The Ctca Inflammatory Breast Cancer Program: Designed For The Unique Needs Of Ibc Patients
Because of the aggressive nature of IBC, CTCA knows its critical to detect and diagnose the disease quickly, develop a comprehensive treatment plan and provide integrative care services that help improve patients treatment outcomes and reduce their side effects.
Thats why we developed the CTCA Inflammatory Breast Cancer Program, where our team of breast cancer experts work quickly to properly diagnose and stage each patient’s disease so she can make more informed decisions about her treatment options. Our breast cancer experts collaborate daily, allowing them to reach a diagnosis more efficiently and provide an individualized care plan designed to allow you to start treatment as soon as possible. The team also offers opportunities to enroll qualified patients in carefully selected clinical trials in areas such as immunotherapy and genomically targeted chemotherapy.
If you believe you may be experiencing symptoms of IBC and want to schedule an appointment for diagnostic testing, or if youre interested in a second opinion for breast cancer at CTCA, or chat online with a member of our team.
Expert
Diagnosis And Staging Of Inflammatory Breast Cancer
Because inflammatory breast cancer forms in layers, your doctor may not feel a distinct lump during a breast exam and a mammogram may not detect one either. However, it is possible to see and feel the skin thickening that often happens with IBC. This skin thickening can also be detected on a mammogram.
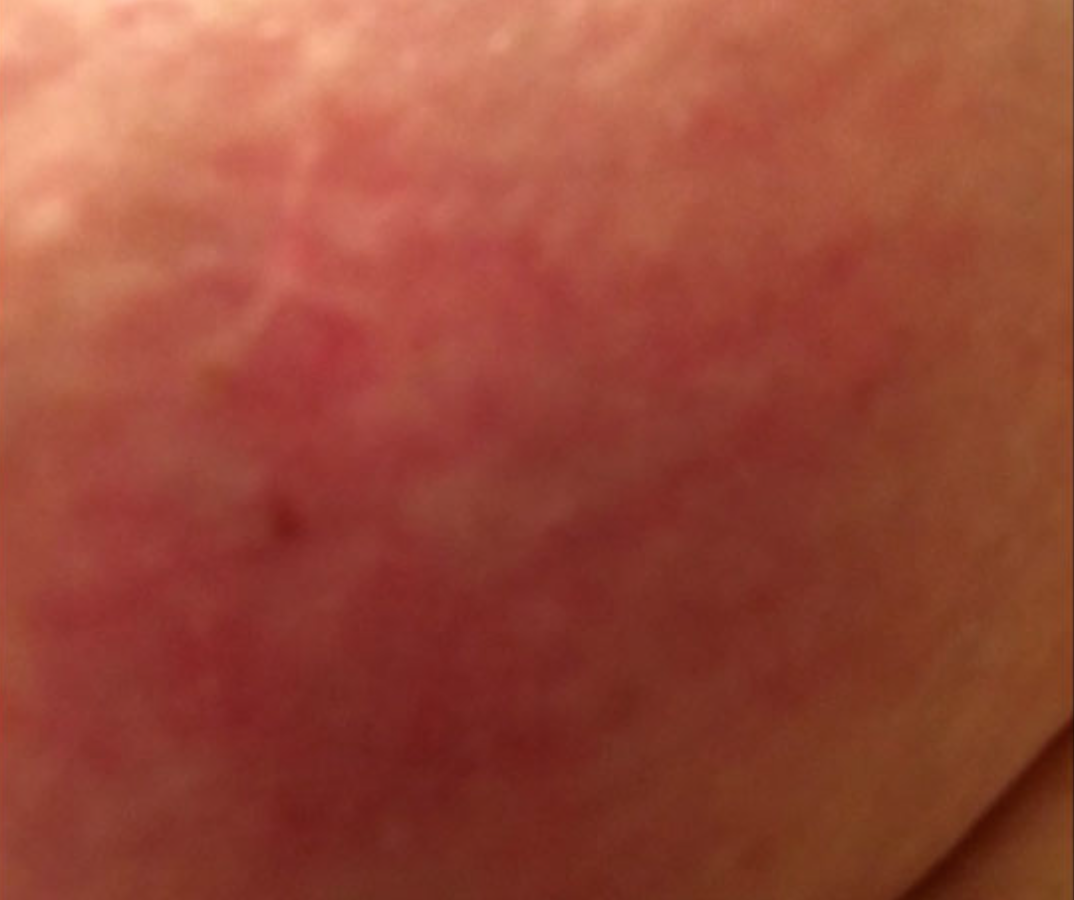
In most cases, inflammatory breast cancer is diagnosed after you or your doctor can see or feel breast changes such as redness, swelling, warmth, or an orange-peel look to the skin. Because IBC grows quickly, it is usually found at a locally advanced stage, meaning that cancer cells have spread into nearby breast tissue or lymph nodes. Just about all people with IBC have evidence of cancer in the lymph nodes. In approximately 1 out of 3 people with IBC, the cancer has spread from the breast to other areas of the body.
