Diagnosing Invasive Lobular Breast Cancer
In many women the cancer is found during breast screening.
Its important that you see your GP if you have any symptoms. They may refer you to a specialist breast clinic. At the breast clinic the doctor or specialist nurse takes your medical history and examines your breasts. They also feel for any swollen lymph nodes under your arms and at the base of your neck.
You have some of the following tests:
- a mammogram
- an ultrasound
- a biopsy a small sample of cells or tissue is taken from your breast and looked at under a microscope
- a breast MRI scan this scan uses magnetic fields to create images of the breast tissue
Triple Negative Breast Cancer
With this type of breast cancer, the breast cancer cells dont have ER+ or PR+ receptors. They dont overproduce the HER2 protein, so hormone therapy isnt very effective.
Instead, triple negative stage 4 breast cancer is usually treated with chemotherapy. Radiation therapy may also be an option, depending on the site of metastasis.
Great Lakes Breast Cancer Consortium
Lobular breast cancer is the second most common type of breast cancer from a histological perspective, but it only represents about 10 to 15 percent of breast cancer cases. Because of its rareness, oncologists have tended to view it and treat it in the same way as the more common ductal breast cancer.
But as more research is performed on lobular cancers, investigators are starting to recognize that it has some distinct features apart from ductal cancer, especially with respect to how it metastasizes and its decreased sensitivity to chemotherapy.
With this in mind, scientists from Cleveland Clinic, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center and Ohio State University have created a lobular breast cancer registry that will include cases from 1990 to the present. The present study is one of the first from this newly created registry.
You May Like: What Organs Does Breast Cancer Affect
Survival Outcomes Between Ilc And Idc Group
Due to significant differences in clinical characteristics between ILC and IDC groups, our research used the propensity score matching method, based on age, histological grade, tumor stage, nodal stage, ER status, PR status, surgery type, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy, to reduce discrepancies in survival outcomes between the two groups. Each ILC patient was matched to one IDC patient. As shown in Table 3, both ILC and IDC groups comprised 29,199 patients with similar baseline clinicopathological characteristics for further analysis.
Table 3 Comparison of clinical characteristics between invasive lobular carcinoma and invasive ductal carcinoma groups after matching.
The median OS was not reached in either group. During follow up, 2,999 patients in the ILC group died and 3,057 patients in the IDC group died. Based on comparison of the unmatched population database, IDC patients exhibited better OS compared to ILC patients. Figure 1 presents the Kaplan-Meier plots of overall survival in patients with ILC compared to those with IDC in the matched population. The median follow-up time for overall survival was 54 months in the ILC cohort and 57 months in the IDC cohort. Shown in Figure 1, ILC and IDC patients have similar OS .
Figure 1 Kaplan-Meier survival curves of all matched patients.
Invasive Pleomorphic Lobular Breast Carcinoma
Invasive lobular breast carcinoma represents somewhere between 5 and 10% of all breast cancer tumors, and lobular carcinomas generally have a much better prognosis than ductal carcinomas. Invasive pleomorphic lobular breast carcinoma is considered a distinctive subtype of invasive lobular carcinomas, accounting for under 0.7% of all breast cancers, and less than 5% of lobular breast carcinomas. Pleomorphic lobular breast carcinoma,however, is highly aggressive, and usually presents as a grade II to III tumor. Pleomorphic lobular carcinoma of the breast seems to develop most often in postmenopausal women, with an average age of about 59.
As compared to lobular invasive carcinoma of a general type, invasive pleomorphic lobular breast carcinoma tends to present with a higher histological grade, a greater degree or vascular invasion, and more multifocality. The rate of metastasis is moderate at about 12%, and the mortality rate due to invasive pleomorphic lobular carcinoma of the breast might be estimated at around 6%. That is significantly higher than for invasive lobular breast carcinoma, which is considered a fairly mild form of breast cancer.
Recommended Reading: Breast Cancer Growth Rate
How Can I Prevent Lobular Breast Cancer
Its impossible to eliminate all risks for developing ILC, but some lifestyle changes can help reduce your overall risk of developing breast cancer. These include:
- If you feel you need to take hormonal therapy for menopause or postmenopausal symptoms, use the lowest dose for the shortest amount of time possible.
