Drug Treatment Before Surgery
You might have chemotherapy as a first treatment to shrink the cancer down.
You might have hormone therapy first if your cancer cells have hormone receptors. But you usually only have this if chemotherapy isnt suitable.
If your cancer cells have particular proteins called HER2 receptors you might also have a targeted cancer drug called trastuzumab .
These treatments might shrink the tumour enough to allow your surgeon to remove just the area of cancer. This is called breast conserving surgery or a wide local excision.
If the cancer doesnt shrink enough, you need to have the whole breast removed . You may be able to have a new breast made . Do speak to your surgeon about this.
Before your surgery the lymph nodes in the armpit are checked for cancer cells.
You usually have radiotherapy to the breast after surgery.
Stage 0 Breast Cancer
Stage 0 is sometimes used to describe abnormal cells that are not invasive cancer. For example, Stage 0 is used for ductal carcinoma in situ . DCIS is diagnosed when abnormal cells are in the lining of a breast duct, but the abnormal cells have not invaded nearby breast tissue or spread outside the duct. Although many doctors dont consider DCIS to be cancer, DCIS sometimes becomes invasive breast cancer if not treated.
Tis, N0, M0
A Swollen Arm Or Hand
You are at risk of long term swelling in your hand and arm after surgery to remove your lymph nodes in the armpit. This is swelling caused by lymph fluid that can’t drain away. It can happen any time after surgery and radiotherapy to your armpit.
Not everyone will get this and it is less likely to happen if you only have a few nodes removed. But it is very important to speak to your specialist nurse or surgeon if you think your arm or hand may be swollen.
Unfortunately, once you have lymphoedema it cant be cured. But early treatment can help to control it. Your nurse will talk to you about ways of preventing lymphoedema.
Read Also: How To Indicate Breast Cancer
How Is Breast Cancer Treated
There are six standard types of treatment for breast cancer: surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy.¹ Your doctor might suggest combinations of these therapies or “adjuvant” therapies, which are used after the primary therapy to help reduce the chances of the cancer coming back. Your doctor may also suggest that you participate in a clinical trial, which is a research study that tests new cancer treatments.
The options for treating men with breast cancer are similar to those for women. A man will typically have surgery followed by hormone therapy, chemotherapy, or radiation.
It is important to mention here that some groups have a harder time accessing breast cancer care than others. Disparities in care negatively affect people who are Black and Latinx, poor, uninsured, LGBTQ+, older, or living in rural areas.²
Cancer In The Lymph Nodes
Cancer can appear in the lymph nodes in 2 ways: it can either start there or it can spread there from somewhere else.
Cancer that starts in the lymph nodes is called lymphoma. You can read more about lymphoma inHodgkin Lymphomaand Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma.
More often, cancer starts somewhere else and then spreads to lymph nodes. That is the focus of this section.
Also Check: Can You Get Cancer From Getting Hit In The Breast
Symptoms If Cancer Has Spread To The Bones
You may have any of these symptoms if your cancer has spread to the bones:
- an ache or pain in the affected bone
- breaks in the bones because they are weaker
- breathlessness, looking pale, bruising and bleeding due to low levels of blood cells – blood cells are made in the bone marrow and can be crowded out by the cancer cells
Sometimes when bones are damaged by advanced cancer, the bones release calcium into the blood. This is called hypercalcaemia and can cause various symptoms such as:
- tiredness
What Is The Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system is a network of tiny vessels and small, bean-shaped organs called lymph nodes that carry lymph throughout the body. Lymph is a clear, colorless fluid that contains a few blood cells. It starts in many organs and tissues. The lymphatic system is part of your immune system. It helps protect and maintain the fluid balance of your body by filtering and draining lymph and waste products away from each body region. The lymphatic system also helps the body fight infection.
Recommended Reading: Untreated Breast Cancer Life Expectancy
Cancer Highjacks The Immune System
The researchers also explored what happens once cancer gets to the lymph nodes. Similar to what other studies have found, it appears that when cancer cells arrive, they shift the amounts and types of immune cells in the lymph nodes.
