Risk Of Developing Invasive Breast Cancer After Dcis
After treatment for DCIS, theres a small risk of:
- DCIS recurrence
- Invasive breast cancer
These risks are higher with lumpectomy plus radiation therapy than with mastectomy . However, overall survival is the same after either treatment .
Higher grade DCIS appears more likely than lower grade DCIS to progress to invasive cancer after treatment .
With close follow-up, invasive breast cancer is usually caught early and can be treated effectively.
Learn more about tumor grade.
If youve been recently diagnosed with DCIS or feel too overwhelmed to know where to begin to gather information, it may be helpful to download and print some of Susan G. Komen®s resources. For example, we have Questions to Ask Your Doctor About Breast Cancer Surgery and Questions to Ask Your Doctor About Radiation Therapy and Side Effects.
You can write on them at your next doctors appointment. Or, you can download, type and save it on your computer, tablet or phone during a telehealth visit using an app such as Adobe. Plenty of space and a notes section are provided to jot down answers to the questions.
There are other Questions to Ask Your Doctor resources on many different breast cancer topics you may wish to download.
What Is The Treatment For Dcis
Lumpectomy with radiation. The standard treatment is breast-preserving surgery with radiation therapy, which results in successful outcomes for most patients. Cancers can be larger than expected, so about 20% of the time, patients need a re-excision lumpectomy another surgery to remove all of the cancer. Typically, the remaining breast will then have radiation therapy to reduce the risk of local recurrence. Lumpectomy plus radiation is a good alternative to mastectomy for treatment of DCIS.
Mastectomy. Some patients have ductal carcinoma in situ in more than one quadrant of the same breast . Sometimes, the DCIS is very large relative to the patients breast size. In these situations, a mastectomy is required to address malignant cells that are more widespread. Radiation therapy is not needed for DCIS treated with mastectomy.
Chemotherapy. Chemotherapy is not needed for DCIS since the disease is noninvasive.
