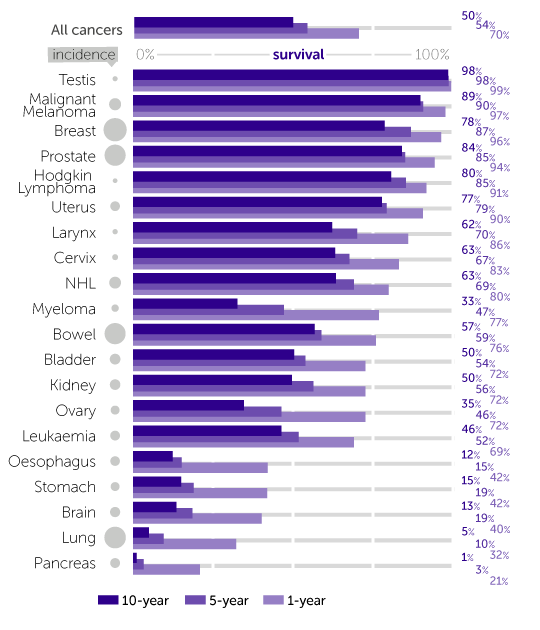
Understanding Breast Cancer Survival Rates
Prognosis varies by stage of breast cancer.
Non-invasive and early stage invasive breast cancers have a better prognosis than later stage cancers .
Breast cancer thats only in the breast and has not spread to the lymph nodes has a better prognosis than breast cancer thats spread to the lymph nodes.
The poorest prognosis is for metastatic breast cancer , when the cancer has spread beyond the breast and nearby lymph nodes to other parts of the body.
Learn more about breast cancer treatment.
How Is Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Diagnosed
Same Day Results
At the Johns Hopkins Breast Center, we know how quickly patients want results from a biopsy or scan if there is a suspicion of breast cancer. We follow strict guidelines for biopsies and pathology reports. Most of our patients will receive the probability of cancer immediately following their biopsy procedure and a pathology confirmation within 24 hours.
Learn more about the steps of diagnosis, including:
- Digital mammography
- Biologic targeted therapy
What Are Cancer Survival Statistics
A key part of making a prognosis is looking at survival rates. These are numbers researchers collect over many years in people with the same type of cancer. These numbers are based on large groups of people. For breast cancer, there are two main measurements:
Breast cancer survivalrates reflect the percentage of women who are alive 5 years or longer after their diagnosis. This means the numbers are based on women who were found to have breast cancer at least 5 years ago. Advances in diagnosing and treating cancer have led to steadily improving survival rates, so the outlook for women diagnosed today is likely better.
Relative survival rates dont take into account the cause of death. Theyre a measure of the percentage of people with cancer who have lived for a certain time after diagnosis, compared with people who did not have cancer.
You May Like: What Is The Prognosis For Stage 4 Breast Cancer
Oncogene Expression May Negatively Affect Breast Cancer Outcome
A relatively new addition to the discussion of breast cancer survival statistics and prognosis is oncogene expression.
An oncogene is a tiny fragment of genetic material which is carried in a chromosome and can cause normal cells to become malignant.
The oncogene HER-2, in particular, has been linked to more aggressive breast cancers.
Around one-third of all breast tumours produce the HER-2 oncogene, and these patients tend to have higher rates of recurrence and lower overall breast cancer survival rates.
According to a 2013 Canadian scientific study, the overall 5-year survival rate of HER-2 positive breast cancer is 88.6%. Furthermore, the relapse-free survival rate for 5 years is 79.4%.
Many Factors Can Affect Your Prognosis
Some of the factors that affect prognosis include:
- The type of cancer and where it is in your body
- The stage of the cancer, which refers to the size of the cancer and if it has spread to other parts of your body
- The cancers grade, which refers to how abnormal the cancer cells look under a microscope. Grade provides clues about how quickly the cancer is likely to grow and spread.
- Certain traits of the cancer cells
- Your age and how healthy you were before cancer
- How you respond to treatment
Learn more about Cancer Staging and Tumor Grade.
Recommended Reading: Invasive Breast Cancer Definition
How Can You Handle Your Feelings About Having Breast Cancer Again
It’s common to have a wide range of emotions. It may be hard to stay hopeful when you are fighting cancer for the second or third time. These ideas may help:
- Get the support you need. Spend time with people who care about you, and let them help you.