- Drink no more than one glass of alcohol per day .
- Exercise for 30 minutes most days.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
If you have any risk factors for developing lobular breast cancer, more frequent screening and follow-up can help detect it in its early stages.
When Do Women Start To Bleed After Menopause
Women are considered in menopause if they have not had a menstrual cycle for at least a year. With life expectancy of women increasing to up to age 80, women may spend more than one-third of their life beyond menopause. RETURN OF BLEEDING IS THIS NORMAL? During menopausal years, women may experience a return of vaginal bleeding.
Also Check: 2cm Breast Cancer
What Is The Difference Between Invasive Lobular Carcinoma And Lobular Carcinoma In Situ
LCIS means the cancer is still contained in the milk glands and has not invaded any other area. ILC is cancer that began growing in the lobules and is invading the surrounding tissue. Cancer staging done by a physician, along with a physical exam and medical history can help identify the best treatment options.
Over 80% of the time, invasive lobular breast cancer is ER+ and HER2-. Sometimes invasive lobular breast cancer can be larger than it appears to be when reviewing a mammogram because of the way it grows. It can be commonly identified as a higher stage cancer.
Invasive lobular carcinoma is known for being a slow growing tumor, usually grade I or II. Slow growing, grade I tumors dont usually respond well to chemotherapy, so hormonal therapy is key for this type of cancer.
If it spreads to other organs, becoming Stage IV breast cancer, it typically goes to the colon, uterus, ovary, stomach, lung, bone, and other areas.
Who Does Invasive Lobular Carcinoma Affect
Women who are 55 or over are most likely to develop invasive lobular carcinoma. Men can develop ILC, too, though its rare. Transwomen have a higher risk of developing breast cancer than cisgender men. Conversely, transmen have a lower risk compared to cisgender women.
Unlike invasive ductal carcinoma , invasive lobular carcinoma usually occurs later in life. Many people are in their early 60s at the time of their diagnosis.
Also Check: Breast Cancer Nodes
Breast Cancer Survival Rates Are Affected By Tumor Grade
Breast cancer grade refers to the size and shape of the malignant breast cancer cells. If the breast cancer cells look very different than normal breast tissue cells, and somewhat random in appearance, they are called poorly differentiated and described as high grade.
There are three main breast cancer grades and these are as follows:-
- Grade 1: The cancer cells are well differentiated and look the most like normal cells. These type of cancers tend to be slow-growing.
- Grade 2: These cancer cells are moderately differentiated. This means that the cells look less like normal cells and tend to grow faster.
- Grade 3: Poorly differentiated cells do not appear like normal cells at all and tend to be very fast growing. Hence, the affect on prognosis.
Microscopic Images of Ductal cell carcinoma in Situ Grades 1, 2 and 3
Higher grade breast cancers tend to have a poorer prognosis.
You will be able to find the Grade of your tumor on your pathology report.
Refining The Histopathology Of Ilc
Fig. 3
Multistep model of evolution of tumours with morphological features indicative of mixed ductal and lobular carcinomas. a Co-existing lesions with both ductal and lobular morphology are frequently clonally related, suggesting shared origins of a common neoplastic clone. Early divergence leads to the co-occurrence of LCIS and DCIS, and in such cases LCIS and associated ILC are likely to be negative for E-cadherin. Tumour cells exhibiting a lobular pattern of growth can also emerge from the ductal pathway, and in such cases E-cadherin might be positive or aberrantly expressed. Modified from McCart Reed et al. . Immunohistochemical staining for E-cadherin in different tumours: b ×10 magnification showing co-existing E-cadherin-positive DCIS and E-cadherin-negative LCIS c showing strong membrane E-cadherin positivity in tumour cell nests and aberrant E-cadherin staining in adjacent single cells. DCIS, ductal carcinoma in situ LCIS, lobular carcinoma in situ IDC, invasive ductal carcinoma ILC, invasive lobular carcinoma – E-cad, E-cadherin loss -/+ E-cad, variable expression
Read Also: Stage 3 Invasive Breast Cancer
Comparison Of Overall Survival Between Invasive Lobular Breast Carcinoma And Invasive Ductal Breast Carcinoma: A Propensity Score Matching Study Based On Seer Database
- 1Department of Breast Cancer, Cancer Center, Guangdong Provincial Peoples Hospital, Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences, Guangzhou, China
- 2Department of Breast and Thyroid Surgery, The Eighth Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Shenzhen, China
Objective: Invasive lobular carcinoma and invasive ductal carcinoma account for most breast cancers. However, the overall survival differences between ILC and IDC remain controversial. This study aimed to compare nonmetastatic ILC to IDC in terms of survival and prognostic factors for ILC.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study used data from the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results Cancer Database . Women diagnosed with nonmetastatic ILC and IDC between 2006 and 2016 were included. A propensity score matching method was used in our analysis to reduce baseline differences in clinicopathological characteristics and survival outcomes. Kaplan-Meier curves and log-rank test were used for survival analysis.