Hormonal therapy. Hormonal therapy may be appropriate for those whose ductal carcinoma in situ is hormone receptor positive.
What Does It Mean If My In
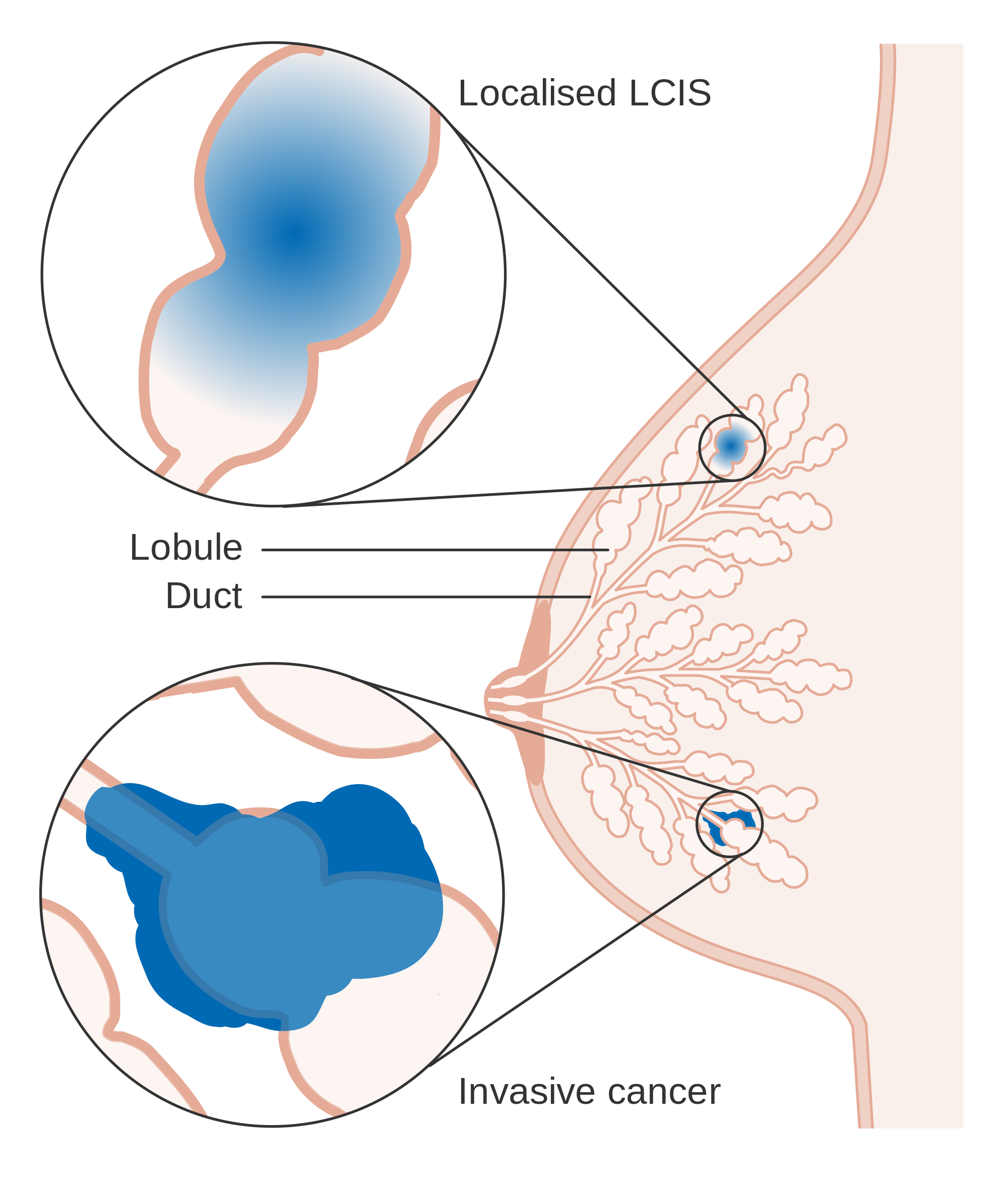
There are 2 main types of in-situ carcinoma of the breast: ductal carcinoma in-situ and lobular carcinoma in situ . Intraductal carcinoma is another name for ductal carcinoma in-situ.
LCIS is discussed on a different page.
Sometimes DCIS and LCIS are both found in the same biopsy.
In-situ carcinoma with duct and lobular features means that the in-situ carcinoma looks like DCIS in some ways and LCIS in some ways , and so the pathologist cant call it one or the other.
If DCIS is left untreated, it can go on to become an invasive cancer, so it is often called a pre-cancer. Still, we dont really understand it well. We dont think that all DCIS would go on to become invasive cancer, but we cant tell which DCIS would be safe to leave untreated. Treatment is aimed at getting rid of all the DCIS, usually by surgery. In some cases, radiation or hormone therapy is given after surgery to lower the chance that it will come back later or that invasive carcinoma will occur.
Don’t Miss: Can I Have Breast Cancer At 20
Survivorship Care After Dcis Treatment
Because of treatments theyve received, many people whove been diagnosed with DCIS have a higher risk of developing other diseases as they age, including high blood pressure, heart disease, and osteoporosis. To make sure youre regularly screened for these and other diseases, experts have developed the idea of survivorship care planning.
Survivorship care plans are written documents made up of two parts.
The first part is a treatment summary, a record of all the treatments youve received.
The second part is basically a roadmap of what you can expect in the years after treatment, including any late or long-term side effects you might have, and a schedule of how youll be monitored for these side effects and other health conditions. This part of the survivorship care plan usually includes:
Treatment And Prognosis For Dcis
Surgery is recommended to treat DCIS. After surgery and radiation therapy, some people take hormone therapy.
With treatment, prognosis for DCIS is usually excellent.
Learn more about treatment for DCIS.
Kornelia Polyak, M.D., Ph.D.Komen Scientific Advisory Board member
Understanding why some patients with DCIS develop invasive breast cancer, while others do not, would help our understanding of drivers of tumor progression and the design of more effective therapies.
Recommended Reading: Best Strain For Breast Cancer
Can Dcis Be Left And Not Treated
Because theres no way of knowing when or if DCIS will become invasive, treatment is usually recommended. Its possible this may lead to unnecessary treatment for some people.
The aim of treatment is to remove all the DCIS from within the breast to reduce the chance of it becoming an invasive cancer.
Research is looking at which cases of DCIS are more likely to develop into invasive breast cancer and which could be closely monitored instead of being treated. If you are diagnosed with low-grade DCIS, you may be invited to join a clinical trial.
If you have any questions or concerns about your diagnosis and treatment, talk to your treatment team.
What Does It Mean If My Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Is Described As Being Low Grade Intermediate Grade Or High Grade Or Nuclear Grade 1 Nuclear Grade 2 Or Nuclear Grade 3 Or Low Mitotic Rate Intermediate Mitotic Rate Or High Mitotic Rate
These are all different ways of describing how the DCIS looks under the microscope:
- DCIS that is high grade, is nuclear grade 3, or has a high mitotic rate is more likely to come back after it is removed with surgery.
- DCIS that is low grade, is nuclear grade 1, or has a low mitotic rate is less likely to come back after surgery.
- DCIS that is intermediate grade, is nuclear grade 2, or has an intermediate mitotic rate falls in between these two.
Patients with higher grade DCIS may need additional treatment.
You May Like: How To Prepare For Chemotherapy For Breast Cancer
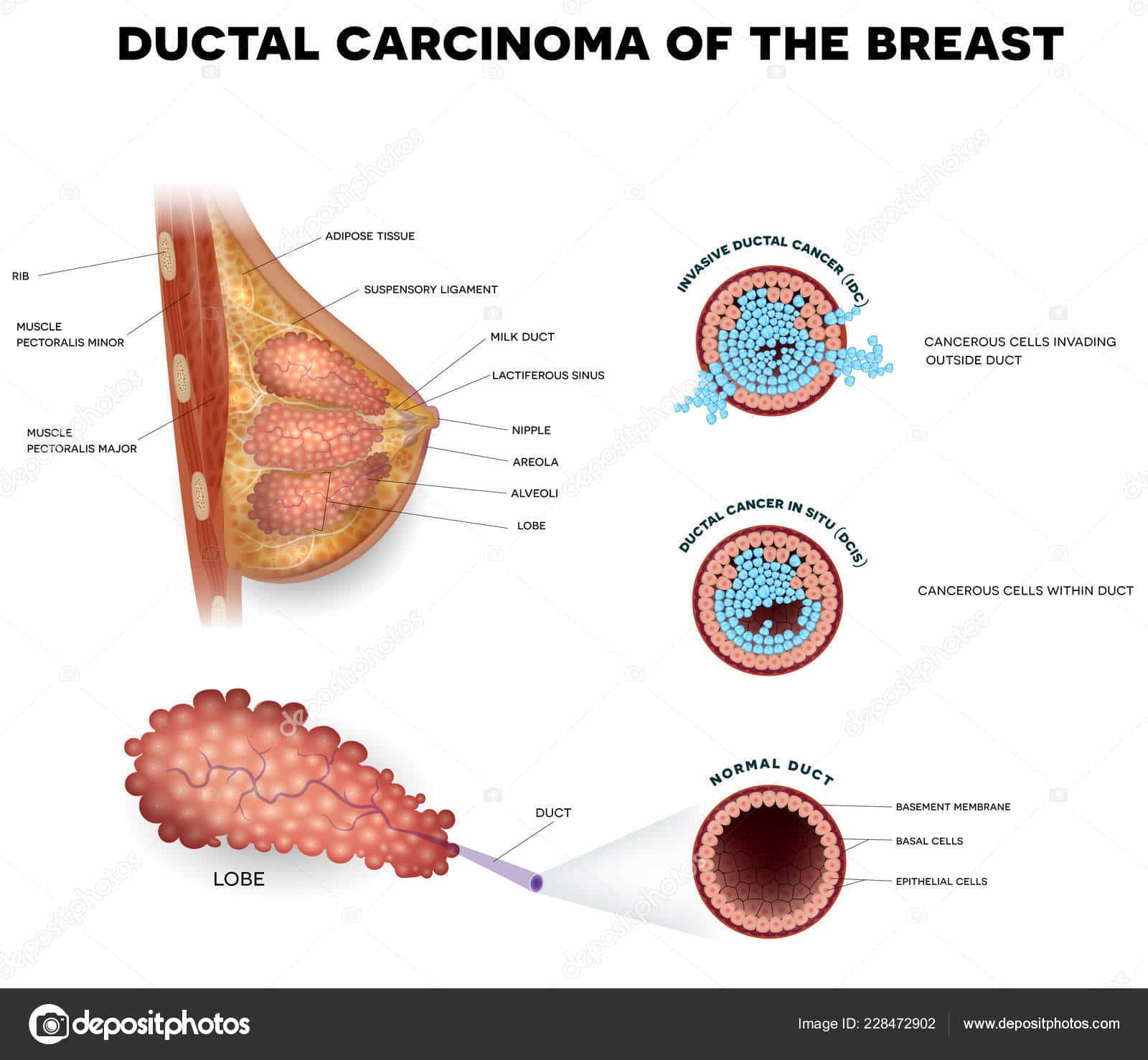
What Is Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
Ductal Carcinoma in Situ , also known as intraductal carcinoma, accounts for one of every five new breast cancer diagnoses. It’s an uncontrolled growth of cells within the breast ducts. Itâs noninvasive, meaning it hasnât grown into the breast tissue outside of the ducts. The phrase “in situ” means “in its original place.”
DCIS is the earliest stage at which breast cancer can be diagnosed. It’s known as stage 0 breast cancer. The vast majority of women diagnosed with it can be cured.
Even though itâs noninvasive, it can lead to invasive cancer. It’s important that women with the disease get treatment. Research shows that the risk of getting invasive cancer is low if youâve been treated for DCIS. If it isnât treated, 30% to 50% of women with DCIS will get invasive cancer. The invasive cancer usually develops in the same breast and in the same area as where the DCIS happened.
Learn More About Dcis And How Bcrf Is Advancing Research To Understand And Treat Stage 0 Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is the most common cancer in women living in the U.S. Of all breast cancer diagnoses in the country, 20-25 percent are ductal carcinoma in situ . The American Cancer Society estimates that about 51,400 new cases of DCIS will be diagnosed this year.
Though it can be very stressful and alarming, DCIS is not life-threateningpractically all patients with stage 0 breast cancer can be cured. Having DCIS can, however, increase ones risk of developing invasive breast cancer. Currently, there is not a way to determine which DCIS cases will become invasive breast cancer and which will not, so DCIS is almost always treated.
Read on to learn what DCIS is and its symptoms, how it is diagnosed and treated, and how BCRF researchers are improving care and learning more about this form of breast cancer.
What is Ductal Carcinoma in Situ ?
Ductal carcinoma in situ is the earliest stage of breast cancer, which is why its sometimes referred to as stage 0 breast cancer. DCIS, by definition, is cancer that starts in the cells lining the milk ducts and remains in the area where it originates . DCIS remains in the milk duct and does not spread through the duct walls into the surrounding breast tissue. Stage 0 breast cancer is considered to be a precursor to invasive, stage 14 breast cancers.
DCIS vs. LCIS
Are there DCIS symptoms? How is DCIS diagnosed?
