What Are The Types Of Breast Cancer
There are several different types of breast cancer, including:
Can cancer form in other parts of the breast?
When we say breast cancer, we usually mean cancers that form in milk ducts or lobules. Cancers can also form in other parts of your breast, but these types of cancer are less common. These can include:
- Angiosarcoma. This rare type of cancer begins in the cells that make up the lining of blood or lymph vessels.
- Phyllodes tumors. Starting in the connective tissue, phyllodes tumors are rare. Theyre usually benign , but they can be malignant in some cases.
How Is Breast Cancer Diagnosed
Your healthcare provider will perform a breast examination and ask about your family history, medical history and any existing symptoms. Your healthcare provider will also recommend tests to check for breast abnormalities. These tests may include:
- Mammogram. These special X-ray images can detect changes or abnormal growths in your breast. A mammogram is commonly used in breast cancer prevention.
- Ultrasonography. This test uses sound waves to take pictures of the tissues inside of your breast. Its used to help diagnose breast lumps or abnormalities.
- Positron emission tomography scanning: A PET scan uses special dyes to highlight suspicious areas. During this test, your healthcare provider injects a special dye into your veins and takes images with the scanner.
- Magnetic resonance imaging : This test uses magnets and radio waves to produce clear, detailed images of the structures inside of your breast.
If your healthcare provider sees anything suspicious on the imaging tests, they may take a biopsy of your breast tissue. Theyll send the sample to a pathology lab for analysis.
After Breast Cancer Has Been Diagnosed Tests Are Done To Find Out If Cancer Cells Have Spread Within The Breast Or To Other Parts Of The Body
The process used to find out whether the cancer has spread within the breast or to other parts of the body is called staging. The information gathered from the staging process determines thestage of the disease. It is important to know the stage in order to plan treatment. The results of some of the tests used to diagnosebreast cancer are also used to stage the disease.
The following tests and procedures also may be used in the staging process:
Read Also: Can Breast Cancer Spread To The Brain
Treatment Of Early Localized Or Operable Breast Cancer
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
- A clinical trial of a new chemotherapy regimen.
- A clinical trial of monoclonal antibody therapy.
For patients with triple-negative or HER2-positive disease, the response to preoperative therapy may be used as a guide in choosing the best treatment after surgery.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Stage 1 Breast Cancer: Treatment And Prognosis
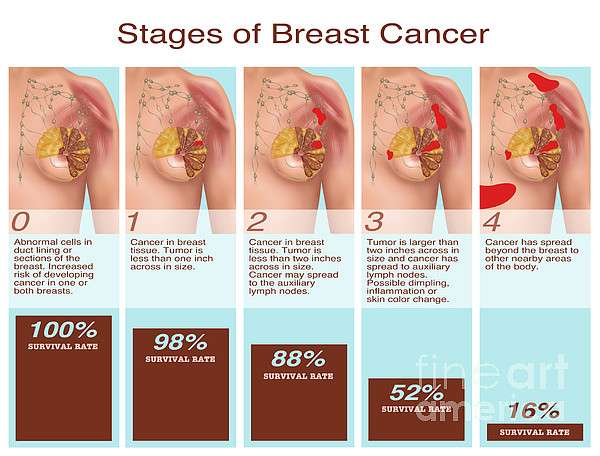
Breast cancer is classified into different stages ranging from 0 to 4. Staging is based on the tumors size and whether tumor cells have spread to other parts of the body. Determining your cancers stage can help your doctor determine your prognosis and the best treatment options.
The TNM staging system which stands for tumor, node, and metastasis is generally used for breast cancer staging. The system stages tumors based on:
- Tumor How large is the primary tumor?
- Node Are there cancer cells in lymph nodes?
- Metastasis Has the cancer metastasized, or spread, to other parts of the body?
Each letter is assigned a number, often with a letter following it. A lower number corresponds to early stage breast cancer, and a higher number indicates more advanced breast cancer.
Other information is also used to better understand the stage of the cancer. This can include:
- Hormone receptor status Whether the cancer contains estrogen receptors or progesterone receptors, proteins that respond to hormones in the body
- Tumor grade A measure of how abnormal the cancer cells look compared to normal cells
- HER2 status Whether the cancer has high levels of a protein called HER2
- Oncotype DX score Results of a genetic test used to predict if a cancer might progress to a more serious form of cancer
Following breast cancer diagnosis, a doctor will determine the most effective treatment based on the cancers stage.
Don’t Miss: What Age Does Breast Cancer Occur
What Is Stage 1 Cancer
Stage 1 cancer typically means the cancer is small and localized to one area, and that it has not spread to the lymph nodes or other parts of the body. Even if the cancer spreads or improves, it will still be referred to by the stage at which it was diagnosed. Cancers at the same stage are often treated similarly. For example, treatment for stage 1 cancer generally includes surgery.
Stage 1 cancer is determined in the five most common cancers in the following ways:
Is Breast Cancer Hereditary
In 5-10% of cases, breast cancer is hereditary. The cancer is caused by specific gene mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes.2 There are several other genes other than BRCA1 and BRCA2 that also help make up this percentage.
