Stage 4 Breast Cancer
Stage 4 breast cancer is also known as secondary breast cancer.
Stage 4 breast cancer means:
- The tumour can be any size
- The lymph nodes may or may not contain cancer cells
- The cancer has spread to other parts of the body such as the bones, lungs, liver or brain
If your cancer is found in the lymph nodes under the arm but nowhere else in the body you do not have stage 4 breast cancer.
Treatment Of Breast Cancer Stages I
The stage of your breast cancer is an important factor in making decisions about your treatment.
Most women with breast cancer in stages I, II, or III are treated with surgery, often followed by radiation therapy. Many women also get some kind of systemic drug therapy . In general, the more the breast cancer has spread, the more treatment you will likely need. But your treatment options are affected by your personal preferences and other information about your breast cancer, such as:
- If the cancer cells have hormone receptors. That is, if the cancer is estrogen receptor -positive or progesterone receptor -positive.
- If the cancer cells have large amounts of the HER2 protein
- How fast the cancer is growing
- Your overall health
- If you have gone through menopause or not
Talk with your doctor about how these factors can affect your treatment options.
Grading Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
DCIS is also graded on how abnormal the cancer cells look and has a similar grading system to that used for invasive breast cancer .
- Grade 1 or low grade DCIS. The cells are growing slower, and look more like normal breast cells. These cells tend to have estrogen and progesterone receptors .
- Grade 2 or intermediate grade. The cells are growing at a speed of and look like cells somewhere between grades 1 and 3.
- Grade 3 or high grade. The cancer cells look very different from normal cells and are growing faster. These cells tend not to have estrogen and progesterone receptors . High grade DCIS is often more likely to turn into invasive breast cancer.
Necrosis is also noted. If there is necrosis, it means the tumor is growing quickly. The term comedo necrosis may be used if a breast duct is filled with dead and dying cells. Comedo necrosis is often linked to a high grade of DCIS and has a higher chance of developing into invasive breast cancer.
You May Like: Does Breast Cancer Cause Heartburn
What Is Breast Cancer
Cancer occurs when changes called mutations take place in genes that regulate cell growth. The mutations let the cells divide and multiply in an uncontrolled way.
Breast cancer is cancer that develops in breast cells. Typically, the cancer forms in either the lobules or the ducts of the breast.
Lobules are the glands that produce milk, and ducts are the pathways that bring the milk from the glands to the nipple. Cancer can also occur in the fatty tissue or the fibrous connective tissue within your breast.
The uncontrolled cancer cells often invade other healthy breast tissue and can travel to the lymph nodes under the arms. Once the cancer enters the lymph nodes, it has access to a pathway to move to other parts of the body.
See pictures and learn more about the structure of the breast.
What Is Cancer Staging
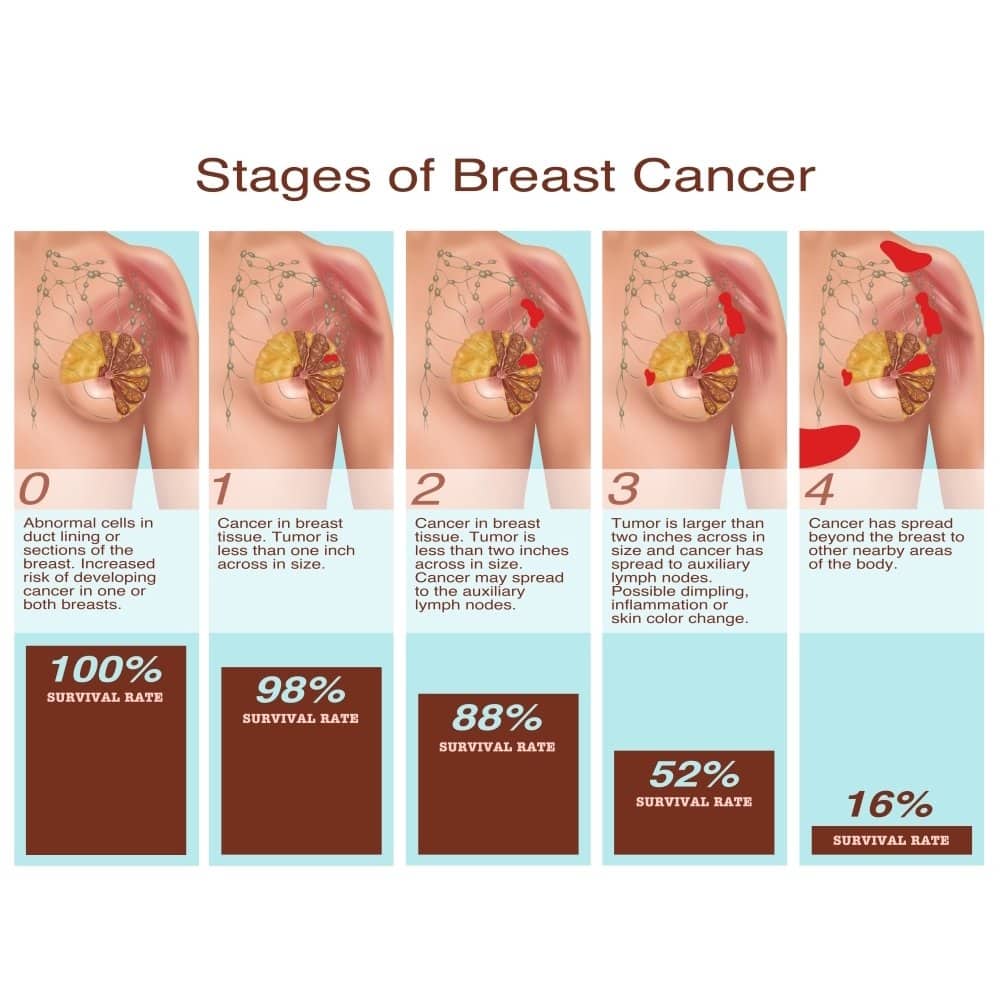
Staging is a way of describing how extensive the breast cancer is, including the size of the tumor, whether it has spread to lymph nodes, whether it has spread to distant parts of the body, and what its biomarkers are.
Staging can be done either before or after a patient undergoes surgery. Staging done before surgery is called the clinical stage, and staging done after surgery is called the pathologic stage. Doctors use diagnostic tests to find out the cancer’s stage, so staging may not be complete until all of the tests are finished. Knowing the stage helps the doctor recommend the best kind of treatment and can help predict a patient’s prognosis, which is the chance of recovery. There are different stage descriptions for different types of cancer.
This page provides detailed information about the system used to find the stage of breast cancer and the stage groups for breast cancer, such as stage IIA or stage IV.
Don’t Miss: How Is Breast Cancer Stage Determined
Starting With Neoadjuvant Therapy
Most often, these cancers are treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. For HER2-positive tumors, the targeted drug trastuzumab is given as well, often along with pertuzumab . This may shrink the tumor enough for a woman to have breast-conserving surgery . If the tumor doesnt shrink enough, a mastectomy is done. Nearby lymph nodes will also need to be checked. A sentinel lymph node biopsy is often not an option for stage III cancers, so an axillary lymph node dissection is usually done.
Often, radiation therapy is needed after surgery. If breast reconstruction is planned, it is usually delayed until after radiation therapy is done. For some, additional chemo is given after surgery as well.
After surgery, some women with HER2-positive cancers will be treated with trastuzumab for up to a year. Many women with HER2-positive cancers will be treated first with trastuzumab followed by surgery and then more trastuzumab for up to a year. If after neoadjuvant therapy, any residual cancer is found at the time of surgery, ado-trastuzumab emtansine may be used instead of trastuzumab. It is given every 3 weeks for 14 doses. For women with hormone receptor-positive cancer that is in the lymph nodes, who have completed a year of trastuzumab, the doctor might also recommend additional treatment with an oral targeted drug called neratinib for a year.
Treatment For Stage 4 Breast Cancer
Treatment for may include the following, either alone or in combination:
- targeted therapy, which targets the protein that allows cancer cells to grow
- immunotherapy, which boosts the bodys ability to fight cancer
In rare cases, a surgeon will operate to try and remove tumors. This is not usually the first option.
However, a doctor may recommend surgery to help relieve pain or other issues that may develop as a result of stage 4 breast cancer. These include spinal cord compression, removing single masses caused by metastasis, and fixing any broken bones.
A doctor may also prescribe medication to treat related symptoms, such as pain.
New treatments and therapies are emerging all the time, and anyone who has breast cancer at any stage can volunteer to try out these new treatments. People considering this should talk with their doctor to see whether any trials are available in their area.
As well as numbers, a zero or an X often follow the letters T, N, and M. According to the AJCC, the meanings are as follows:
The stages of breast cancer help doctors and individuals understand how far cancer affects the body and which treatment options may be effective. However, other factors can also play a role in making treatment decisions.
They include:
The outlook for breast cancer will depend on the stage at diagnosis, the type of cancer the person has, and other factors.
The average survival rates according to the stage at diagnosis, says SEER, were:
| Stage | |
| Unknown stage | 2% |
Don’t Miss: Does Ocrevus Cause Breast Cancer
Diagnosis Of Breast Cancer
To determine if your symptoms are caused by breast cancer or a benign breast condition, your doctor will do a thorough physical exam in addition to a breast exam. They may also request one or more diagnostic tests to help understand whats causing your symptoms.