Our results demonstrated that ILC and IDC patients had similar OS after PSM. However, ILC patients with high risk indicators had worse OS compared to IDC patients by subgroup analysis.
The Genomic Landscape Of Ilc And Its Morphological Variants
Recent large, landmark studies have built on previous foundational molecular studies in ILC to comprehensively define the pattern of somatic mutations and structural alterations present in primary ILC . Despite increasing numbers of samples profiled across a number of high impact studies including from TCGA and RATHER cohorts, the frequency of CDH1 mutations in ILC is variably reported . It is interesting to note that in studies examining LCIS, in which microdissection was employed to enrich for neoplastic cells, the frequency of CDH1 mutation is 8194%, suggesting that some of this variability may be related to the sensitivity of sequencing platforms used when analysing a tumour type with a diffuse growth pattern and hence samples of potentially low tumour cellularity.
Also Check: Stage 4 Breast Cancer Life Expectancy Without Treatment
What Should A Person With Stage 3 Breast Cancer Expect From Treatment
Stage 3 treatment options vary widely and may consist of mastectomy and radiation for local treatment and hormone therapy or chemotherapy for systemic treatment. Nearly every person with a Stage 3 diagnosis will do best with a combination of two or more treatments.
Chemotherapy is always given first with the goal to shrink the breast cancer to be smaller within the breast and within the lymph nodes that are affected. This is known as neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
Other possible treatments include biologic targeted therapy and immunotherapy. There may be various clinical trial options for interested patients with Stage 3 breast cancer.
Inoperable Breast Cancer Is Often Still Treatable
Stage 3C breast cancer is divided into operable and inoperable stage 3C breast cancer. However, the term inoperable is not the same as untreatable.
If your physician uses the word inoperable, it may simply mean that a simple surgery at this time would not be enough to get rid of all the breast cancer that is within the breast and the tissue around the breast. There must be healthy tissue at all of the margins of the breast when it is removed. Keep in mind that the breast tissue goes beyond the breast mound it goes up to the clavicle and down to a few inches below the breast mound. There must also be tissue to close the chest wound after the surgery is performed.
Another treatment method may be used first to shrink the breast cancer as much as possible before surgery is considered.
Read Also: What Happens If Breast Cancer Is Not Treated
Hormone Receptor Status Influences Breast Cancer Survival Rates
The hormone receptor status of a breast tumour is not usually included in formal discussions of prognosis.
Each breast tumour will potentially have a different hormone receptor status. When a breast cancer tumour tests positive for the hormones estrogen and progesterone, it implies two things:-
Therefore, due to improvements in treatments, overall survival rates will be higher for hormone receptor positive breast tumors than for those that are hormone negative.