DCIS treatment
Is DCIS cancer? Should DCIS be treated like invasive breast cancer?
BCRF Research into DCIS
Also Check: What Percentage Of Triple Negative Breast Cancer Returns
After Surgery What Other Treatments Might Be Needed
For those who have a mastectomy for DCIS, there is usually no need for additional treatment because the risk of the cancer coming back is very low. After a lumpectomy, there is still a risk that the DCIS may come back or become invasive cancer. To reduce this risk, the two main treatments are radiation therapy and, if the DCIS cells have the estrogen receptor, hormone therapy. These hormone-blocking drugs include tamoxifen, which blocks the estrogen receptor, and aromatase inhibitors, which block estrogen production.
Probably the hardest decision faced by people with DCIS is whether to have one of these additional treatments after a lumpectomy. A lot of factors must be considered, including the size and grade of the DCIS, how close the DCIS cells were to the final margin, and the age of the person at diagnosis. Younger patients tend to have a higher risk of recurrence compared to older individuals. And then as a doctor, I need to consider how each of my patients thinks about risk. For example, a 10% risk of recurrence in the next ten years can mean completely different things to two different people. Some patients want to do everything to lower their risk, while others are happy to just have it watched closely.
Sex Life And Fertility
Breast cancer treatments can have a direct effect on your sex life.
For example, surgery may affect how you think and feel about your body . It can take time to adjust to changes to your body. If you have a partner, it can help to talk openly with them about your feelings.
Some treatments for DCIS may cause menopausal symptoms. Doctors do not recommend hormone replacement therapy . This is because it contains oestrogen, which could encourage breast cancer cells to grow.
Your cancer doctor or breast care nurse will also advise you not to use contraception that contains hormones.
Don’t Miss: Can Breast Cancer Be Passed Down From Paternal Grandmother
What Does It Mean If My Report On Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Mentions Estrogen Receptor Or Progesterone Receptor
ER and PR are special tests that the pathologist does that are important in predicting response of the DCIS to hormone therapy . Testing for ER is done for most cases of DCIS, but testing for PR is not typically needed. Results for ER and PR are reported separately and can be reported in different ways:
- Negative, weakly positive, positive
- Percent positive with something saying whether the staining is weak, moderate, or strong
Ask your doctor how these results will affect your treatment.
What Is The Significance Of The Reported Size Of The Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
If the entire tumor or area of DCIS is removed , the pathologist will say how big the DCIS is by measuring how long it is across , either by looking at it under the microscope or by gross examination of the tissue taken out at surgery. Another way to measure DCIS is to note the number of microscopic slides that contain DCIS. For example, the report may say that DCIS was found in 3 slides.
On needle biopsy, measurements of the area of DCIS are not often reported because this type of biopsy only samples a part of the tumor. Later, when the entire area of DCIS is removed , an accurate measurement can be done.
The larger the area of DCIS, the more likely it is to come back after surgery. Doctors use information about the size of the DCIS when recommending further treatments.
Also Check: Does Anyone Survive Metastatic Breast Cancer
How Is Dcis Diagnosed
If a doctor sees the calcifications on your mammogram, he or she will recommend more tests, which could include a breast biopsy. During the biopsy, a doctor or other health care provider takes samples of cells or tissues from your body. The cells are examined by a pathologist a doctor who checks for signs of disease in body tissues. The pathologist looks at the cells under a microscope to see if cancer is present.
A particular kind of biopsy called a stereotactic core needle biopsy can diagnose DCIS. This is a nonsurgical, outpatient procedure. After giving you medicine to numb the breast area, the doctor or technologist collects cells from the area of concern using a needle guided by mammography.
What Should I Expect After A Dcis Diagnosis
The outlook after DCIS diagnosis, Sun says, is encouraging. With continued, rigorous monitoring, the prognosis for DCIS is excellent, she explains. Your doctor will recommend a regular screening schedule to guard against recurrence in the original breast, and to monitor the other breast for any signs of malignancy.