In mice, for example, there were fewer cancer-killing immune cells in lymph nodes that were invaded by melanoma than in lymph nodes that were cancer-free, the researchers found.
There were also more immune cells called T-regulatory cells in lymph nodes that were invaded by melanoma cells.
And in tissue samples from people with head and neck cancer, there were more T-regs in lymph nodes where cancer had invaded than in lymph nodes that were cancer-free.
The main role of T-regs is to protect healthy cells from attack by other immune cells that have gone off the rails. By doing so, T-regs help prevent autoimmune diseases and chronic inflammation. But T-regs can sometimes get mixed up, protecting unhealthy cells that should be eliminated, like cancer cells.
Thats exactly what the researchers appeared to see in their mouse studies: In mice that were bred to lack T-regs, melanoma tumors were less able to spread to the lungs.
The scientists then removed T-regs from the lymph nodes of mice where melanoma had or hadnt invaded. They transferred the T-regs into other mice with melanoma that hadnt invaded the lymph nodes. Only the T-regs from lymph nodes with cancer helped melanoma cells spread to the lungs, the researchers found.
Breast Cancer Staging And Lymph Nodes
After an initial cancer diagnosis, youll need to know if it has spread beyond the primary tumor. If you have enlarged lymph nodes, your doctor may be able to perform a needle biopsy. Otherwise, the lymph nodes can be checked when you have breast surgery.
Your doctor will assign a clinical stage based on:
- a physical exam
- imaging tests
- a biopsy of the tumor
After surgery, youll have more detailed information from the breast tissue and lymph nodes. This information helps provide the pathological stage.
Lymph node involvement is a key factor in staging breast cancer. In the TNM staging system:
- T is for tumor size
- N represents lymph node involvement
- M is for metastasis
Heres a closer look at what to know about cancer cells and lymph node involvement.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Three Types Of Breast Cancer
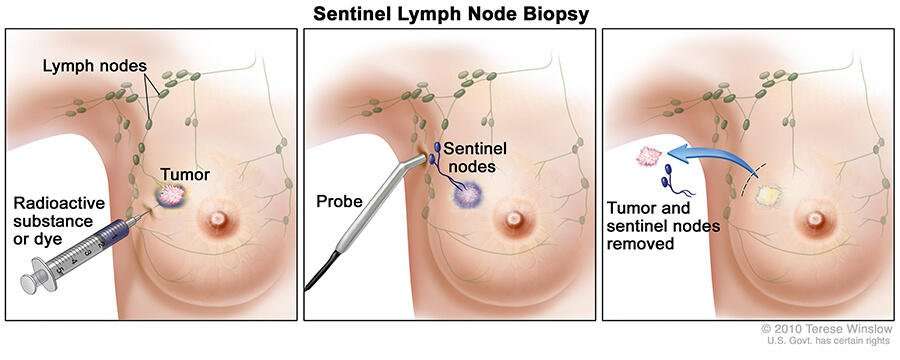
Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy
In a sentinel lymph node biopsy , the surgeon finds and removes the first lymph node to which a cancer is likely to spread . A radioactive substance and/or a blue dye is injected into the tumor, the area around it, or the area around the nipple. Lymph vessels will carry these substances along the same path that the cancer would likely take. The first lymph node the dye or radioactive substance travels to will be the sentinel node.
After the substance has been injected, the sentinel node can be found either by using a special machine to detect radioactivity in the nodes, or by looking for nodes that have turned blue. Sometimes, both methods are used. The surgeon cuts the skin over the lymph node area and removes the node containing the dye or radioactivity.
The few removed lymph nodes are then checked closely in the lab for cancer cells by a pathologist. Sometimes, this is done during the surgery. Because there is a chance that other lymph nodes in the same area will also have cancer if cancer is found in the sentinel lymph node, the surgeon may go ahead with an axillary dissection to remove more lymph nodes while you are still on the operating table. If no cancer cells are seen in the node at the time of the surgery, or if they are not checked by a pathologist at the time of the surgery, they will be examined more closely over the next several days.
Based on the studies that have looked at this, skipping the ALND may be an option for:
Breast Cancer Metastasis: Secondary Sites
Over the years there have been significant improvements and advancements in the diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer. Indeed, breast cancer is now considered to be a manageable disease.
However, there are still over half a million deaths worldwide from breast cancer and over 90% of these women die of metastasis. Consequently, research into metastasis is of vital importance in overcoming deaths from metastatic breast cancers.
Stage IV or metastatic breast cancer, as mentioned earlier, are cancer cells that have spread from the breast to distant sites around the body. Common secondary sites are:-
- Bone: .
Recommended Reading: Can Smoking Cause Breast Cancer
What Are Cancer Survival Statistics
A key part of making a prognosis is looking at survival rates. These are numbers researchers collect over many years in people with the same type of cancer. These numbers are based on large groups of people. For breast cancer, there are two main measurements:
Breast cancer survivalrates reflect the percentage of women who are alive 5 years or longer after their diagnosis. This means the numbers are based on women who were found to have breast cancer at least 5 years ago. Advances in diagnosing and treating cancer have led to steadily improving survival rates, so the outlook for women diagnosed today is likely better.
Relative survival rates donât take into account the cause of death. Theyâre a measure of the percentage of people with cancer who have lived for a certain time after diagnosis, compared with people who did not have cancer.
Regional Recurrence Within Three Years Carries A Less Favorable Prognosis But Overall Survival Statistics Are Still Good
Generally speaking, if the breast cancer returns regionally lymph nodes) within the first five years following original treatment, the overall likelihood of survival is thought to be somewhat poorer.
Five-year overall survival after an isolated chest wall recurrence is 68% and after intra-breast recurrence it is 81%.
In one 2010 medical research study, the ten year overall survival rate was estimated at 84% for women without recurrence. However, this figure goes down to 49% for women with a locoregional recurrence and 72% for women with a second primary tumour.
A large 2015 study examined the impact of the time of the disease free interval on survival rates. For women with a locoregional recurrence that happened in the first 18 months, the ten year overall survival rate is around 30%. The overall 10 year survival rate for those whose recurrence happened within 3 years goes up to 50%. Furthermore, for those who suffered a recurrence after 3 years the ten year overall survival rate increases to 70%.
This recent study clearly demonstrates that the longer the time span since the primary prognosis and treatment to the recurrence, the better the long-term prognosis.
| 33 | 30 |
The rate of distance breast cancer metastasis and overall survival is most favorable for women in which the recurrence occurred locally and after five years.
However, women with a same-breast recurrence within five years have a distant metastasis rate of about 61%, which are slightly poorer odds.
You May Like: Is Stage Two Breast Cancer Curable
Where Can Breast Cancer Spread
The most common places for breast cancer to spread to are the lymph nodes, bone, liver, lungs and brain. The symptoms you may experience will depend on where in the body the cancer has spread to. You might not have all of the symptoms mentioned here.
Remember other conditions can cause these symptoms. They don’t necessarily mean that you have cancer that has spread. But if you have symptoms that you are worried about, discuss them with your GP, cancer specialist, or breast care nurse so that you can be checked.
What Is Stage Ii Breast Cancer
Stage II describes cancer that is in a limited region of the breast but has grown larger. It reflects how many lymph nodes may contain cancer cells. This stage is divided into two subcategories.
Stage IIA is based on one of the following:
- Either there is no tumor in the breast or there is a breast tumor up to 20 millimeters , plus cancer has spread to the lymph nodes under the arm.
- A tumor of 20 to 50 millimeters is present in the breast, but cancer has not spread to the lymph nodes.
Stage IIB is based on one of these criteria:
- A tumor of 20 to 50 millimeters is present in the breast, along with cancer that has spread to between one and three nearby lymph nodes.
- A tumor in the breast is larger than 50 millimeters, but cancer has not spread to any lymph nodes.
Read Also: When Is Chemo Used For Breast Cancer
Types Of Breast Cancer
In order to understand breast cancer and how to treat it, it’s important to understand how breasts work. Female breasts are supposed to produce milk. In order to do this, breasts are made up of lobules — glands that produce milk — and ducts which carry the milk from the lobule to the nipple . The ducts and lobules are surrounded by fatty breast tissue.
Breast cancer can form either in the lobules or in the ducts. A cancer that forms in the lobules is known as lobular carcinoma while a cancer that forms in the ducts is known as ductal carcinoma.
The ducts and lobules are connected like branches on a tree trunk, forming a closed system. The only openings out of the system are at the nipple. Thus, a breast cancer that is contained within this closed system is said to be in-situ or non-invasive. A breast cancer that has spread into the surrounding breast tissue is called invasive.
Staging And Grading Of Breast Cancer
Knowing the stage and grade of the cancer helps your doctors plan the best treatment for you.
On this page
Your specialist doctor needs certain information about the cancer to advise you on the best treatment for you. This includes:
- the stage of the cancer
- the grade of the cancer
- whether the cancer has receptors for hormones or a protein called HER2.
This information comes from the results of all the tests you have had, including:
- the biopsy, when the tissue was examined
- other tests that were done on the cells.
Your specialist doctor and nurse will talk to you about this. They will explain how it helps you and your doctor decide on your treatment plan.
We understand that waiting to know the stage and grade of your cancer can be a worrying time. Were here if you need someone to talk to. You can:
Read Also: Donations For Breast Cancer Research
Types Of Lymph Node Surgery
Even if the nearby lymph nodes are not enlarged, they will still need to be checked for cancer. This can be done in two different ways. Sentinel lymph node biopsy is the most common way and only a few lymph nodes are removed. But in some cases, an axillary lymph node dissection , which removes more lymph nodes, might be needed.
Lymph node surgery is often done as part of the main surgery to remove the breast cancer, but sometimes it might be done as a separate operation.
Stage The Stage Is The Main Prognostic Factor For Breast Cancer There Is Less Risk That Early Stage Breast Cancer Will Come Back So It Has A More Favourable Prognosis Breast Cancer Diagnosed At A Later Stage Has A Greater Risk Of Recurrence So It Has A Less Favourable Prognosis Doctors Will Consider If Cancer Has Spread To Lymph Nodes And The Size Of The Tumour When They Predict A Prognosis
If cancer has spread to lymph nodes
Whether or not cancer has spread to lymph nodes is the most important prognostic factor for breast cancer. Breast cancer that has spread to lymph nodes has a higher risk of coming back and a less favourable prognosis than breast cancer that has not spread to the lymph nodes.
The number of lymph nodes that contain cancer is also important. The more positive lymph nodes there are, the higher the risk that breast cancer will come back. Breast cancer that has spread to 4 or more lymph nodes has the highest risk for recurrence.
The size of the tumour
The size of the tumour is the 2nd most important prognostic factor for breast cancer. The tumour size will affect prognosis no matter how many lymph nodes have cancer in them.
Breast tumours that are 5 cm or larger are more likely to come back after treatment than smaller tumours. Breast tumours that are smaller than 1 cm and have not spread to the lymph nodes have a very favourable prognosis.
Read Also: Breast Cancer Pac Phone Calls
Scar Tissue In The Armpit
Some women develop scar tissue in the armpit after lymph node removal. The connective tissues in the armpit get inflamed, which forms one or more tight bands. This usually happens within the first few weeks or months after the operation.
The scar tissue is called cording or banding or axillary web syndrome. It can feel something like a guitar string. It can extend down the arm past the elbow, possibly as far as the wrist or thumb.
Cording is harmless but can be painful and can limit your arm movement. Massaging the area regularly can help. Tell your breast care nurse if you develop cording. They can refer you to a physiotherapist. They can show you how to massage the area and teach you stretching exercises. It usually gets better within a few months. Taking anti inflammatory painkillers may also help. Speak to your nurse or doctor about taking these.
-
Early Breast Cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines 2019F Cardoso and others
-
Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network, September 2013
-
A systematic review of axillary web syndrome WM Yeung and others