Endogenous Sex Hormones And Risk Of Breast Cancer
Several lines of evidence have long suggested that sex hormones play a central role in the etiology of breast cancer. As noted above, rates of breast cancer increase rapidly in the premenopausal years, but the rate of increase slows sharply at menopause, when endogenous hormone levels decline. In addition, several reproductive variables that alter estrogen status affect risk of breast cancer for example, early age at menarche and late age at menopause increase risk of breast cancer. After menopause, adipose tissue is the major source of estrogen, and obese postmenopausal women have both higher levels of endogenous estrogen and a higher risk of breast cancer. In addition, hormonal manipulations such as antiestrogens evaluated in randomized controlled trials prevent breast cancer.
Trends In Incidence And Mortality Around The World
Since the 1950s, breast cancer incidence has been increasing in many of the lower-risk countries, as well as in high-risk Western countries. Some of the recent increases in incidence in high-risk populations may be due in part to greater use of mammography, as in the United States. This appears to be the case in Sweden and in England and Wales. However, in Norway, a substantial increase in breast cancer incidence occurred between 1983 and 1993 despite low use of mammographic screening.
Breast cancer incidence rates have nearly doubled in recent decades in traditionally low-risk countries such as Japan and Singapore and in the urban areas of China. Dramatic changes in lifestyle in such regions brought about by growing economies, increasing affluence, and increases in the proportion of women in the industrial workforce have affected the population distribution of established breast cancer risk factors, including age at menarche and fertility and nutritional status, including height and weight. These changes have resulted in a convergence toward the risk-factor profile of Western countries.
Examples Of Mortality Rates Versus Number Of Deaths
Say, town A has a population of 100,000 and town B has a population of 1,000. Over a year, say there are 100 breast cancer deaths in town A and 100 breast cancer deaths in town B.
The number of breast cancer deaths in each town is the same. However, many more people live in town A than live in town B. So, the mortality rates are quite different.
In town A, there were 100 breast cancer deaths among 100,000 people. This means the mortality rate was less than one percent .
In town B, the mortality rate was 10 percent .
Although the number of deaths was the same in town A and town B, the mortality rate was much higher in town B than in town A .
Lets look at another example. In 2022, its estimated among women there will be :
- 100 breast cancer deaths in Washington, D.C.
- 730 breast cancer deaths in Alabama
- 4,690 breast cancer deaths in California
Of the 3, California has the highest number of breast cancers. However, that doesnt mean it has the highest rate of breast cancer. These numbers dont take into account the number of women who live in each place. Fewer women live in Alabama and Washington, D.C. than live in California.
Other factors may vary by place as well, such as the age and race/ethnicity of women. So, to compare breast cancer mortality rates, we need to look at mortality rates.
In 2022, the estimated mortality rates are :
- 25 per 100,000 women in Washington, D.C.
- 21 per 100,000 women in Alabama
- 19 per 100,000 women in California
Read Also: What R The Signs Of Breast Cancer
Fact : Research Studies Document A Compounding Of Breast Cancer Risk Factors For Girls And Young Women That Underscores The Duty For Full And Accurate Informed Consent
According to breast cancer surgeon, Dr. Angela Lanfranchi, a girl or young woman who undergoes an abortion, increases her risk of breast cancer in four ways: he creates in her breasts more places for cancers to start, which is an independent effect she loses the protective effect that a full-term pregnancy would have afforded her she increases the risk of premature delivery of future pregnancies and she lengthens her susceptibility window .
Not unlike cardiac risk factors , having more than one risk factor compounds the risk of breast cancer via synergistic mechanisms. In the previously noted investigation of triple-negative breast cancer, women 40 years of age have an elevated risk that is 3.5-fold, if they began using OCs at age 22 years or later . Those women who began OCs before age 18 years, nearly doubled this risk . In fact, this multivariate analysis found that more recent OC usage and youthful usage were the strongest predictors of breast cancer, even surpassing a positive family history.
In 1987, the Seattle-Puget Sound Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results cancer registry data for women aged 2544 years revealed that the incidence of breast cancer had increased by 22 percent between the time periods 19741977 and 19821984. This research team, which included Daling, reported an annual increase of 2.5 percent .