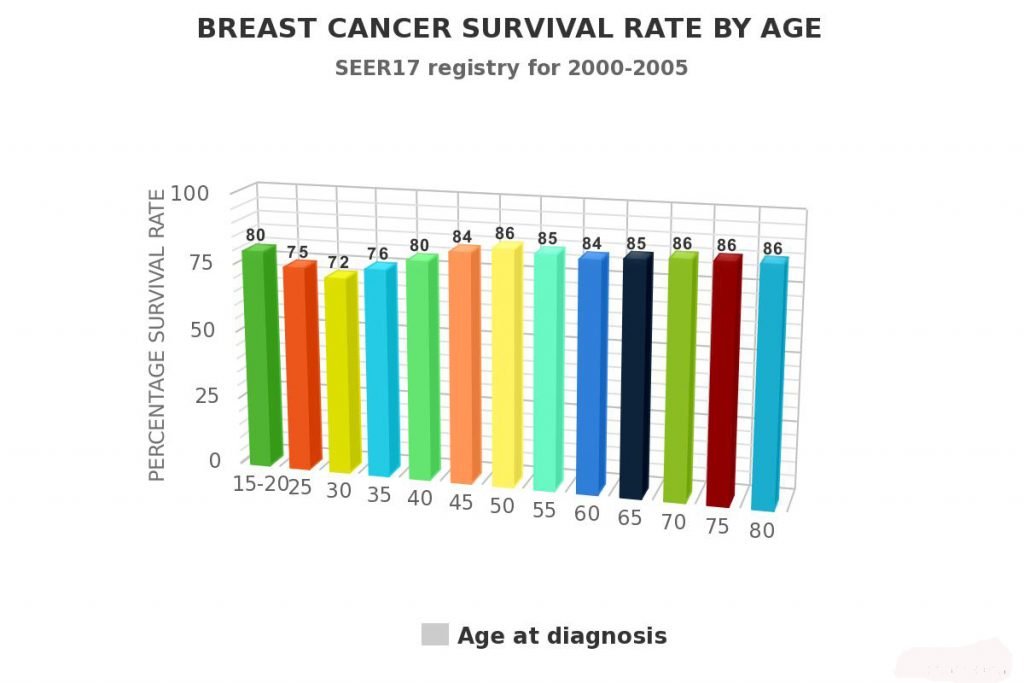
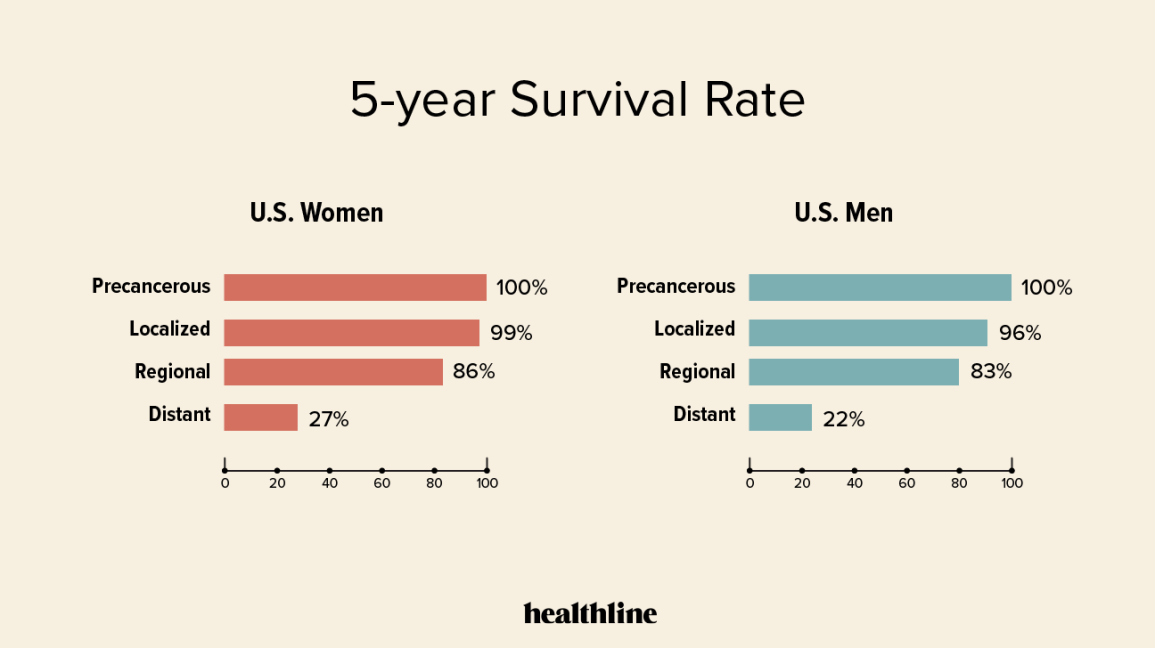
What Are The Prognosis And Survival Rates Of Invasive Lobular Cancer
As with most cancers, breast cancer is divided into stages. The more advanced and aggressive the symptoms of cancer the higher the level. The earlier that breast cancer is detected, and treatment started, the better the chances of a complete recovery.