If youve been diagnosed with inflammatory breast cancer, its completely understandable if youre feeling overwhelmed. Keep in mind, though, that there are a variety of treatment options available for IBC.
Signs And Symptoms Of Inflammatory Breast Cancer
Inflammatory breast cancer causes a number of signs and symptoms, most of which develop quickly , including:
- Swelling of the skin of the breast
- Redness involving more than one-third of the breast
- Pitting or thickening of the skin of the breast so that it may look and feel like an orange peel
- A retracted or inverted nipple
- One breast looking larger than the other because of swelling
- One breast feeling warmer and heavier than the other
- A breast that may be tender, painful or itchy
- Swelling of the lymph nodes under the arms or near the collarbone
Tenderness, redness, warmth, and itching are also common symptoms of a breast infection or inflammation, such as mastitis if youre pregnant or breastfeeding. Because these problems are much more common than IBC, your doctor might suspect infection at first as a cause and treat you with antibiotics.
This may be a good first step, but if your symptoms dont get better in 7 to 10 days, more tests need to be done to look for cancer. The possibility of IBC should be considered more strongly if you have these symptoms and are not pregnant or breastfeeding, or have been through menopause.
IBC grows and spreads quickly, so the cancer may have already spread to nearby lymph nodes by the time symptoms are noticed. This spread can cause swollen lymph nodes under your arm or above your collar bone. If the diagnosis is delayed, the cancer can spread to distant sites.
Recommended Reading: Can Stage 3 Breast Cancer Be Cured
How Do You Treat Inflammatory Breast Cancer
To treat IBC, a combination of strategies is used, including chemotherapy, surgery, radiation therapy, and possibly targeted therapies.
- Chemotherapy: Neoadjuvant chemotherapy refers to the chemotherapy that is administered before surgery so that the cancer reduces in size and the operation is easier. It is recommended that at least 6 cycles of neoadjuvant chemotherapy be administered over the course of 4- to 6 months before the tumor is surgically removed.
- Surgery: The standard surgery for IBC is called a modified radical mastectomy. During this surgery, the entire breast and nearly all the lymph nodes in the adjoining arm are removed. The surgery may also involve the removal of the tissue over the chest muscles, and sometimes a small chest muscle called the pectoralis minor.
- Radiation: Radiation therapy is often recommended following surgical breast removal to kill any remaining cancer cells.
- Targeted therapy: IBCs often produce greater than normal amounts of the HER2 protein, hence drugs such as trastuzumab that target this protein can be given before as well as after surgery.
- Hormone therapy: IBCs are usually negative for estrogen and progesterone receptors. Therefore, hormone therapy is usually ineffective in this type of cancer.
