What Is Fat Necrosis
Fat necrosis is a condition in which painless, round, firm lumps caused by damaged and disintegrating fatty tissues form in the breast tissue. Fat necrosis often occurs in women with very large breasts or who have had a bruise or blow to the breast. This condition may also be the result of a lumpectomy and radiation from a prior cancerous lump. In some cases, healthcare providers will watch the lump through several menstrual cycles. He or she may want to do a mammogram before deciding whether to remove it. These lumps are not cancerous and they do not increase your risk of cancer.
How Much Do Anastrozole And Exemestane Lower The Risk Of Breast Cancer
Studies have shown that both anastrozole and exemestane can lower the risk of breast cancer in postmenopausal women who are at increased risk of the disease.
In one large study, taking anastrozole for five years lowered the risk of developing estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer by 53 percent. In another study, taking exemestane for three years lowered the risk of developing estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer by 65 percent.
The most common side effects seen with anastrazole and exemestane are joint pains, decreased bone density, and symptoms of menopause .
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 12/31/2018.
References
Appearance Of Cancer Cells
The appearance, or differentiation, of the cancer cells is another factor in cancer staging. Doctors grade cancer cells according to how similar they appear to noncancerous cells under a microscope.
Healthcare professionals classify cancer cells that are close to resembling healthy cells as being low grade or well differentiated. These cancers typically grow more slowly.
High grade, or poorly differentiated, cancer cells appear very different from normal cells and tend to grow faster.
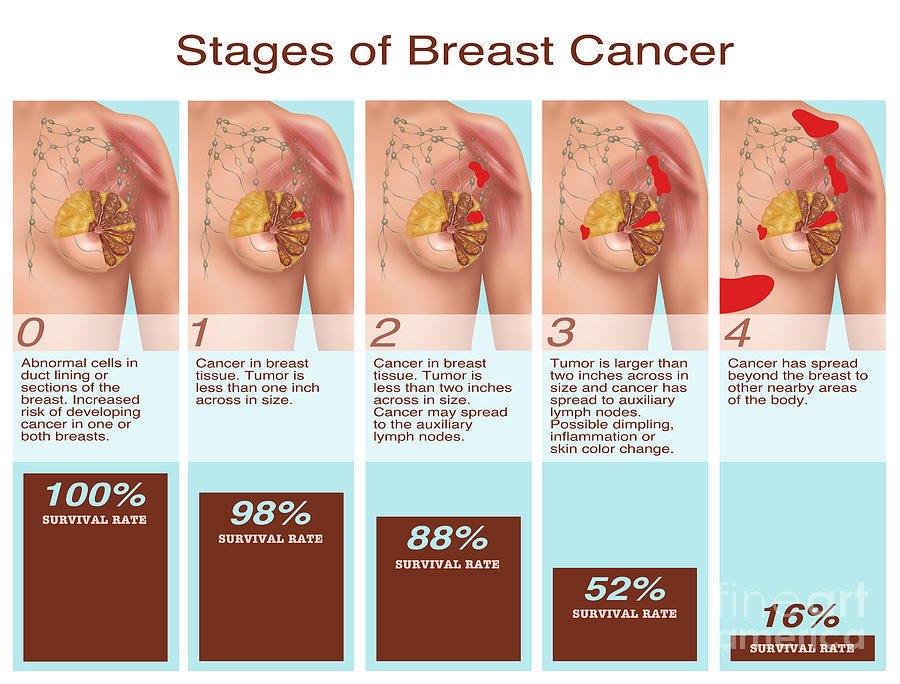
After assessing the different characteristics of the breast cancer, doctors use the information to determine its overall stage from 04.
Here is an overview of each breast cancer stage :
- Stage 0: This cancer is noninvasive and is only present inside the milk duct. This stage includes ductal carcinoma in situ.
- Stage 1: These are small tumors that either have not spread to the lymph nodes or have only affected a small area of the sentinel lymph node.
- Stage 2: These are larger tumors that have spread to some nearby lymph nodes.
- Stage 3: These tumors are large or growing into surrounding tissues, such as breast skin, muscle, and lymph nodes.
- Stage 4: These are tumors that started in the breast but have spread to other parts of the body.
When recommending treatment options for breast cancer, a doctor will take into account:
Treatment options can include:
Early detection and diagnosis of breast cancer can significantly improve a persons outlook.