The survival rates for patients with Invasive Lobular Breast Cancer are relatively high. Statistics show that following treatment about 78% of patients live at least another five years which is the baseline calculation for cancer survival. Around 50% of patients had a 30-year survival rate.
You May Like: Estrace Breast Cancer
How Is Invasive Lobular Breast Cancer Diagnosed
At times it is found when searching for lumps and bumps when doing a breast self examination a large percentage of Invasive Breast Cancer diagnosis is made when women have their annual mammogram. Sometimes, if the symptoms are identified by a primary care physician, the patient will be referred to a specialist such as Dr. Gorman.
The first thing Dr. Gorman will do is take down your medical history and then perform a physical examination. Part of this examination may also include checking your lymph nodes, both under your arms and at the base of your neck. This helps to identify if there is cancer present and if it has spread outside of the lobules.
Dr. Gorman has many years of clinical experience in this field, and so after the examination, she will normally conduct some other tests. The type of test chosen will normally depend on your age, but some of the tests used include:
An Ultrasound This test tends to be the preferred choice for any woman under the age of 35A Breast X-Ray, which is more commonly referred to as a Mammogram.A Biopsy In this test, a small sample of cells or tissue is taken from the concerning area. The cells or tissue is then sent off to the laboratory for closer examination under the microscope.An MRI Scan of the breast This provides a more advanced view of the breast than a standard Mammogram.
A New Synthetic Lethal Weapon
The protein E-cadherin is responsible for holding cells together in the right place, acting like a cellular Velcro. Changes in the E-cadherin gene are one of the most frequent alterations in human cancer, with 13% of breast cancers and 90% of lobular breast cancers containing E-cadherin mutations. Despite how common alterations in this protein are, there are currently no treatments that specifically target this weakness in breast tumours, because little was understood about how this defect affects the tumour. Professor Lord wanted to find out more about cells with E-cadherin defects, and see if he could find a synthetic lethal gene partner that could form the basis of an efficient new treatment.
His team therefore tested 80 drugs in the lab to see if any of them led to the death of E-cadherin deficient breast cancer cells and they were successful. They found that a drug blocking the protein ROS1 a type of cell surface receptor – killed these cells. The team confirmed these results in mouse models of lobular breast cancer, and also found that the drug could kill tumour cells that had become resistant to anti-hormone therapy.
Creating brand new drugs can take a long time, but luckily drugs that block ROS1 already exist crizotinib is a drug currently used to treat advanced lung cancers, and could be a potential new treatment for lobular breast cancers that have an E-cadherin mutation.
Read Also: Signs Of Breast Cancer Returning
Ultrasound Images Often Show Intracystic Elements
Sonograms of pleomorphic breast carcinoma tend to present as either low echo tumors with distinct circumscription or tumors well-distributed internal echoes. Ultrasound often reveals intracystic features within the tumor as well.
Magnetic resonance imaging is sometimes used in the diagnosis of pleomorphic breast carcinoma, and will tend to show showed a homogeneous hyperintense cystic mass on T2-weighted images, and contrast-enhanced MRI might show contrast enhancement in irregular portions of the tumor walls.