Diagnosis Of Breast Cancer
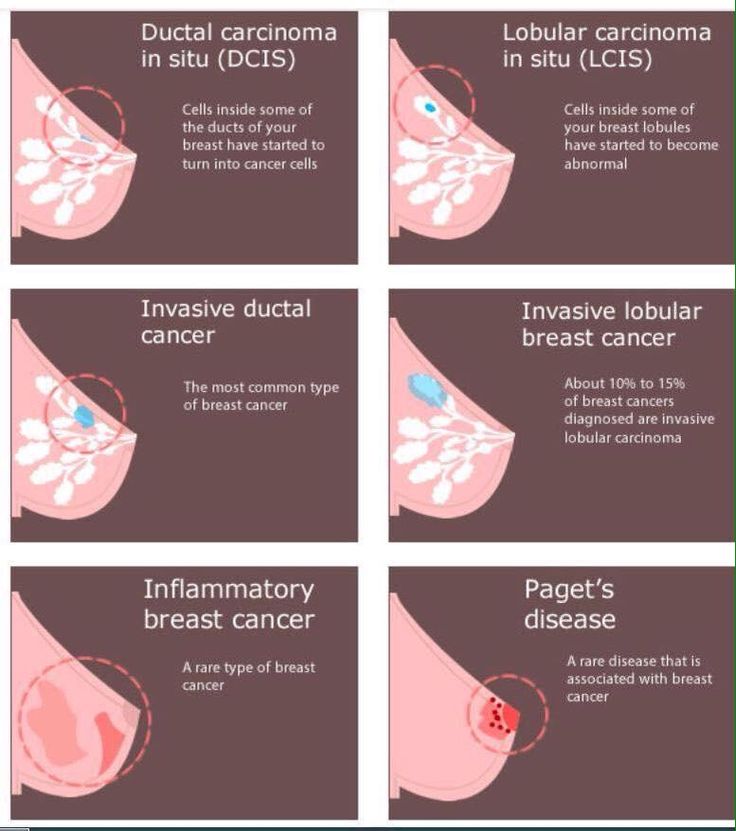
To determine if your symptoms are caused by breast cancer or a benign breast condition, your doctor will do a thorough physical exam in addition to a breast exam. They may also request one or more diagnostic tests to help understand whats causing your symptoms.
Tests that can help diagnose breast cancer include:
- Mammogram. The most common way to see below the surface of your breast is with an imaging test called a mammogram. Many women ages 40 and older get annual mammograms to check for breast cancer. If your doctor suspects you may have a tumor or suspicious spot, they will also request a mammogram. If an abnormal area is seen on your mammogram, your doctor may request additional tests.
- Ultrasound. A breast ultrasound uses sound waves to create a picture of the tissues deep in your breast. An ultrasound can help your doctor distinguish between a solid mass, such as a tumor, and a benign cyst.
Your doctor may also suggest tests such as an MRI or a breast biopsy.
If you dont already have a primary care doctor, you can browse doctors in your area through the Healthline FindCare tool.
Also Check: Can Getting Hit In Your Breast Cause Cancer
Risk Factors For Breast Cancer
There are several risk factors that increase your chances of getting breast cancer. However, having any of these doesnt mean you will definitely develop the disease.
Some risk factors cant be avoided, such as family history. You can change other risk factors, such as quitting smoking, if you smoke. Risk factors for breast cancer include:
While there are risk factors you cant control, following a healthy lifestyle, getting regular screenings, and taking any preventive measures your doctor recommends can help reduce your risk for developing breast cancer.
What Are The Early Signs And Symptoms Of Inflammatory Breast Cancer
Unlike more common types of breast cancer, this type generally doesnât show up as a lump. The disease grows as nests or sheets under the skin.
Symptoms of inflammatory breast cancer may include:
- Pain in the breast
- Skin changes in the breast area. You may find pink or reddened areas often with the texture and thickness of an orange.
- A bruise on the breast that doesn’t go away
- Sudden swelling of the breast
- Itching of the breast
- Swelling of the lymph nodes under the arm or in the neck
These changes often happen quickly, over a period of weeks.
Recommended Reading: Did Anne Hathaway Have Breast Cancer
Survival Rates For Inflammatory Breast Cancer
Inflammatory breast cancer is considered an aggressive cancer because it grows quickly, is more likely to have spread at the time its found, and is more likely to come back after treatment than other types of breast cancer. The outlook is generally not as good as it is for other types of breast cancer.
Survival rates can give you an idea of what percentage of people with the same type and stage of cancer are still alive a certain amount of time after they were diagnosed. They cant tell you how long you will live, but they may help give you a better understanding of how likely it is that your treatment will be successful.
Keep in mind that survival rates are estimates and are often based on previous outcomes of large numbers of people who had a specific cancer, but they cant predict what will happen in any particular persons case. These statistics can be confusing and may lead you to have more questions. Talk with your doctor about how these numbers may apply to you, as he or she is familiar with your situation.
My Inflammatory Breast Cancer Story
When the nurse phoned me at 8:30 a.m. on December 15, 2015 to ask if I could make it to the hospital the same day, I knew it was serious. Receiving confirmation that same morning that I had breast cancer was devastating.
The diagnosis: stage III, HER2 positive and hormone receptor-negative inflammatory breast cancer with bone abnormalities located at the sternum and at one vertebra.
As the mom of three young children , I couldnt help but think the worst. I could not stop crying.
It was urgent for me to go through all the required testing to determine the extent of the cancer. I had to get a breast ultrasound with a biopsy, a mammogram, a chest X-ray and an abdominal ultrasound the same day. I met with the oncologist in the afternoon.
It was one appointment after the other, but the tears kept coming. I was telling myself that it wasnt real. That everything was going too fast. That it was impossible. That I couldnt die right now.
The oncologist I met that afternoon said something that I will never forget: We need to put out the fire. Now. Everything was going quickly and his remark kept my mind busy while bringing me comfort I was taken care of. The nurse navigator referred me to a psychologist.
Back home, I surfed the Web. Inflammatory breast cancer is aggressive and spreads rapidly. Chances of survival are low. It wasnt very reassuring, so I stopped reading. I had panic attacks and suffered acute anxiety.
Update on Caroline Corriveaus story
Read Also: What Are The Chances Of Getting Breast Cancer Twice
Chemotherapy Hormone Therapy And Her2
Treatments after surgery and radiation therapy depend on prior treatment and tumor characteristics :
- If chemotherapy was not completed before surgery, the remaining chemotherapy is given after surgery.
- HER2-positive IBC is treated with HER2-targeted therapy before and/or after surgery.
- Hormone receptor-positive IBC is treated with hormone therapy.
Survival For Inflammatory Breast Cancer
Many factors can influence life expectancy for women with inflammatory breast cancer. These include:
- the exact position of the cancer
- how big the cancer is and whether it has spread only to the lymph nodes or to other organs
- how abnormal the cancer cells look under the microscope
- your age
- whether the cancer cells have receptors for hormone therapies
- how well the cancer responds to treatment
Inflammatory breast cancer can develop quickly and may spread to other parts of the body. So, in general, the outlook with this type is not as good as for women diagnosed with other types of breast cancer. But doctors think that the outlook is improving as breast cancer treatment improves.
You May Like: Did Anne Hathaway Have Breast Cancer
What Is A Breast Ridge
The anatomy and development of the breast Often theres a ridge of fat at the bottom of the breastthe inframammary ridge. This ridge is perfectly normal, and is the result of the fact that we walk upright and our breasts fold over themselves. The areola is the darker area of the breast surrounding the nipple.
British Columbia Specific Information
Breast cancer is the most common type of cancer in women in British Columbia. Breast cancer can occur in men as well, but it is not as common. Tests and treatments for breast cancer vary from person to person, and are based on individual circumstances. Certain factors such as your age, family history, or a previous breast cancer diagnosis may increase your risk of developing breast cancer. For information about your specific risk factors, speak with your health care provider.
A number of screening methods, including mammograms in women, can help find and diagnose breast cancer. The decision to have a mammogram or use any other screening method may be a difficult decision for some women. While screening for breast cancer is often recommended, it is not mandatory. Speak with your health care provider for information regarding how to get screened, the facts and myths about screening tests, how to maintain your breast health, and to get help making an informed decision.
For more information about breast cancer and breast cancer screening, visit:
If you have questions about breast cancer or medications, speak with your health care provider or call 8-1-1 to speak with a registered nurse or pharmacist. Our nurses are available anytime, every day of the year, and our pharmacists are available every night from 5:00 p.m. to 9:00 a.m.
You May Like: Can Stage 1 Breast Cancer Be Cured
Stage 4 Inflammatory Breast Cancer Treatment
Cancer thats spread to more distant areas of the body is typically treated using one or a combination of the systemic therapies mentioned above. These include:
- chemotherapy
Its unclear exactly what causes IBC to occur. In general, cancer develops due to genetic changes. These can happen due to a variety of factors, such as:
- genetic changes inherited from your parents
- errors that naturally occur during cell division
- damage to DNA through environmental exposures
Sometimes mutations can happen in genes that are associated with cell growth and division. When this happens, cells can begin to grow and divide out of control.
In IBC, cells in the breast ducts or lobules begin to rapidly grow and divide. As cancer cells build up, they block the lymph vessels in the skin of the breast. These leads to the redness, swelling, and dimpling associated with IBC.
There are a few risk factors associated with developing IBC. These include:
- Age. IBC typically occurs in younger women.
- Weight. People that have overweight or obesity are more likely to develop IBC.
- Race. Research shows that IBC occurs more frequently in Black women compared with white women.
Re: Inflammatory Breast Cancer So Easily Misdiagnosed
Hi when i read what you had been through it was like reading about myself. May 2008 i went to my docs with 1 breast very red, sore, huge painful etc and was sent home with antibiotics for masitis. this went on for 2month till eventually they referred me. Aug 2008 i was diagnosed with inflamatary breast cancer. Had Ec chemo till nov then had a double mastectomy and all nodes on the affected side removed. Lump was only 4mm but 8/9 nodes had cancer. I then went on and had 12 weeks of taxol and then followed with 3 weeks of radio. I was very tired after all the treatment but got on with my family life looking after my hubby and 3 kids. I really did think it was something i had won till i found a lump in my neck in oct 2009. After nagging eventually they scanned and did a biopsy and found the cancer was back. I have 4 specs on lungs and started exeloda chemo tabs immediately. Bone scan clear. I am still in shock and keep saying why me. On 3rd cycle now and after the 4th they will scan me to make sure it is working if so i will get another 4 cycles, then left in limbo till they grow back. I am going to fight this, i am not leaving my 3 children 3,6 and 9 with no mum. Hubby bin fantastic. would love you to keep in touch and stay positive and we can fight this horrible disease. justine x
Read Also: Did Anne Hathaway Have Breast Cancer
Breast Exam By Your Doctor
The same guidelines for self-exams provided above are true for breast exams done by your doctor or other healthcare professional. They wont hurt you, and your doctor may do a breast exam during your annual visit.
If youre having symptoms that concern you, its a good idea to have your doctor do a breast exam. During the exam, your doctor will check both of your breasts for abnormal spots or signs of breast cancer.
Your doctor may also check other parts of your body to see if the symptoms youre having could be related to another condition.
What Complications Are Associated With Inflammatory Breast Cancer
Treatment for IBC can bring its own set of complications, such as lymphedema after removal of lymph nodes.
Because IBC develops so quickly, the condition has usually spread to other tissues by the time it is diagnosed. This metastasis can create a need for additional treatment to other areas of the body. IBC is also more likely to recur compared to other forms of breast cancer.
Read Also: How To Cure Breast Cancer With Baking Soda
What Are The Symptoms
Inflammatory breast cancer can cause one or more of these symptoms:
- A breast that is swollen, red, and warm
- A breast that is tender or painful
- An area of itching in the breast
- A recent change in the nipple. Sometimes the nipple pulls back into the breast instead of pointing outward. This is called a retracted nipple.
- A change in the skin, especially an area that looks thick and pitted, like an orange peel. Sometimes there are ridges in the skin and small bumps that look like a rash or hives.
- An area of the breast that looks bruised
- Swollen lymph glands in the armpit
- One or more lumps in the breast