These genes can develop abnormally which may then be passed down through family generations, increasing the chance of breast cancers.2
Also Check: Bob Red Mill Baking Soda Cancer
Also Check: Can You Recover From Stage 4 Breast Cancer
Why Is Staging Important
During your initial diagnosis, you and your cancer team will work together to develop a treatment plan. Staging allows you to answer the following questions:
- How does this cancer typically progress?
- Which treatments may work?
Some of the staging may be even more in-depth, but in general, its designed to prepare a more tailored approach to your disease. Your care team will be able to explain any new terms and what they mean for you.
Expert cancer care
Cancer Cure And All Clear
Many people who have cancer want to know if theyre cured. You may hear words like cure and all clear in the media.
Cured means theres no chance of the breast cancer coming back. However, its not possible to be sure that breast cancer will never come back. Treatment for breast cancer will be successful for most people, and the risk of recurrence gets less as time goes on. Recurrence, unfortunately, can happen even many years after treatment, so no one can say with certainty that youre definitely cured.
All clear, or in remission which is another term you may have heard used, means theres no obvious sign of cancer at the moment.
If your breast cancer has spread to other parts of your body this will affect your prognosis. Secondary breast cancer can be treated, sometimes for many years, but not cured. Find out more about secondary breast cancer.
In order to be as clear as possible, your treatment team is more likely to talk about your chances of survival over a period of time or the possibility of remaining free of breast cancer in the future.
Dont Miss: Tubular Cancer Of The Breast
Don’t Miss: How To Beat Metastatic Breast Cancer
What Causes Breast Cancer
Breast cancer develops when abnormal cells in your breast divide and multiply. But experts dont know exactly what causes this process to begin in the first place.
However, research indicates that are several risk factors that may increase your chances of developing breast cancer. These include:
- Age. Being 55 or older increases your risk for breast cancer.
- Sex. Women are much more likely to develop breast cancer than men.
- Family history and genetics. If you have parents, siblings, children or other close relatives whove been diagnosed with breast cancer, youre more likely to develop the disease at some point in your life. About 5% to 10% of breast cancers are due to single abnormal genes that are passed down from parents to children, and that can be discovered by genetic testing.
- Smoking. Tobacco use has been linked to many different types of cancer, including breast cancer.
- Alcohol use. Research indicates that drinking alcohol can increase your risk for certain types of breast cancer.
- Obesity. Having obesity can increase your risk of breast cancer and breast cancer recurrence.
- Radiation exposure. If youve had prior radiation therapy especially to your head, neck or chest youre more likely to develop breast cancer.
- Hormone replacement therapy. People who use hormone replacement therapy have a higher risk of being diagnosed with breast cancer.
What Does Cancer Grade Mean
Breast cancers are given a grade according to:
- How different the cancer cells are to normal breast cells
- How quickly they are growing
The grade of a cancer is different to the cancer stage.
A cancers grade is determined when a doctor looks at the cancer cells under a microscope, using tissue from a biopsy or after breast cancer surgery.
Read Also: Does Medicaid Cover Breast Reconstruction After Cancer
How Does Tumor Size And Location Affect Treatment
Its important for your doctor and entire healthcare team to know the cancers stage in order to plan treatment. Treatment for breast cancer takes into account the tumors size, location, and spread, if there is any.
For example, cancers that are considered early stage may be treated with localized treatments, like surgery and radiation. This cancer may have a better prognosis.
For advanced-stage cancers, a doctor may use systemic treatments. These include chemotherapy, hormone therapy, targeted therapy, and more. Radiation may also be used for advanced-stage cancer, but other treatments will likely be used in conjunction.
Talk To Your Doctor To Find Out What Your Breast Cancer Stage Is And How It Is Used To Plan The Best Treatment For You

After surgery, your doctor will receive a pathology report that describes the size and location of the primary tumor, the spread of cancer to nearby lymph nodes, tumor grade, and whether certain biomarkers are present. The pathology report and other test results are used to determine your breast cancer stage.
You are likely to have many questions. Ask your doctor to explain how staging is used to decide the best options to treat your cancer and whether there are clinical trials that might be right for you.
The treatment of breast cancer depends partly on the stage of the disease.
For treatment options for stage IIIB, inoperable stage IIIC, and inflammatory breast cancer, see Treatment of Locally Advanced Inflammatory Breast Cancer.
For treatment options for cancer that has recurred near the area where it first formed , see Treatment of Locoregional Recurrent Breast Cancer.
For treatment options for stage IV breast cancer or breast cancer that has recurred in distant parts of the body, see Treatment of Metastatic Breast Cancer.
Recommended Reading: What Is Er Pr Positive Breast Cancer
The Stages Of Breast Cancer
Breast cancer stages are defined by the cancers characteristics including the size of the tumor, whether it has spread to the lymph nodes, and whether its progressed to other parts of the body. Knowing the stage can help you and your physician determine possible outcomes, treatment options, and find clinical trials that may be a good fit.
Doctors classify the stages of breast cancers using the TNM system T standing for the size of the tumor and whether it has invaded nearby tissues, N stands for whether the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes, and M whether it has spread to tissues beyond the breast.