Tests that can help your doctor diagnose breast cancer include:
- Mammogram. The most common way to see below the surface of your breast is with an imaging test called a mammogram. Many women ages 40 and older get annual mammograms to check for breast cancer. If your doctor suspects you may have a tumor or suspicious spot, they will also request a mammogram. If an atypical area is seen on your mammogram, your doctor may request additional tests.
- Ultrasound. A breast ultrasound uses sound waves to create a picture of the tissues deep in your breast. An ultrasound can help your doctor distinguish between a solid mass, such as a tumor, and a benign cyst.
Your doctor may also suggest tests such as an MRI or a breast biopsy.
If you dont already have a primary care doctor, you can browse doctors in your area through the Healthline FindCare tool.
How Do Doctors Stage Breast Cancer
Staging breast cancers is complex, and considers different types of information gathered from:
- Tests and imaging, such as blood tests, mammograms, ultrasound, MRI, CT scans and PET scans.
- Biopsy results, which can reveal clinical features to determine the aggressiveness of cancer cells.
- Genetic profiling of cancer cells to look for characteristics that may make them respond to particular forms of medical treatment.
- Post-surgical pathology that can see the growth patterns of tumors and gauge their invasiveness.
Read Also: Breast Cancer Metastasis To Adrenal Gland Symptoms
What Is A Breast Cancers Grade
Cancer cells are given a grade when they are removed from the breast and checked in the lab. The grade is based on how much the cancer cells look like normal cells. The grade is used to help predict your outcome and to help figure out what treatments might work best.
A low grade number usually means the cancer is slower-growing and less likely to spread.
A high grade number means a faster-growing cancer thats more likely to spread.
An intermediate grade number means the cancer is growing faster than a grade 1 cancer but slower than a grade 3 cancer.
Remission And Risk Of Recurrence
Complete remission means all signs of cancer are gone.
Sometimes, cancer cells left behind after treatment eventually form new tumors. Cancer can recur locally, regionally, or in distant sites. While this can happen anytime, its most likely within the first five years.
After you finish treatment, regular monitoring should include doctor visits, imaging tests, and blood testing to look for signs of cancer.
Recommended Reading: Where Does Breast Cancer Metastasis
Factors Influencing How Quickly Breast Cancer Tumors Grow
Several factors may influence how quickly breast cancer tumors grow. These factors include:
- Your age. People under 40 are likely to have more aggressive breast cancer.
- Menopause status. If you havent completed menopause, the hormones of menstruation may impact cancer growth.
- History of breast cancer. A family or personal history of this cancer may increase the risk of an aggressive type.
- The type of breast cancer. Some types are more aggressive than others.
- Hormone treatment. If you had hormone replacement therapy with menopause, the chances of an aggressive form of cancer are higher.
Tnm Classification For Breast Cancer

The American Joint Committee on Cancer provides two principal groups for breast cancer staging: anatomic, which is based on extent of cancer as defined by tumor size , lymph node status , and distant metastasis and prognostic, which includes anatomic TNM plus tumor grade and the status of the biomarkers human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 , estrogen receptor , and progesterone receptor . The prognostic stage group is preferred for patient care and is to be used for reporting of all cancer patients in the United States.
In turn, prognostic stages are divided into clinical and pathological groups. Pathological stage applies to patients who have undergone surgery as the initial treatment for breast cancer. It includes all information used for clinical staging plus findings at surgery and pathological findings from surgical resection. Pathological prognostic stage does not apply to patients who received neoadjuvant therapy . See the tables below.
Table. TNM Classification for Breast Cancer
Read Also: Is All Breast Cancer Hereditary
Research Related To Breast Cancer Classification And Implications For Clinical Practice
Researcher: Dr. Sunil Lakhani, University of Queensland
Dr Lakhani recently published practice-changing findings that contributed to a new classification of a rare breast cancer, called metaplastic breast tumours, by the World Health Organisation. Learn more about his research here.
Breast cancer staging is based on tumour size, the extent that cancer has spread to other parts of the body and other clinical factors. Your doctor will use diagnostic information such as medical imaging including mammogram and/or ultrasound, and other diagnostic tests, such as a biopsy of the breast tissue and draining lymph nodes to determine the stage of the cancer.
Once the stage of the cancer has been determined, it is expressed on a scale of 0 to IV. Stage 0 refers to pre-invasive breast cancers, including ductal carcinoma in situ . Stage I and II are referred to as early breast cancer. Stage III is referred to as locally advanced breast cancer. Stage IV is called advanced or metastatic breast cancer. See above for more information.
