How Long Does It Take For Breast Cancer To Grow My Doctor Just Examined My Breasts A Month Ago And Today I Found A Lump Is It Possible That Breast Cancer Could Have Developed So Quickly
Answer from the expert staff of breast cancer research at the Robert W. Franz Cancer Research Center at Providence Portland Medical Center:
Like a lot of cancers, breast cancer grows by simple cell division. It begins as one malignant cell, which then divides and becomes two bad cells, which divide again and become four bad cells, and so on. Breast cancer has to divide 30 times before it can be felt. Up to the 28th cell division, neither you nor your doctor can detect it by hand.
With most breast cancers, each division takes one to two months, so by the time you can feel a cancerous lump, the cancer has been in your body for two to five years. It can certainly seem like a lump appeared out of nowhere especially if you or your doctor have recently examined your breasts and not felt anything suspicious but in reality, the cancer has simply doubled that one last time necessary to be noticeable. By the time you can feel it, a breast tumor is usually a little more than one-half inch in size about a third the size of a golf ball. It has also been in your body long enough to have had a chance to spread.
Its important to realize that there are two types of mammograms:
You May Like: Did Anne Hathaway Have Breast Cancer
What Are Dense Breasts
Breasts contain glandular, connective and fatty tissue. Breast density is a term used to describe the different proportions of these tissue types as detected by a mammogram. Dense breasts have relatively high amounts of connective and/or glandular tissue and low amounts of fatty tissue. Only a mammogram can show if a woman has dense breasts. Breast density is not related to how the breasts look, feel, their size or firmness.
On a mammogram, connective or fibrous tissue appears white while fatty tissue appears dark. Because breast cancers also appear white, this may make it more difficult for specialists to identify cancer in women with dense breasts. However, even with dense breasts, a screening mammogram is still the most effective method to detect breast cancer early for women over age 50.
Dense breasts also tend to be more common in younger women or women with a lower body mass index. In addition, breast density tends to decrease as women become older.
Testing For Proteins And Genes
The breast cancer cells will be tested for certain proteins called estrogen and progesterone receptors. If the cancer has these proteins, it’s called a hormone receptor positive breast cancer. The cells are also tested to see if the cancer makes too much of the HER2 protein. If it does, it’s called a HER2-positive cancer. These cancers are sometimes easier to treat. If the cancer doesn’t test positive for any of these proteins, it’s called a triple-negative breast cancer.
The cells might also be tested for certain genes, which can help decide if chemo might be helpful and how likely it is that the cancer will come back. Ask your doctor to explain the tests they plan to do, and what the results might mean.
You May Like: Neoplasm Breast Cancer
How Is Breast Cancer Treated
If the tests find cancer, you and your doctor will develop a treatment plan to eradicate the breast cancer, to reduce the chance of cancer returning in the breast, as well as to reduce the chance of the cancer traveling to a location outside of the breast. Treatment generally follows within a few weeks after the diagnosis.
The type of treatment recommended will depend on the size and location of the tumor in the breast, the results of lab tests done on the cancer cells, and the stage, or extent, of the disease. Your doctor will usually consider your age and general health as well as your feelings about the treatment options.
Breast cancer treatments are local or systemic. Local treatments are used to remove, destroy, or control the cancer cells in a specific area, such as the breast. Surgery and radiation treatment are local treatments. Systemic treatments are used to destroy or control cancer cells all over the body. Chemotherapy and hormone therapy are systemic treatments. A patient may have just one form of treatment or a combination, depending on her individual diagnosis.
Dont Miss: Stage 3 Advanced Breast Cancer
Tests For Skin Metastases

A member of your treatment team will examine you and look at your skin. Theyll also discuss any other symptoms you have.
To confirm a diagnosis of secondary breast cancer in the skin, you may have a punch biopsy. Youll be given a local anaesthetic before a tiny cutter device is used to take a very small piece of tissue from the area. Its not unusual for the area to bleed a little after the biopsy so youll usually be given a small dressing or plaster afterwards.
You may also have a CT scan, also known as a CAT scan, to check for any other areas of spread. This type of scan uses x-rays to take a series of detailed pictures of the body. Its painless but during the CT scan you have to lie still for around half an hour. Sometimes you will have dye injected into a vein, usually in your arm, before you have the scan so that different areas can be seen more clearly.
