ductal carcinoma in situ.
For patients presenting nipple discharge, a ductogram can be performed to identify the area of tumor which can be seen as a filling defect in the duct or a cut off of filling of the duct with contrast, or a narrowing of the duct . The medical history should include a detailed family history of cancer as well as hormonal risk factors.
Figure 4.
Ductogram showing filling of papillary DCIS.
Lobular carcinoma in situ
Staging
Table I. TNM staging of breast cancer.