- Take good care of yourself. Get plenty of rest, and eat nourishing foods.
- Talk about your feelings. Find a support group where you can share your experience.
- Stay positive. Do things each day that will help you stay calm and relaxed.
If your emotions are too much to handle, be sure to tell your doctor. You may be able to get counselling or other types of help.
You may want to think about planning for the future. An advance care plan lets doctors know what type of life-support measures you want if your health gets much worse. You can also choose a substitute decision-maker to make decisions in case you aren’t able to. If you put your wishes in writing, you can make it easier for your loved ones and others to know what you want.
Best Breast Cancer Breakthroughs Of 2021
It seems unbelievable that were ready to review the best breast cancer breakthroughs of 2021, but here we are! This year has flown by and many exciting discoveries have been made in the field of breast cancer research.
According to a study conducted using 2020 statistics and published in “CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians”, breast cancer surpassed lung cancer as the most common type of cancer diagnosed around the world. There were an estimated 2.3 million new cases of breast cancer in 2020, which represents a whopping 11.7 percent of all cases of cancer diagnosed around the world last year. As a result, breast cancer research is now more important than ever and fortunately, new discoveries are being made with astonishing speed.
This year has brought us a lot of new information surrounding breast cancer. Researchers have given us very positive news to discuss, from the discovery of a positive association between a plant-based diet and lower breast cancer risk, to the fact that regular exercise could help relieve chemo brain during chemotherapy. Additionally, new treatments are currently being studied and show a lot of potential for the future, and older medications have also been found to have a positive impact on breast cancer treatments.
We never fail to be amazed by these discoveries at the end of every year and 2021 is no exception. Keep reading to discover some of the best breast cancer breakthroughs of 2021.
Also Check: Breast Cancer Staging Prognosis
Why Does Breast Cancer Come Back After Treatment
Even with the best treatment, cancer can come back. If just a few cancer cells remain in your body after your initial treatment, those cells can spread through the blood or lymph system and grow. This may happen from a few months to many years after the first diagnosis.
If your breast cancer has come back, you may second-guess your previous treatment choices. But the fact is, there is no guarantee with any treatment. Now it is time to make new decisions and explore other treatment options.
The Malm Breast Cancer Database
The study cohort consists of all cases of invasive female breast cancer in Malmö, Sweden, diagnosed between 1 January 1961 and 31 December 1991. They were all treated at the same institution, Malmö University Hospital, and no referrals were made to or from the hospital for patients with breast cancer. All residents in Sweden are registered by a unique 10-digit ID number. Breast cancer patients were identified by review of clinical notes and record-linkage with the Swedish Cancer Registry, forming the basis of the Malmö Breast Cancer Database. This was all completed by one surgeon, who also validated all breast cancer diagnoses by reviewing histological material, X-ray examinations, and medical records . The present study was approved by the regional ethical committee in Lund, Sweden .
Don’t Miss: What Is Hr Positive Breast Cancer
When Should I Go To The Emergency Room
You might also have unusually strong side effects from your cancer treatment. While your healthcare provider likely gave you medication to help control your side effects, you should go to the emergency room if your side effects continue despite medication.
Many cancer treatments affect your immune system, increasing the chance you will develop infections. Symptoms that might require an emergency room visit during treatment are:
- Fever of 100.5 and above.
- Chills.
- Persistent nausea and vomiting.
What Questions Should I Ask My Doctor
You will have lots of questions about your cancer, starting with your diagnosis. Here are some basic questions you might ask:
- What is triple negative breast cancer?
- How do you know my cancer is triple negative breast cancer?
- Why did I get this cancer?
- Do I need genetic testing?
- Has my breast cancer spread, and if so, how far has it spread?
- What is the stage of my cancer?
- What is my prognosis or expected outcome?
- What treatments do you recommend?
- Why do you recommend those treatments?
- What are those treatment side effects?
- Will I need surgery? If so, what surgery do you recommend and why?
- Im interested in participating in clinical trials. Are you able to help me find one?
- Do you know if there are any local support groups?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Triple negative breast cancer is one of the more challenging breast cancers to treat. You might be discouraged by what you have read about triple negative breast cancer. But there are a number of very effective treatments for triple negative breast cancer, including immunotherapy, chemotherapy, surgery and radiation. And every day researchers learn more about this rare cancer. Their knowledge is your power. If youre concerned you arent getting the straight story about your cancer, ask your healthcare provider to walk you through your diagnosis and treatment options.