Lifetime Risk Of Breast Cancer Worldwide
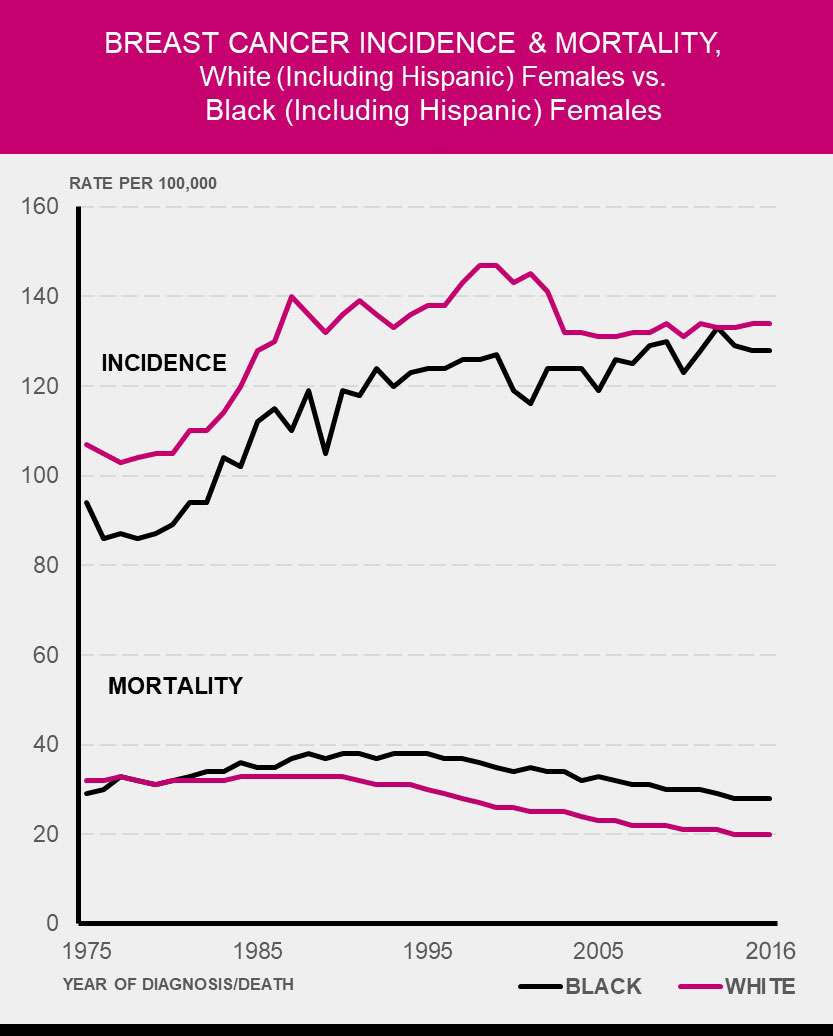
Women who live in developed countries tend to have a higher lifetime risk of breast cancer than women who live in developing countries .
Although we dont know all the reasons for these differences, lifestyle and reproductive factors likely play a large role .
Low screening mammography rates and incomplete reporting can make rates of breast cancer in developing countries look lower than they truly are and may also explain some of these differences.
Read Also: Do Vegetarians Get Breast Cancer
The Very Latest Trends In Breast Cancer By Country Mortality Rates
A study using data from the World Health Organization between 1987 2013 was presented by Pizot at the 2016 San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium.
This large research study found that the mortality rate from breast cancer have decreased in 39 out of 47 countries. The US and most European countries saw a marked in breast cancer mortality over the last 25 years.
However worldwide there were a few disparities. South Korea and some Latin American nations saw an increase in breast cancer deaths. South Korea had an 83% overall increase in mortality rates across all age groups.
For the Latin American countries, Brazil and Colombia also saw an increase in mortality rates whilst Argentina and Chile saw a in breast cancer mortality rates.
Fact : The Breast Cancer Epidemic Is A Relatively Recent Occurrence
There is now substantial evidence that there is an alarming increase in the incidence of breast cancer. Only four decades ago, there was much less concern regarding the rate of new cases.
The concern about breast cancer was at low ebb and had been so for approximately the first seventy years of the twentieth century. Breast cancer merited a mere two paragraphs in a 1973 American Cancer Society overview, as this update focused on other more noteworthy cancers . The American Cancer Society reported in 1973, In women less than 65 years of age, the breast cancer death rate has shown little fluctuation and is almost unchanged since 1914 .
You May Like: Is Stage 2 Breast Cancer Considered Early Stage
Androgens And Breast Cancer Risk
Androgens have been hypothesized to increase breast cancer risk either directly, by increasing the growth and proliferation of breast cancer cells, or indirectly, by their conversion to estrogen. In postmenopausal women, the best summary of evidence on circulating androgens and breast cancer risk is from the pooled analysis of 9 prospective studies described above. Testosterone was positively associated with breast cancer risk: the RRs for increasing quintile category were 1.3 , 1.6 , 1.6 , and 2.2 .
Findings were generally similar for other androgens with RRs of 2 or more comparing top versus bottom quintiles for androstenedione, dehydroepiandrosterone, and for dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate. When estradiol was added to the statistical models, RRs for the androgens were only modestly attenuated, suggesting an independent effect of circulating androgens on cancer risk.
