Physical Emotional And Social Effects Of Cancer
In general, cancer and its treatment cause physical symptoms and side effects, as well as emotional, social, and financial effects. Managing all of these effects is called palliative care or supportive care. It is an important part of your care that is included along with treatments intended to slow, stop, or eliminate the cancer.
Supportive care focuses on improving how you feel during treatment by managing symptoms and supporting patients and their families with other, non-medical needs. Any person, regardless of age or type and stage of cancer, may receive this type of care. And it often works best when it is started right after a cancer diagnosis. People who receive supportive care along with treatment for the cancer often have less severe symptoms, better quality of life, and report that they are more satisfied with treatment.
Supportive care treatments vary widely and often include medication, nutritional changes, relaxation techniques, emotional and spiritual support, and other therapies.
-
Music therapy, meditation, stress management, and yoga for reducing anxiety and stress.
-
Meditation, relaxation, yoga, massage, and music therapy for depression and to improve other mood problems.
-
Meditation and yoga to improve general quality of life.
-
Acupressure and acupuncture to help with nausea and vomiting from chemotherapy.
Radiation Therapy Uses High Energy X
Its a localised treatment affecting only the area which is specifically targeted. Although some healthy tissue may be in the treatment area, it generally has the ability to repair itself, unlike cancer cells.
In early breast cancer, radiation therapy is used with the aim of getting rid of any malignant or pre-cancerous cells remaining in the breast following partial mastectomy or lumpectomy. This reduces the risk of developing a local recurrence of cancer in the breast in the future. Radiation therapy is also used to treat the chest wall after mastectomy if the cancer has high-risk features.
The regional lymph nodes in the axilla , supraclavicular fossa or internal mammary chain may also be treated in some cases.
In these settings, large international trials have demonstrated that radiation therapy reduces the incidence of local breast cancer recurrence.
Radiation therapy is usually given after surgery, once the wounds have healed. For people needing chemotherapy, radiation is given after that treatment has been completed.
Why Does Radiation Therapy Cause Side Effects
In this type of treatment, high doses of radiation therapy are used to destroy cancer cells. Side effects come from damage to healthy cells and tissues near the treatment area.
There have been major research advances in radiation therapy over recent years that have made it more precise. This has reduced this treatment’s side effects compared to radiation therapy techniques used in the past.
Some people experience few or no side effects from radiation therapy. Other people experience more severe side effects. Reactions to radiation therapy often start during the second or third week of treatment. Or, they may last for several weeks after the final treatment. Some side effects may be long term. Talk with your treatment team about what you can expect.
Also Check: Can Breast Cancer Cause Shortness Of Breath
Radiation Therapy Timing And Breast Reconstruction
The timing of radiation treatment in your overall breast cancer treatment plan depends on your individual situation and the characteristics of the breast cancer.
In many cases, radiation therapy is given after surgery. If chemotherapy is planned after surgery, radiation usually follows chemotherapy.
If youre having mastectomy and have decided to have breast reconstruction, its important to know that radiation can cause a reconstructed breast to lose volume and change color, texture, and appearance.
In particular, radiation therapy is known to cause complications with implant reconstruction. Research also suggests that a reconstructed breast may interfere with radiation therapy reaching the area affected by cancer, though this can vary on a case-by-case basis.
For these reasons, some surgeons advise waiting until after radiation and other treatments, such as chemotherapy, are completed before breast reconstruction surgery is done.
Other surgeons may recommend a more staged approach, which places a tissue expander after mastectomy to preserve the shape of the breast during radiation treatments. Once radiation is completed and the tissues have recovered, the expander that was used to maintain the shape of the breast is removed and replaced with tissue from another part of the body or a breast implant.
Changes In The Shape Size And Feel Of The Breast

In time radiotherapy can cause the breast tissue to change shape or shrink in size a little. This can happen to your natural breast tissue or a reconstructed breast.
After radiotherapy, the breast might feel hard and less stretchy. This is due to a side effect called radiation fibrosis. This side effect is usually mild.