Don’t Miss: What Is Hr Positive Breast Cancer
Frequently Occurring Breast Cancer
Lobular carcinoma in situ : The term, in situ, refers to cancer that has not spread past the area where it initially developed. LCIS is a sharp increase in the number of cells within the milk glands of the breast.
Ductal carcinoma in situ : DCIS, the most common type of non-invasive breast cancer, is confined to the ducts of the breast. For example, ductal comedocarcinoma.
Typical Structure associated with ductal carcinoma
Recurrence Of Metastatic Breast Cancer
Metastatic breast cancer is considered a chronic disease, so it doesnt go away and recur.
But in recent years, people under age 50 have seen a particularly strong decline in death rates due to breast cancer, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention .
These declines are due in part to improved screening and treatment for the disease.
There are a few general facts that are helpful to know about breast cancer outlook:
- Breast cancer is the most common cancer diagnosis in the United States, according to the
You May Like: What Are The Symptoms Of Stage 1 Breast Cancer
What Is The Treatment For Triple Negative Breast Cancer
Healthcare providers and researchers are making significant progress on TNBC treatments. Recent clinical trials are testing new combinations of drugs and new approaches to existing treatments. Some existing treatments are:
- Chemotherapy: Providers might combine chemotherapy and surgery, with chemotherapy being used to shrink your tumor before surgery or after surgery to kill cancer cells throughout your body.
- Surgery: This could be a lumpectomy to remove an individual lump, or a mastectomy to remove an entire breast. Providers then perform a sentinel node biopsy or axillary node surgery to look for signs your breast cancer has spread to your lymph nodes.
- Radiation therapy: Post-surgery radiation therapy helps reduce the chances your cancer will return or recur.
- Immunotherapy: This treatment stimulates your immune system to produce more cancer-fighting cells or help healthy cells identify and attack cancer cells. Immunotherapy can be added to chemotherapy to before surgery to shrink the tumor. You might also receive immunotherapy for about a year after your surgery and post-surgery radiation therapy.
What Affects Survival
Your outlook depends on the stage of the cancer when it was diagnosed. This means how big it is and whether it has spread.
The type of cancer and grade of the cancer cells can also affect your survival. Grade means how abnormal the cells look under the microscope.
Your general health and fitness also affect survival, the fitter you are, the better you may be able to cope with your cancer and treatment.
Another factor that can affect survival is whether the cancer cells have receptors for particular cancer drugs.
Read Also: Breast Cancer Spread To Lungs Prognosis
Can Tnbc Be Prevented
Researchers dont know all the factors that cause triple negative breast cancer. They have identified the BRAC1 gene mutation as one potential cause for triple negative breast cancer. Unfortunately, you cant prevent BRAC1 because you inherit this gene mutation from your parents.
But there are steps that help prevent breast cancers, including TNBC:
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Exercise on a regular basis.
- Know your family medical history.
- Monitor your breast health. Studies show 95% of women whose breast cancer was treated before it could spread were alive four years after diagnosis.
- Talk to your healthcare provider about genetic testing for the BRCA gene if you have a family history of breast cancer, ovarian cancer, pancreatic or prostate cancer. If you have the BRCA gene, there are steps you can take to prevent breast cancer.
What Is Stage 4 Breast Cancer
Also known as metastatic breast cancer, the cancer in this stage has spread beyond the breast, underarm and internal mammary lymph nodes to other parts of the body near to or distant from the breast. The cancer has spread elsewhere in the body. The affected areas may include the bones, brain, lungs or liver and more than one part of the body may be involved.
At stage 4, TNM designations help describe the extent of the disease. Higher numbers indicate more extensive disease. Most commonly, stage 4 breast cancer is described as:,
- T: T1, T2, T3 or T4 depends on the size and/or extent of the primary tumor.
- N1: Cancer has spread to the lymph nodes.
- M1: The disease has spread to other sites in the body.
Don’t Miss: What Is Hr Positive Breast Cancer
What Is Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is the most common cancer in women in Australia and the second most common cancer to cause death in women, after lung cancer.
Breast cancer is the abnormal growth of the cells lining the breast lobules or ducts. These cells grow uncontrollably and have the potential to spread to other parts of the body. Both men and women can develop breast cancer, although it is uncommon in men. Transwomen, non-binary people can also get breast cancer.
