Tests Are Used To Screen For Different Types Of Cancer When A Person Does Not Have Symptoms
Scientists study screening tests to find those with the fewest harms and most benefits. Cancer screening trials also are meant to show whether early detection helps a person live longer or decreases a persons chance of dying from the disease. For some types of cancer, the chance of recovery is better if the disease is found and treated at an early stage.
What Is Breast Cancer Staging
To determine the stage of your cancer, doctors look at how large your tumor is, where it is, and if it has spread. They also look at your medical history, physical exams, diagnostic tests, and tests of your tumor and lymph nodes.
- Early-stage breast cancer includes stages 0, I, II and IIIA .
- In stage 0, there are abnormal cells in the ducts or lobes of the breast. They have not broken through the wall of the duct or spread.
- In stages I, II, and IIIA, there is a tumor. It may have spread to lymph nodes under the arm, but it has not spread anywhere else.
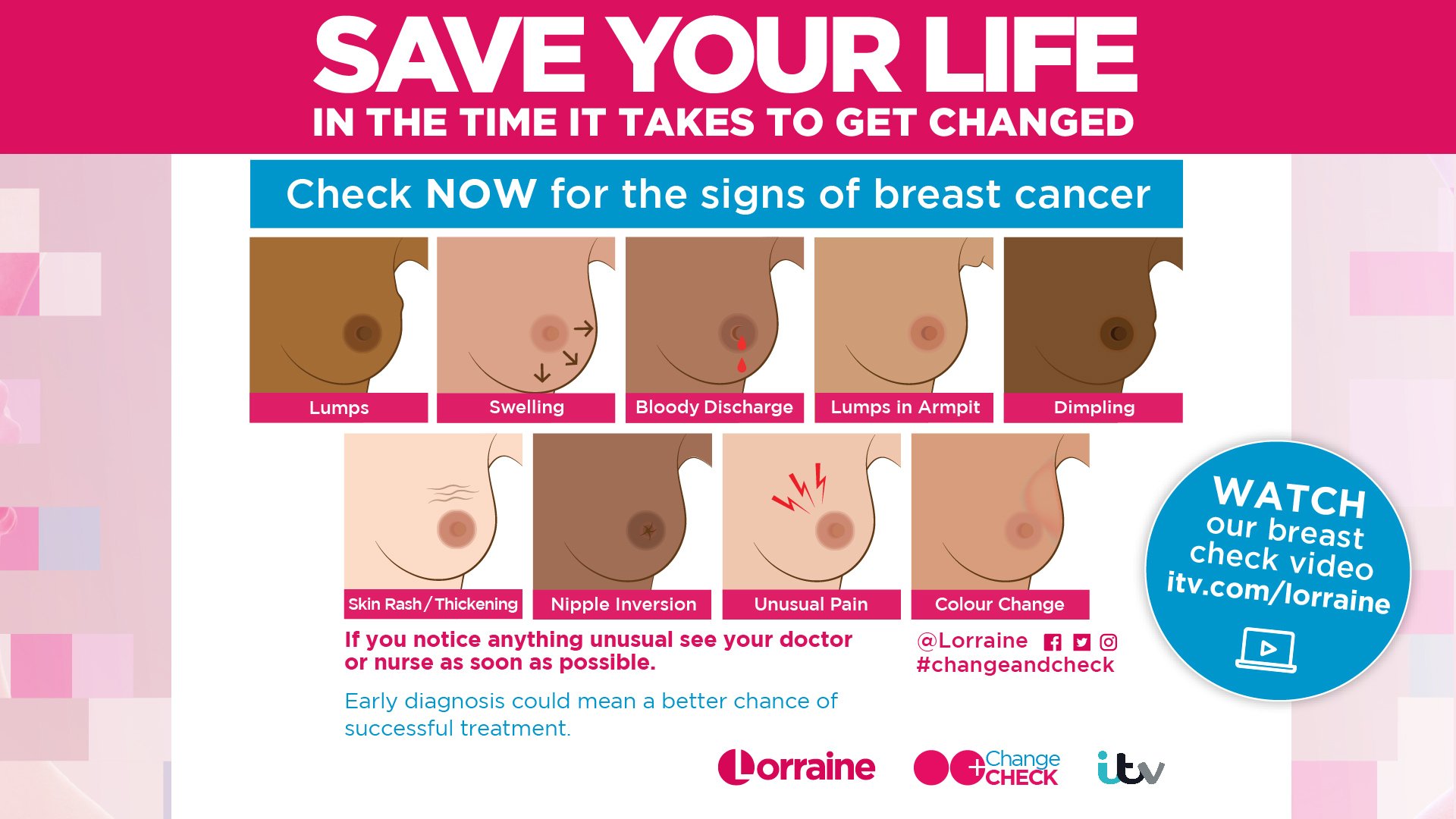
American Cancer Society Breast Self Exam Instructions
The best time for breast self examination is about a week after your period ends, when your breasts are not swollen or tender. If you are not having regular periods, do BSE on the same day every month.
- Lie down with a pillow under your right shoulder and place your right arm behind your head.
- Use the finger pads of the three middle fingers on your left hand to feel for lumps in the right breast.
- Press firmly enough to know how your breast feels. A firm ridge in the lower curve of each breast is normal. If you’re not sure how hard to press, talk with your doctor or nurse.
- Move around the breast in a circular, up and down line, or wedge pattern. Be sure to do it the same way every time, check the entire breast area, and remember how your breast feels from month to month.
- Repeat the exam on your left breast, using the finger pads of the right hand.
- If you find any changes, see your doctor right away.
- Repeat the examination of both breasts while standing, with one arm behind your head. The upright position makes it easier to check the upper and outer part of the breasts . This is where about half of breast cancers are found. You may want to do the standing part of the BSE while you are in the shower. Some breast changes can be felt more easily when your skin is wet and soapy.
- Right after your BSE, check your breasts in front of a mirror for any dimpling of the skin, changes in the nipple, redness, or swelling.
Also Check: What Is The Prognosis For Stage 4 Breast Cancer
The Harms Of Mammography Include The Following:
False-positive test results can occur.
Screening test results may appear to be abnormal even though no cancer is present. A false-positive test result is usually followed by more tests , which also have risks.
When a breast biopsy result is abnormal, getting a second opinion from a different pathologist may confirm a correct breast cancer diagnosis.
Most abnormal test results turn out not to be cancer. False-positive results are more common in the following:
- Younger women .
- Women who have had previous breast biopsies.
- Women with a family history of breast cancer.
- Women who take hormones for menopause.
False-positive results are more likely the first time screening mammography is done than with later screenings. For every ten women who have a single mammogram, one will have a false-positive result. The chance of having a false-positive result goes up the more mammograms a woman has. Comparing a current mammogram with a past mammogram lowers the risk of a false-positive result.
The skill of the radiologist also can affect the chance of a false-positive result.
False-positive results can lead to extra testing and cause anxiety.
If a mammogram is abnormal, more tests may be done to diagnose cancer. Women can become anxious during the diagnostic testing. Even if it is a false-positive test and cancer is not diagnosed, the result can lead to anxiety anywhere from a few days to years later.
False-negative test results can delay diagnosis and treatment.
Does A Benign Breast Condition Mean That I Have A Higher Risk Of Getting Breast Cancer
Benign breast conditions rarely increase your risk of breast cancer. Some women have biopsies that show a condition called hyperplasia . This condition increases your risk only slightly.
When the biopsy shows hyperplasia and abnormal cells, which is a condition called atypical hyperplasia, your risk of breast cancer increases somewhat more. Atypical hyperplasia occurs in about 5% of benign breast biopsies.
Recommended Reading: What Is A Malignant Neoplasm Of The Breast
Does Breast Cancer Affect Women Of All Races Equally
All women, especially as they age, are at some risk for developing breast cancer. The risks for breast cancer in general arent evenly spread among ethnic groups, and the risk varies among ethnic groups for different types of breast cancer. Breast cancer mortality rates in the United States have declined by 40% since 1989, but disparities persist and are widening between non-Hispanic Black women and non-Hispanic white women.
Statistics show that, overall, non-Hispanic white women have a slightly higher chance of developing breast cancer than women of any other race/ethnicity. The incidence rate for non-Hispanic Black women is almost as high.
Non-Hispanic Black women in the U.S. have a 39% higher risk of dying from breast cancer at any age. They are twice as likely to get triple-negative breast cancer as white women. This type of cancer is especially aggressive and difficult to treat. However, it’s really among women with hormone positive disease where Black women have worse clinical outcomes despite comparable systemic therapy. Non-Hispanic Black women are less likely to receive standard treatments. Additionally, there is increasing data on discontinuation of adjuvant hormonal therapy by those who are poor and underinsured.
In women under the age of 45, breast cancer is found more often in non-Hispanic Black women than in non-Hispanic white women.
What Is A Breast Self
Breast self-exam is a step-by-step process performed by a woman to check and examine her breast and underarm areas for any changes. BSE, unfortunately, is not a perfect procedure for determining the presence of breast cancer. Therefore, BSE should not be used in place of, but in addition to, other forms of breast cancer screening, such as mammograms.
Recommended Reading: What Is Treatment For Stage 2 Breast Cancer
Tests To Stage Breast Cancer
After youre diagnosed with breast cancer, the next step is identifying your stage. Knowing the stage is how your doctor determines the best course of treatment. Staging depends on the size and location of the tumor and whether it has spread outside your breast to nearby lymph nodes and other organs. The speed of growth and the likelihood that the growth will spread is another component of staging.
Cancer cells that spread to lymph nodes can travel to different parts of your body. During the staging process, your doctor may order a complete blood panel including, liver function and kidney function tests, and a mammogram of your other breast to check for signs of a tumor. A doctor may also test for breast cancer tumor markers, CA 27-29 and CA 15-3.
Your doctor may also use any of the following tests to determine the extent of your cancer and assist with diagnosis:
Taking Charge: Screening For Breast Cancer
When health professionals talk about screening for a disease, they mean using some sort of test to see if a person has a particular condition. The purpose of screening is to detect and treat cancer earlier, because, in general, early treatment improves the chances of survival. There are several screening tests for breast cancer. Which ones you use depend on your age and other risk factors.
Also Check: What Is Stage 3a Breast Cancer
How To Check Breasts By Youself
You can check your breasts in the shower, lying down or in front of a mirrow.
In the Shower: While you’re in the shower or bath, it is easier to check your breasts for lumps because your hands are wet .
There are few steps that will help you to check your breast:
Lying down:Women with larger breasts may find it easier to check for lumps when lying down, since their breasts will be flatter. There are few steps for breast self-exam by lying down:
In front of a mirror:Checking your breast in front of the mirror is a good way to see your breast clearly. During this procedure check your skin for inflammation, irritation, or rashes. Look for discharge from the nipples, which might indicate infection. There are few steps that will help you for checking breasts in front of a mirror:
Undergoing Medical Screening For Breast Cancer
Don’t Miss: Is Weight Gain A Symptom Of Breast Cancer
How Do Tamoxifen Raloxifene Anastrozole And Exemestane Reduce The Risk Of Breast Cancer
If you are at increased risk for developing breast cancer, four medications tamoxifen , raloxifene , anastrozole , and exemestane may help reduce your risk of developing this disease. These medications act only to reduce the risk of a specific type of breast cancer called estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. This type of breast cancer accounts for about two-thirds of all breast cancers.
Tamoxifen and raloxifene are in a class of drugs called selective estrogen receptor modulators . These drugs work by blocking the effects of estrogen in breast tissue by attaching to estrogen receptors in breast cells. Because SERMs bind to receptors, estrogen is blocked from binding. Estrogen is the fuel that makes most breast cancer cells grow. Blocking estrogen prevents estrogen from triggering the development of estrogen-receptor-positive breast cancer.
Anastrozole and exemestane are in a class of drugs called aromatase inhibitors . These drugs work by blocking the production of estrogen. Aromatase inhibitors do this by blocking the activity of an enzyme called aromatase, which is needed to make estrogen.
Who Gets Breast Cancer

Breast cancer is the most common cancer among women other than skin cancer. Increasing age is the most common risk factor for developing breast cancer, with 66% of breast cancer patients being diagnosed after the age of 55.
In the US, breast cancer is the second-leading cause of cancer death in women after lung cancer, and it’s the leading cause of cancer death among women ages 35 to 54. Only 5 to 10% of breast cancers occur in women with a clearly defined genetic predisposition for the disease. The majority of breast cancer cases are “sporadic, meaning there is no definitive gene mutation.
You May Like: Mammary Ductal Carcinoma
Tests To Determine Specific Types Of Treatment
You’ll also need tests that show whether the cancer will respond to specific types of treatment.
The results of these tests can give your doctors a more complete picture of the type of cancer you have and how to treat it.
In some cases, breast cancer cells can be stimulated to grow by hormones that occur naturally in your body, such as oestrogen and progesterone.
If this is the case, the cancer may be treated by stopping the effects of the hormones or by lowering the level of these hormones in your body. This is known as hormone therapy.
During a hormone receptor test, a sample of cancer cells will be taken from your breast and tested to see if they respond to either oestrogen or progesterone.
If the hormone is able to attach to the cancer cells using a hormone receptor, they’re known as hormone-receptor positive.
While hormones can encourage the growth of some types of breast cancer, other types are stimulated by a protein called human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 .
These types of cancers can be diagnosed using a HER2 test and are treated with medicine that blocks the effects of HER2. This is known as targeted therapy.
Want to know more?
How Much Do Anastrozole And Exemestane Lower The Risk Of Breast Cancer
Studies have shown that both anastrozole and exemestane can lower the risk of breast cancer in postmenopausal women who are at increased risk of the disease.
In one large study, taking anastrozole for five years lowered the risk of developing estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer by 53 percent. In another study, taking exemestane for three years lowered the risk of developing estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer by 65 percent.
The most common side effects seen with anastrazole and exemestane are joint pains, decreased bone density, and symptoms of menopause .
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 12/31/2018.
References
Read Also: 2cm Breast Cancer
Breast Cancer Is The Second Leading Cause Of Death From Cancer In American Women
Women in the United States get breast cancer more than any other type of cancer except for skin cancer.
Breast cancer is more likely to occur as a woman ages. It occurs more often in White women than in Black women, but Black women die from breast cancer more often than White women.
Breast cancer rarely occurs in men. Because men with breast cancer usually have a lump that can be felt, screening tests are not likely to be helpful.
How Is A Breast Cancer Treated
The type of treatment recommended depends on the size and type of the tumor, its growth rate, and the general health of the patient. Treatment options include:
- Surgery: Surgery can consist of mastectomy or breast conservation therapy .
- Mastectomy is an operation to remove the entire breast, and usually the entire nipple. Often an axillary sampling is also done which removes the glands under the arm called axillary nodes. The surgeon may evaluate just one or two nodes or may perform a more extensive axillary dissection to check for disease spread. Mastectomy sometimes requires a hospital stay. A drainage tube is sometimes temporarily left in the surgical cavity after a mastectomy to help prevent fluid accumulation. Women who undergo a mastectomy have the option of breast reconstruction.
- BCT surgery removes the breast tumor and a margin of surrounding normal tissues. Radiation therapy usually follows lumpectomy to eliminate any microscopic cancer cells in the remaining breast tissue. The purpose of BCT is to give women the same cure rate they would have if they were treated with a mastectomy but to leave the breast intact, with an appearance and texture as close as possible to what they had before treatment. The surgeon may remove some lymph nodes by performing a sentinel lymph node procedure or axillary dissection at the same time as the lumpectomy procedure or later.
You May Like: What Does Invasive Breast Cancer Mean
Breast Cancer Cell Lines
Part of the current knowledge on breast carcinomas is based on in vivo and in vitro studies performed with cell lines derived from breast cancers. These provide an unlimited source of homogenous self-replicating material, free of contaminating stromal cells, and often easily cultured in simple standard media. The first breast cancer cell line described, BT-20, was established in 1958. Since then, and despite sustained work in this area, the number of permanent lines obtained has been strikingly low . Indeed, attempts to culture breast cancer cell lines from primary tumors have been largely unsuccessful. This poor efficiency was often due to technical difficulties associated with the extraction of viable tumor cells from their surrounding stroma. Most of the available breast cancer cell lines issued from metastatic tumors, mainly from pleural effusions. Effusions provided generally large numbers of dissociated, viable tumor cells with little or no contamination by fibroblasts and other tumor stroma cells.Many of the currently used BCC lines were established in the late 1970s. A very few of them, namely MCF-7, T-47D, MDA-MB-231 and SK-BR-3, account for more than two-thirds of all abstracts reporting studies on mentioned breast cancer cell lines, as concluded from a Medline-based survey.
Metabolic markers