Sometimes the breast can shrink a little over time. This is because radiotherapy can make the breast tissue contract so that the breast gradually gets smaller.
An implant in a reconstructed breast can become hard and may need replacing.
Let your surgeon know of any changes, they may be able to do some minor surgical adjustments to improve the look.
You May Like: What Does Breast Cancer Affect
When Radiotherapy Is Used
Radiotherapy may be used in the early stages of cancer or after it has started to spread.
It can be used to:
- try to cure the cancer completely
- make other treatments more effective for example, it can be combined with chemotherapy or used before surgery
- reduce the risk of the cancer coming back after surgery
- relieve symptoms if a cure is not possible
Radiotherapy is generally considered the most effective cancer treatment after surgery, but how well it works varies from person to person.
Pain And Skin Changes
During and just after treatment, your treated breast may be sore. Talk with your health care provider about using mild pain relievers such as ibuprofen, naproxen or acetaminophen to ease breast tenderness.
The treated breast may also be rough to the touch, red , swollen and itchy. Sometimes the skin may peel, as if sunburned. Your health care provider may suggest special creams to ease this discomfort.
Sometimes the skin peels further and the area becomes tender and sensitive. Its most common in the skin folds and the underside of the breast. If this occurs, let your radiation team know. They can give you creams and pads to make the area more comfortable until it heals.
Fatigue is common during radiation therapy and may last for several weeks after treatment ends.
Fatigue is mainly a short-term problem, but for some, it can persist .
You may feel like you dont have any energy and may feel tired all of the time. Resting may not help.
Regular exercise, even just walking for 20 minutes every day, may help reduce fatigue . Getting a good nights sleep is also important.
Talk with your health care provider if you are fatigued or have insomnia .
Learn more about fatigue and insomnia.
You May Like: What Stage Is Breast Cancer In Lymph Nodes
Higher Risk Of Infections
All breast cancer therapies can weaken your immune response and raise your risk of infection. Common areas for infection include:
Chemotherapy and radiation therapy for breast cancer can stop your body from making white blood cells, which fight infections. Try to stay out of large crowds and away from sick adults and children for 7 to 10 days after you have chemotherapy. That’s when you usually have the fewest white blood cells.
Contact your doctor right away if you get sick. You might notice:
- Colored mucus in saliva or nasal drainage
- Fever of 100.5 degrees F or higher
- Sore or burning throat
- Swelling, redness, warmth, or pus at injury site
- Cough or shortness of breath
Your doctor might recommend antibiotics as a precaution. Or they may suggest you get a flu shot before you start chemotherapy.
If your white blood cell counts are too low, your doctor may give you a treatment called G-CSF or GM-CSF .
Association Of Antihormonal Therapy With Long
Compared to patients who did not receive endocrine therapy, those who used antihormonal drugs more often reported hot flashes and vaginal dryness , while hair loss was less common . Dry eyes and visual disturbances were experienced by roughly one-third of patients taking these drugs.
Among the subclasses of antihormonal drugs, aromatase inhibitors were associated with a relatively high prevalence of joint pain, whereas loss of libido was prevalent with gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogs .
Don’t Miss: How Big Are The Lumps In Breast Cancer
How Breast Cancer Is Treated
In cancer care, doctors specializing in different areas of cancer treatmentsuch as surgery, radiation oncology, and medical oncologywork together with radiologists and pathologists to create a patients overall treatment plan that combines different types of treatments. This is called a multidisciplinary team. Cancer care teams include a variety of other health care professionals, such as physician assistants, nurse practitioners, oncology nurses, social workers, pharmacists, counselors, nutritionists, and others. For people older than 65, a geriatric oncologist or geriatrician may also be involved in their care. Ask the members of your treatment team who is the primary contact for questions about scheduling and treatment, who is in charge during different parts of treatment, how they communicate across teams, and whether there is 1 contact who can help with communication across specialties, such as a nurse navigator. This can change over time as your health care needs change.
A treatment plan is a summary of your cancer and the planned cancer treatment. It is meant to give basic information about your medical history to any doctors who will care for you during your lifetime. Before treatment begins, ask your doctor for a copy of your treatment plan. You can also provide your doctor with a copy of the ASCO Treatment Plan form to fill out.
Learn more about making treatment decisions.
When Is Radiation Therapy Recommended
Radiation therapy is usually recommended:
- after breast-conserving surgery
- after a mastectomy if pathology results suggest the risk of recurrence is high or if the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes, you may have radiation to the chest wall and lymph nodes above the collarbone
- if the sentinel node has cancer cells you may have radiation to the armpit instead of axillary dissection.
You will usually start radiation therapy within eight weeks of surgery. If youre having chemotherapy after surgery, radiation therapy will begin about 34 weeks after chemotherapy has finished. In some cases, radiation therapy may be offered after neoadjuvant chemotherapy and before surgery.
Recommended Reading: Does Getting Breast Implants Increase Risk Of Cancer
Radiation Therapy After Mastectomy
A mastectomy is a surgery to remove the entire breast. Rarely is radiation therapy required for these patients. However, your oncologist might recommend it if there are enough risk factors for the cancer returning in the future, such as the number of affected lymph nodes, your BRCA gene status, and the size and location of the cancer.
Changes To The Look And Feel Of The Breast
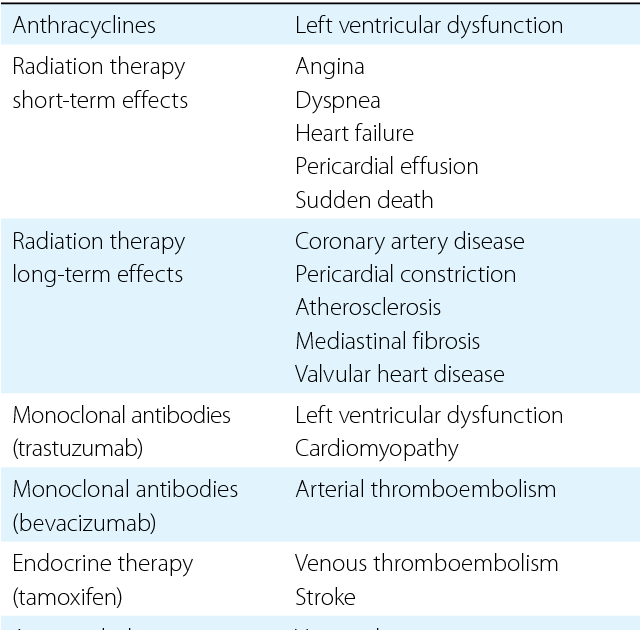
Radiation therapy may cause the breast to feel firmer and to be slightly smaller in volume. There may be some permanent discolouration of the skin in the treatment area and visible small red blood vessels may develop.
Your radiation oncologist will discuss with you the very small risks of long-term damage to normal tissue in the treatment area, such as changes in the lungs underlying the chest wall, rib fracture, heart problems if you have a left-sided breast cancer, nerve damage causing weakness in the arm, or lymphoedema of the arm or breast. There is an extremely small risk of inducing a second cancer in the treatment area many years after your breast cancer radiotherapy.
It is felt that the benefit of radiation therapy using modern radiation techniques outweighs the potential risks of treatment and your radiation oncologist will discuss this with you.
Read Also: Can Lung Cancer Spread To The Breast
Pain In The Breast Or Chest Area
You may have aches, twinges or sharp pains in the breast or chest area.
Although these are usually mild, they can continue for months or even years, but they usually become milder and less frequent over time.
You may also have stiffness and discomfort around the shoulder and breast or chest area during and after treatment.
Continuing to do arm and shoulder exercises during radiotherapy and for several months afterwards may help minimise or prevent stiffness or discomfort.
Short Term Side Effects
The following list includes some of the most common side effects of radiation therapy for breast cancer. Remember that the treatment can affect each patient differently and you may not experience these problems. Talk with your care team about what you can expect from your specific treatment.
- Skin irritation: Your skin may become red, irritated, dry, or sensitive. This may start to look like a sunburn. The skin may also become darker under the arm and under the breast. In more severe cases, the skin can peel, and moist ulcers can occur. Treat the skin gently to avoid further irritation, and bathe carefully using only warm water and mild soap. Avoid perfumed or scented lotions or soaps, as these may cause further irritation. Avoid spending too much time in the sun, which can worsen the irritation.
- Mild fatigue that generally gets better a month or two after treatment ends.
- Some patients have mild tenderness in the breast or chest wall.
- Some patients have swelling to the ipsilateral arm that may make the movement of that arm more difficult. Any swelling should be brought to the attention of your oncology team.
- Reduced blood counts, including neutropenia , anemia , or thrombocytopenia .
You May Like: When To Start Breast Cancer Screening
What Is Radiation Recall
Radiation recall is a rash that looks like a severe sunburn. It is rare but it can happen when certain types of chemotherapy are given during or soon after external-beam radiation therapy.
The rash appears on the part of the body that received radiation therapy. Symptoms may include redness, tenderness, swelling, wet sores, and peeling skin.
Typically, these effects start within days or weeks of starting radiation therapy. But they can also appear months or years later. Doctors treat radiation recall with medications called corticosteroids. Rarely, it may be necessary to wait until the skin heals to continue with chemotherapy.
Breast Cancer: Types Of Treatment
Have questions about breast cancer? Ask here.
ON THIS PAGE: You will learn about the different types of treatments doctors use for people with breast cancer. Use the menu to see other pages.
This section explains the types of treatments, also known as therapies, that are the standard of care for early-stage and locally advanced breast cancer. Standard of care means the best treatments known. When making treatment plan decisions, you are encouraged to discuss with your doctor whether clinical trials are an option. A clinical trial is a research study that tests a new approach to treatment. Doctors learn through clinical trials whether a new treatment is safe, effective, and possibly better than the standard treatment. Clinical trials can test a new drug and how often it should be given, a new combination of standard treatments, or new doses of standard drugs or other treatments. Some clinical trials also test giving less drug or radiation treatment or doing less extensive surgery than what is usually done as the standard of care. Clinical trials are an option for all stages of cancer. Your doctor can help you consider all your treatment options. Learn more about clinical trials in the About Clinical Trials and Latest Research sections of this guide.
You May Like: Estradiol Does Not Cause Breast Cancer
Where Do I Start
You first will meet with a radiation oncologist to decide if radiation therapy is a recommended treatment option for your particular situation. If you and your doctors decide to proceed, then you will have an extended consultation in which you discuss the details of your treatment. This includes the exact area to treat, the amount of radiation you will receive, the length of treatment time and potential treatment side effects. The radiation oncologist will also answer any questions you may have. These issues vary for each person, so it is important to make an individual treatment plan.
When Does Someone With Breast Cancer Get Radiation Therapy
The timing for radiation therapy depends on several factors. The treatment may take place:
- After a lumpectomy: A lumpectomy removes the cancerous tumor, leaving most of the breast. Radiation therapy lowers your risk of cancer coming back in the remaining breast tissue or nearby lymph nodes as well as reduces your chance of passing away of breast cancer.
- After a mastectomy: Most people dont get radiation therapy after a mastectomy . Your provider may recommend radiation if the tumor was larger than 5 cm if theres cancer in surrounding lymph nodes, skin tissue or muscle or if all the cancer can’t be removed .
- Before surgery: Rarely, healthcare providers use radiation to shrink a tumor before surgery.
- Instead of surgery: Sometimes, providers use radiation therapy to shrink a tumor that they cant surgically remove . A tumor may be unresectable due to its size or location. Or you may not be a candidate for surgery because of concerns about your health.
- To treat cancer spread: Stage 4 breast cancer is cancer that spreads to other parts of the body. Your provider may use radiation therapy to treat cancer that spreads to other parts of the body.
If you had surgery, radiation therapy typically starts about one month after the incision heals if chemotherapy is not received. Some individuals receive chemotherapy after surgery, followed by radiation therapy. You may get the two treatments at the same time.
Recommended Reading: Can Hickeys Give You Breast Cancer