Transgender and gender-diverse people can also get breast cancer. A transgender woman taking medication to lower male hormones and boost female hormones may have an increased risk of developing breast cancer.
It is estimated that 19,866 women and 164 men in Australia will be diagnosed with breast cancer in 2021.
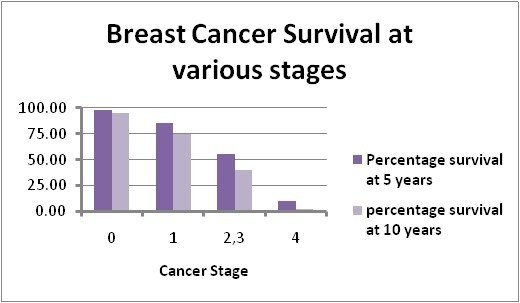
In Australia, the overall five year survival rate for breast cancer in females is 91%. If the cancer is limited to the breast, 96% of patients will be alive five years after diagnosis this figure excludes those who die from other diseases. If the cancer has spread to the regional lymph nodes, five year relative survival drops to 80%.
Treatment depends on the extent of the cancer.
Clinical Correlations Treatment And Outcome Data
ACC was originally described in 1996 , with a limited number of reported cases in the English literature. Foschini et al. listed 45 ACCs with a further 2 cases since reported . Some studies include very limited or no follow-up data. is an adapted version of the table reported by Foschini et al. including only those patients for whom follow-up data were available and updated with recent literature. In approximately half of the patients follow-up was less than 2 years .
It is difficult to draw firm conclusions regarding the prognosis of breast ACC from available literature in view of morphological variation within and between tumours in the published studies. It is our opinion that low-grade pure ACC is a bland tumour type that overlaps with microglandular adenosis and is associated with indolent biological behaviour, and is, therefore, unlikely to benefit from aggressive adjuvant chemotherapy. ACCs with high-grade areas or admixed with other BC types are likely to behave more aggressively and may account for some of the reported events in the literature. Currently, there is no evidence to support withholding systemic chemotherapy in ACC with high-grade features if clinically indicated. Further data on their response to therapy is needed.
Read Also: Suspicious Malignancy Breast
When Is Radiation Usually Used To Treat Stage 2 Breast Cancer
According to the American Cancer Society, radiation therapy may be used after a breast-conserving surgery, or lumpectomy, to mitigate the risk of cancer cells recurring in the same breast or nearby lymph nodes. After a mastectomy, an oncologist may determine that radiation is necessary if the tumor was larger than 5 cm, if there was lymph node involvement, or if cancer was found outside of surgical margins.
Where To Find Cancer Statistics

NCI collects and reports on cancer statistics through its SEER Program, which stands for Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results. From the Cancer Stat Facts page on the SEER web site, you can find answers to the most commonly asked questions about cancer statistics for many cancer types. You can also browse the latest SEER Cancer Statistics Review.
Also Check: What To Expect From Chemotherapy For Breast Cancer
What Is Stage 2 Breast Cancer
Also known as invasive breast cancer, the tumor in this stage measures between 2 cm to 5 cm, or the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes under the arm on the same side as the breast cancer. Stage 2 breast cancer indicates a slightly more advanced form of the disease. At this stage, the cancer cells have spread beyond the original location and into the surrounding breast tissue, and the tumor is larger than in stage 1 disease. However, stage 2 means the cancer has not spread to a distant part of the body.
At stage 2, a tumor may be detected during a breast self-exam as a hard lump within the breast. Breast self-exams and routine screening are always important and can often lead to early diagnosis, when the cancer is most treatable.
Stage 2 breast cancer is divided into two categories:
Stage 2A: One of the following is true:
- There is no tumor within the breast, but cancer has spread to the axillary lymph nodes, or
- The tumor in the breast is 2 cm or smaller and cancer has spread to the axillary lymph nodes, or
- The tumor in the breast measures 2 cm to 5 cm but cancer has not spread to the axillary lymph nodes.
Stage 2B: One of the following is true:
- The tumor measures 2 cm to 5 cm and cancer has spread to the axillary lymph nodes, or
- The tumor is larger than 5 cm but cancer has not spread to the axillary lymph nodes.
At stage 2, TNM designations help describe the extent of the disease. Most commonly, stage 2 breast cancer is described as: