Tumour Dormancy And Reawakening
Tumour dormancy is generally defined as a prolonged state of asymptomatic micrometastatic disease. In cancer of the breast or prostate, cancer cells can remain dormant for years and even decades before recurring as metastatic disease. During this latent period, patients are considered to be disease-free due to the lack of any symptoms of illness and because they have no detectable neoplasms by clinical imaging. Often described as one of the most wicked cancer cell misbehaviours, tumour dormancy shares many features in common with chronic diseases. Yet, its nature appears to be reversible, as myriad mechanisms have been shown to induce a switch to reawaken indolent DTCs . Furthermore, tumour dormancy is not exclusively a phenomenon of end-stage tumorigenesis, as it can apply to the presence of occult neoplasms until clinical diagnosis , and/or to MRD left behind after treatment . Attention, however, must be paid to the molecular underpinnings of these two scenarios as mechanistic differences between primary and metastatic dormancy might exist.
What Is The Survival Rate Of Recurrent Breast Cancer
For women who experienced a local recurrence within 5 years of diagnosis, the 10-year mortality rate from date of recurrence was 53.1% for women who experienced a local recurrence 510 years from diagnosis, the 10-year actuarial mortality from date of recurrence was 34.8% for women who experienced a local recurrence
Cellular And Tumour Mass Dormancy
Two different models of tumour dormancycellular and tumour mass dormancyhave been proposed. Cellular dormancy refers to the presence of solitary or small cell clusters of DTCs that exist in a G0/G1 growth-arrested state and result from quiescence, senescence or differentiation. An inability to properly adhere to the ECM,, reduced signalling through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase /AKT pathway and a low ratio of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase to the stress-induced kinase p38, are some of the plethoras of predominantly cell-intrinsic mechanisms that have been reported to induce cellular dormancy. On the other hand, escape from cellular dormancy has been shown to occur upon increased matrix stiffness through TGF1 expression, following the release of neutrophil extracellular traps by inflammatory neutrophils, and as a result of aberrant activation of the adhesion protein vascular cell adhesion protein 1 in indolent breast DTCs lodged in the bone marrow via engaging 41-expressing osteoclasts.
Recommended Reading: Stage 4 Triple Positive Breast Cancer
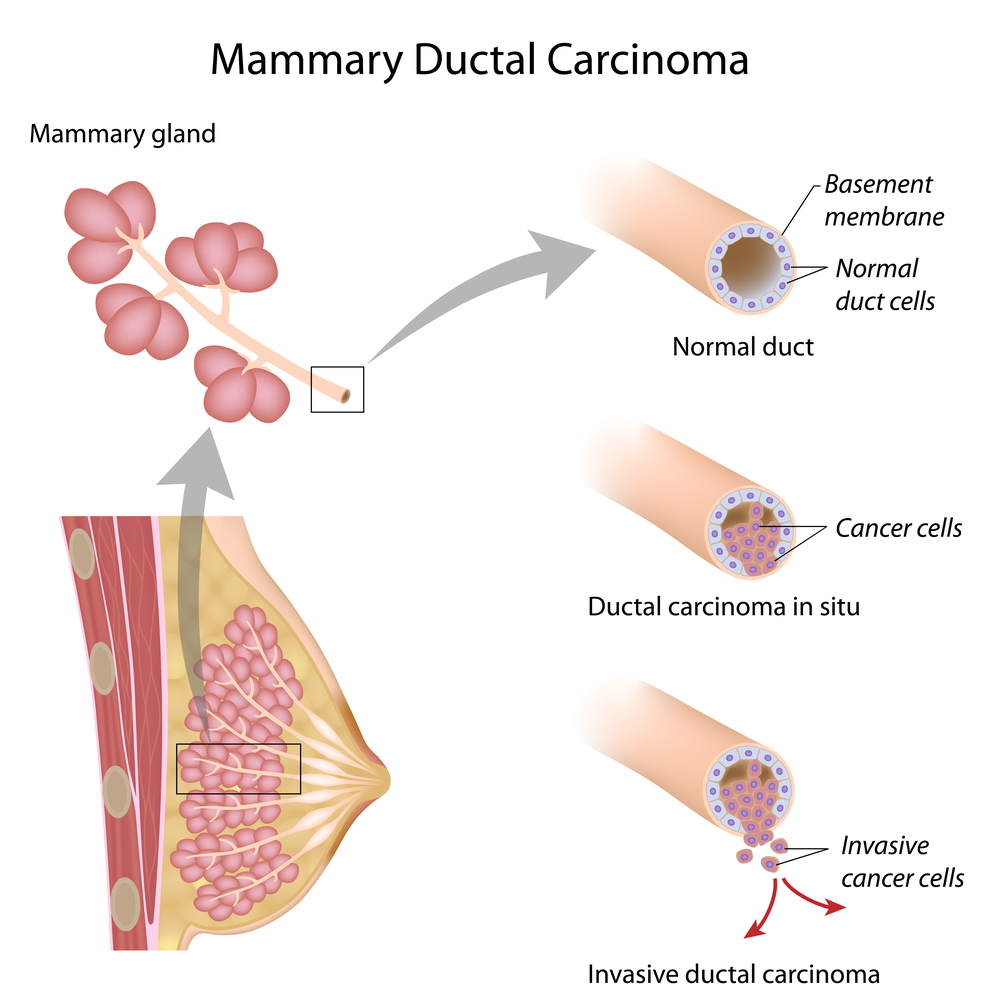
What Is Stage 0 Dcis
Stage 0 breast cancer, ductal carcinoma in situ is a non-invasive cancer where abnormal cells have been found in the lining of the breast milk duct. In Stage 0 breast cancer, the atypical cells have not spread outside of the ducts or lobules into the surrounding breast tissue. Ductal Carcinoma In Situ is very early cancer that is highly treatable, but if its left untreated or undetected, it can spread into the surrounding breast tissue.