- lymph node involvement
Don’t Miss: Cancer In Both Breasts Survival Rate
Where Breast Cancer Starts
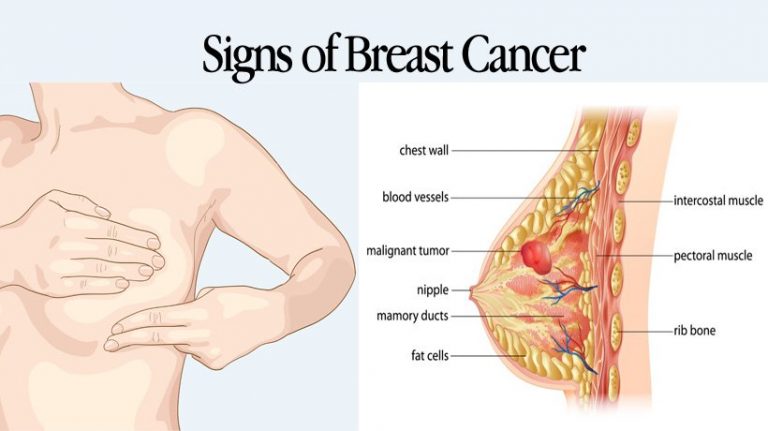
Breast cancers can start from different parts of the breast. The breast is an organ that sits on top of the upper ribs and chest muscles. There is a left and right breast and each one has mainly glands, ducts, and fatty tissue. In women, the breast makes and delivers milk to feed newborns and infants. The amount of fatty tissue in the breast determines the size of each breast.
The breast has different parts:
- Lobules are the glands that make breast milk. Cancers that start here are called lobular cancers.
- Ducts are small canals that come out from the lobules and carry the milk to the nipple. This is the most common place for breast cancer to start. Cancers that start here are called ductal cancers.
- The nipple is the opening in the skin of the breast where the ducts come together and turn into larger ducts so the milk can leave the breast. The nipple is surrounded by slightly darker thicker skin called the areola. A less common type of breast cancer called Paget disease of the breast can start in the nipple.
- The fat and connective tissue surround the ducts and lobules and help keep them in place. A less common type of breast cancer called phyllodes tumor can start in the stroma.
- Blood vessels and lymph vessels are also found in each breast. Angiosarcoma is a less common type of breast cancer that can start in the lining of these vessels. The lymph system is described below.
To learn more, see Types of Breast Cancer.
What Questions Should I Ask My Doctor
If you have benign breast disease, you may want to ask your healthcare provider:
- What is the best treatment for me?
- Am I at risk for more breast lumps?
- How frequently should I get a mammogram or other cancer screening?
- How can I lower my risk of breast cancer?
- Should I use a different birth control method?
- Can I use hormone replacement therapy?
- Should I look out for signs of complications?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Its hard not to panic when you discover a breast lump. Fortunately, most lumps arent cancerous. Your healthcare provider can order the appropriate tests to determine whats causing benign breast disease. Most people dont need treatment lumps go away on their own. If you have a benign condition that increases your chances of developing breast cancer later on, talk to your provider about preventive measures and screenings.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 06/22/2020.
References
Don’t Miss: Breast Cancer Stage 1 Grade 3
Diagnosing And Treating Breast Cancer At Ctca
Finding a breast lump can be scary. That’s why, when confirming whether a lump is cancer, many women choose to seek out a breast cancer expert who can provide answers with the sense of urgency and commitment to accuracy they deserve.
Many patients come to CTCA for a breast cancer diagnosisand for second opinionsbecause of our expert, comprehensive cancer care. We only treat cancer at CTCA, and our Breast Cancer Centers recognize the value in dedicating a multidisciplinary team of experts to a specific cancer type, especially one as complex as breast cancer.
At the Breast Cancer Centers at each of our CTCA hospitals, located across the nation, our cancer experts are devoted to a single missiontreating breast cancer patients with compassion and precision. Each patients care team is led by a medical oncologist and coordinated by a registered oncology nurse, who helps track the various appointments, follow up on tests and answer questions that come up along the way. Your care team also may include a breast surgeon, radiation oncologist, radiologist, pathologist and a plastic and reconstructive surgeon with advanced training in helping patients restore function and appearance. Fertility preservation and genetic testing are also available for qualifying patients who need them.
No matter where you decide to go to assess your breast lump, while researching your options, look for a facility and a care team with the expertise you need and the credentials you trust.