Also Check: Stage 3 Breast Cancer Aggressive
When To See Your Gp
See your GP if you have:
- a lump in your breast
- any other worrying symptoms, such as nipple discharge
- a history of breast cancer in members of your family and you’re worried about your chances of getting it
It’s very unlikely you have cancer, but it’s best to get your symptoms checked. Your GP will examine your breast and can refer you for tests and scans for breast cancer if needed.
If you do not have symptoms but have a clear family history of breast cancer, your GP may refer you to a genetic specialist to discuss your risk of getting it.
There are some inherited genes that increase your risk of cancer and a blood test can be done to check for these. Read about testing for cancer risk genes.
How Is Breast Swelling Treated
Your doctors recommended treatment plan will depend on the cause of your breast swelling.
If the swelling is caused by an infection, they may prescribe antibiotics. You can also learn how to keep your breast tissue clean and dry to prevent further infection.
If the swelling is caused by hormonal changes related to your menstrual cycle, your doctor may prescribe birth control pills, which can relieve breast swelling and other symptoms of PMS in some women.
If youre already using hormonal contraceptives, they may encourage you to switch to another type.
If youre diagnosed with breast cancer, your doctors recommended treatment plan will depend on the type, location, and stage of your cancer. They may prescribe chemotherapy, radiation therapy, surgery, or a combination.
Here are a few tips for relieving discomfort associated with breast swelling.
- Wear a supportive bra or make sure your bra fits properly.
- Apply a cloth-covered heat pack or ice pack to your breasts for up to 10 minutes at a time.
- Use over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen .
Recommended Reading: Stage 3 Breast Cancer Treatment
What Are The Stages Of Breast Cancer
There are two different staging systems for breast cancer. One is called anatomic staging while the other is prognostic staging. The anatomic staging is defined by the areas of the body where the breast cancer is found and helps to define appropriate treatment. The prognostic staging helps medical professionals communicate how likely a patient is to be cured of the cancer assuming that all appropriate treatment is given.
The anatomic staging system is as follows:
Stage 0 breast disease is when the disease is localized to the milk ducts .
Stage I breast cancer is smaller than 2 cm across and hasnt spread anywhere including no involvement in the lymph nodes.
Stage II breast cancer is one of the following:
- The tumor is less than 2 cm across but has spread to the underarm lymph nodes .
- The tumor is between 2 and 5 cm .
- The tumor is larger than 5 cm and has not spread to the lymph nodes under the arm .
Stage III breast cancer is also called locally advanced breast cancer. The tumor is any size with cancerous lymph nodes that adhere to one another or to surrounding tissue . Stage IIIB breast cancer is a tumor of any size that has spread to the skin, chest wall, or internal mammary lymph nodes .
Stage IV breast cancer is defined as a tumor, regardless of size, that has spread to areas away from the breast, such as bones, lungs, liver or brain.
Also Check: Breast Cancer Age Of Onset
What Are Some Common Types Of Benign Breast Lumps
There are many possible causes of non-cancerous breast lumps. Two of the most common causes of benign single breast lumps are cysts and fibroadenomas. In addition, several other conditions can present themselves as lumps, such as fat necrosis and sclerosing adenosis. Only your healthcare provider can diagnose your breast lump.
Recommended Reading: Did Anne Hathaway Have Breast Cancer
Tests At The Breast Cancer Clinic
If you have suspected breast cancer you’ll be referred to a specialist breast cancer clinic for further tests. This referral will be because of your symptoms or because your mammogram has shown an abnormality,
Mammogram and breast ultrasound
If you have symptoms and have been referred to a specialist breast unit by your GP, you’ll probably be invited to have a mammogram if you are over 35 years old. This is an X-ray of your breasts. You may also need an ultrasound scan.
If your cancer was detected through the BreastCheck screening programme, you may need another mammogram or ultrasound scan.
Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to produce an image of the inside of your breasts. It helps to determine the nature of a lump or of the abnormality. It may be needed to find out if a lump in your breast is solid or contains liquid.
Your breasts are made up of thousands of tiny glands that produce milk. This glandular tissue contains a higher concentration of breast cells than other breast tissue, making it denser.
Dense breast tissue can make a mammogram difficult to read. Lumps or areas of abnormal tissue are harder to spot.
Younger women tend to have denser breasts. This is why mammography is not routinely performed in women under 35 years. As you get older, the amount of glandular tissue in your breasts decreases and is replaced by fat. This means your breasts become less dense.