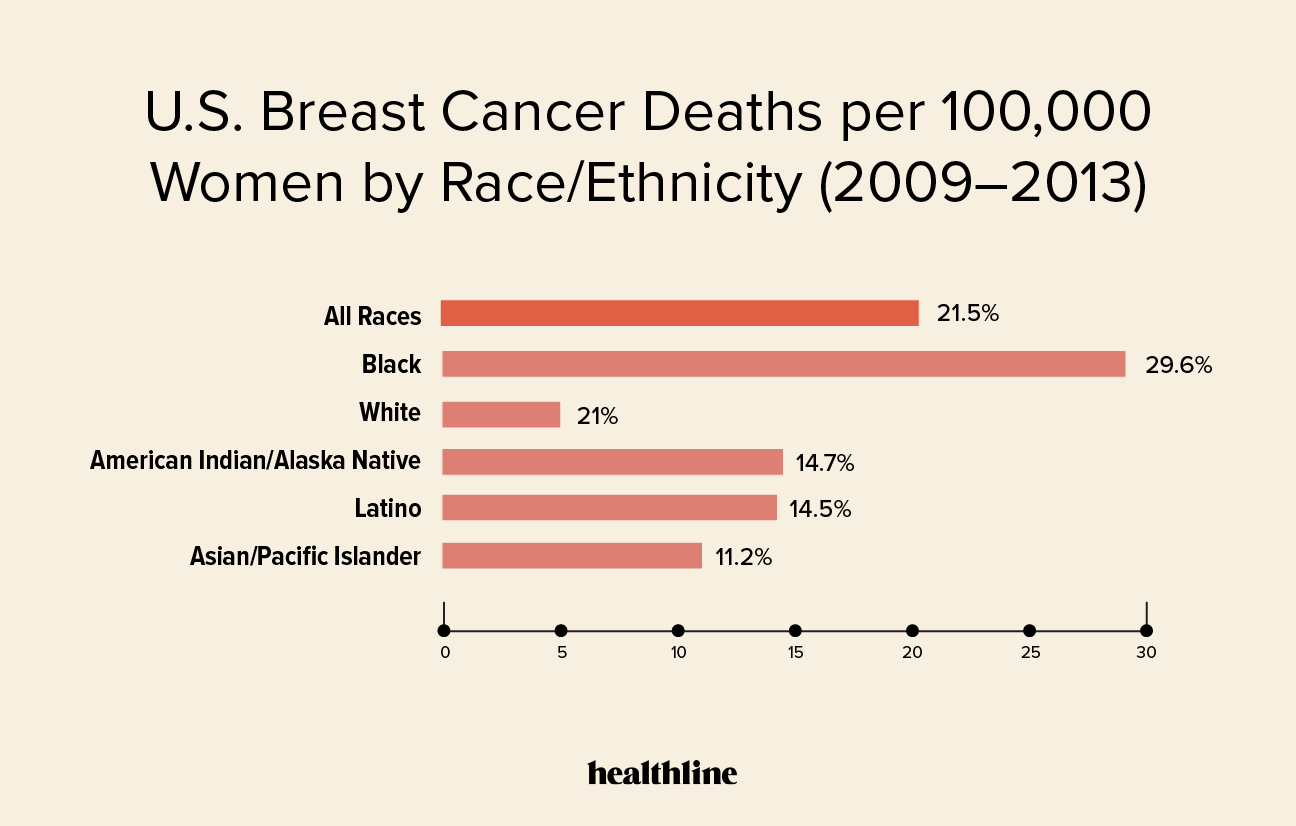
Examples Of Rates Versus Numbers
Say, town A has a population of 100,000 and town B has a population of 1,000. Over a year, say there are 100 breast cancer deaths in town A and 100 breast cancer deaths in town B.
The number of breast cancer deaths in each town is the same. However, many more people live in town A than live in town B. So, the mortality rates are quite different.
In town A, there were 10 breast cancer deaths among 100,000 people. This means the mortality rate was less than 1 percent .
In town B, the mortality rate was 10 percent .
Although the number of deaths was the same in town A and town B, the mortality rate was much higher in town B than in town A .
Lets look at another example. In 2021, its estimated among women there will be :
- 100 breast cancer deaths in Washington, D.C.
- 720 breast cancer deaths in Alabama
- 4,730 breast cancer deaths in California
Of the 3, California has the highest number of breast cancers. However, that doesnt mean it has the highest breast cancer rate. These numbers dont take into account the number of women who live in each state. Fewer women live in Alabama and Washington, D.C. than live in California.
Other factors may vary by state as well, such as the age and race/ethnicity of women. So, to compare breast cancer mortality rates, we need to look at mortality rates.
In 2021, the estimated mortality rates are :
- 26 per 100,000 women in Washington, D.C.
- 22 per 100,000 women in Alabama 22
- 19 per 100,000 women in California 20
You May Like: Stage 3 Invasive Ductal Carcinoma