Expert
What Do Breast Cancer Lumps Feel Like
Lumps in the breasts can be a serious concern, and people who perform regular self-exams often wonder exactly what breast cancer lumps feel like and how to tell them apart from non-cancerous, or benign, lumps. Breast cancer lumps are usually very hard and are often irregularly shaped. In the early stages, they may be about the same size as a pea, and can feel dimpled, much like the surface of a golf ball. Often, a cancerous lump cannot be moved around in the breast, and pressing on the area doesn’t usually cause discomfort.
Another potential indicator that a lump is a cancerous is when the skin becomes dimpled or puckered right above it. If the lump is in the nipple, the nipple could become inverted any lump accompanied by pink or bloody discharge may also be a cause for concern. Bruises on the breasts that appear suddenly can be a symptom of breast cancer, as well. Cancerous lumps may be found both near the surface of the breast and deeper inside, closer to the chest wall. They may also occur in the armpit area.
Read Also: Malignant Neoplasm Of Breast Meaning
Myth : A Breast Lump Is Probably Cancer
Most breast lumps women feel — 8 out of 10 — aren’t cancer. It’s more common for them to be a cyst or a fibroadenoma . Some lumps come and go during a woman’s menstrual cycle.
You can’t tell what it is by how it feels.
“It’s always important to know your own body and detect a change which may need to be evaluated,” says Beth Overmoyer, director of the Inflammatory Breast Cancer Program at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston. “If it is cancer, then you may have saved your life.”
How Long Does It Take For Breast Cancer To Grow My Doctor Just Examined My Breasts A Month Ago And Today I Found A Lump Is It Possible That Breast Cancer Could Have Developed So Quickly
Answer from the expert staff of breast cancer research at the Robert W. Franz Cancer Research Center at Providence Portland Medical Center:
Like a lot of cancers, breast cancer grows by simple cell division. It begins as one malignant cell, which then divides and becomes two bad cells, which divide again and become four bad cells, and so on. Breast cancer has to divide 30 times before it can be felt. Up to the 28th cell division, neither you nor your doctor can detect it by hand.
With most breast cancers, each division takes one to two months, so by the time you can feel a cancerous lump, the cancer has been in your body for two to five years. It can certainly seem like a lump appeared out of nowhere especially if you or your doctor have recently examined your breasts and not felt anything suspicious but in reality, the cancer has simply doubled that one last time necessary to be noticeable. By the time you can feel it, a breast tumor is usually a little more than one-half inch in size about a third the size of a golf ball. It has also been in your body long enough to have had a chance to spread.
Its important to realize that there are two types of mammograms:
Don’t Miss: Breast Cancer Gene Name
Types Of Breast Cancer
There are many different types of breast cancer. The type is determined by the specific kind of cells in the breast that are affected. Most breast cancers are carcinomas. The most common breast cancers such as ductal carcinoma in situ and invasive carcinoma are adenocarcinomas, since the cancers start in the gland cells in the milk ducts or the lobules . Other kinds of cancers can grow in the breast, like angiosarcoma or sarcoma, but are not considered breast cancer since they start in different cells of the breast.
Breast cancers are also classified by certain types of proteins or genes each cancer might make. After a biopsy is done, breast cancer cells are tested for proteins called estrogen receptors and progesterone receptors, and the HER2 gene or protein. The tumor cells are also closely looked at in the lab to find out what grade it is. The specific proteins found and the tumor grade can help decide the stage of the cancer and treatment options.
To learn more about the specific tests done on breast cancer cells, see Understanding a Breast Cancer Diagnosis.
First Of All Dont Be Panic
Remember, about 80 to 85 percent of pea-sized lumps in breast are benign, meaning they arent made of cancer cells. This is particularly true in women under the age of 40. Also if youve been having regular mammograms with negative results, its more likely that the lump youre feeling is not cancerous.
Noncancerous breast lump diseases include:
-
Fibroadenomas: Solid breast tumors that usually happen in teenage girls and women under age 30.
-
Fibrocystic breast disease: A condition where a woman has painful lumps in her breasts.
-
Ductal or lobular hyperplasia: An overgrowth of the cells that line the milk glands.
-
Cysts, abscesses, or infection: Sac-like structure that can be filled with fluid or pus.
-
Mastitis: An infection of the milk ducts.
-
Lipomas: A slow-growing, fatty lump that grows between the skin and the underlying muscle.
-
Intraductal papillomas: Benign tumor that forms in milk duct thats common in women over 40.
-
Fat necrosis: When part of the fatty tissue of the breast is damaged from injury.