Coping With The Fear Of Recurrence
Coping with the fear of recurrence can be challenging, especially when the risk of recurrence persists as with estrogen receptor-positive breast cancers. In the past, many people sensed that if they hit the five-year mark, the chances they were home free were high. Longer-term research has, unfortunately, dispelled this belief.
Some degree of fear can be a good thing. An awareness that breast cancer can come back often prompts people to be careful with follow-up appointments and to pursue healthy lifestyle changes to reduce risk. Yet, too much fear can be paralyzing.
If you’re struggling with this fear, seeking professional help can be wise. And in fact, there have even been studies linking psychological support with survival.
You May Like: Lymphatic Cancer Stage 3
Staging And Grading Of Breast Cancer
Knowing the stage and grade of the cancer helps your doctors plan the best treatment for you.
On this page
Your specialist doctor needs certain information about the cancer to advise you on the best treatment for you. This includes:
- the stage of the cancer
- the grade of the cancer
- whether the cancer has receptors for hormones or a protein called HER2.
This information comes from the results of all the tests you have had, including:
- the biopsy, when the tissue was examined
- other tests that were done on the cells.
Your specialist doctor and nurse will talk to you about this. They will explain how it helps you and your doctor decide on your treatment plan.
We understand that waiting to know the stage and grade of your cancer can be a worrying time. Were here if you need someone to talk to. You can:
Breast Cancer May Come Back Even Many Years After Treatment
- Tags:Postmenopausal, Pre- or Perimenopausal, Early-stage: Stage IA, Early-stage: Stage IB, Early-stage: Stage IIA, Early-stage: Stage IIB, Early-stage: Stage IIIA, Progesterone-Receptor Positive, Estrogen-Receptor Positive, Planning/Considering Hormonal Therapy, Invasive or Infiltrating Ductal Carcinoma, Invasive or Infiltrating Lobular Carcinoma, Luminal A Breast Cancer, and Luminal B Breast Cancer
A study shows that there is a risk of breast cancer coming back even many years after surgery and other treatments to reduce that risk.
The researchers looked at the health histories of almost 3,000 women who didn’t have early-stage breast cancer come back during the 5 years after diagnosis and initial treatment. Breast cancer that comes back within 5 years of diagnosis and initial treatment is called “early recurrence.” Breast cancer that comes back more than 5 years after diagnosis and initial treatment is called “late recurrence.”
Ten years after initial diagnosis and treatment, 11% of the women in the study had a late recurrence. At 15 years after initial diagnosis and treatment, 20% of the women had a late recurrence.
The study showed that the risk of late recurrence was more likely when:
- the cancer was later stage at the time of diagnosis the risk of late recurrence at 10 years after initial diagnosis and treatment was:
- 7% with stage I cancer
- 11% with stage II
- 13% with stage III
Recommended Reading: Can Breast Cancer Be Cured
Metastasis Is A Highly Inefficient Yet Lethal Process
In the next few sections, we introduce the concept of tumour dormancy and discuss its ties with DTC dissemination in order to highlight how its reversible nature might alter the equilibrium between unsuccessful and successful metastases, thus possibly dictating the timing of metastatic relapse, or whether relapse occurs at all. We then focus on two key determinants of relapse in HR+ breast cancer: the extrinsic effect of targeted therapy, and the consequences of intrinsic HR function modulation.
Signs Of Breast Cancer Recurrence
The signs of cancer recurrence depend on where the cancer resurfaces. You might not see or feel any signs of a local recurrence, and, if you do, it will probably be a slight change in or around your breast or underarm area. More often than not, your provider might find evidence of a local recurrence during a physical exam or mammogram.