Biopsy
Can You Tell When Exactly My Breast Cancer Started
Often times, one of the most frequently asked questions I get when someone is diagnosed with breast cancer is when did it begin? says Roesch. And the general rule is that we really cant tell for sure when the cancer popped up. We can look at the subtype of breast cancer to perhaps get a better understanding if it was weeks vs. months for example, but theres no way to tell for sure.
Also Check: Symptoms Stage 4 Breast Cancer
Other Types Of Breast Cancer
Other less common types of breast cancer include invasive lobular breast cancer, which develops in the cells that line the milk-producing lobules, inflammatory breast cancer and Paget’s disease of the breast.
It’s possible for breast cancer to spread to other parts of the body, usually through the lymph nodes or the bloodstream. If this happens, it’s known as “secondary” or “metastatic” breast cancer.
Treatment For Inflammatory Breast Cancer
The treatment for inflammatory breast cancer can be slightly different to other types of breast cancer.
Chemotherapy
You usually have chemotherapy as your first treatment. This is called neo adjuvant chemotherapy. It helps to control the cancer cells in the breast and reduces the swelling. It also aims to destroy any cancer cells that might have spread elsewhere in the body.
Surgery
After chemotherapy you have surgery unless there is a reason why this isnt suitable for you. You are most likely to have your whole breast removed .
Some women might be able to have breast conserving surgery. For this type of surgery, the surgeon removes the area of cancer and a surrounding area of healthy tissue. But for most women, mastectomy is the best option.
The surgeon usually removes the lymph nodes under your armpit.
Radiotherapy
After surgery you have radiotherapy to the remaining breast tissue. This is to help stop the cancer coming back.
Other drug treatment you may have
You have hormone therapy tablets for some years if your breast cancer has hormone receptors. Your doctor might recommend that you also have targeted cancer therapy, such as trastuzumab and pertuzumab, if your cancer has receptors for those drugs.
Breast reconstruction
You may be able to have breast reconstruction after you have finished your treatment . Do ask your surgeon, they can tell you whether this is suitable for you.
Read Also: De Novo Metastatic Breast Cancer Symptoms
You May Like: Cancer Stage 3b
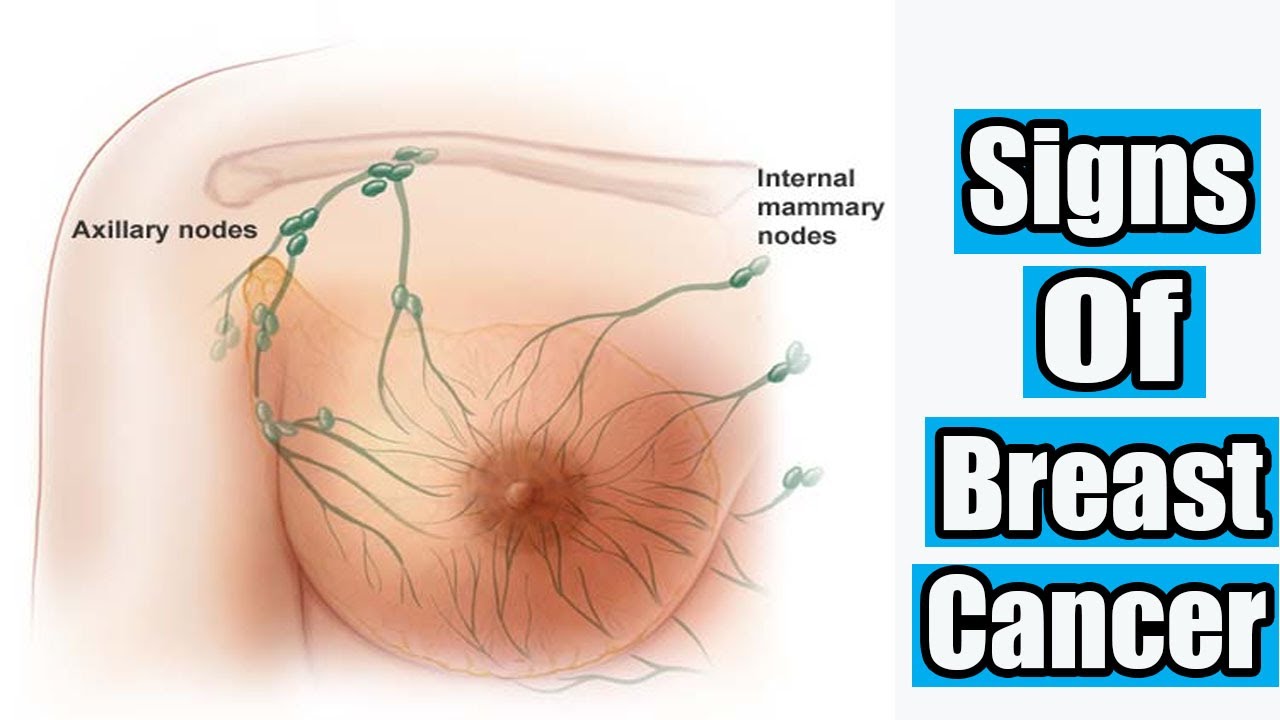
Where Is The First Place Breast Cancer Spreads
The first place that breast cancer commonly spreads to outside the breast are the lymph nodes in the armpit . Surgery is usually needed to remove one or more lymph nodes to help check for breast cancer spread. This operation to remove lymph nodes in the armpit is known as axillary surgery.
Breast cancer found in the lymph nodes will impact the breast cancers staging, and the treatment plan will often be affected as well.
If cancer is found in the lymph nodes, there is a higher chance that cells have travelled through the lymphatic system and bloodstream to spread to other parts of the body. In this instance, treatment with systemic therapies, such as chemotherapy, is likely to be recommended.
If cancer is found in a large number of axillary nodes, radiotherapy may also be recommended to kill any breast cancer cells that remain in the armpit but cannot be removed by surgery.
More Information About The Tnm Staging System
The T category describes the original tumor:
- TX means the tumor cant be assessed.
- T0 means there isnt any evidence of the primary tumor.
- Tis means the cancer is in situ .
- T1, T2, T3, T4: These numbers are based on the size of the tumor and the extent to which it has grown into neighboring breast tissue. The higher the T number, the larger the tumor and/or the more it may have grown into the breast tissue.
The N category describes whether or not the cancer has reached nearby lymph nodes:
- NX means the nearby lymph nodes cant be assessed, for example, if they were previously removed.
- N0 means nearby lymph nodes do not contain cancer.
- N1, N2, N3: These numbers are based on the number of lymph nodes involved and how much cancer is found in them. The higher the N number, the greater the extent of the lymph node involvement.
The M category tells whether or not there is evidence that the cancer has traveled to other parts of the body:
- MX means metastasis cant be assessed.
- M0 means there is no distant metastasis.
- M1 means that distant metastasis is present.
You May Like: Anne Hathaway Boob Job
Don’t Miss: Can Weight Gain Be A Symptom Of Breast Cancer
What Is A Breast Made Of
Both men and women have breasts, but women have more breast tissue than men.
The female breast is made of different components, including:
- lobules, which produce breast milk
- ducts, which carry milk to the nipple
- fatty tissue and connective tissue, which surround the lobules and ducts.
All breasts contain fatty and fibrous tissue. Lobules can also be referred to as glandular tissue. The male breast has ducts but few or no lobes or lobules.
Breast tissue extends from the collarbone to lower ribs, sternum and armpit.
What Causes Breast Cancer
Breast cancer happens when there are changes in the genetic material . Often, the exact cause of these genetic changes is unknown.
But sometimes these genetic changes are inherited, meaning that you are born with them. Breast cancer that is caused by inherited genetic changes is called hereditary breast cancer.
There are also certain genetic changes that can raise your risk of breast cancer, including changes called BRCA1 and BRCA2. These two changes also raise your risk of ovarian and other cancers.
Besides genetics, your lifestyle and the environment can affect your risk of breast cancer.
You May Like: Symptoms Of Stage 3 Breast Cancer
Hormones And Hormone Medicine
Hormone replacement therapy
Hormone replacement therapy is associated with an increased risk of developing breast cancer. However, the risk is a very low one.
Contraceptive pill
Women who use the contraceptive pill have a slightly increased risk of developing breast cancer. The risk starts to decrease once you stop taking the pill. Your risk of breast cancer is back to normal 10 years after stopping.
Does A Benign Breast Condition Mean That I Have A Higher Risk Of Getting Breast Cancer
Benign breast conditions rarely increase your risk of breast cancer. Some women have biopsies that show a condition called hyperplasia . This condition increases your risk only slightly.
When the biopsy shows hyperplasia and abnormal cells, which is a condition called atypical hyperplasia, your risk of breast cancer increases somewhat more. Atypical hyperplasia occurs in about 5% of benign breast biopsies.
Recommended Reading: Average Age Of Breast Cancer Onset