-
Duct ectasia: When the breast duct walls thicken, which can then get blocked and lead to fluid build-up.
-
Complex lesions or scars from past breast biopsies.
Some of these diseases need no treatment, but some do need, so you may still want to pay a visit to your doctor for early diagnosis and treatment.
Don’t Miss: Is Weight Loss A Symptom Of Breast Cancer
Breast Lumps: Why Size Movability And Pain Matter
Your breasts are made up of fat, nerves, blood vessels, fibrous connective tissue, and glandular tissue, as well as an intricate system of milk-producing lobules , and ducts . This anatomy in and of itself creates a lumpy, uneven terrain.
A lump in the breast distinguishes itself from this background of normal irregularities. Harmless breast lumps can be solid and unmovable, like a dried bean or movable, soft, and fluid-filled you can roll it between your fingers like a grape. A lump may be pea-size, smaller than a pea, or even several inches across, although this larger size is rare.
What typically differentiates a benign breast lump from a cancerous breast lump is movement. That is, a fluid-filled lump that rolls between the fingers is less likely to be cancerous than a hard lump in your breast that feels rooted in place.
Another rule of thumb has to do with pain. Breast cancer does not usually cause pain. Benign conditions sometimes do, although there are exceptions to this rule as well. For instance, a rare form of breast cancer, inflammatory breast cancer, may cause symptoms such as aching, tenderness, pain, or burning in the breast.
The only way to know the status of a lump for sure is through medical tests, such as an ultrasound, a mammogram, or a fine needle aspiration , in which your doctor uses a tiny needle to extract a bit of the lump for laboratory examination.
RELATED: What Is a Skin Lump? Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention
Cancer Tumors Versus Cysts And Fibroadenomas
Cysts, which are fluid-filled lumps, are common in the breast and are benign. They form when fluid builds up inside breast glands, and tend to be smooth or round. Fibroadenomas, which are benign tumors made up of glandular and connective breast tissue, are usually smooth and firm or rubbery to the touch. Both of these conditions tend to affect younger women fibroadenomas are most common in women in their 20s and 30s, and cysts are most common in women under 40.
Despite these common descriptions, it is impossible to tell by touch whether a lump is cancer.
Recommended Reading: Anne Hathaway Breast Cancer
Educate Yourself On What Is Not Normal
Usually if a pea-sized lump in breast is cancerous, it will have these symptoms:
-
It is a hard mass.
-
It is not painful.
-
The edges arent smooth.
-
The mass doesnt move when you push it.
-
It is in the outside and upper part of the breast.
-
It gets bigger over time.
Still, be sure that not every single cancerous lump in the breast will have these criteria. A lump that is cancerous could be rounded or soft and painful.
Many women also have very dense breast tissue that makes it more difficult to detect changes or lumps. It is even difficult to find lumps and tumors on mammograms in women with dense, thick breast tissue. If you examine yourself on a regular basis, it will be easier to find changes in your breast tissue.
Why Do I Have A Pea
Breast cysts. If you find a breast lump that feels round, smooth and firm, it could be a cyst a dilated milk duct filled with fluid. A breast cyst can be large or small, and the surrounding breast tissue may be tender. A breast cyst may appear before your menstrual period and get smaller or disappear afterward.
Also Check: Anne Hathaway’s Breasts
How Much Do Tamoxifen And Raloxifene Lower The Risk Of Breast Cancer
Multiple studies have shown that both tamoxifen and raloxifene can reduce the risk of developing estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer in healthy postmenopausal women who are at high risk of developing the disease. Tamoxifen lowered the risk by 50 percent. Raloxifene lowered the risk by 38 percent. Overall, the combined results of these studies showed that taking tamoxifen or raloxifene daily for five years reduced the risk of developing breast cancer by at least one-third. In one trial directly comparing tamoxifen with raloxifene, raloxifene was found to be slightly less effective than tamoxifen for preventing breast cancer.
Both tamoxifen and raloxifene have been approved for use to reduce the risk of developing breast cancer in women at high risk of the disease. Tamoxifen is approved for use in both premenopausal women and postmenopausal women . Raloxifene is approved for use only in postmenopausal women.
Less common but more serious side effects of tamoxifen and raloxifene include blood clots to the lungs or legs. Other serious side effects of tamoxifen are an increased risk for cataracts and endometrial cancers. Other common, less serious shared side effects of tamoxifen and raloxifene include hot flashes, night sweats, and vaginal dryness.