A distant recurrence will typically produce some symptoms, but because many of those breast cancer symptoms are common to other health problems, it can be hard to tell if theyre due to a distant recurrence or something else. Have an open conversation with your cancer care team about any symptoms youre having, especially if they last more than two weeks.
Pay special attention to these symptoms, which could signal a cancer recurrence:
- Blood in your urine or stools
- Any new lumps or areas of swelling
Don’t Miss: What Is Stage 3a Cancer
Symptoms Of Lobular Breast Cancer
Lobular breast cancer sometimes begins without symptoms. It may show as an abnormal area on a mammogram, which leads to further examination.
Spotting ILC on a mammogram can be difficult because the cancer cells spread in a line rather than in a distinctive lump, as in IDC. Magnetic resonance imaging imaging is reported to provide more sensitive images that may show the cancer better.
The first symptom of ILC is sometimes a thickening or hardening of a portion of the breast. This thickening can be felt by touch, but it feels different from the classic lump associated with IDC, the more common breast cancer.
Other symptoms of ILC may include:
- swelling or fullness in a part of the breast, or in the whole breast
- a change in the skin texture in a part of the breast
- dimpling in the breast
The exact cause of ILC is currently unknown. But there are some risk factors that are associated with ILC. These can include:
- being female
- older age
- taking hormone replacements, for menopause for example
Although people can be diagnosed with lobular breast cancer at any age, its most common in women ages 55 years and older. Research suggests that hormone replacement therapy after menopause, especially with progesterone, may increase the risk of this type of cancer.
Am I Still At Risk Of Local Recurrence If I Have Had A Mastectomy
Yes. Local recurrence can also happen after a mastectomy, although the likelihood is usually low.
Some of the signs of local recurrence after mastectomy include
- A lump or raised bump in or under the skin, especially near the previous mastectomy scar
- Changes to the skin, including redness or thickening
After reconstruction a local recurrence can appear at the suture line of the flap or in front of the implant. When its in the skin itself, it is red and raised. Reconstruction rarely if ever hides a recurrence. With implants, the recurrences are in front of the implant. With a flap, the recurrences are not in the flap itself but along the edge of the breast skin.
Local recurrence after mastectomy is often described as a chest wall recurrence, which isnt entirely accurate because it implies that the cancer is in the muscle or bone. But usually such a recurrence appears in the skin and fat where the breast was before, and only rarely does it include the muscle.
Ninety percent of local recurrences following mastectomy happen within the first five years after the mastectomy. Approximately 20 to 30 percent of women with local recurrences after mastectomy have already been diagnosed with metastatic disease, and another 20 to 30 percent will develop it within a few months of diagnosis. Therefore, just as with local recurrences after breast conservation, tests should be done to look for distant disease.
Read Also: How Breast Cancer Affects The Body
How Common Is Breast Cancer Recurrence
Most local recurrences of breast cancer occur within five years of a lumpectomy. You can lower your risk by getting radiation therapy afterward. You have a 3% to 15% chance of breast cancer recurrence within 10 years with this combined treatment. Based on genetic testing, your provider may recommend additional treatments to further reduce your risk.
Recurrence rates for people who have mastectomies vary:
- There is a 6% chance of cancer returning within five years if the healthcare providers didnt find cancer in axillary lymph nodes during the original surgery.
- There is a one in four chance of cancer recurrence if axillary lymph nodes are cancerous. This risk drops to 6% if you get radiation therapy after the mastectomy.
Breast Cancer Is A Heterogeneous Disease

Based on the presence or absence of the oestrogen receptor and progesterone receptor , and the expression and amplification of the human epidermal growth factor receptor type 2 , breast cancer can be divided into three clinical subtypes: hormone-receptor -positive , HER2-positive and triple-negative ., In the United States, 71% of breast cancers are HR+, 17% are HER2+ and 12% are TN. Following the discovery of five intrinsic molecular subgroups of the disease based on a 50-gene expression classifier luminal A, luminal B, HER2-enriched, basal-like and normal-likeit became apparent that a large degree of unappreciated molecular heterogeneity exists across and within each subtype of breast cancer. While TN and HER2+ patients often present with basal-like and HER2-enriched cancers, respectively, HR+ women are usually diagnosed with luminal A or luminal B tumours. However, despite sharing some common traits, luminal A cancers are generally ER+, PR high and Ki67 low, resulting in low-grade, slow-proliferating neoplasms, whereas luminal B tumours are typically ER+, PR variable and Ki67 variable, translating into more aggressive cancers with a higher proliferative rate.
Recommended Reading: Breast Cancer Remission Rate
Who Is At Risk Of Breast Cancer Recurrence
Everyone who has received a breast cancer diagnosis is at risk of recurrence, however the risk differs markedly depending on a number of factors listed below. Some breast cancers, when diagnosed very early when small and without lymph node involvement, have an excellent prognosis and are very unlikely to recur. On the contrary, larger cancers, with lymph node involvement or with a more invasive behaviour, are unfortunately at a higher risk of recurrence.