Among premenopausal women, data on circulating androgens are more limited. No association was found between testosterone and breast cancer risk in two prospective studies, but a positive association for receptor-positive tumors was found in Nurses Health Study II. Again, the data are too limited to draw any firm conclusions relating androgen levels to breast cancer risk in premenopausal women.
Breast Cancer Diagnosis And Incidence Rates In Canada: 2016 Statistics
As in many other developed countries, breast cancer remains the most commonly diagnosed cancer amongst Canadian women.
According to the Canadian Cancer Society statistics, around 25,700 Canadian women will be diagnosed with breast cancer in 2016. This figure relates to 130.1 cases per 100,000 women in the same year.
The actual number of women diagnosed with breast cancer in Canada has increased steadily over the years, due to a growing population. However, incidence rates have remained relatively stable since the 1980s.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Youngest Age To Have Breast Cancer
Unique Challenges For Young Adults
Breast cancer in young adults is just different. We are at a different phase of our lives and encounter unique challenges compared to older persons. These challenges may significantly impact our quality and length of life. Some of the unique challenges and issues young adults face:
- The possibility of early menopause and sexual dysfunction brought on by breast cancer treatment
- Fertility issues, because breast cancer treatment can affect a womanâs ability and plans to have children
- Many young women are raising small children while enduring treatment and subsequent side effects
- Young breast cancer survivors have a higher prevalence of psychosocial issues such as anxiety and depression13
- Questions about pregnancy after diagnosis
- Heightened concerns about body image, especially after breast cancer-related surgery and treatment
- Whether married or single, intimacy issues may arise for women diagnosed with breast cancer
- Challenges to financial stability due to workplace issues, lack of sufficient health insurance and the cost of cancer care
Mammography And Rates Of Early Detection Over Time
During the 1980s and 1990s, diagnoses of early-stage breast cancer in the U.S., including ductal carcinoma in situ , increased greatly . This was likely due to the increased use of screening mammography during this time .
Among women 50 and older, rates of DCIS increased from 7 cases per 100,000 women in 1980 to 83 cases per 100,000 women in 2008 . From 2012-2016, rates of DCIS declined by about 2 percent per year .
You May Like: Does Tumor Size Matter In Breast Cancer
Type Dosage And Mode Of Delivery Of Estrogen
Growing epidemiologic data now address the effects of dose and type of estrogen on breast cancer risk. Data from the pooled analysis show no significant differences in the magnitude of risk were observed according to either the type of estrogen used or the estrogen dose . Although the effect of estrogen use on breast cancer risk could be reasonably hypothesized to vary by mode of estrogen delivery , no important differences were observed in the largest study to date. The Million Women Study included over 40,000 users of transdermal estrogen and observed no significant difference in RR of breast cancer compared to that among the 60,000 users of oral therapy .
Estimated Incidence Of Breast Cancer By 10 Year Age Group For Women In Canada
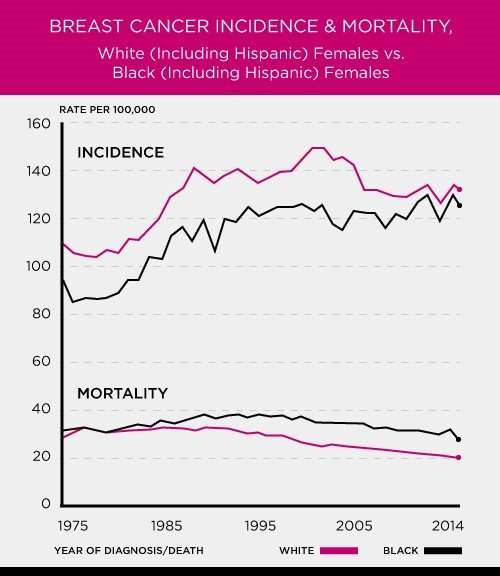
As the above bar chart shows, the incidence of breast cancer for women aged 20-29 is very very low. There is a small increase in breast cancer incidence for women in their 30s, then a significant increase for women in their 40s.
For women aged 50-59, there is a large increase in breast cancer incidence. Indeed, the incidence rate almost doubles for women in their 40s. Then the breast cancer incidence rate more or less levels off for women in their 60s to eighties, but remains rather high.
You May Like: What Percentage Of Women Will Get Breast Cancer
Weight And Weight Change During Adulthood
Attained weight and weight change in adults provides the most sensitive measures of the balance between long-term energy intake and expenditure. The inverse relation between body weight and incidence of premenopausal breast cancer has been consistently seen as summarized in a systematic review and meta-analysis of both case-control and cohort studies. Heavier premenopausal women, even at the upper limits of what are considered to be healthy weights, have more irregular menstrual cycles and increased rates of anovulatory infertility, suggesting that their lower risk may be due to fewer ovulatory cycles and less exposure to ovarian hormones. Increased rates of menstrual irregularity and anovulatory infertility are also seen among very lean women, but such women are uncommon in Western populations.
In both case-control and prospective studies conducted in Western countries, the association between BMI and risk of breast cancer among postmenopausal breast cancer has been weakly positive. The reduction in breast cancer risk associated with being overweight in early adult life is strongly inverse during premenopausal years and appears to persist throughout later life, thus attenuating the effect of postmenopausal adiposity. Thus, an elevated BMI in a postmenopausal woman represents two opposing risks: a protective effect due to the correlation between early weight and postmenopausal weight and an adverse effect due to elevated estrogens after menopause.
Receptor Status And Histologic Subtypes Of Breast Cancer
Consistent evidence from larger epidemiologic studies shows combination estrogen plus progestin and unopposed estrogen therapy are associated with increased risk of estrogen receptorpositive breast cancer. While the WHI did not observe any significant difference in the distribution of invasive cancer by receptor status, the trial had limited power to detect an association with fewer than 500 cases of breast cancer. While it has been suggested that risk is limited to lobular subtypes of breast cancer, most evidence does not support this claim, and, given the higher proportion of receptor-positive tumors in lobular rather than ductal cancers, a stronger RR observed for lobular cancer would be expected for this subset of breast cancers.
Also Check: What Is Stage 1 Breast Cancer
Active And Passive Smoking
The relationship between active cigarette smoking and risk of breast cancer has been extensively evaluated in both case-control and cohort studies collectively, the data provide strong evidence against any major overall relationship, as the 2004 Report of the US Surgeon General concluded the data suggest no causal relationship between active smoking and breast cancer. The question of passive or secondhand smoke exposure and risk of breast cancer was extensively reviewed in the 2006 report of the Surgeon General. After thorough evaluation of the many epidemiologic studies, the report concluded that the overall evidence is mixed and does not strongly or consistently support a causal relationship between secondhand smoke and breast cancer.
How Has The Risk Of Being Diagnosed With Breast Cancer Changed In Recent Years
For a woman born in the 1970s in the United States, the lifetime risk of being diagnosed with breast cancer, based on breast cancer statistics from that time, was just under 10% .
The last five annual SEER Cancer Statistics Review reports show the following estimates of lifetime risk of breast cancer, all very close to a lifetime risk of 1 in 8:
- 12.83%, based on statistics for 2014 through 2016
- 12.44%, based on statistics for 2013 through 2015
- 12.41%, based on statistics for 2012 through 2014
- 12.43%, based on statistics for 2011 through 2013
- 12.32%, based on statistics for 2010 through 2012
SEER statisticians expect some variability from year to year. Slight changes may be explained by a variety of factors, including minor changes in risk factor levels in the population, slight changes in breast cancer screening rates, or just random variability inherent in the data.
Selected Reference
Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, et al. . SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 19752017, National Cancer Institute. Bethesda, MD, , based on November 2019 SEER data submission, posted to the SEER web site, April 2020.
Related Resources
- Reviewed:December 16, 2020
Want to use this content on your website or other digital platform? Our syndication services page shows you how.
Read Also: Is Her2 Positive Breast Cancer Curable
Fact : Breast Cancer Occurrence Decreased Dramatically After Many Us Women Stopped Combined Hormone Replacement Therapy In 2002
The history of HRT is an ongoing and century-long story of efforts to treat menopausal symptoms including vasomotor instability. From the beginning of these efforts, however, there has also been a sub-text of preserving feminine youthfulness and attractiveness. This section summarizes the key historical points in the medical efforts to treat this condition, as well as the growth in the understanding of the associated risks. Menopause was first recognized in the medical literature in the late 1800s, but the twentieth century ushered in a quest for treatment to maintain youthfulness, sexual health, and vitality in women . Unfortunately, the history of HRT includes grandiose claims, now disproved, and multiple, now substantiated harms to women, including breast cancer.
Facts About Breast Cancer In The United States
- In 2022, an estimated 287,500 new cases of invasive breast cancer will be diagnosed in women in the U.S. as well as 51,400 new cases of non-invasive breast cancer.
- 65% of breast cancer cases are diagnosed at a localized stage , for which the 5-year relative survival rate is 99%.
- This year, an estimated 43,550 women will die from breast cancer in the U.S.
- Although rare, men get breast cancer too. In 2022, an estimated 2,710 men will be diagnosed with breast cancer in the U.S. and approximately 530 men will die from breast cancer.
- 1 in 8 women in the United States will be diagnosed with breast cancer in her lifetime
- Breast cancer is the most common cancer in American women, except for skin cancers. It is estimated that in 2022, approximately 30% of all new women cancer diagnoses will be breast cancer.
- There are over 3.8 million breast cancer survivors in the United States.
- On average, every 2 minutes a woman is diagnosed with breast cancer in the United States.
Don’t Miss: Can You Get Breast Cancer At 25