The five stages include:
- Stage 0: Non-invasive cancers that are isolated to their original location
- Stage I: Invasive in nearby tissues and has a tumor size of less than 2cm
- Stage II: Cancer has spread to the lymph nodes but not outside of the breast tissues, tumor size of between 2-5cm
- Stage III: The cancer has reached muscles and skin, invaded the lymph nodes, but has not spread to tissues outside of the breast tissues, the tumor is bigger than 5cm
- Stage IV: Invasive cancers that have spread to other parts of the body
To learn more about the TNM staging system and your specific case, please consult with your physician.
Permission To Use This Summary
PDQ is a registered trademark. The content of PDQ documents can be used freely as text. It cannot be identified as an NCI PDQ cancer information summary unless the whole summary is shown and it is updated regularly. However, a user would be allowed to write a sentence such as NCIs PDQ cancer information summary about breast cancer prevention states the risks in the following way: .
The best way to cite this PDQ summary is:
PDQ® Adult Treatment Editorial Board. PDQ Breast Cancer Treatment . Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute. Updated < MM/DD/YYYY> . Available at: . Accessed < MM/DD/YYYY> .
Images in this summary are used with permission of the author, artist, and/or publisher for use in the PDQ summaries only. If you want to use an image from a PDQ summary and you are not using the whole summary, you must get permission from the owner. It cannot be given by the National Cancer Institute. Information about using the images in this summary, along with many other images related to cancer can be found in Visuals Online. Visuals Online is a collection of more than 3,000 scientific images.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Five Signs Of Breast Cancer
Stages Of Breast Cancer
Staging describes or classifies a cancer based on how much cancer there is in the body and where it is when first diagnosed. This is often called the extent of cancer. Information from tests is used to find out the size of the tumour, what part of the breast has cancer, whether the cancer has spread from where it first started and where the cancer has spread. Your healthcare team uses the stage to plan treatment and estimate the outcome .
The most common staging system for breast cancer is the TNM system. For breast cancer there are 5 stages stage 0 followed by stages 1 to 4. Often the stages 1 to 4 are written as the Roman numerals I, II, III and IV. Generally, the higher the stage number, the more the cancer has spread. Talk to your doctor if you have questions about staging.
When describing the stage of breast cancer, sometimes doctors group them as follows:
In situ breast cancer The cancer cells are only in the duct or lobule where they started and have not grown into nearby breast tissue . It is stage 0.
Early stage breast cancer The tumour is smaller than 5 cm and the cancer has not spread to more than 3 lymph nodes. It includes stages 1A, 1B and 2A.
Locally advanced breast cancer The tumour is larger than 5 cm. The cancer may have spread to the skin, the muscles of the chest wall or more than 3 lymph nodes. It includes stages 2B, 3A, 3B and 3C. Inflammatory breast cancer is also considered locally advanced breast cancer.
Find out more about .
T Categories For Breast Cancer
T followed by a number from 0 to 4 describes the main tumor’s size and if it has spread to the skin or to the chest wall under the breast. Higher T numbers mean a larger tumor and/or wider spread to tissues near the breast.
TX: Primary tumor cannot be assessed.
T0: No evidence of primary tumor.
Tis: Carcinoma in situ
T1 : Tumor is 2 cm or less across.
T2: Tumor is more than 2 cm but not more than 5 cm across.
T3: Tumor is more than 5 cm across.
T4 : Tumor of any size growing into the chest wall or skin. This includes inflammatory breast cancer.
You May Like: Signs Of Breast Cancer In Armpit
Treatment For Stage 1 Breast Cancer
Doctors can offer a variety of for stage 1 breast cancer, although surgery is the primary treatment.
Surgery
A lumpectomy or mastectomy are both viable surgical options for people with stage 1 breast cancer. A doctor will decide what surgery is most appropriate depending on the location of the primary tumor, how large it is, the size of the breast, family history, genetics, and the persons preference.
The doctor may also carry out a biopsy on one or more lymph nodes.
After removing the tissue, they will send it to a laboratory for further tests. The results will help inform decisions on the next stage of treatment.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy is a standard treatment for stage 1 breast cancer. However, the decision will depend on factors such the age of the person, the type of cancer, the size of the tumor, and whether there are cancer cells in the lymph nodes.
Hormone therapy
If the breast cancer is ER+ or PR+, hormone therapy may be effective. Hormone therapy works by preventing the growth of estrogen, which helps cancer grow, by blocking estrogen from attaching to tissue and fuelling cancer growth, or both.
Hormone therapy can reach cancer cells in the breast, as well as other areas of the body, and it can reduce the risk of cancer returning.
Chemotherapy
However, the
Stage 2 breast cancer also has subcategories known as 2A and 2B.
Determining Breast Cancer Stage
In breast cancer, stage is based on the size and location of the primary tumor, the spread of cancer to nearby lymph nodes or other parts of the body, tumor grade, and whether certain biomarkers are present.
The TNM system, the grading system, and the biomarker status are combined to find out the breast cancer stage.
Also Check: Is It Possible To Get Breast Cancer At 16