What Should A Person With Stage 0 Or Stage 1 Breast Cancer Expect Regarding Treatment
Even though Stage 0 breast cancer is considered non-invasive, it does require treatment, typically surgery or radiation, or a combination of the two. Chemotherapy is usually not part of the treatment regimen for earlier stages of cancer.
Stage 1 is highly treatable, however, it does require treatment, typically surgery and often radiation, or a combination of the two. Additionally, you may consider hormone therapy, depending on the type of cancer cells found and your additional risk factors. Like stage 0, Chemotherapy is often not necessary for earlier stages of cancer.
Material on this page courtesy of National Cancer Institute
You May Like: Lumpectomy And Chemo
Distant Recurrence Risk Of Hormone
- Tags:Estrogen-Receptor Positive, Progesterone-Receptor Positive, Lymph Nodes Removed, 0 Involved, Lymph Nodes Removed, 1-9 Involved, Preparing for/Undergoing Hormonal Therapy, and Hormonal Therapy After Surgery
After surgery, women diagnosed with early-stage, hormone-receptor-positive breast cancer usually take hormonal therapy medicine to reduce the risk of the cancer coming back . Recurrence can be local , regional , or distant/metastatic .
Hormonal therapy given after surgery is called adjuvant hormonal therapy.
Hormonal therapy medicines work in two ways:
There are several types of hormonal therapy medicines. Tamoxifen, a selective estrogen receptor modulator , is one of the most well-known. Tamoxifen can be used to treat both premenopausal and postmenopausal women. The aromatase inhibitors:
- Arimidex
- Aromasin
- Femara
have been shown to be more effective at reducing recurrence risk in postmenopausal women and are now used more often than tamoxifen to treat women whove gone through menopause.
For many years, the standard of care was for a woman to take hormonal therapy for 5 years after breast cancer surgery. In 2012 and 2013, large studies found that 10 years of tamoxifen was better than 5 because it:
- lowered the incidence of breast cancer recurrence
- reduced the number of deaths from breast cancer
- improved overall survival
The women were all younger than 75 when they were first diagnosed, and all were diagnosed between 1976 and 2011.
None of the cancers were metastatic.
Answers From The Community
-
Carool
First, I believe that, when it is said that, say, 95% of Stage 1 breast cancer patients have a 5-year survival rate, it means that 95% of those with Stage 1 breast cancer will survive for AT LEAST 5 years. Most of those people will go on to live for many years after that.
With regard to chemo, I was Stage 1 , but my breast cancer was HER2-positive , so my oncologist recommended four rounds of chemo . Nowadays, there is Herceptin for HER2+ patients, but 15 years ago, when I was diagnosed, Herceptin was given to treat only metastatic disease. Many factors are involved in whether or not chemo is recommended .
See what your oncologist recommends. I’d advise not making up your mind until you know more. Chemo is doable, and it’s best to use all tools in the toolbox, even though some of them aren’t very appealing. All the best to you – Carool
cbanks
These are great questions and suggest talking with your oncologist. For me, I support what our friends above have mentioned. I wanted the cancer gone so I did and still do whatever the doc recommends. For me I asked allot of questions, asked for advise and made the decions . It is important to have comfort level and trust with your doctor. I found by having that It really made treatment and after treatment less stressful. Good luck with your decisions and look forward to hearing more of your journey. Peace!
Read Also: Malignant Neoplasm Of Breast Meaning
How A Breast Cancers Stage Is Determined
Your pathology report will include information that is used to calculate the stage of the breast cancer that is, whether it is limited to one area in the breast, or it has spread to healthy tissues inside the breast or to other parts of the body. Your doctor will begin to determine this during surgery to remove the cancer and look at one or more of the underarm lymph nodes, which is where breast cancer tends to travel first. He or she also may order additional blood tests or imaging tests if there is reason to believe the cancer might have spread beyond the breast.
The breast cancer staging system, called the TNM system, is overseen by the American Joint Committee on Cancer . The AJCC is a group of cancer experts who oversee how cancer is classified and communicated. This is to ensure that all doctors and treatment facilities are describing cancer in a uniform way so that the treatment results of all people can be compared and understood.
In the past, stage number was calculated based on just three clinical characteristics, T, N, and M:
- the size of the cancer tumor and whether or not it has grown into nearby tissue
- whether cancer is in the lymph nodes
- whether the cancer has spread to other parts of the body beyond the breast
Numbers or letters after T, N, and M give more details about each characteristic. Higher numbers mean the cancer is more advanced. Jump to more detailed information about the TNM system.
Jump to a specific breast cancer stage to learn more: