Dont Routinely Use Sentinel Node Biopsy In Clinically Node Negative Women 70 Years Of Age With Early Stage Hormone Receptor Positive Her2 Negative Invasive Breast Cancer
Endocrine therapy is standard treatment for all patients with hormone receptor positive breast cancer. The omission of sentinel lymph node biopsy in patients with non-palpable axillary lymph nodes in those women 70 years of age treated with endocrine therapy does not result in increased rates of locoregional recurrence and does not impact breast cancer mortality. Patients 70 years of age with early-stage, hormone receptor positive, HER2 negative breast cancer and no palpable axillary lymph nodes can be safely treated without axillary staging. Axillary staging can be individually considered, if the results may impact radiation therapy recommendations and/or systemic therapy decisions.
These items are provided solely for informational purposes and are not intended as a substitute for consultation with a medical professional. Patients with any specific questions about the items on this list or their individual situation should consult their physician.
Surgical Technique Of Sentinel Node Analysis
The currently surgical technique of sentinel node analysis is globally accepted . The patient receives an injection of colloid the day before or the morning of the procedure and undergoes a lympho-scintigraphy. A card is given to the surgeon for the result.
On the day of surgery, at the beginning of the operation, the patient is anesthetized, a mini dose of blue patent is injected in peri-areolar and subcutaneously? A mini incision is made and the surgeon with a probe reads the radio activity, and looks for the blue of the ganglion , which is removed and checked with the probe . A noise of radioactivity is given and the piece is sent to the pathologist for the continuation of the examination.
However, it is necessary to discuss the differences between the histological and cytological analysis of a lymph sentinel node during surgery, as the results can be discordant .
Immune Response To The Sentinel Lymph Node In The Setting Of Breast Cancer
Much in the way of studying the immune response in a sentinel lymph node closest to the cancer has led to the findings that breast cancers and melanomas have the ability to down regulate a host’s immune response in the lymph node. The anti-tumor immune functions of the lymph node are blunted by the cancer’s ability to suppress the immune system because of cancer derived cytokines, prostaglandins, gangliosides, and lipoprotein antigens that are transmitted via the lymphatics from the tumor to the lymph nodes.11–14 With the recent interest in immune scores in the tumor microenvironment the immune response in the sentinel node may provide valuable clinical information regarding the host response to breast cancer.
Recommended Reading: How Do Men Get Breast Cancer
Surgery To Remove Lymph Nodes
Breast cancer can spread to other parts of the body. If it does spread, it usually first spreads to the lymph nodes in the armpit close to the breast. These lymph nodes drain the lymphatic fluid from the breast and arm.
It is important to know if there are cancer cells in the lymph nodes in the armpit and how many. This helps the doctors work out the stage of your cancer and plan the best treatment for you.
Summary Of Critical Appraisal

The included guidelines had a clear scope and purpose, the recommendations were specific and unambiguous, the methods used for formulating the recommendations were clearly described in most guidelines, health benefits, side effects, and risks were stated in the recommendations, and the procedures for updating the guidelines provided and target users of the guideline are clearly defined. Other than the ESMO guideline, the methods for searching for and selecting the evidence were clear. This rigour of development and clarity of presentation would increase the users confidence in the accuracy and reliability of the recommendations. Cost factors were considered in two guidelines,, and not in the rest. It was unclear whether the guidelines were piloted among target users, or whether patients views and preferences were sought. All specialties related to the assessment and management of breast cancer were included in the development of the guidelines.
Details of the critical appraisal of the included studies are presented in .
Read Also: Does Breast Cancer Hurt Before Diagnosis
What Happens During A Sentinel Node Biopsy
Once the sentinel lymph node has been identified, a biopsy will be performed to take a sample of tissue for additional testing.
This testing should be able to reveal whether cancer cells have made it to this lymph node. This is done immediately after or at the same time as sentinel node mapping.
During the biopsy, your doctor will make a small incision over the sentinel lymph node. The lymph node is then removed through this incision and sent to a pathologist for testing.
Types Of Lymph Node Surgery
Even if the nearby lymph nodes are not enlarged, they will still need to be checked for cancer. This can be done in two different ways. Sentinel lymph node biopsy is the most common way and only a few lymph nodes are removed. But in some cases, an axillary lymph node dissection , which removes more lymph nodes, might be needed.
Lymph node surgery is often done as part of the main surgery to remove the breast cancer, but sometimes it might be done as a separate operation.
Also Check: What Age Group Is Most Likely To Get Breast Cancer
What Are The Benefits Of Slnb
SNLB helps doctors stage cancers and estimate the risk that tumor cells have developed the ability to spread to other parts of the body. If the sentinel node is negative for cancer, a patient may be able to avoid more extensive lymph node surgery, reducing the potential complications associated with having many lymph nodes removed.
Axillary Lymph Node Dissection
In this procedure, anywhere from about 10 to 40 lymph nodes are removed from the area under the arm and checked for cancer spread. ALND is usually done at the same time as a mastectomy or breast-conserving surgery , but it can be done in a second operation. ALND may be needed:
- If a previous SLNB has shown 3 or more of the underarm lymph nodes have cancer cells
- If swollen underarm or collarbone lymph nodes can be felt before surgery or seen on imaging tests and a FNA or core needle biopsy shows cancer
- If the cancer has grown large enough to extend outside the lymph node
- If the SLNB is positive for cancer cells after chemotherapy was given to shrink the tumor before surgery
You May Like: What Does Stage 4 Metastatic Breast Cancer Mean
When Is Sentinel Node Biopsy Not Recommended
Some patients with breast cancer are still best treated with complete axillary clearance rather than with sentinel node biopsy. Axillary clearance is usually recommended when the cancer is found in the lymph glands on imaging and biopsy before surgery.
In some of these cases, sentinel node biopsy is performed at the time of full axillary clearance. This is to ensure that if the cancer drains to lymph nodes near the collarbone and breast bone areas, these may be sampled.
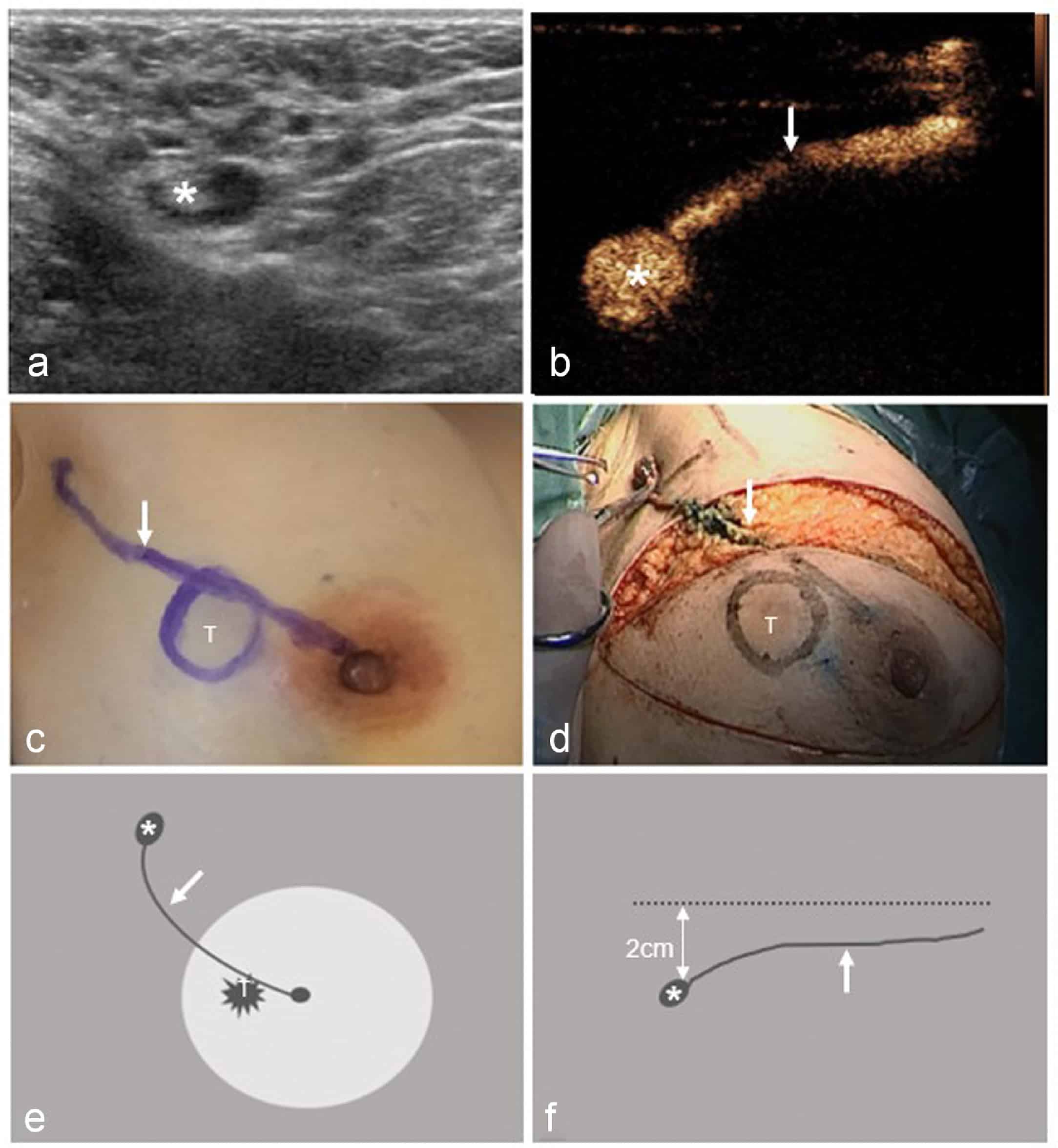
Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy
In a sentinel lymph node biopsy , the surgeon finds and removes the first lymph node to which a cancer is likely to spread . A radioactive substance and/or a blue dye is injected into the tumor, the area around it, or the area around the nipple. Lymph vessels will carry these substances along the same path that the cancer would likely take. The first lymph node the dye or radioactive substance travels to will be the sentinel node.
After the substance has been injected, the sentinel node can be found either by using a special machine to detect radioactivity in the nodes, or by looking for nodes that have turned blue. Sometimes, both methods are used. The surgeon cuts the skin over the lymph node area and removes the node containing the dye or radioactivity.
The few removed lymph nodes are then checked closely in the lab for cancer cells by a pathologist. Sometimes, this is done during the surgery. Because there is a chance that other lymph nodes in the same area will also have cancer if cancer is found in the sentinel lymph node, the surgeon may go ahead with an axillary dissection to remove more lymph nodes while you are still on the operating table. If no cancer cells are seen in the node at the time of the surgery, or if they are not checked by a pathologist at the time of the surgery, they will be examined more closely over the next several days.
Based on the studies that have looked at this, skipping the ALND may be an option for:
You May Like: Which Screening Is Used To Test For Breast Cancer
Potential Risks Or Complications
Like every type of surgical procedure, sentinel lymph biopsy comes with a risk of some complications. Most people have no or mild side effects such as:
If you received blue dye, your urine may change color for the next 24 to 48 hours until the dye can leave your body.
A potentially painful complication of lymph node removal is lymphedema, which is a buildup of lymph fluid that can cause swelling. According to a
, researchers found that the sentinel node identification rates vary depending on which substance is injected. They found that successful identification rates were:
- 100% for dual tracers
- 99.4% for radioisotopes
- 89.1% for blue dye
A positive result on your biopsy suggests that the cancer has spread to the sampled lymph node and may have spread to other organs or lymph nodes.
A negative result suggests that cancer hasnt spread from the original tumor to your lymph nodes or organs.
Its possible to have a false-negative result where cancer cells arent seen in the biopsy even though the cancer has spread beyond its original site.
In a 2020 study, researchers found that sentinel lymph node biopsy correctly identified cancer in 91% of node samples in people with lobular carcinoma of the breast.
Older and obese people tend to have more false negatives than people who are younger or arent obese.
The next step depends on whether your biopsy result is positive or negative. Either way, your healthcare team can help you determine your treatment options.
Analysis Of The Sentinel Node Ganglion Have Revolutionized Breast Cancer Surgery
Aims: detect macro metastases , micro metastases . Isolated tumor cells or clusters 0.2 mm are often only detected by immunohistochemistry.
Technical:
– Imperative: cut the ganglion every 2 mm, either vertically or transversely .
– Recommended: 3 depths .
Results: All macroscopic and micro metastases are detected.
Recommended Reading: Can An Injury To The Breast Cause Cancer
Getting The Results During Surgery
In some hospitals, the surgeon gets the results of the sentinel lymph node biopsy during the operation. This is called an intra operative assessment. They can remove the rest of the nodes if necessary. You then avoid having a second operation.
Your surgeon will explain this to you before your operation, so you know what to expect.
Are There Side Effects Of A Sentinel Node Biopsy
Sentinel node surgery is a much less invasive procedure than an axillary dissection. The risks do include pain and discomfort in the armpit that does improve over time. You may have some permanent, partial sensation loss in the armpit and upper, inner arm. There is a slight risk of mild lymphedema. If your surgeon uses blue dye during the surgery to help find the sentinel nodes, there is a 1 to 2 % chance of having an allergic reaction to the dye.
You May Like: When Is Breast Cancer In Remission
What Is Sentinel Node Mapping Used For
Sentinel node mapping is used to predict which lymph node is the most downstream from your primary cancer site. Its usually used to help stage breast cancers and melanoma.
A sentinel node biopsy can then help confirm or rule out the spread of cancer, but the first step is determining which lymph node is best to biopsy.
Mapping is done before a biopsy using a mildly radioactive liquid thats injected into the site of your primary cancer or tumor.
Once the liquid has been injected, the area is massaged and a technician will use some type of imaging device to tract where the radioactive fluid is headed.
This will tell them the direction of the lymph flow from the primary cancer site and, ideally, lead them to the sentinel lymph node.
What If The Sentinel Node Biopsy Is Positive
If the pathologist sees cancer cells in a sentinel node, the biopsy is said to be positive. If this happens your surgeon might recommend that you have further surgery to remove all of the glands under your arm or have radiotherapy to the glands. In other cases, no further treatment will be needed.
If the sentinel node biopsy is negative , no further treatment to the armpit is required.
Read Also: What Does Cancer Feel Like In Breast
What Are The Benefits Of This Test
A sentinel node biopsy allows your provider to stage cancer accurately. It may also help you avoid unnecessary surgery.
If cancer cells arent in the sentinel nodes, its highly unlikely that cancer has spread to other lymph nodes or parts of the body. Your provider wont need to remove other lymph nodes.
When Is Axillary Dissection Needed
Some women with 1-2 positive sentinel nodes who have a lumpectomy and will have whole breast radiation therapy may not need axillary dissection .
Most people with one or more positive sentinel nodes who have a mastectomy will need an axillary dissection or radiation therapy to the axillary lymph nodes .
If you have a positive sentinel lymph node, talk with your health care team about whether you need an axillary dissection.
Recommended Reading: Can Hitting Breast Cause Breast Cancer
Current Standard Of Care For Slnbblue Dye And/or Technetium Labelled Nanocolloid
The traditional SLNB techniques proposed by Giuliano et al. and Krag et al. have been developed both as single technique and as dual complementary procedure: the choice is determined by surgeon and institutional preference. Giuliano et al. reported a 93% SLN identification rate using BD alone, while Krag et al. reported a 82% SLN identification rate using only RI and gamma probe.
James et al. accurately described best practices for both of these tracers besides to the main problems linked to them.
The most used RI tracer is the Technetium 99m , 99mTc-sulfur colloid in USA and 99m Tc-nanocolloid human serum albumin in Europe. It can be injected before surgery around the tumor, intradermally or into the subareolar plexus. Intradermal injection of radiocolloid appears to be superior to subdermal injection . Recently Berrocal et al. described the intraoperative injection of 99mTc in a large series of patients: they reported this method as convenient, effective, safe, and comfortable for the patient with a SLN DR that was essentially 100% . A handheld scintillation counter is used to guide the surgeon to the labeled LNs. LNs are removed following the 10% rule .
Lymphoscintigraphy is not suggested to be used as routine but only in the cases at higher risk of failing the SLN identification .
The constraints of the existing combined SLNB technique have led to the development of alternative methods which will be the object of the following description and review.
Peritumoral Injection Of Radioactive Colloid

This technique was first described by Krag et al and subsequently by a number of workers . About 450 µCi of filtered technetium-labeled sulfur colloid is injected at the periphery of the tumor or at the site of the previous excisional biopsy. Before making the incision, the location of greatest radioactivity is found transcutaneously using a hand-held gamma probe. The axillary incision is then made to include the area of greatest activity. The lymph nodes with the highest radioactivity counts are removed as sentinel nodes. Although this technique is easier to perform than the blue dye method, it still needs technical expertise. Some authors feel that peritumoral injection of radioactive colloid results in significant diffusion of the radioactive tracer with the resultant background radioactivity obscuring the often slightly radioactive sentinel nodes in the axilla. This is especially problematic for upper outer quadrant tumors which form the majority of breast cancers .
Also Check: How To Reverse Breast Cancer
What Should I Expect After The Test
After the procedure, you can expect to be sore near your incision. Talk to your healthcare provider about taking over-the-counter or prescription pain medication while your incision heals. The area may be tender for several days following the procedure. Your arm may feel stiff if the sentinel node was in your armpit.
Ask your healthcare provider when you can return to your regular activities. Most people need to wait several weeks before running, exercising or lifting. Youll need to keep your incision clean and give it time to heal.
Breast Cancer Cells In Sentinel Lymph Node Don’t Affect Survival
Journal of the American Medical Association
- The standard technique involves staining the biopsy tissue so the pathologist can see the physical characteristics of cancer cells under a microscope.
- If the standard technique failed to find cancer cells, a more precise technique — immunohistochemistry — was used. IHC “tags” breast cancer cells using special antibodies that attach to proteins only found in breast cancer cells. The “tagged” cancer cells can be seen under a microscope.
Recommended Reading: Which Type Of Breast Cancer Has The Poorest Prognosis
What Are Sentinel Nodes
Sentinel nodes are simply the first nodes draining a cancerous region. For breast cancer, they are usually located in the armpit. Thats why healthcare providers test the sentinel nodes to see if cancer has spread beyond the original tumor.
If theres no sign of cancer in the sentinel nodes, its unlikely that cancer has spread to other lymph nodes. If the test detects cancer cells in the sentinel nodes, your provider may recommend removing other lymph nodes to check for cancer.