Our expectation is for a complete resolution of the problem with proper treatment. This is a local disease and treatment by surgery can be sufficient. Chemotherapy isnt necessary, and in some cases, hormone medication and radiation arent either.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Symptoms Of Male Breast Cancer
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Stages
Results from these tests will show the stage of your cancer. Staging is the name for the process doctors use to figure out if and how far breast cancer has spread. Knowing the stage will help guide your treatment.
Doctors can use the results from your diagnostic testing to gather information about the tumor. They group it by a system known as TNM:
- Tumor : How large is the primary tumor? Where is it?
- Node : Has the tumor spread to your lymph nodes? Where? How much?
- Metastasis : Has the cancer spread to other body parts? Which ones? How much?
To stage your cancer, your doctor combines the TNM results with the tumor grade .
Stages include:
- Stage 0: This is noninvasive cancer. Its only in the ducts and hasnt spread .
- Stage IA: The tumor is small and invasive, but it hasnt spread to your lymph nodes .
- Stage IB: Cancer has spread to the lymph nodes. Its larger than 0.2 mm but less than 2 mm in size. Theres either no sign of a tumor in the breast or there is, but its 20 mm or smaller .
- Stage IIA: Any one of these:
- Theres no sign of a tumor in the breast. The cancer has spread to between 1 and 3 underarm lymph nodes, but not to any distant body parts .
- The tumor is 20 mm or smaller and has spread to underarm lymph nodes .
- The tumor is between 20 mm and 50 mm but hasnt spread to nearby nodes .
What Is The Prognosis For People With Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
Because DCIS is contained within a specific area of your breast and hasnt spread, the disease can be controlled and cured with appropriate treatment. After treatment, outcomes are usually excellent. DCIS rarely recurs following treatment.
Even in those instances where DCIS does recur, the cancer isnt life-threatening.
Also Check: What Stage Is Her2 Positive Breast Cancer
Future Directions In Dcis
DCIS research is directed mainly at improving treatment and, above all, at preventing progression to invasive disease. As researchers continue to study the pathology of DCIS, they are finding that certain tumor characteristics help predict the treatment most likely to reduce the chance of recurrence. For example, some forms of breast cancer require estrogen in order to grow tumors that do are termed estrogen receptorpositive . Tamoxifen belongs to a class of drugs called selective estrogen-receptor modulators , which act by blocking estrogen receptors. Tamoxifen is more likely to prevent a recurrence in women with ER-positive DCIS than in women with ER-negative disease.
The use of aromatase inhibitors, which block estrogen production in the peripheral tissues and breast tissue, is being investigated in a trial of postmenopausal women with ER-positive DCIS. For women whose DCIS is ER-negative but who have the HER-2/neu gene, researchers are exploring the use of trastuzumab and lapatinib , which block the tumor growth factors produced by that gene.
A new way to administer radiation that is showing some promise in clinical trials is accelerated partial breast irradiation, in which the tumor site alone is treated for five days with a lighter dose of radiation. In another approach, intraoperative radiation therapy, a one-time dose of radiation is delivered to the involved area of the breast after the tumor has been removed but before the incision is closed.
Competing Risks Analysis By Age And Year Of Diagnosis
Table Table22 lists the results of competing risks analysis of the 20-year rates for different causes of mortality. After stratifying patients according to age50, 5170, and> 70 years, the long-term rates of heart-related, disease-specific, and other causes of deaths were calculated. In the univariate analysis given the competing risks, the cardiac mortality rate of left-sided tumor laterality was significantly higher than that of right-sided tumor laterality in patients aged50 years, with estimated 20-year rates of 0.67% and 0.51% , respectively . However, there were no significant differences between the left- and right-sided tumor for 5170 years and> 70 years .
You May Like: Triple-negative Breast Cancer Symptoms