Stage 0 refers to pre-invasive breast cancers, including ductal carcinoma in situ . This means that there are abnormal cells present, but they are contained inside the milk duct in the case of DCIS, or lobule , in the case of lobular carcinoma in situ .
Invasive breast cancer occurs when cancer cells within the milk duct or lobules break or invade through normal breast tissue. It can be Stage I, II, III or IV.
Before We Talk About Cancer Treatment We Should Also Know About The Importance Of Staging As The Stage At Which The Breast Cancer Is Diagnosed The Amount Of Treatment Required Will Be Extraordinary Here’s How Breast Cancer Treatment Changes With Each Stage
Breast cancer is mainly divided into 4 stages – stage 1 is where the lump is pretty small and it is confined to the breast, so usually we can say that it’s less than 2 cm and the size of a gooseberry while in the second stage, the lump is the size of a lemon and it’s without any change in the contour of the breast. When it goes to the third stage, there could be a small lump in the breast as well as the armpit or axilla. When it comes to stage 4,the disease in the breast is spread to a distant organ such as bones, lungs, liver and very rarely to the brain.
In an interview with HT Lifestyle, Dr Sushruta Mysore Shankar, Consultant Breast Surgeon and Surgical Oncologist at SPARSH Hospital, elaborated, Like all cancers, breast cancer has the following stages – Early breast cancer: When the cancer is limited only to the breast. It is confined and very much inside the breast. Locally advanced breast cancer: The breast cancer involving the chest wall, the skin above or it is spread to the lymph nodes in the axilla or armpit. Most advanced stage or the Metastatic breast cancer: When the breast cancer has already spread to other organs in the body, which is most commonly the liver, lungs, bone and brain. It can also spread to other organs but these are the most common or vital organs. This is the final and the most advanced stage and also called the 4th stage of breast cancer.
Breast cancer treatment at different stages:
Avoiding chemotherapy in early stages:
Recommended Reading: What Should You Eat If You Have Breast Cancer
T Categories For Breast Cancer
T followed by a number from 0 to 4 describes the main tumor’s size and if it has spread to the skin or to the chest wall under the breast. Higher T numbers mean a larger tumor and/or wider spread to tissues near the breast.
TX: Primary tumor cannot be assessed.
T0: No evidence of primary tumor.
Tis: Carcinoma in situ
T1 : Tumor is 2 cm or less across.
T2: Tumor is more than 2 cm but not more than 5 cm across.
T3: Tumor is more than 5 cm across.
T4 : Tumor of any size growing into the chest wall or skin. This includes inflammatory breast cancer.
About Breast Cancer Staging And Grades
Staging means how big the cancer is and whether it has spread. Grading means how abnormal the cancer cells look under a microscope.
Doctors use the stage and grade of a cancer to help them decide which treatment you need.
There are different systems used in the UK to stage breast cancer. The most common one is the TNM system. Another is the number staging system.
Your doctor might also talk about early, locally advanced or secondary breast cancer.
Recommended Reading: How Many Women Get Breast Cancer
What Is The Survival Outlook For Breast Cancer
According to the National Cancer Institute , the percentage of patients surviving five years after diagnosis is:
- 99 percent for breast cancer that is still local to the breast
- 86 percent for breast cancer that has spread just outside the breast
- 29 percent for breast cancer that has spread to more distant parts of the body
The NCI also lists the five-year survival rate for breast cancer overall as 90.6 percent for women and 83 percent for men.
N Categories For Breast Cancer
N followed by a number from 0 to 3 indicates whether the cancer has spread to lymph nodes near the breast and, if so, how many lymph nodes are involved.
Lymph node staging for breast cancer is based on how the nodes look under the microscope, and has changed as technology has gotten better. Newer methods have made it possible to find smaller and smaller groups of cancer cells, but experts haven’t been sure how much these tiny deposits of cancer cells influence outlook.
Its not yet clear how much cancer in the lymph node is needed to see a change in outlook or treatment. This is still being studied, but for now, a deposit of cancer cells must contain at least 200 cells or be at least 0.2 mm across for it to change the N stage. An area of cancer spread that is smaller than 0.2 mm doesn’t change the stage, but is recorded with abbreviations that indicate the type of special test used to find the spread.
If the area of cancer spread is at least 0.2 mm , but still not larger than 2 mm, it is called a micrometastasis . Micrometastases are counted only if there aren’t any larger areas of cancer spread. Areas of cancer spread larger than 2 mm are known to influence outlook and do change the N stage. These larger areas are sometimes called macrometastases, but are more often just called metastases.
NX: Nearby lymph nodes cannot be assessed .
N0: Cancer has not spread to nearby lymph nodes.
N1c: Both N1a and N1b apply.
N3: Any of the following:
N3a: either:
N3b: either:
Don’t Miss: Where Do Breast Cancer Lumps Occur